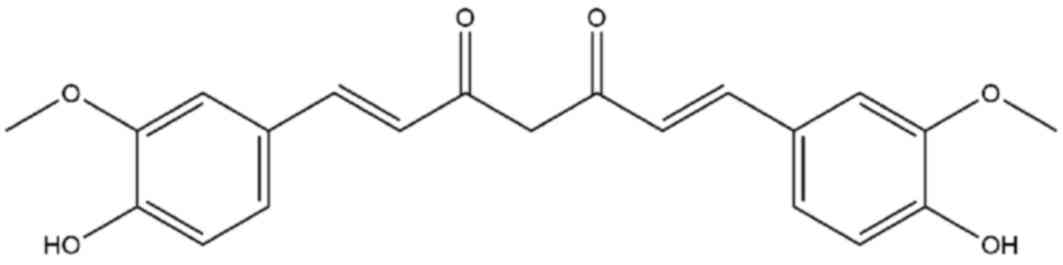
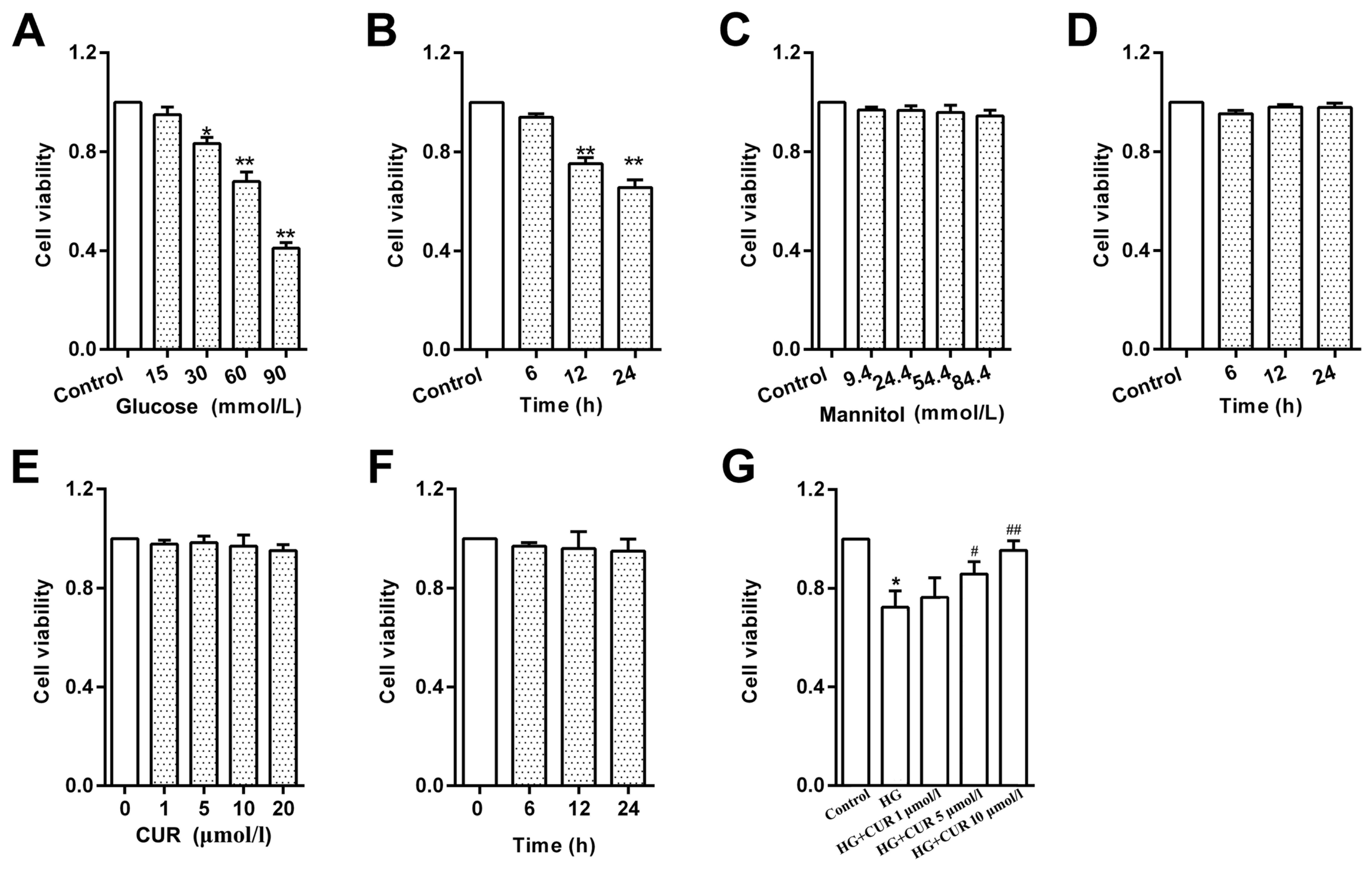
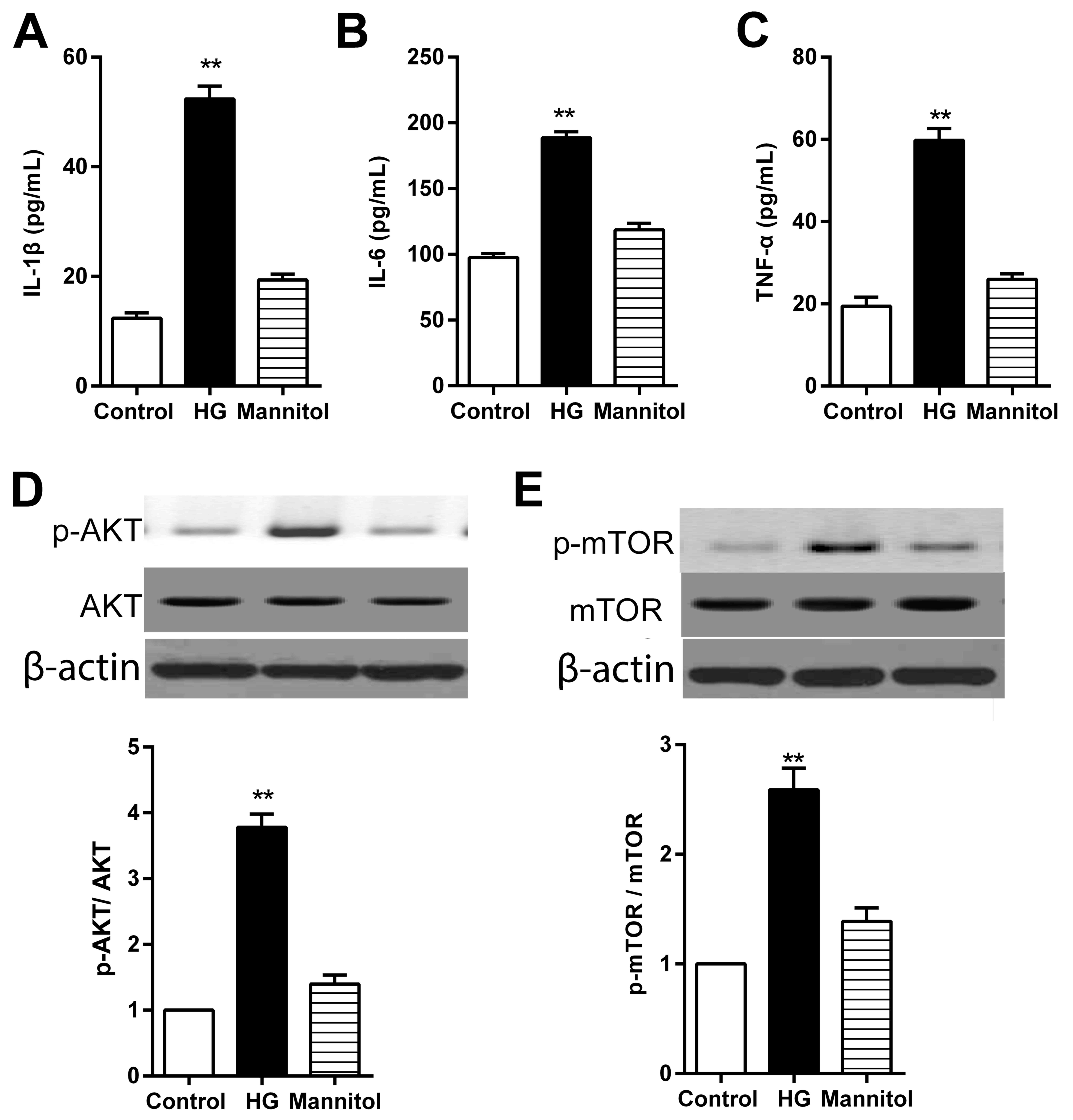
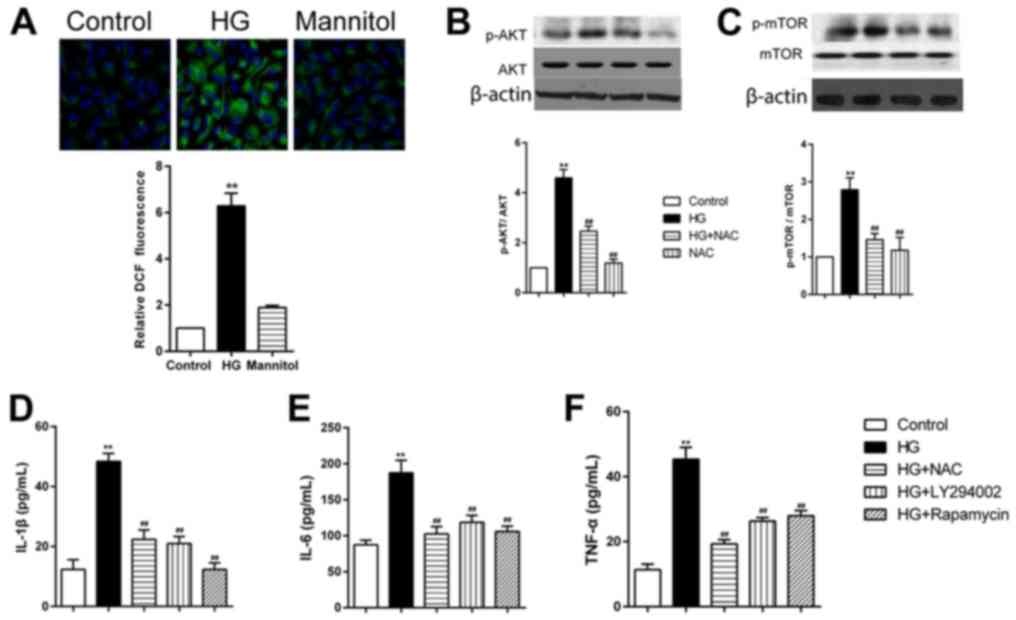
|
1
|
Chang LY, Lee AC and Sue W: Prevalence of
diabetic retinopathy at first presentation to the retinal screening
service in the greater Wellington region of New Zealand 2006–2015,
and implications for models of retinal screening. N Z Med J.
130:78–88. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Maugh TH II: Diabetic retinopathy: New
ways to prevent blindness. Science. 192:539–540. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ahmed MS and Tahrani A: Diabetic
retinopathy in cystic fibrosis related diabetes. Diabetologia.
60:S472–S473. 2017.
|
|
4
|
Byberg S, Jorgensen ME, Larsen M,
Lundandersen H and Vistisen D: Risk score for diabetic retinopathy.
Diabetes. 66:A1612017.
|
|
5
|
Bajestani NS, Kamyad AV, Esfahani EN and
Zare A: Prediction of retinopathy in diabetic patients using type-2
fuzzy regression model. Eur J Oper Res. 264:859–869. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zvornicanin J and Zvorničanin E: Imaging
in diabetic retinopathy. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 22:5312015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pasquel FJ, Hendrick AM, Ryan M, Cason E,
Ali MK and Narayan KM: Cost-effectiveness of different diabetic
retinopathy screening modalities. J Diabetes Sci Technol.
10:301–307. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jenkins AJ, Joglekar MV, Hardikar AA,
Keech AC, O'Neal DN and Januszewski AS: Biomarkers in diabetic
retinopathy. Rev Diabet Stud. 12:159–195. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hurley B: Therapeutic revolution in the
management of diabetic retinopathy. Can J Ophthalmol. 52 Suppl
1:S1–S2. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vaziri K, Schwartz SG, Relhan N, Kishor KS
and Flynn HW Jr: New therapeutic approaches in diabetic
retinopathy. Rev Diabet Stud. 12:196–210. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tang J and Kern TS: Inflammation in
diabetic retinopathy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 30:343–358. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rangasamy S, McGuire PG and Das A:
Diabetic retinopathy and inflammation: Novel therapeutic targets.
Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 19:52–59. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Joussen AM, Poulaki V, Le ML, Koizumi K,
Esser C, Janicki H, Schraermeyer U, Kociok N, Fauser S, Kirchhof B,
et al: A central role for inflammation in the pathogenesis of
diabetic retinopathy. FASEB J. 18:1450–1452. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Abcouwer SF and Antonetti DA: A role for
systemic inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol
Vis Sci. 54:23842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Behl T, Kaur I and Kotwani A: Implication
of oxidative stress in progression of diabetic retinopathy. Surv
Ophthalmol. 61:187–196. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kowluru RA and Mishra M: Oxidative stress,
mitochondrial damage and diabetic retinopathy. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1852:2474–2483. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kowluru RA, Kowluru A, Mishra M and Kumar
B: Oxidative stress and epigenetic modifications in the
pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Prog Retin Eye Res. 48:40–61.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Calderon GD, Juarez OH, Hernandez GE,
Punzo SM and De la Cruz ZD: Oxidative stress and diabetic
retinopathy: Development and treatment. Eye (Lond). 31:1122–1130.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Choudhury AK, Raja S, Mahapatra S,
Nagabhushanam K and Majeed M: Synthesis and evaluation of the
anti-oxidant capacity of curcumin glucuronides, the major curcumin
metabolites. Antioxidants (Basel). 4:750–767. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mandal MN, Patlolla JM, Zheng L, Agbaga
MP, Tran JT, Wicker L, Kasus-Jacobi A, Elliott MH, Rao CV and
Anderson RE: Curcumin protects retinal cells from light-and oxidant
stress-induced cell death. Free Radic Biol Med. 46:672–679. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xie M, Fan D, Zhao Z, Li Z, Li G, Chen Y,
He X, Chen A, Li J, Lin X, et al: Nano-curcumin prepared via
supercritical: Improved anti-bacterial, anti-oxidant and
anti-cancer efficacy. Int J Pharm. 496:732–740. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baghdasaryan A, Claudel T, Kosters A,
Gumhold J, Silbert D, Thüringer A, Leski K, Fickert P, Karpen SJ
and Trauner M: Curcumin improves sclerosing cholangitis in Mdr2-/-
mice by inhibition of cholangiocyte inflammatory response and
portal myofibroblast proliferation. Gut. 59:521–530. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bisht S, Khan MA, Bekhit M, Bai H, Cornish
T, Mizuma M, Rudek MA, Zhao M, Maitra A, Ray B, et al: A polymeric
nanoparticle formulation of curcumin (NanoCurc™) ameliorates
CCl4-induced hepatic injury and fibrosis through reduction of
pro-inflammatory cytokines and stellate cell activation. Lab
Invest. 91:1383–1395. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fu Y, Gao R, Cao Y, Guo M, Wei Z, Zhou E,
Li Y, Yao M, Yang Z and Zhang N: Curcumin attenuates inflammatory
responses by suppressing TLR4-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway in
lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol.
20:54–58. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Das L and Vinayak M: Anti-carcinogenic
action of curcumin by activation of antioxidant defence system and
inhibition of NF-κB signalling in lymphoma-bearing mice. Biosci
Rep. 32:161–170. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Heng MC: Curcumin targeted signaling
pathways: Basis for anti-photoaging and anti-carcinogenic therapy.
Int J Dermatol. 49:608–622. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Samuels TL, Pearson AC, Wells CW, Stoner
GD and Johnston N: Curcumin and anthocyanin inhibit pepsin-mediated
cell damage and carcinogenic changes in airway epithelial cells.
Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 122:632–641. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Aldebasi YH, Aly SM and Rahmani AH:
Therapeutic implications of curcumin in the prevention of diabetic
retinopathy via modulation of anti-oxidant activity and genetic
pathways. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 5:194–202.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Steigerwalt R, Nebbioso M, Appendino G,
Belcaro G, Ciammaichella G, Cornelli U, Luzzi R, Togni S, Dugall M,
Cesarone MR, et al: Meriva®, a lecithinized curcumin
delivery system, in diabetic microangiopathy and retinopathy.
Panminerva Med. 54:11–16. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Su Q, Wang Y, Yang X, Li XD, Qi YF, He XJ
and Wang YJ: Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress apoptosis
by estrogen protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells through
the PI3 Kinase-Akt signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem.
118:4568–4574. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mao N, Cheng Y, Shi XL, Wang L, Wen J,
Zhang Q, Hu QD and Fan JM: Ginsenoside Rg1 protects mouse podocytes
from aldosterone-induced injury in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
35:513–522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ahsan H: Diabetic retinopathy-biomolecules
and multiple pathophysiology. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 9:51–54. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
White C, DiStefano T and Olabisi R: The
influence of substrate modulus on retinal pigment epithelial cells.
J Biomed Mater Res A. 105:1260–1266. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Okamura N, Ito Y, Shibata MA, Ikeda T and
Otsuki Y: Fas-mediated apoptosis in human lens epithelial cells of
cataracts associated with diabetic retinopathy. Med Electron
Microsc. 35:234–241. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhou W, Yu W, Xie W, Huang L, Xu Y and Li
X: The role of SLIT-ROBO signaling in proliferative diabetic
retinopathy and retinal pigment epithelial cells. Mol Vis.
17:1526–1536. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim DI, Park MJ, Lim SK, Choi JH, Kim JC,
Han HJ, Kundu TK, Park JI, Yoon KC, Park SW, et al:
High-glucose-induced CARM1 expression regulates apoptosis of human
retinal pigment epithelial cells via histone 3 arginine 17
dimethylation: Role in diabetic retinopathy. Arch Biochem Biophys.
560:36–43. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Song MK, Roufogalis BD and Huang TH:
Reversal of the caspase-dependent apoptotic cytotoxicity pathway by
taurine from Lycium barbarum (Goji Berry) in human retinal pigment
epithelial cells: Potential benefit in diabetic retinopathy. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012:3237842012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kaštelan S, Tomić M, Gverović Antunica A,
Salopek Rabatić J and Ljubić S: Inflammation and pharmacological
treatment in diabetic retinopathy. Mediators Inflamm.
2013:2131302013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
El-Asrar AM: Role of inflammation in the
pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol.
19:70–74. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sun J, Huang P, Liang J, Li J, Shen M, She
X, Feng Y, Luo X, Liu T and Sun X: Cooperation of Rel family
members in regulating Aβ1-40-mediated pro-inflammatory
cytokine secretion by retinal pigment epithelial cells. Cell Death
Dis. 8:e31152017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Singh M and Tyagi SC: Homocysteine
mediates transcriptional changes of the inflammatory pathway
signature genes in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Int J
Ophthalmol. 10:696–704. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kutty RK, Samuel W, Duncan T, Postnikova
O, Jaworski C, Nagineni CN and Redmond TM: Proinflammatory cytokine
interferon-γ increases the expression of BANCR a long non-coding
RNA, in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Cytokine. 104:147–150.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shah MS and Brownlee M: Molecular and
cellular mechanisms of cardiovascular disorders in diabetes. Circ
Res. 118:1808–1829. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu T, Peng Y, Yan S, Li N, Chen Y and Lan
T: Andrographolide ameliorates atherosclerosis by suppressing
pro-inflammation and ROS generation-mediated foam cell formation.
Inflammation. 41:1681–1689. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang Y and Tabas I: Emerging roles of
mitochondria ROS in atherosclerotic lesions: Causation or
association? J Atheroscler Thromb. 21:381–390. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kanellakis P, Pomilio G, Walker C, Husband
A, Huang JL, Nestel P, Agrotis A and Bobik A: A novel antioxidant
3,7-dihydroxy-isoflav-3-ene (DHIF) inhibits neointimal hyperplasia
after vessel injury attenuating reactive oxygen species and nuclear
factor-kappaB signaling. Atherosclerosis. 204:66–72. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen W, Zhao M, Zhao S, Lu Q, Ni L, Zou C,
Lu L, Xu X, Guan H, Zheng Z and Qiu Q: Activation of the
TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway contributes to inflammation in
diabetic retinopathy: A novel inhibitory effect of minocycline.
Inflamm Res. 66:157–166. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wu X, Long L, Liu J, Zhang J, Wu T, Chen
X, Zhou B and Lv TZ: Gambogic acid suppresses inflammation in
rheumatoid arthritis rats via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Mol
Med Rep. 16:7112–7118. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Choi YH, Jin GY, Li LC and Yan GH:
Inhibition of protein kinase C delta attenuates allergic airway
inflammation through suppression of PI3K/Akt/mTOR/HIF-1 alpha/VEGF
pathway. PLoS One. 8:e817732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Weber WM, Hunsaker LA, Abcouwer SF, Deck
LM and Vander Jagt DL: Anti-oxidant activities of curcumin and
related enones. Bioorg Med Chem. 13:3811–3820. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Edwards RL, Luis PB, Varuzza PV, Joseph
AI, Presley SH, Chaturvedi R and Schneider C: The anti-inflammatory
activity of curcumin is mediated by its oxidative metabolites. J
Biol Chem. 292:21243–21252. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Fazal Y, Fatima SN, Shahid SM and Mahboob
T: Effects of curcumin on angiotensin-converting enzyme gene
expression, oxidative stress and anti-oxidant status in
thioacetamide-induced hepatotoxicity. J Renin Angiotensin
Aldosterone Syst. 16:1046–1051. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tian B, Zhao Y, Liang T, Ye X, Li Z, Yan
D, Fu Q and Li Y: Curcumin inhibits urothelial tumor development by
suppressing IGF2 and IGF2-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
J Drug Target. 25:626–636. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cianciulli A, Calvello R, Porro C, Trotta
T, Salvatore R and Panaro MA: PI3k/Akt signalling pathway plays a
crucial role in the anti-inflammatory effects of curcumin in
LPS-activated microglia. Int Immunopharmacol. 36:282–290. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|