|
1
|
Abalos E, Cuesta C, Grosso AL, Chou D and
Say L: Global and regional estimates of preeclampsia and eclampsia:
A systematic review. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Repro Biol. 170:1–7.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
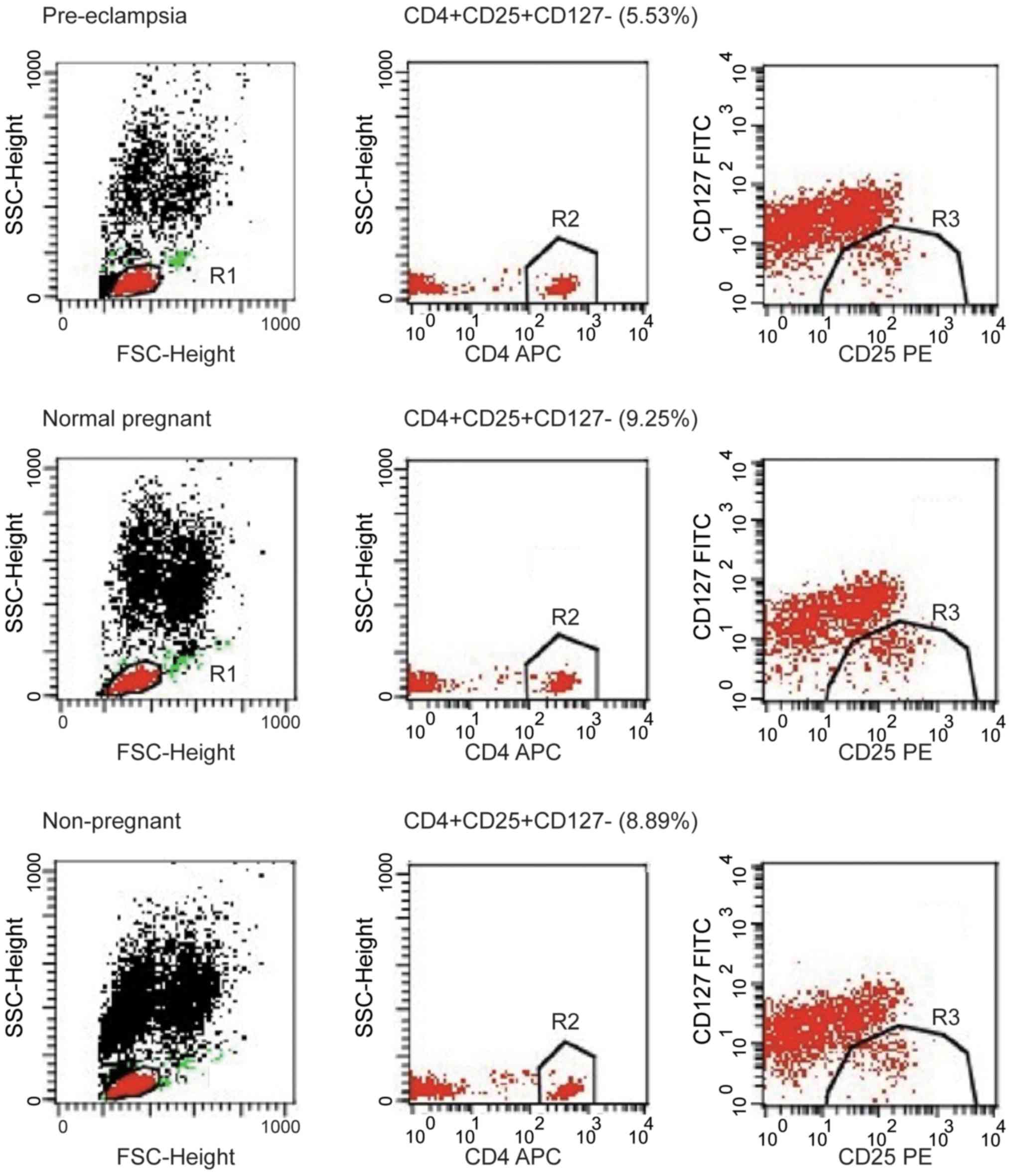
|
Moore-Maxwell CA and Robboy SJ: Placental
site trophoblastic tumor arising from antecedent molar pregnancy.
Gynecol Oncol. 92:708–712. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ilekis JV, Reddy UM and Roberts JM:
Preeclampsia-A pressing problem: An executive summary of a national
institute of child health and human development workshop. Reprod
Sci. 14:508–523. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lok CA, Jebbink J, Nieuwland R, Faas MM,
Boer K, Sturk A and Van Der Post JA: Leukocyte activation and
circulating leukocyte-derived microparticles in preeclampsia. Am J
Reprod Immunol. 61:346–359. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M
and Toda M: Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T
cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a
single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune
diseases. J Immunol. 155:1151–1164. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aluvihare VR, Kallikourdis M and Betz AG:
Regulatory T cells mediate maternal tolerance to the fetus. Nat
Immuno. 5:266–271. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Xiong YH, Yuan Z and He L: Effects of
estrogen on CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cell in
peripheral blood during pregnancy. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 6:748–752.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Heikkinen J, Mottonen M, Alanen A and
Lassila O: Phenotypic characterization of regulatory T cells in the
human decidua. Clin Exp Immunol. 136:373–378. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zenclussen AC, Gerlof K, Zenclussen ML,
Sollwedel A, Bertoja AZ, Ritter T, Kotsch K, Leber J and Volk HD:
Abnormal T-cell reactivity against paternal antigens in spontaneous
abortion: Adoptive transfer of pregnancy-induced
CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells prevents fetal
rejection in a murine abortion model. Am J Pathol. 166:811–822.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sasaki Y, Darmochwal-Kolarz D, Suzuki D,
Sakai M, Ito M, Shima T, Shiozaki A, Rolinski J and Saito S:
Proportion of peripheral blood and decidual CD4+
CD25bright regulatory T cells in pre-eclampsia. Clin Exp
Immunol. 149:139–145. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Darmochwal-Kolarz D, Saito S, Rolinski J,
Tabarkiewicz J, Kolarz B, Leszczynska-Gorzelak B and Oleszczuk J:
Activated T lymphocytes in pre-eclampsia. Am J Reprod Immunol.
58:39–45. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nakashima A, Shima T, Inada K, Ito M and
Saito S: The balance of the immune system between T cells and NK
cells in miscarriage. Am J Reprod Immunol. 67:304–310. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Koucky M, Malickova K, Cindrova-Davies T,
Germanova A, Parizek A, Kalousova M, Hajek Z and Zima T: Low levels
of circulating T-regulatory lymphocytes and short cervical length
are associated with preterm labor. J Reprod Immunol. 106:110–117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiong H, Zhou C and Qi G: Proportional
changes of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+
regulatory T cells in maternal peripheral blood during pregnancy
and labor at term and preterm. Clin Invest Med. 33:E4222010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sakaguchi S, Ono M, Setoguchi R, Yagi H,
Hori S, Fehervari Z, Shimizu J, Takahashi T and Nomura T:
Foxp3+ CD25+ CD4+ natural
regulatory T cells in dominant self-tolerance and autoimmune
disease. Immunol Rev. 212:8–27. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sasaki Y, Sakai M, Miyazaki S, Higuma S,
Shiozaki A and Saito S: Decidual and peripheral blood
CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in early
pregnancy subjects and spontaneous abortion cases. Mol Hum Reprod.
10:347–353. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cristofalo R, Bannwart-Castro CF,
Magalhaes CG, Borges VT, Peracoli JC, Witkin SS and Peracoli MT:
Silibinin attenuates oxidative metabolism and cytokine production
by monocytes from preeclamptic women. Free Radic Res. 47:268–275.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Peracoli JC, Bannwart-Castro CF, Romao M,
Weel IC, Ribeiro VR, Borges VT, Rudge MV, Witkin SS and Peracoli
MT: High levels of heat shock protein 70 are associated with
pro-inflammatory cytokines and may differentiate early- from
late-onset preeclampsia. J Reprod Immunol. 100:129–134. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Figueiredo AS and Schumacher A: The T
helper type 17/regulatory T cell paradigm in pregnancy. Immunology.
148:13–21. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Darmochwal-Kolarz D, Kludka-Sternik M,
Tabarkiewicz J, Kolarz B, Rolinski J, Leszczynska-Gorzelak B and
Oleszczuk J: The predominance of Th17 lymphocytes and decreased
number and function of Treg cells in preeclampsia. J Reprod
Immunol. 93:75–81. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Santner-Nanan B, Peek MJ, Khanam R,
Richarts L, Zhu E, Fazekas de St Groth B and Nanan R: Systemic
increase in the ratio between Foxp3+ and IL-17-producing
CD4+ T cells in healthy pregnancy but not in
preeclampsia. J Immunol. 183:7023–7030. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Alijotas-Reig J, Llurba E and Gris JM:
Potentiating maternal immune tolerance in pregnancy: A new
challenging role for regulatory T cells. Placenta. 35:241–248.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Z, Liu H, Shi Y, Xu N, Wang Y, Li A
and Song W: Increased circulating Th22 cells correlated with Th17
cells in patients with severe preeclampsia. Hypertens Pregnancy.
36:100–107. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu W, Putnam AL, Xu-Yu Z, Szot GL, Lee
MR, Zhu S, Gottlieb PA, Kapranov P, Gingeras TR, Fazekas de St
Groth B, et al: CD127 expression inversely correlates with FoxP3
and suppressive function of human CD4+ T reg cells. J
Exp Med. 203:1701–1711. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Miyara M and Sakaguchi S: Human
FoxP3+CD4+ regulatory T cells: Their knowns
and unknowns. Immunol Cell Biol. 89:346–351. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Seddiki N, Santner-Nanan B, Martinson J,
Zaunders J, Sasson S, Landay A, Solomon M, Selby W, Alexander SI,
Nanan R, et al: Expression of interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-7 receptors
discriminates between human regulatory and activated T cells. J Exp
Med. 203:1693–1700. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Aerts NE, Dombrecht EJ, Ebo DG, Bridts CH,
Stevens WJ and De Clerck LS: Activated T cells complicate the
identification of regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell
Immunol. 251:109–115. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huntzinger E and Izaurralde E: Gene
silencing by microRNAs: Contributions of translational repression
and mRNA decay. Nat Rev Genet. 12:99–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Morales-Prieto DM, Ospina-Prieto S,
Chaiwangyen W, Schoenleben M and Markert UR: Pregnancy-associated
miRNA-clusters. J Reprod Immunol. 97:51–61. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xu X, Kriegel AJ, Liu Y, Usa K, Mladinov
D, Liu H, Fang Y, Ding X and Liang M: Delayed ischemic
preconditioning contributes to renal protection by upregulation of
miR-21. Kidney Int. 82:1167–1175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lin Z, Murtaza I, Wang K, Jiao J, Gao J
and Li PF: miR-23a functions downstream of NFATc3 to regulate
cardiac hypertrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:12103–12108. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shen XC, Lu Y and Qian ZY: Effects of
crocetin on the matrix metalloproteinases in cardiac hypertrophy
induced by norepinephrine in rats. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 8:201–208.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R,
Gilad S, Barad O, Barzilai A, Einat P, Einav U, Meiri E, et al:
Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human
microRNAs. Nat Genet. 37:766–770. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pineles BL, Romero R, Montenegro D, Tarca
AL, Han YM, Kim YM, Draghici S, Espinoza J, Kusanovic JP, Mittal P,
et al: Distinct subsets of microRNAs are expressed differentially
in the human placentas of patients with preeclampsia. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 196:e261–e266. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chim SS, Shing TK, Hung EC, Leung TY, Lau
TK, Chiu RW and Lo YM: Detection and characterization of placental
microRNAs in maternal plasma. Clin Chem. 54:482–490. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mouillet JF, Chu T, Hubel CA, Nelson DM,
Parks WT and Sadovsky Y: The levels of hypoxia-regulated microRNAs
in plasma of pregnant women with fetal growth restriction.
Placenta. 31:781–784. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao M, Wang LT, Liang GP, Zhang P, Deng
XJ, Tang Q, Zhai HY, Chang CC, Su YW and Lu QJ: Up-regulation of
microRNA-210 induces immune dysfunction via targeting FOXP3 in
CD4+ T cells of psoriasis vulgaris. Clin Immunol.
150:22–30. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Auerbach L, Hafner T, Huber JC and Panzer
S: Influence of low-dose oral contraception on peripheral blood
lymphocyte subsets at particular phases of the hormonal cycle.
Fertil Steril. 78:83–89. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
No authors listed, : Report of the
national high blood pressure education program working group on
high blood pressure in pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 183:S1–S22.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Redman CW, Sacks GP and Sargent IL:
Preeclampsia: An excessive maternal inflammatory response to
pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 180:499–506. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Walker MR, Kasprowicz DJ, Gersuk VH,
Benard A, Van Landeghen M, Buckner JH and Ziegler SF: Induction of
FoxP3 and acquisition of T regulatory activity by stimulated human
CD4+CD25 T cells. J Clin Invest. 112:1437–1443. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jianjun Z, Yali H, Zhiqun W, Mingming Z
and Xia Z: Imbalance of T-cell transcription factors contributes to
the Th1 type immunity predominant in pre-eclampsia. Am J Reprod
Immunol. 63:38–45. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Saito S, Nakashima A, Shima T and Ito M:
Th1/Th2/Th17 and regulatory T-cell paradigm in pregnancy. Am J
Reprod Immunol. 63:601–610. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T,
Strom TB, Oukka M, Weiner HL and Kuchroo VK: Reciprocal
developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector
TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 441:235–238. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Molvarec A, Czegle I, Szijarto J and Rigo
J Jr: Increased circulating interleukin-17 levels in preeclampsia.
J Reprod Immunol. 112:53–57. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Szarka A, Rigo J Jr, Lazar L, Beko G and
Molvarec A: Circulating cytokines, chemokines and adhesion
molecules in normal pregnancy and preeclampsia determined by
multiplex suspension array. BMC Immunol. 11:592010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Toldi G, Rigo J Jr, Stenczer B, Vasarhelyi
B and Molvarec A: Increased prevalence of IL-17-producing
peripheral blood lymphocytes in pre-eclampsia. Am J Reprod Immunol.
66:223–229. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cross D and Cambier JC: Transforming
growth factor beta 1 has differential effects on B cell
proliferation and activation antigen expression. J Immunol.
144:432–439. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Travis MA and Sheppard D: TGF-β activation
and function in immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 32:51–82. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bilate AM and Lafaille JJ: Induced
CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in immune
tolerance. Annu Rev Immunol. 30:733–758. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Josefowicz SZ, Lu LF and Rudensky AY:
Regulatory T cells: Mechanisms of differentiation and function.
Annu Rev Immunol. 30:531–564. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cretney E, Kallies A and Nutt SL:
Differentiation and function of Foxp3 effector regulatory T cells.
Trends Immunol. 34:74–80. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Klein S, Kretz CC, Krammer PH and Kuhn A:
CD127low/− and FoxP3+ expression levels
characterize different regulatory T-cell populations in human
peripheral blood. J Invest Dermatol. 130:492–499. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Mazzucchelli R, Hixon JA, Spolski R, Chen
X, Li WQ, Hall VL, Willette-Brown J, Hurwitz AA, Leonard WJ and
Durum SK: Development of regulatory T cells requires IL-7Rα
stimulation by IL-7 or TSLP. Blood. 112:3283–3292. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|