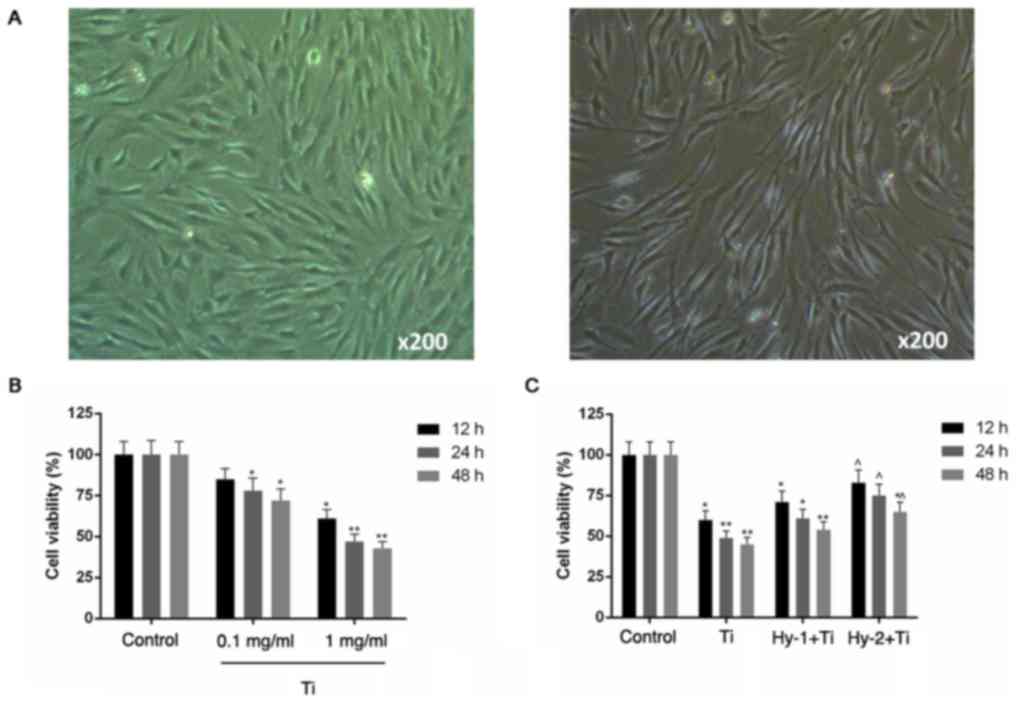
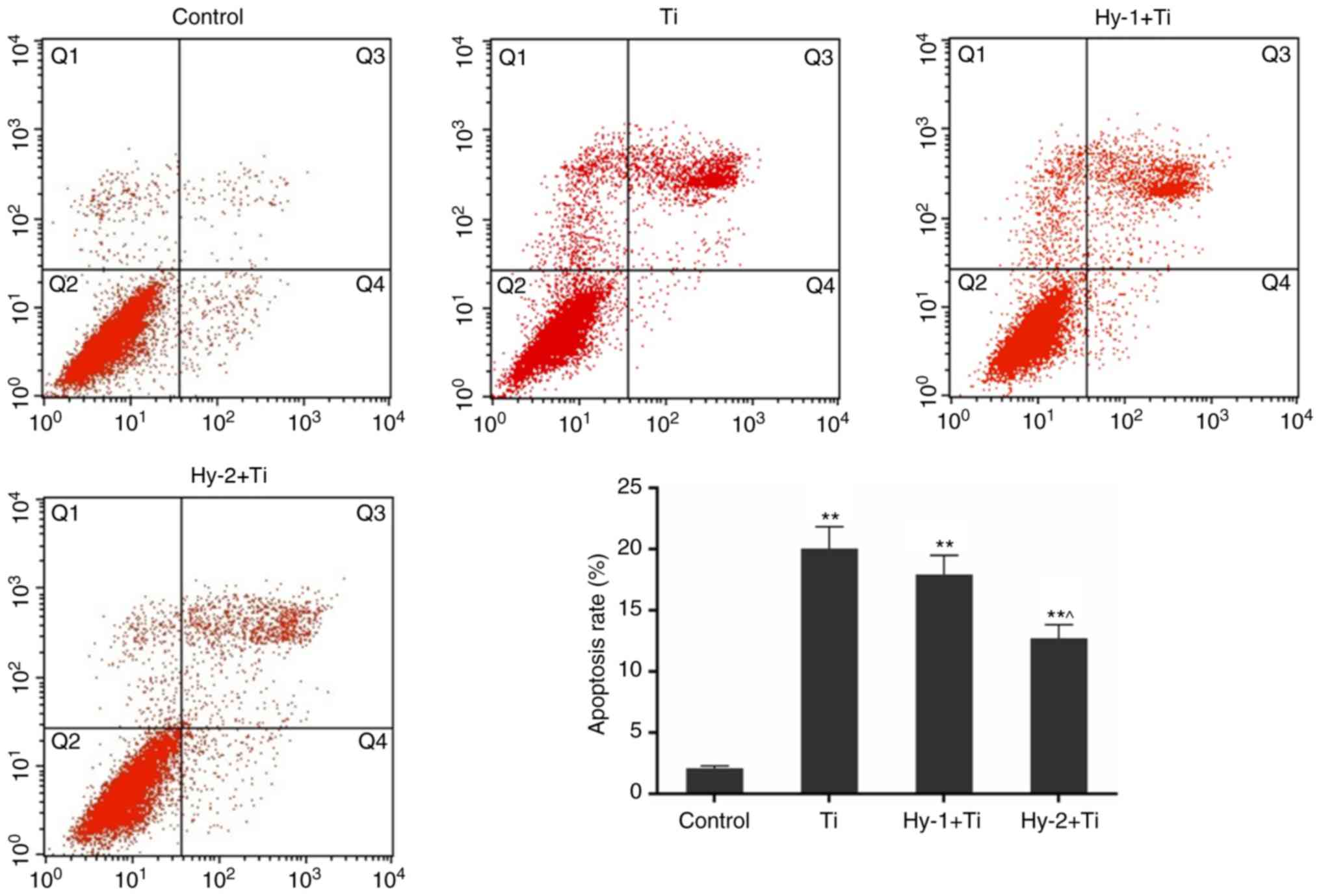
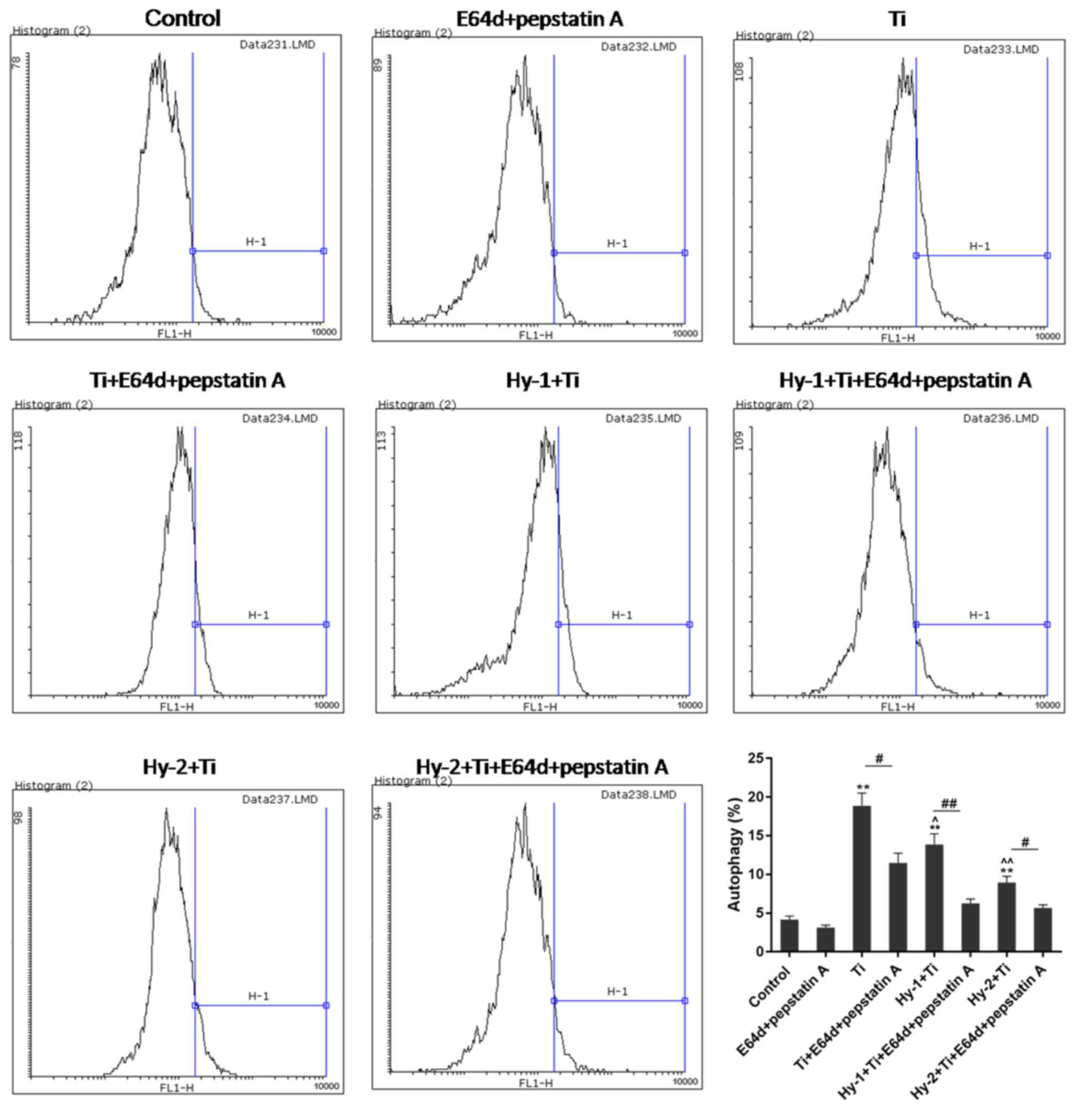
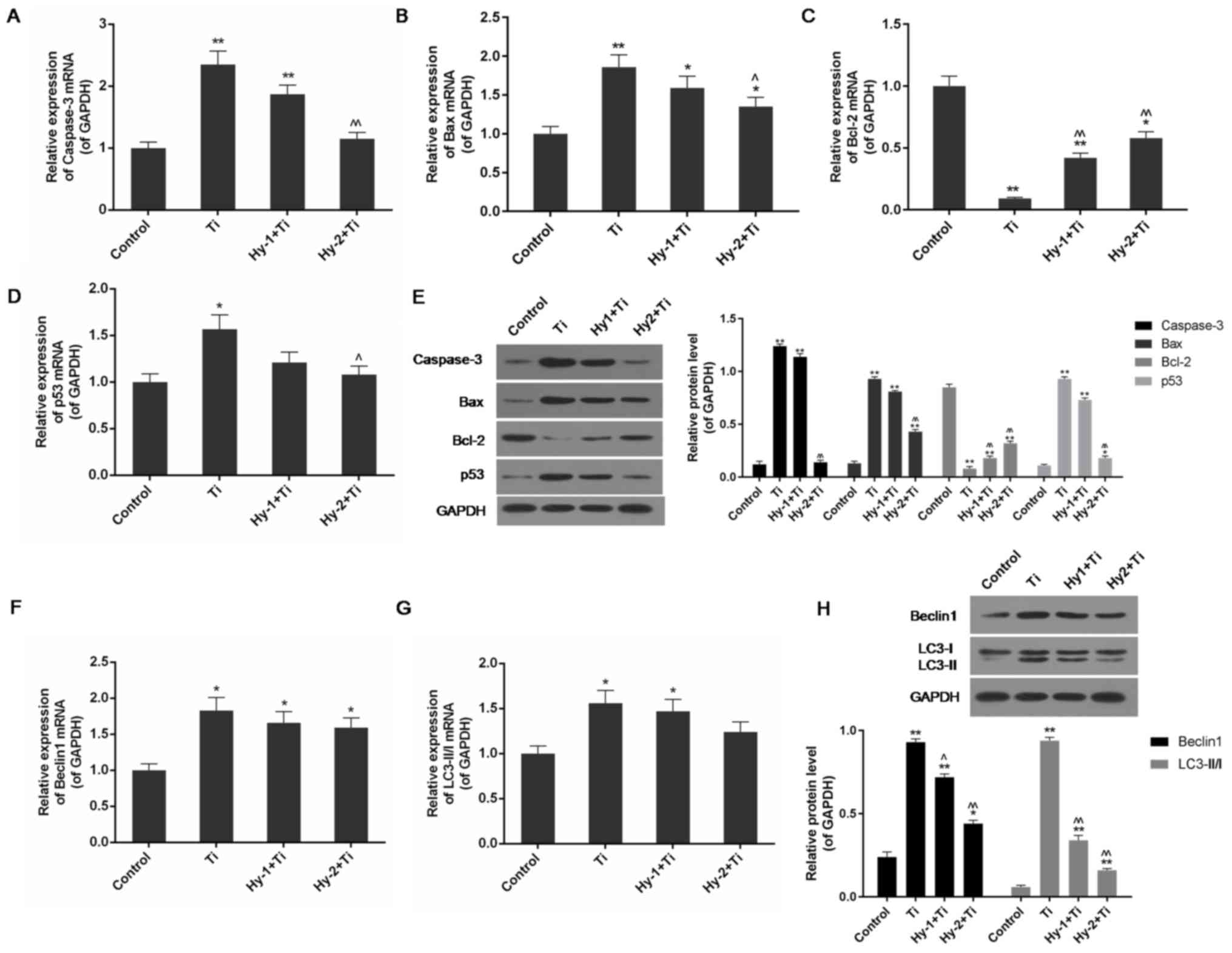
|
1
|
Amirhosseini M, Andersson G, Aspenberg P
and Fahlgren A: Mechanical instability and titanium particles
induce similar transcriptomic changes in a rat model for
periprosthetic osteolysis and aseptic loosening. Bone Rep. 7:17–25.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Haynes DR, Crotti TN and Zreiqat H:
Regulation of osteoclast activity in peri-implant tissues.
Biomaterials. 25:4877–4885. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lochner K, Fritsche A, Jonitz A, Hansmann
D, Mueller P, Mueller-Hilke B and Bader R: The potential role of
human osteoblasts for periprosthetic osteolysis following exposure
to wear particles. Int J Mol Med. 28:1055–1063. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Piao MJ, Kang KA, Zhang R, Ko DO, Wang ZH,
You HJ, Kim HS, Kim JS, Kang SS and Hyun JW: Hyperoside prevents
oxidative damage induced by hydrogen peroxide in lung fibroblast
cells via an antioxidant effect. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1780:1448–1457. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang XN, Li JM, Yang Q, Feng B, Liu SB,
Xu ZH, Guo YY and Zhao MG: Anti-apoptotic effects of hyperoside via
inhibition of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors. Pharmacol Rep.
62:949–955. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Choi JH, Kim DW, Yun N, Choi JS, Islam MN,
Kim YS and Lee SM: Protective effects of hyperoside against carbon
tetrachloride-induced liver damage in mice. J Nat Prod.
74:1055–1060. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Haas JS, Stolz ED, Betti AH, Stein AC,
Schripsema J, Poser GL and Rates SM: The anti-immobility effect of
hyperoside on the forced swimming test in rats is mediated by the
D2-like receptors activation. Planta Med. 77:334–339. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ku SK, Kwak S, Kwon OJ and Bae JS:
Hyperoside inhibits high-glucose-induced vascular inflammation in
vitro and in vivo. Inflammation. 37:1389–1400. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li W, Liu M, Xu YF, Feng Y, Che JP, Wang
GC and Zheng JH: Combination of quercetin and hyperoside has
anticancer effects on renal cancer cells through inhibition of
oncogenic microRNA-27a. Oncol Rep. 31:117–124. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Y, Wang M, Dong H, Yu X and Zhang J:
Anti-hypoglycemic and hepatocyte-protective effects of hyperoside
from Zanthoxylum bungeanum leaves in mice with
high-carbohydrate/high-fat diet and alloxan-induced diabetes. Int J
Mol Med. 41:77–86. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Q, Xiao S and Xia Y: TWEAK/Fn14
activation participates in skin inflammation. Mediators Inflamm.
2017:67468702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tallroth K, Eskola A, Santavirta S,
Konttinen YT and Lindholm TS: Aggressive granulomatous lesions
after hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 71:571–575. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Harris WH: Osteolysis and particle disease
in hip replacement. A review. Acta Orthop Scand. 65:113–123. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Santavirta S, Takagi M, Gomez-Barrena E,
Nevalainen J, Lassus J, Salo J and Konttinen YT: Studies of host
response to orthopedic implants and biomaterials. J Long Term Eff
Med Implants. 9:67–76. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Knowles HJ and Athanasou NA: Acute hypoxia
and osteoclast activity: A balance between enhanced resorption and
increased apoptosis. J Pathol. 218:256–264. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schmalzried TP, Jasty M and Harris WH:
Periprosthetic bone loss in total hip arthroplasty. Polyethylene
wear debris and the concept of the effective joint space. J Bone
Joint Surg Am. 74:849–863. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wataha JC: Predicting clinical biological
responses to dental materials. Dent Mater. 28:23–40. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cooper HJ, Ranawat AS, Potter HG, Foo LF,
Koob TW and Ranawat CS: Early reactive synovitis and osteolysis
after total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 468:3278–3285.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Matzinger P: Tolerance, danger, and the
extended family. Annu Rev Immunol. 12:991–1045. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Konttinen Y, Imai S and Suda A:
Neuropeptides and the puzzle of bone remodeling. State of the art.
Acta Orthop Scand. 67:632–639. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
King KY and Goodell MA: Inflammatory
modulation of HSCs: Viewing the HSC as a foundation for the immune
response. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:685–692. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Murray PJ and Wynn TA: Protective and
pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat Rev Immunol.
11:723–737. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee YH, Cheng FY, Chiu HW, Tsai JC, Fang
CY, Chen CW and Wang YJ: Cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, apoptosis
and the autophagic effects of silver nanoparticles in mouse
embryonic fibroblasts. Biomaterials. 35:4706–4715. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Buckley CD: Why does chronic inflammation
persist: An unexpected role for fibroblasts. Immunol Lett.
138:12–14. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nathan C and Ding A: Nonresolving
inflammation. Cell. 140:871–882. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vermes C, Chandrasekaran R, Jacobs JJ,
Galante JO, Roebuck KA and Glant TT: The effects of particulate
wear debris, cytokines, and growth factors on the functions of
MG-63 osteoblasts. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 83-A:201–211. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fritz EA, Glant TT, Vermes C, Jacobs JJ
and Roebuck KA: Titanium particles induce the immediate early
stress responsive chemokines IL-8 and MCP-1 in osteoblasts. J
Orthop Res. 20:490–498. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kusano K, Miyaura C, Inada M, Tamura T,
Ito A, Nagase H, Kamoi K and Suda T: Regulation of matrix
metalloproteinases (MMP-2, −3, −9, and −13) by interleukin-1 and
interleukin-6 in mouse calvaria: Association of MMP induction with
bone resorption. Endocrinology. 139:1338–1345. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Takei H, Pioletti DP, Kwon SY and Sung KL:
Combined effect of titanium particles and TNF-alpha on the
production of IL-6 by osteoblast-like cells. J Biomed Mater Res.
52:382–387. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Landgraeber S, von Knoch M, Löer F, Wegner
A, Tsokos M, Hussmann B and Totsch M: Extrinsic and intrinsic
pathways of apoptosis in aseptic loosening after total hip
replacement. Biomaterials. 29:3444–3450. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huk OL, Zukor DJ, Ralston W, Lisbona A and
Petit A: Apoptosis in interface membranes of aseptically loose
total hip arthroplasty. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 12:653–658. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cho DH, Jo YK, Hwang JJ, Lee YM, Roh SA
and Kim JC: Caspase-mediated cleavage of ATG6/Beclin-1 links
apoptosis to autophagy in HeLa cells. Cancer Lett. 274:95–100.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yoo BH, Wu X, Derouet M, Haniff M,
Eskelinen EL and Rosen K: Hypoxia-induced downregulation of
autophagy mediator Beclin 1 reduces the susceptibility of malignant
intestinal epithelial cells to hypoxia-dependent apoptosis.
Autophagy. 5:1166–1179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
She C, Zhu LQ, Zhen YF, Wang XD and Dong
QR: Activation of AMPK protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced
osteoblast apoptosis through autophagy induction and NADPH
maintenance: New implications for osteonecrosis treatment? Cell
Signal. 26:1–8. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lai EH, Hong CY, Kok SH, Hou KL, Chao LH,
Lin LD, Chen MH, Wu PH and Lin SK: Simvastatin alleviates the
progression of periapical lesions by modulating autophagy and
apoptosis in osteoblasts. J Endod. 38:757–763. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Allaeys I, Marceau F and Poubelle PE:
NLRP3 promotes autophagy of urate crystals phagocytized by human
osteoblasts. Arthritis Res Ther. 15:R1762013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xia X, Kar R, Gluhak-Heinrich J, Yao W,
Lane NE, Bonewald LF, Biswas SK, Lo WK and Jiang JX:
Glucocorticoid-induced autophagy in osteocytes. J Bone Miner Res.
25:2479–2488. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jia J, Yao W, Guan M, Dai W, Shahnazari M,
Kar R, Bonewald L, Jiang JX and Lane NE: Glucocorticoid dose
determines osteocyte cell fate. FASEB J. 25:3366–3376. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Colell A, Ricci JE, Tait S, Milasta S,
Maurer U, Bouchier-Hayes L, Fitzgerald P, Guio-Carrion A,
Waterhouse NJ, Li CW, et al: GAPDH and autophagy preserve survival
after apoptotic cytochrome c release in the absence of caspase
activation. Cell. 129:983–997. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang C, Yu H, Shen Y, Ni X, Shen S and
Das UN: Polyunsaturated fatty acids trigger apoptosis of colon
cancer cells through a mitochondrial pathway. Arch Med Sci.
11:1081–1094. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kertmen H, Gurer B, Yilmaz ER, Kanat MA,
Arikok AT, Ergüder BI, Hasturk AE, Ergil J and Sekerci Z:
Antioxidant and antiapoptotic effects of darbepoetin-α against
traumatic brain injury in rats. Arch Med Sci. 11:1119–1128.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Schendel SL and Reed JC: Measuring pore
formation by Bcl-2 family proteins. Methods Enzymol. 322:274–282.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shimizu S, Narita M and Tsujimoto Y: Bcl-2
family proteins regulate the release of apoptogenic cytochrome c by
the mitochondrial channel VDAC. Nature. 399:483–487. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kubicka-Sierszen A and Grzegorczyk JŁ: The
influence of infectious factors on dendritic cell apoptosis. Arch
Med Sci. 11:1044–1051. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lauwers GY, Wahl SJ, Melamed J and
Rojas-Corona RR: p53 expression in precancerous gastric lesions: An
immunohistochemical study of PAb 1801 monoclonal antibody on
adenomatous and hyperplastic gastric polyps. Am J Gastroenterol.
88:1916–1919. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yue Y, Yang Y, Shi L and Wang Z:
Suppression of human hepatocellular cancer cell proliferation by
Brucea javanica oil-loaded liposomes via induction of apoptosis.
Arch Med Sci. 11:856–862. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Olivares-Illana V and Fahraeus R: p53
isoforms gain functions. Oncogene. 29:5113–5119. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chen Y, McMillan-Ward E, Kong J, Israels
SJ and Gibson SB: Oxidative stress induces autophagic cell death
independent of apoptosis in transformed and cancer cells. Cell
Death Differ. 15:171–182. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tassa A, Roux MP, Attaix D and Bechet DM:
Class III phosphoinositide 3-kinase--Beclin1 complex mediates the
amino acid-dependent regulation of autophagy in C2C12 myotubes.
Biochem J. 376:577–586. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liang XH, Kleeman LK, Jiang HH, Gordon G,
Goldman JE, Berry G, Herman B and Levine B: Protection against
fatal Sindbis virus encephalitis by beclin, a novel
Bcl-2-interacting protein. J Virol. 72:8586–8596. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Arsov I, Li X, Matthews G, Coradin J,
Hartmann B, Simon AK, Sealfon SC and Yue Z: BAC-mediated transgenic
expression of fluorescent autophagic protein Beclin 1 reveals a
role for Beclin 1 in lymphocyte development. Cell Death Differ.
15:1385–1395. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li R, Ma M, Li L, Zhao L, Zhang T, Gao X,
Zhang D, Zhu Y, Peng Q, Luo X and Wang M: The protective effect of
autophagy on DNA damage in mouse spermatocyte-derived cells exposed
to 1800 MHz radiofrequency electromagnetic fields. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 48:29–41. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Mizushima N: Methods for monitoring
autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:2491–2502. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Konttinen YT, Zhao D, Beklen A, Ma G,
Takagi M, Kivelä-Rajamäki M, Ashammakhi N and Santavirta S: The
microenvironment around total hip replacement prostheses. Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 28–38. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ren PG, Irani A, Huang Z, Ma T, Biswal S
and Goodman SB: Continuous infusion of UHMWPE particles induces
increased bone macrophages and osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
469:113–122. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gallo J, Raska M, Mrázek F and Petrek M:
Bone remodeling, particle disease and individual susceptibility to
periprosthetic osteolysis. Physiol Res. 57:339–349. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gross TS, King KA, Rabaia NA, Pathare P
and Srinivasan S: Upregulation of osteopontin by osteocytes
deprived of mechanical loading or oxygen. J Bone Miner Res.
20:250–256. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chen D, Guo Y, Mao X and Zhang X:
Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase down-regulates
the inflammatory osteolysis response to titanium particles in a
murine osteolysis model. Inflammation. 35:1798–1806. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Iwata Y, Wada T, Furuichi K, Sakai N,
Matsushima K, Yokoyama H and Kobayashi K: p38 Mitogen-activated
protein kinase contributes to autoimmune renal injury in MRL-Fas
lpr mice. J Am Soc Nephrol. 14:57–67. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhang L, Bao D, Li P, Lu Z, Pang L, Chen
Z, Guo H, Gao Z and Jin Q: Particle-induced SIRT1 downregulation
promotes osteoclastogenesis and osteolysis through ER stress
regulation. Biomed Pharmacother. 104:300–306. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Feng W, Li J, Liao S, Ma S, Li F, Zhong C,
Li G, Wei Y, Huang H, Wei Q, et al: Gö6983 attenuates titanium
particle-induced osteolysis and RANKL mediated osteoclastogenesis
through the suppression of NFκB/JNK/p38 pathways. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 503:62–70. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|