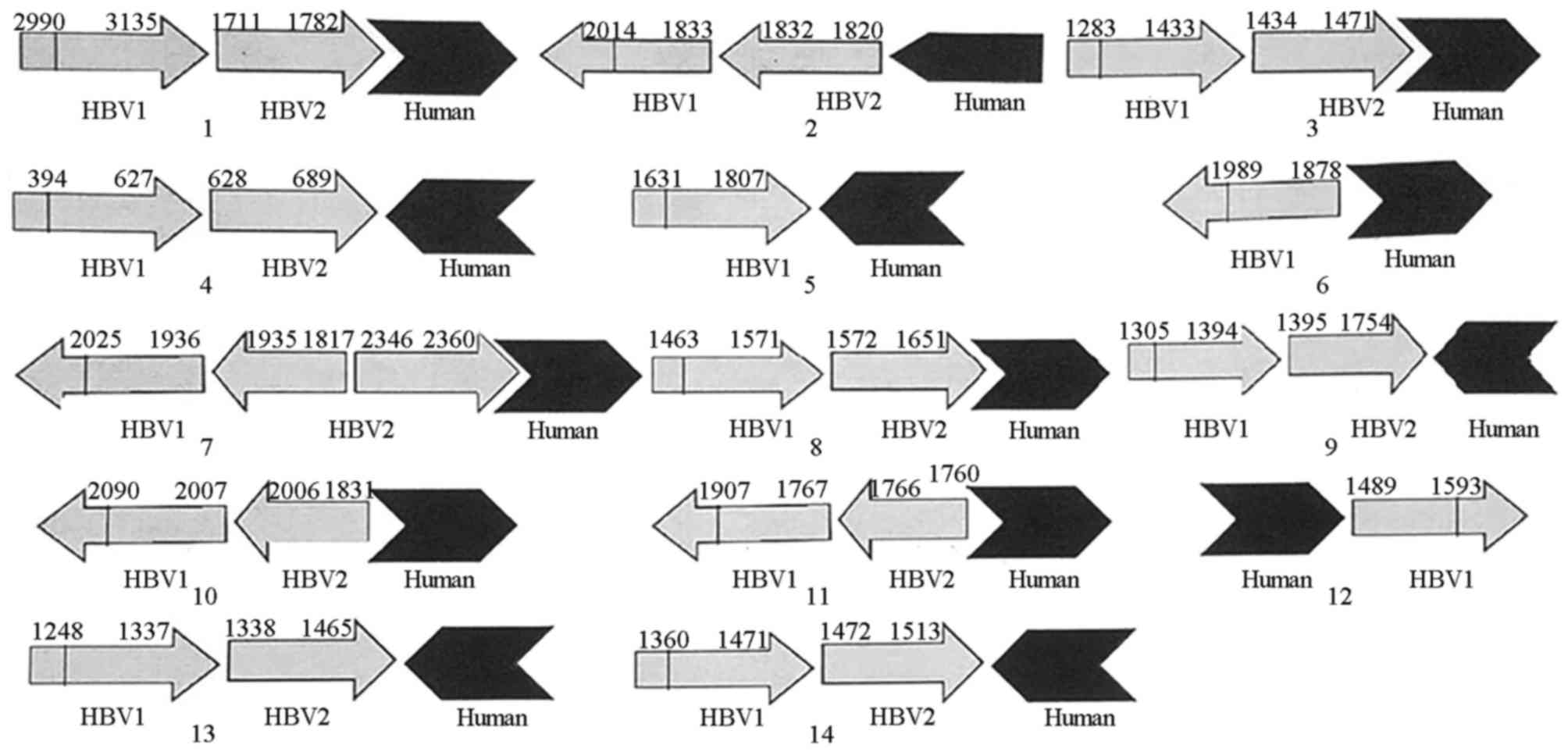
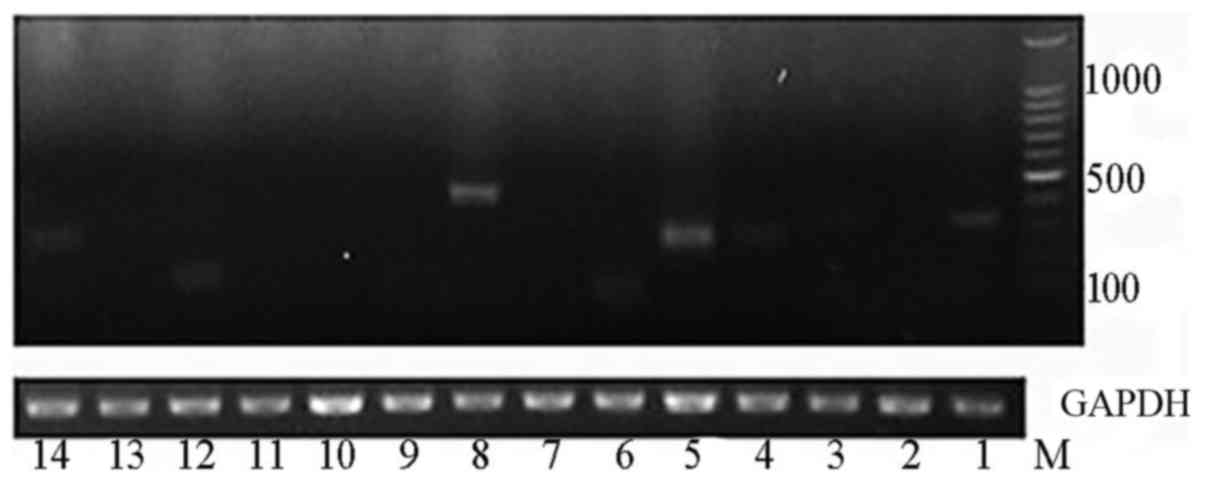
|
1
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lok AS and McMahon BJ: Chronic Hepatitis
B. Hepatology. 45:507–539. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Murakami Y, Saigo K, Takashima H, Minami
M, Okanoue T, Bréchot C and Paterlini-Bréchot P: Large scaled
analysis of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA integration in HBV related
hepatocellular carcinomas. Gut. 54:1162–1168. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Saigo K, Yoshida K, Ikeda R, Sakamoto Y,
Murakami Y, Urashima T, Asano T, Kenmochi T and Inoue I:
Integration of hepatitis B virus DNA into the myeloid/lymphoid or
mixed-lineage leukemia (MLL4) gene and rearrangements of MLL4 in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hum Mutat. 29:703–708. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tamori A, Yamanishi Y, Kawashima S,
Kanehisa M, Enomoto M, Tanaka H, Kubo S, Shiomi S and Nishiguchi S:
Alteration of gene expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma
with integrated hepatitis B virus DNA. Clin Cancer Res.
11:5821–5826. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang Z, Jhunjhunwala S, Liu J, Haverty
PM, Kennemer MI, Guan Y, Lee W, Carnevali P, Stinson J, Johnson S,
et al: The effects of hepatitis B virus integration into the
genomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Genome Res.
22:593–601. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sung WK, Zheng H, Li S, Chen R, Liu X, Li
Y, Lee NP, Lee WH, Ariyaratne PN, Tennakoon C, et al: Genome-wide
survey of recurrent HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Nat Genet. 44:765–769. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Toh ST, Jin Y, Liu L, Wang J, Babrzadeh F,
Gharizadeh B, Ronaghi M, Toh HC, Chow PK, Chung AY, et al: Deep
sequencing of the hepatitis B virus in hepatocellular carcinoma
patients reveals enriched integration events, structural
alterations and sequence variations. Carcinogenesis. 34:787–798.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao LH, Liu X, Yan HX, Li WY, Zeng X,
Yang Y, Zhao J, Liu SP, Zhuang XH, Lin C, et al: Genomic and
oncogenic preference of HBV integration in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Nat Commun. 7:129922016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chinese Society of Hepatology and Chinese
Society of Infectious Diseases. Chinese Medical Association, The
guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B (2010
version). Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi (Chinese J Hepatol).
19:13–24. 2011.
|
|
11
|
Belloni L, Allweiss L, Guerrieri F,
Pediconi N, Volz T, Pollicino T, Petersen J, Raimondo G, Dandri M
and Levrero M: IFN-α inhibits HBV transcription and replication in
cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic
regulation of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome. J Clin Invest.
122:529–537. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Werle-Lapostolle B, Bowden S, Locarnini S,
Wursthorn K, Petersen J, Lau G, Trepo C, Marcellin P, Goodman Z,
Delaney WE 4th, et al: Persistence of cccDNA during the natural
history of chronic hepatitis B and decline during adefovir
dipivoxil therapy. Gastroenterology. 126:1750–1758. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zheng Q, Bai L, Zheng S, Liu M, Zhang J,
Wang T, Xu Z, Chen Y, Li J and Duan Z: Efficient inhibition of duck
hepatitis B virus DNA by the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Mol Med Rep.
16:7199–7204. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tu T, Budzinska MA, Vondran FWR, Shackel
NA and Urban S: Hepatitis B virus DNA integration occurs early in
the viral life cycle in an in vitro infection model via
NTCP-dependent uptake of enveloped virus particles. J Virol. Feb
7–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Murakami Y, Minami M, Daimon Y and Okanoue
T: Hepatitis B virus DNA in liver, serum, and peripheral blood
mononuclear cells after the clearance of serum hepatitis B virus
surface antigen. J Med Virol. 72:203–214. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sims D, Sudbery I, Ilott NE, Heger A and
Ponting CP: Sequencing depth and coverage: Key considerations in
genomic analyses. Nat Rev Genet. 15:121–132. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hosaka T, Suzuki F, Kobayashi M, Hirakawa
M, Kawamura Y, Yatsuji H, Sezaki H, Akuta N, Suzuki Y, Saitoh S, et
al: HBcrAg is a predictor of post-treatment recurrence of
hepatocellular carcinoma during antiviral therapy. Liver Int.
30:1461–1470. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dandri M, Burda MR, Bürkle A, Zuckerman
DM, Will H, Rogler CE, Greten H and Petersen J: Increase in de novo
HBV DNA integrations in response to oxidative DNA damage or
inhibition of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation. Hepatology. 35:217–223. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bill CA and Summers J: Genomic DNA
double-strand breaks are targets for hepadnaviral DNA integration.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:11135–11140. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hu Z, Zhu D, Wang W, Li W, Jia W, Zeng X,
Ding W, Yu L, Wang X and Wang L: Genome-wide profiling of HPV
integration in cervical cancer identifies clustered genomic hot
spots and a potential microhomology-mediated integration mechanism.
Nat Genet. 47:158–163. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mladenov E, Magin S, Soni A and Iliakis G:
DNA double-strand-break repair in higher eukaryotes and its role in
genomic instability and cancer: Cell cycle and
proliferation-dependent regulation. Semin. Cancer Biol. 37–38.
51–64. 2016.
|
|
22
|
Hu X, Lin J, Xie Q, Ren J, Chang Y, Wu W
and Xia Y: DNA double-strand breaks, potential targets for HBV
integration. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 30:265–270.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hastings PJ, Ira G and Lupski JR: A
microhomology-mediated break-induced replication model for the
origin of human copy number variation. PLoS Genet. 5:e10003272009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yoo S, Wang W, Wang Q, Fiel MI, Lee E,
Hiotis SP and Zhu J: A pilot systematic genomic comparison of
recurrence risks of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular
carcinoma with low- and high-degree liver fibrosis. BMC Med.
150:2142017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wooddell CI, Yuen MF, Chan HL, Gish RG,
Locarnini SA, Chavez D, Ferrari C, Given BD, Hamilton J, Kanner SB,
et al: RNAi-based treatment of chronically infected patients and
chimpanzees reveals that integrated hepatitis B virus DNA is a
source of HBsAg. Sci Transl Med. 9:eaan02412017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ruan P, Zhou B, Dai X, Sun Z, Guo X, Huang
J and Gong Z: Predictive value of intrahepatic hepatitis B virus
covalently closed circular DNA and total DNA in patients with acute
hepatitis B and patients with chronic hepatitis B receiving
anti-viral treatment. Mol Med Rep. 9:1135–1141. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Thompson AJ, Nguyen T, Iser D, Ayres A,
Jackson K, Littlejohn M, Slavin J, Bowden S, Gane EJ, Abbott W, et
al: Serum hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen
titers: Disease phase influences correlation with viral load and
intrahepatic hepatitis B virus markers. Hepatology. 51:1933–1944.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mason WS, Low HC, Xu C, Aldrich CE,
Scougall CA, Grosse A, Clouston A, Chavez D, Litwin S, Peri S, et
al: Detection of clonally expanded hepatocytes in chimpanzees with
chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Virol. 83:8396–8408. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|