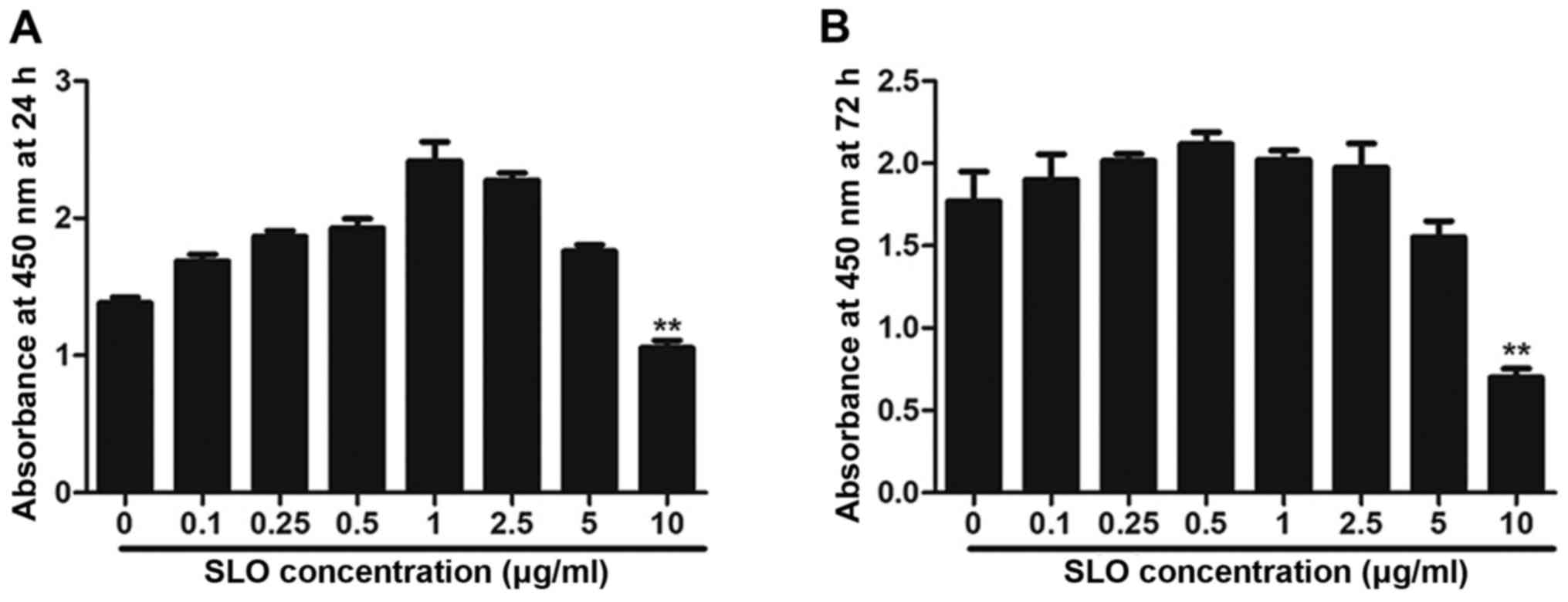
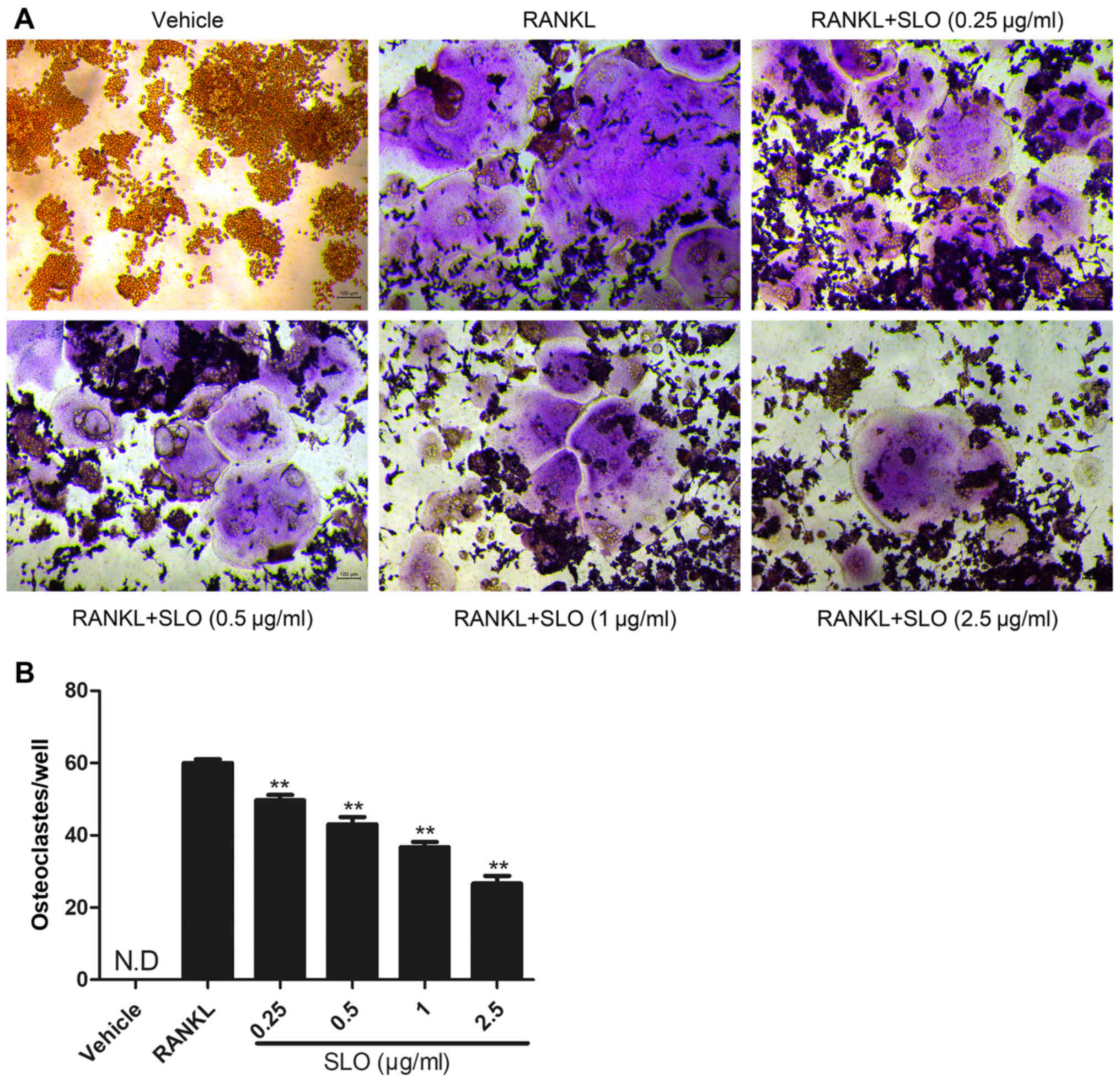
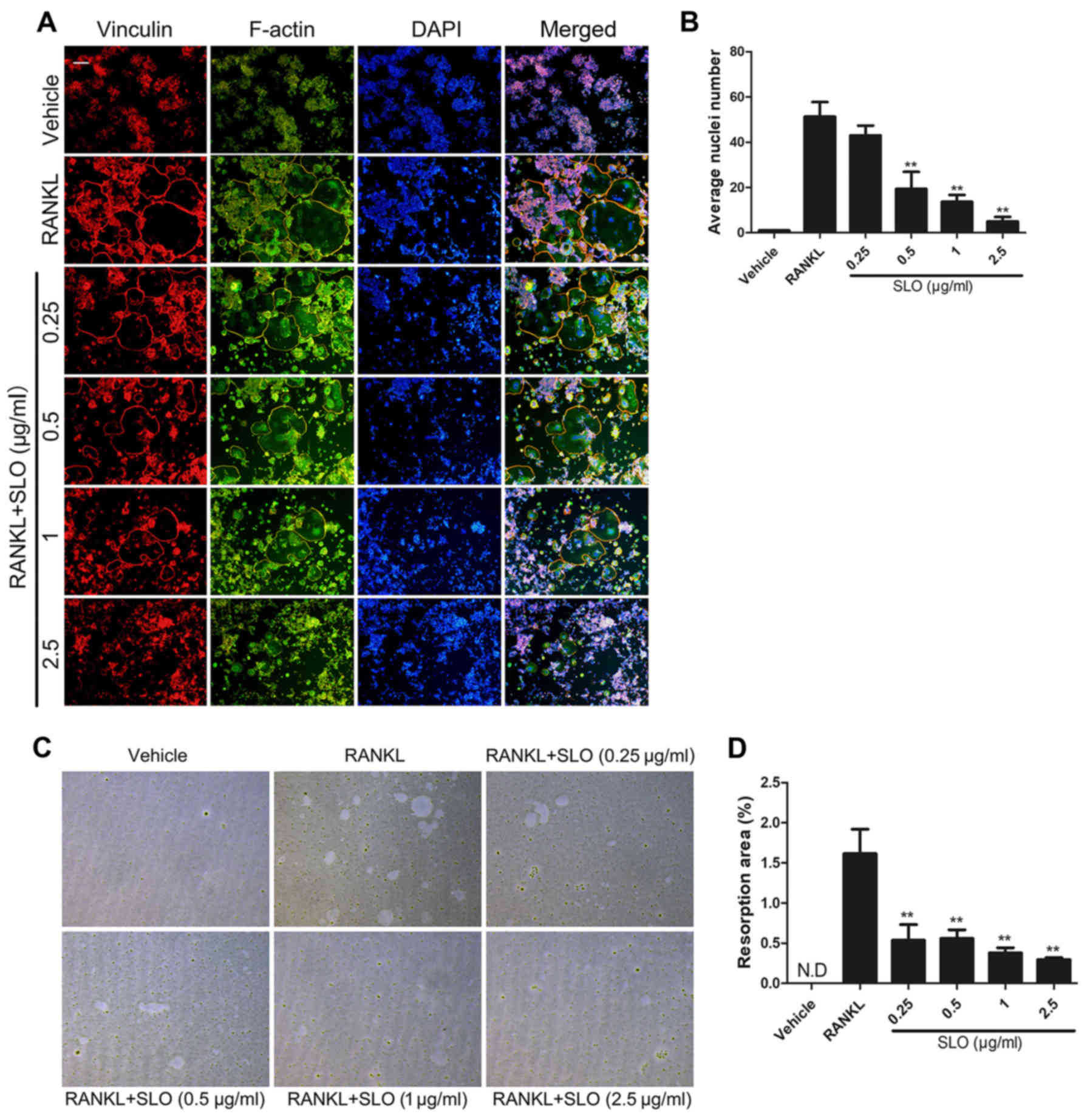
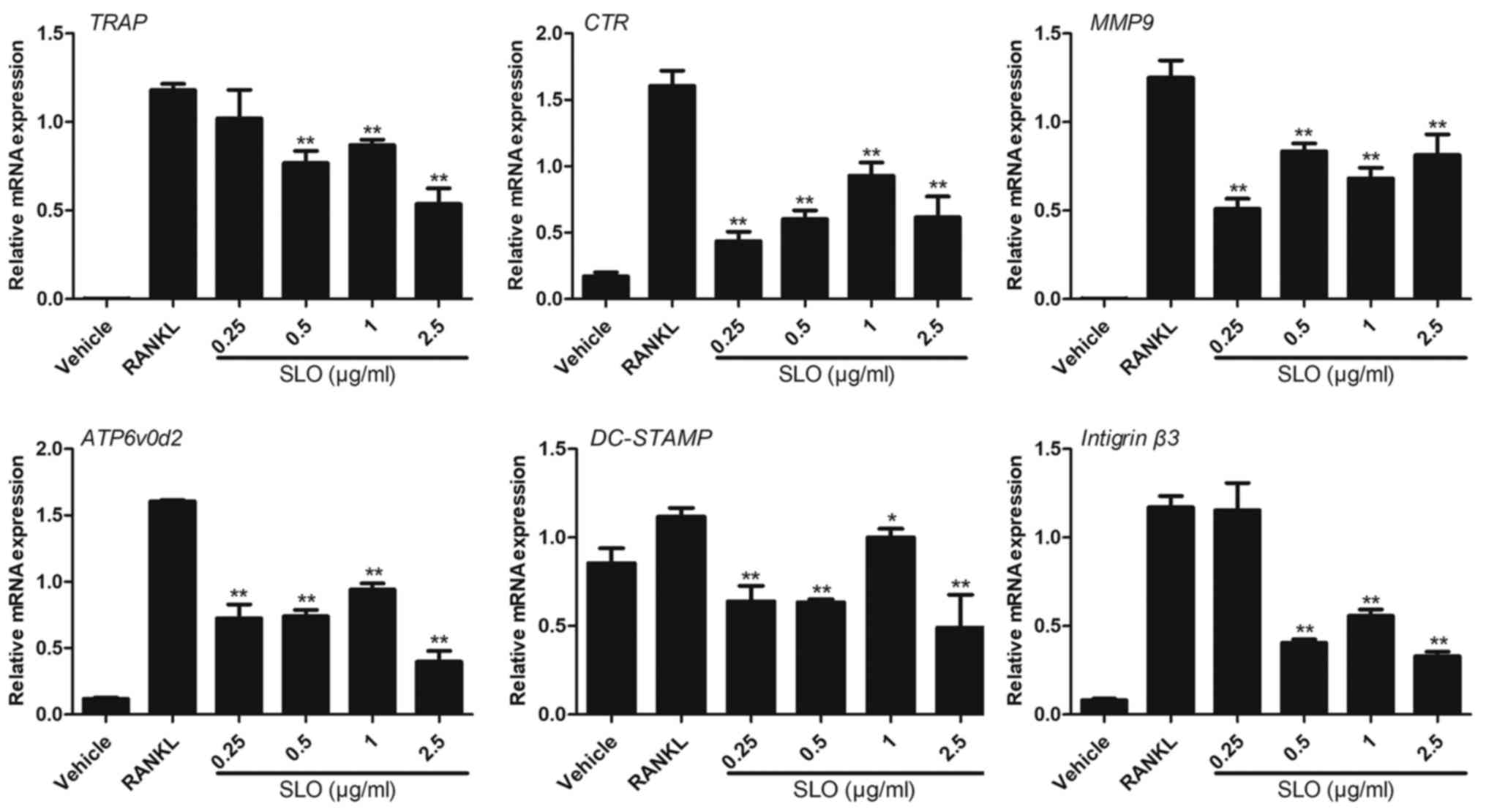
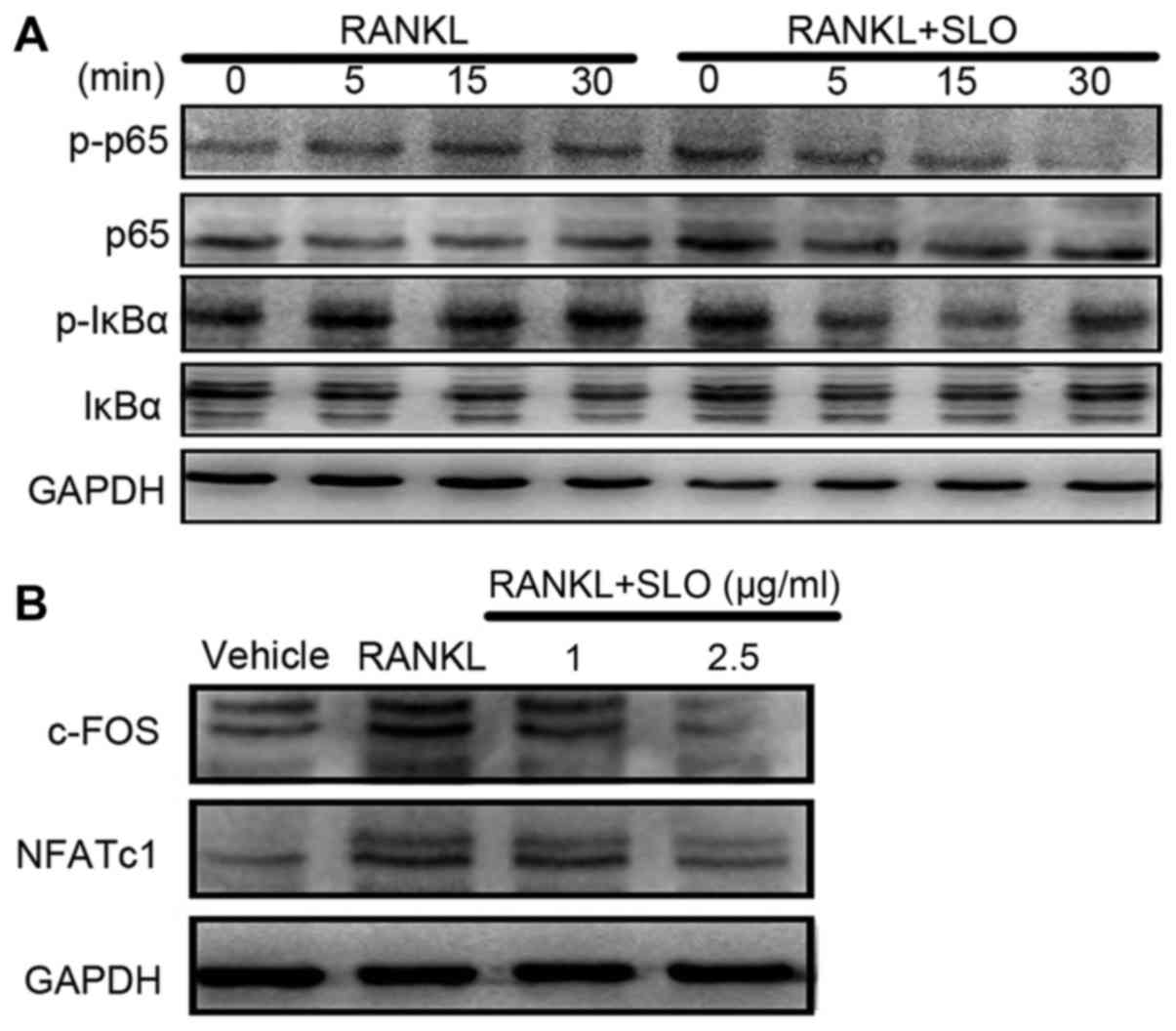
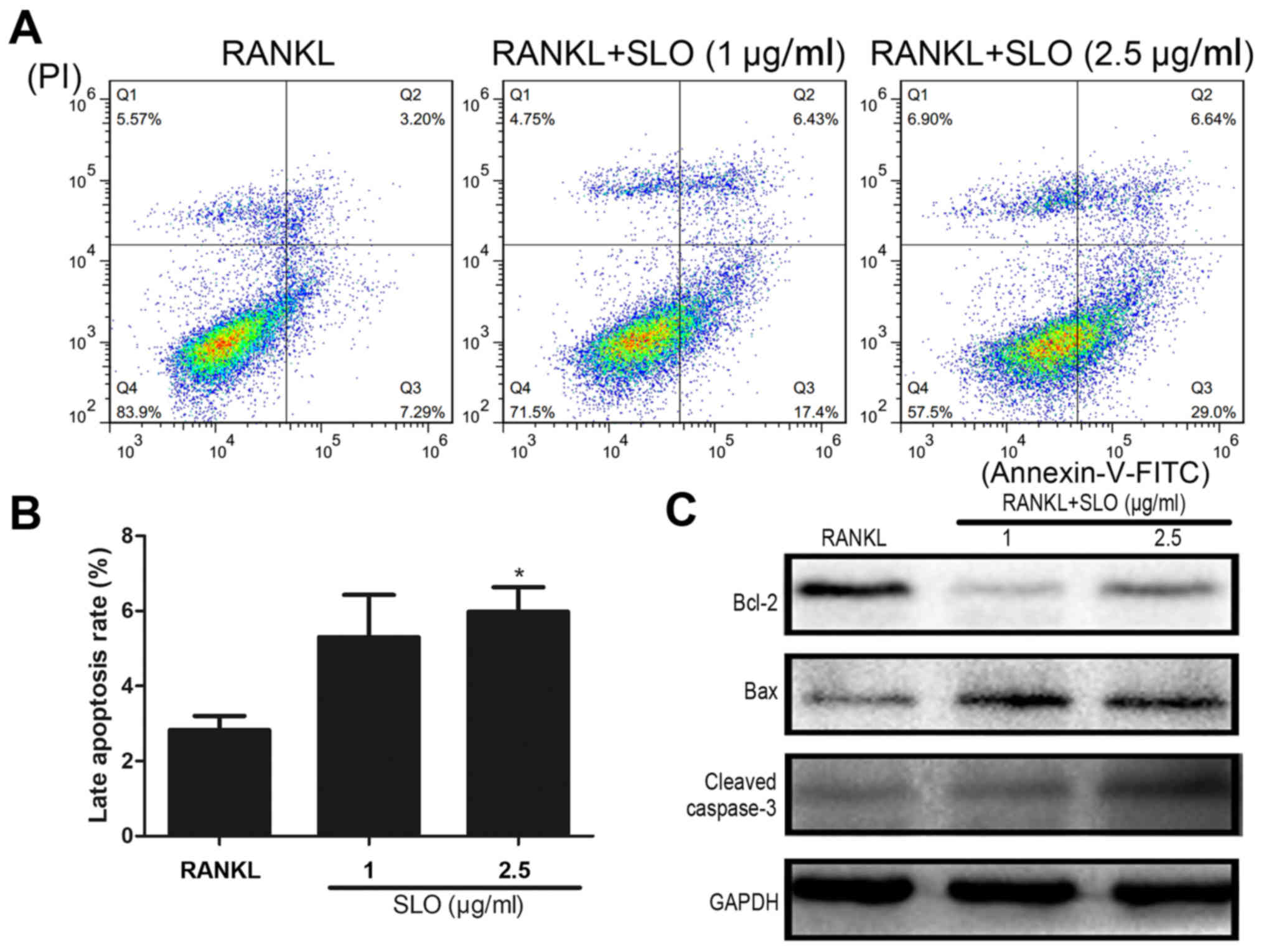
|
1
|
Harada S and Rodan GA: Control of
osteoblast function and regulation of bone mass. Nature.
423:349–355. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kim J, Yang J, Park OJ, Kang SS, Kim WS,
Kurokawa K, Yun CH, Kim HH, Lee BL and Han SH: Lipoproteins are an
important bacterial component responsible for bone destruction
through the induction of osteoclast differentiation and activation.
J Bone Miner Res. 28:2381–2391. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Moriarty TF, Schlegel U, Perren S and
Richards RG: Infection in fracture fixation: Can we influence
infection rates through implant design? J Mater Sci Mater Med.
21:1031–1035. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schattner A and Vosti KL: Bacterial
arthritis due to beta-hemolytic streptococci of serogroups A, B, C,
F and G: Analysis of 23 cases and a review of the literature.
Medicine (Baltimore). 77:122–139. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pichichero ME and Casey JR: Systematic
review of factors contributing topenicillin treatment failure in
Streptococcus pyogenes pharyngitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck
Surg. 137:851–857. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nilsson M, Sørensen OE, Mörgelin M,
Weineisen M, Sjöbring U and Herwald H: Activation of human
polymorphonuclear eutrophils by streptolysin O from
Streptococcus pyogenes leads to the release of
proinflammatory mediators. Thromb Haemost. 95:982–990. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Anderluh G and Lakey J: Proteins: Membrane
binding and pore formation. Preface. Adv Exp Med Biol. 677:v–vi.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hotze EM, Wilson-Kubalek E, Farrand AJ,
Bentsen L, Parker MW, Johnson AE and Tweten RK: Monomer-monomer
interactions propagate structural transitions necessary for pore
formation by the cholesterol-dependent cytolysins. J Biol Chem.
287:24534–24543. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bhakdi S, Bayley H, Valeva A, Walev I,
Walker B, Kehoe M and Palmer M: Staphylococcal alpha-toxin,
streptolysin-O, and Escherichia coli hemolysin: Prototypes of
pore-forming bacterial cytolysins. Arch Microbiol. 165:73–79. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bricker AL, Carey VJ and Wessels MR: Role
of NADase in virulence in experimental invasive group A
streptococcal infection. Infect Immun. 73:6562–6566. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
O'Seaghdha M and Wessels MR: Streptolysin
O and its co-toxin NAD-glycohydrolase protect group A
Streptococcus from Xenophagic killing. PLoS Pathog.
9:e10033942013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bastiat-Sempe B, Love JF, Lomayesva N and
Wessels MR: Streptolysin O and NAD-glycohydrolase prevent
phagolysosome acidification and promote group A
streptococcus survival in macrophages. MBio. 5:e01690–14.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Carapetis JR, Steer AC, Mulholland EK and
Weber M: The global burden of group A streptococcal diseases.
Lancet Infect Dis. 5:685–694. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Walker MJ, Barnett TC, McArthur JD, Cole
JN, Gillen CM, Henningham A, Sriprakash KS, Sanderson-Smith ML and
Nizet V: Disease manifestations and pathogenic mechanisms of group
a Streptococcus. Clin Microbiol Rev. 27:264–301. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Good MF, Batzloff M and Pandey M:
Strategies in the development of vaccines to prevent infections
with group A streptococcus. Hum Vaccin Immunother.
9:2393–2397. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pichichero ME: Group A beta-hemolytic
streptococcal infections. Pediatr Rev. 19:291–302. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Freiberg JA, Mciver KS and Shirtliff ME:
In vivo expression of Streptococcus pyogenes immunogenic
proteins during tibial foreign body infection. Infect Immun.
82:3891–3899. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sakurai A, Okahashi N, Nakagawa I,
Kawabata S, Amano A, Ooshima T and Hamada S: Streptococcus
pyogenes infection induces septic arthritis with increased
production of the receptor activator of the NF-kappaB ligan. Infect
Immun. 71:6019–6026. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Matsui H, Nakatani Y, Yoshida H, Takizawa
A, Takeuchi O, Øverby A, Takahashi T, Murayama SY and Matsuo K:
Flesh-eating Streptococcus pyogenes triggers the expression
of receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand. Cell Microbiol.
18:1390–1404. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Okahashi N, Sakurai A, Nakagawa I,
Fujiwara T, Kawabata S, Amano A and Hamada S: Infection by
Streptococcus pyogenes induces the receptor activator of
NF-kappaB ligand expression in mouse osteoblastic cells. Infect
Immun. 71:948–955. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Barnes PJ and Karin M: Nuclear
factor-kappsBb: A pivotal transcription factor in chronic
inflammatory diseases. N Engl J Med. 336:1066–1071. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, Kelley MJ,
Dunstan CR, Burgess T, Elliott R, Colombero A, Elliott G, Scully S,
et al: Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates
osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell. 93:165–176. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ghosh S and Karin M: Missing pieces in the
NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell. 109 Suppl:S81–S96. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nepal M, Choi HJ, Choi BY, Yang MS, Chae
JI, Li L and Soh Y: Hispidulin attenuates bone resorption and
osteoclastogenesis via the RANKL-induced NF-kappaB and NFATc1
pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 715:96–104. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yamashita T, Yao Z, Li F, Zhang Q, Badell
IR, Schwarz EM, Takeshita S, Wagner EF, Noda M, Matsuo K, et al:
NF-kappaB p50 and p52 regulate receptor activator of NF-kappaB
ligand (RANKL) and tumor necrosis factor-induced osteoclast
precursor differentiation by activating c-Fos and NFATc1. J Biol
Chem. 282:18245–18253. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cywes Bentley C, Hakansson A, Christianson
J and Wessels MR: Extracellular group A Streptococcus
induces keratinocyte apoptosis by dysregulating calcium signaling.
Cell Microbiol. 7:945–955. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Timmer AM, Timmer JC, Pence MA, Hsu LC,
Ghochani M, Frey TG, Karin M, Salvesen GS and Nizet V: Streptolysin
O promotes group A Streptococcus immune evasion by
accelerated macrophage apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 284:862–871. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Scorrano L and Korsmeyer SJ: Mechanisms of
cytochrome c release by proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 304:437–444. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tai TW, Chen CY, Su FC, Tu YK, Tsai TT,
Lin CF and Jou IM: Reactive oxygen species are required for
zoledronic acid-induced apoptosis in osteoclast precursors and
mature osteoclast-like cells. Sci Rep. 7:442452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kinning E, McMillan M, Shepherd S,
Helfrich M, Hof RV, Adams C, Read H, Wall DM and Ahmed SF: An
unbalanced rearrangement of chromosomes 4: 20 is associated with
childhood osteoporosis and reduced caspase-3 levels. J Pediatr
Genet. 5:167–173. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shan RF, Zhou YF, Peng AF and Jie ZG:
Inhibition of Aurora-B suppresses HepG2 cell invasion and migration
via the PI3K/Akt/NF-kB signaling pathway in vitro. Exp Ther
Med. 8:1005–1009. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nehra R, Riggins RB, Shajahan AN, Zwart A,
Crawford AC and Clarke R: BCL2 and CASP8 regulation by NF-kappaB
differentially affect mitochondrial function and cell fate in
antiestrogen-sensitive and-resistant breast cancer cells. FASEB J.
24:2040–2055. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Henrotin Y, Clutterbuck AL, Allaway D,
Lodwig EM, Harris P, Mathy-Hartert M, Shakibaei M and Mobasheri A:
Biological actions of curcumin on articular chondrocytes.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 18:141–149. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kiekow CJ, Figueiró F, Dietrich F, Vechia
LD, Pires EN, Jandrey EH, Gnoatto SC, Salbego CG, Battastini AM and
Gosmann G: Quercetin derivative induces cell death in glioma cells
by modulating NF-κB nuclear translocation and Caspase-3 activation.
Eur J Pharm Sci. 84:116–122. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cortés G and Wessels MR: Inhibition of
dendritic cell maturation by group A Streptococcus. J Infect
Dis. 200:1152–1161. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Walev I, Hombach M, Bobkiewicz W, Fenske
D, Bhakdi S and Husmann M: Resealing of large transmembrane pores
produced by streptolysin O in nucleated cells is accompanied by
NF-kappaB activation and downstream events. FASEB J. 16:237–239.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lorenzo J: Interactions between immune and
bone cells: New insights with many remaining questions. J Clin
Invest. 106:749–752. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|