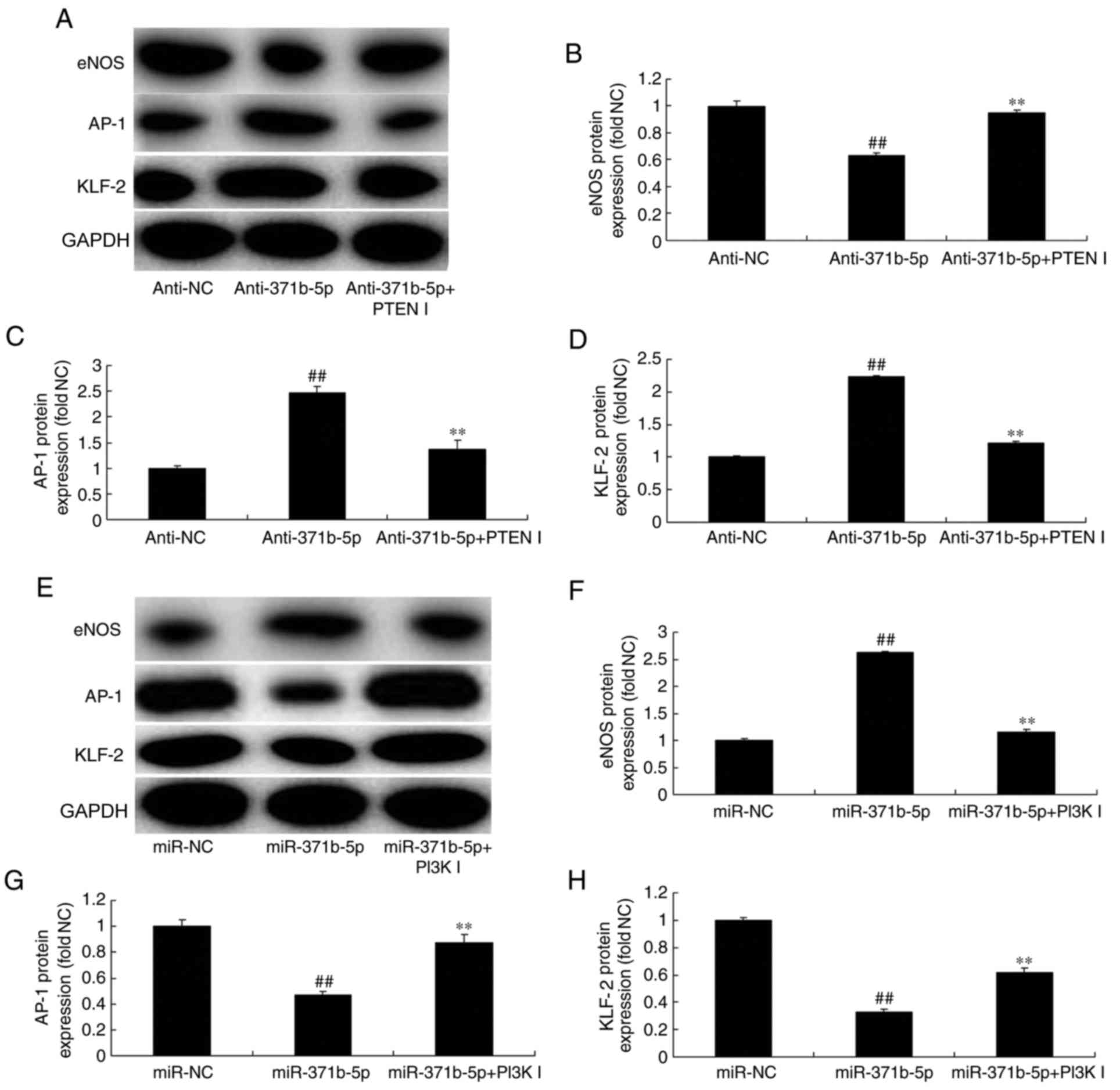
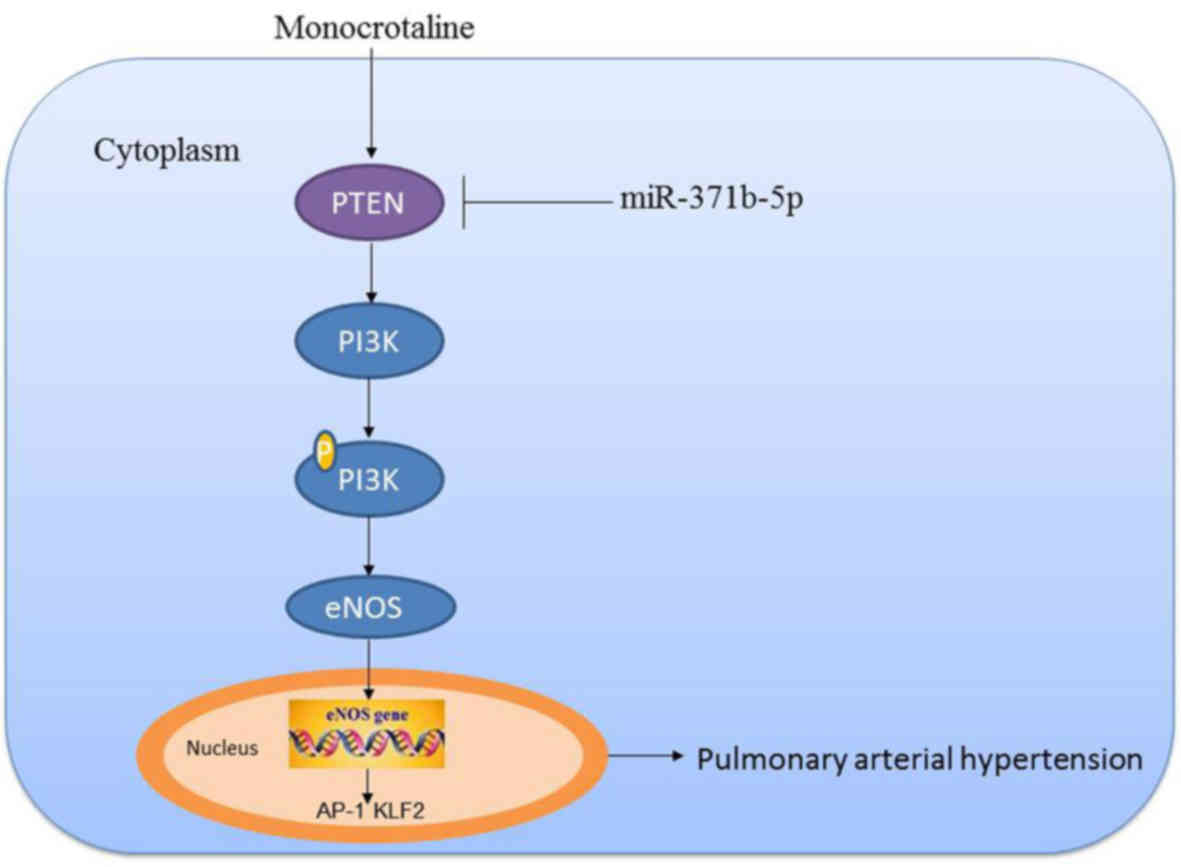
|
1
|
Wu C, Guo J, Liu H, Pudasaini B, Yang W,
Zhao Q, Wang L and eLiu J: The correlation of decreased heart rate
recovery and chronotropic incompetence with exercise capacity in
idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension patients. Biomed Res
Int. 2017:34154012017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Galie N, Barbera JA, Frost AE, Ghofrani
HA, Hoeper MM, McLaughlin VV, Peacock AJ, Simonneau G, Vachiery JL,
Grünig E, et al: Initial use of ambrisentan plus tadalafil in
pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 373:834–844. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li S, Ma Q, Yang Y, Lu J, Zhang Z, Jin M
and Cheng W: Novel goal-directed hemodynamic optimization therapy
based on major vasopressor during corrective cardiac surgery in
patients with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension: A pilot
study. Heart Surg Forum. 19:E297–E302. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dahan D, Hien TT, Tannenberg P, Ekman M,
Rippe C, Boettger T, Braun T, Tran-Lundmark K, Tran PK, Swärd K and
Albinsson S: MicroRNA-dependent control of serotonin-induced
pulmonary arterial contraction. J Vasc Res. 54:246–256. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xiao T, Xie L, Huang M and Shen J:
Differential expression of microRNA in the lungs of rats with
pulmonary arterial hypertension. Mol Med Rep. 15:591–596. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nie X, Shi Y, Yu W, Xu J, Hu X and Du Y:
Phosphorylation of PTEN increase in pathological right ventricular
hypertrophy in rats with chronic hypoxia induced pulmonary
hypertension. Chin Med J (Engl). 127:338–342. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu Y, Cao Y, Sun S, Zhu J, Gao S, Pang J,
Zhu D and Sun Z: Transforming growth factor-beta1 upregulation
triggers pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation and
apoptosis imbalance in rats with hypoxic pulmonary hypertension via
the PTEN/AKT pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 77:141–154. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ha D, Mester J, Eng C and Farha S:
Pulmonary arterial hypertension in a patient with Cowden syndrome
and the PTEN mutation. Pulm Circ. 4:728–731. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yao L, Lu P, Li Y, Yang L, Feng H, Huang
Y, Zhang D, Chen J and Zhu D: Osthole relaxes pulmonary arteries
through endothelial phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-eNOS-NO
signaling pathway in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 699:23–32. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li L, Zhang X, Li X, Lv C, Yu H, Xu M,
Zhang M, Fu Y, Meng H and Zhou J: TGF-beta1 inhibits the apoptosis
of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells and contributes to
pulmonary vascular medial thickening via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Mol
Med Rep. 13:2751–2756. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rabie T, Muhlhofer W, Bruckner T, Schwab
A, Bauer AT, Zimmermann M, Bonke D, Marti HH and Schenkel J:
Transient protective effect of B-vitamins in experimental epilepsy
in the mouse brain. J Mol Neurosci. 41:74–79. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shea S, Lima J, Diez-Roux A, Jorgensen NW
and McClelland RL: Socioeconomic status and poor health outcome at
10 years of follow-up in the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis.
PLoS One. 11:e01656512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Saggar R, Khanna D, Vaidya A,
Derhovanessian A, Maranian P, Duffy E, Belperio JA, Weigt SS, Dua
S, Shapiro SS, et al: Changes in right heart haemodynamics and
echocardiographic function in an advanced phenotype of pulmonary
hypertension and right heart dysfunction associated with pulmonary
fibrosis. Thorax. 69:123–129. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rothman AM, Arnold ND, Pickworth JA,
Iremonger J, Ciuclan L, Allen RM, Guth-Gundel S, Southwood M,
Morrell NW, Thomas M, et al: MicroRNA-140-5p and SMURF1 regulate
pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Clin Invest. 126:2495–2508.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sahoo S, Meijles DN, Al Ghouleh I, Tandon
M, Cifuentes-Pagano E, Sembrat J, Rojas M, Goncharova E and Pagano
PJ: MEF2C-MYOCD and leiomodin1 suppression by miRNA-214 promotes
smooth muscle cell phenotype switching in pulmonary arterial
hypertension. PLoS One. 11:e01537802016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao H, Lin G, Shi M, Gao J, Wang Y, Wang
H, Sun H and Cao Y: The mechanism of neurogenic pulmonary edema in
epilepsy. J Physiol Sci. 64:65–72. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ravi Y, Selvendiran K, Meduru S, Citro L,
Naidu S, Khan M, Rivera BK, Sai-Sudhakar CB and Kuppusamy P:
Dysregulation of PTEN in cardiopulmonary vascular remodeling
induced by pulmonary hypertension. Cell Biochem Biophys.
67:363–372. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ravi Y, Selvendiran K, Naidu SK, Meduru S,
Citro LA, Bognár B, Khan M, Kálai T, Hideg K, Kuppusamy P and
Sai-Sudhakar CB: Pulmonary hypertension secondary to left-heart
failure involves peroxynitrite-induced downregulation of PTEN in
the lung. Hypertension. 61:593–601. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Quan Y, Wang Z, Gong L, Peng X, Richard
MA, Zhang J, Fornage M, Alcorn JL and Wang D: Exosome miR-371b-5p
promotes proliferation of lung alveolar progenitor type II cells by
using PTEN to orchestrate the PI3K/Akt signaling. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 8:1382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li L, Xu M, Li X, Lv C, Zhang X, Yu H,
Zhang M, Fu Y, Meng H and Zhou J: Platelet-derived growth factor-B
(PDGF-B) induced by hypoxia promotes the survival of pulmonary
arterial endothelial cells through the PI3K/Akt/Stat3 pathway. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 35:441–451. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yuan P, Wu WH, Gao L, Zheng ZQ, Liu D, Mei
HY, Zhang ZL and Jing ZC: Oestradiol ameliorates monocrotaline
pulmonary hypertension via NO, prostacyclin and endothelin-1
pathways. Eur Respir J. 41:1116–1125. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li H, Lu W, Cai WW, Wang PJ, Zhang N, Yu
CP, Wang DL, Liu BC and Sun W: Telmisartan attenuates
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary artery endothelial dysfunction
through a PPAR gamma-dependent PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway. Pulm
Pharmacol Ther. 28:17–24. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|