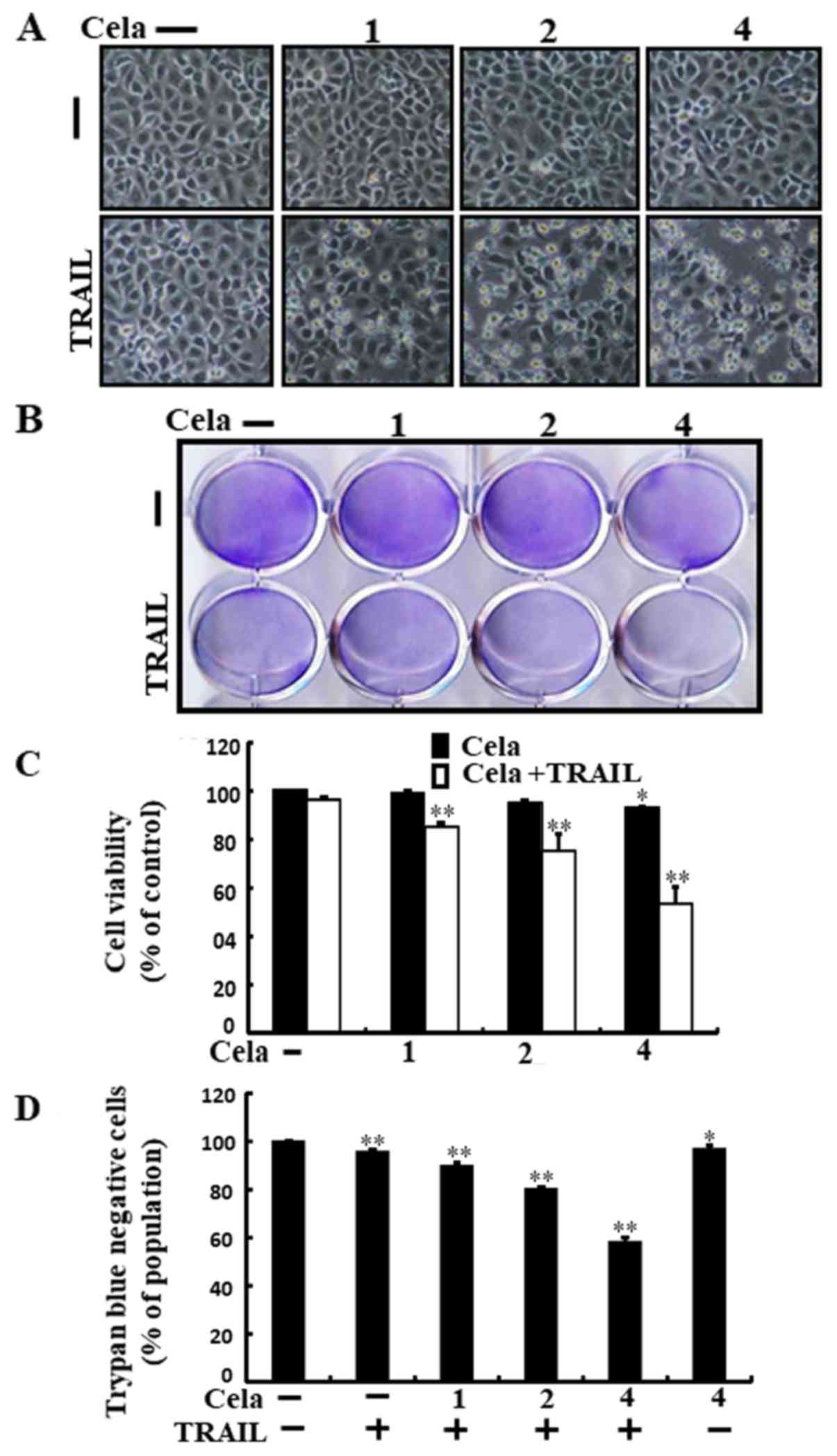
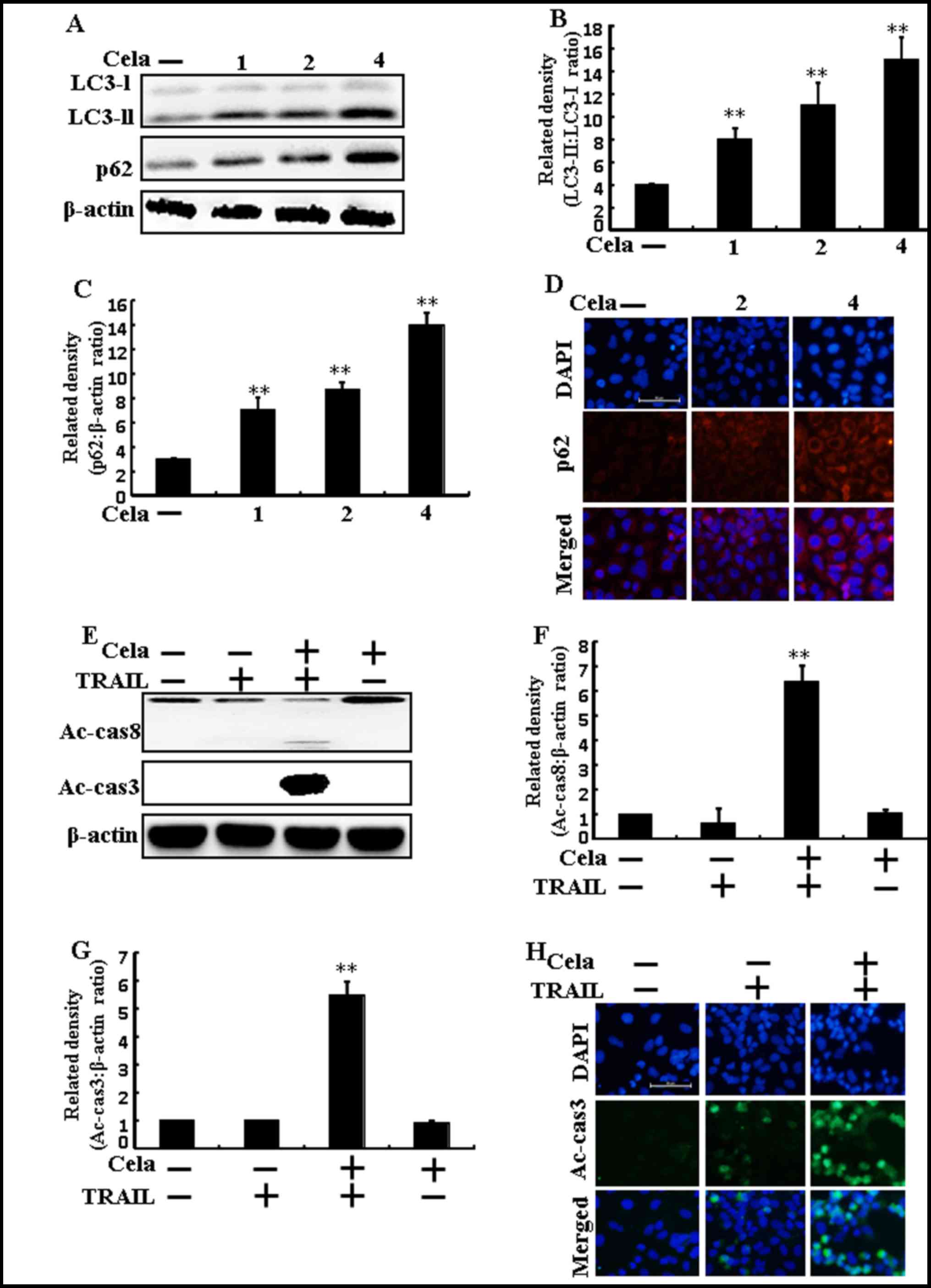
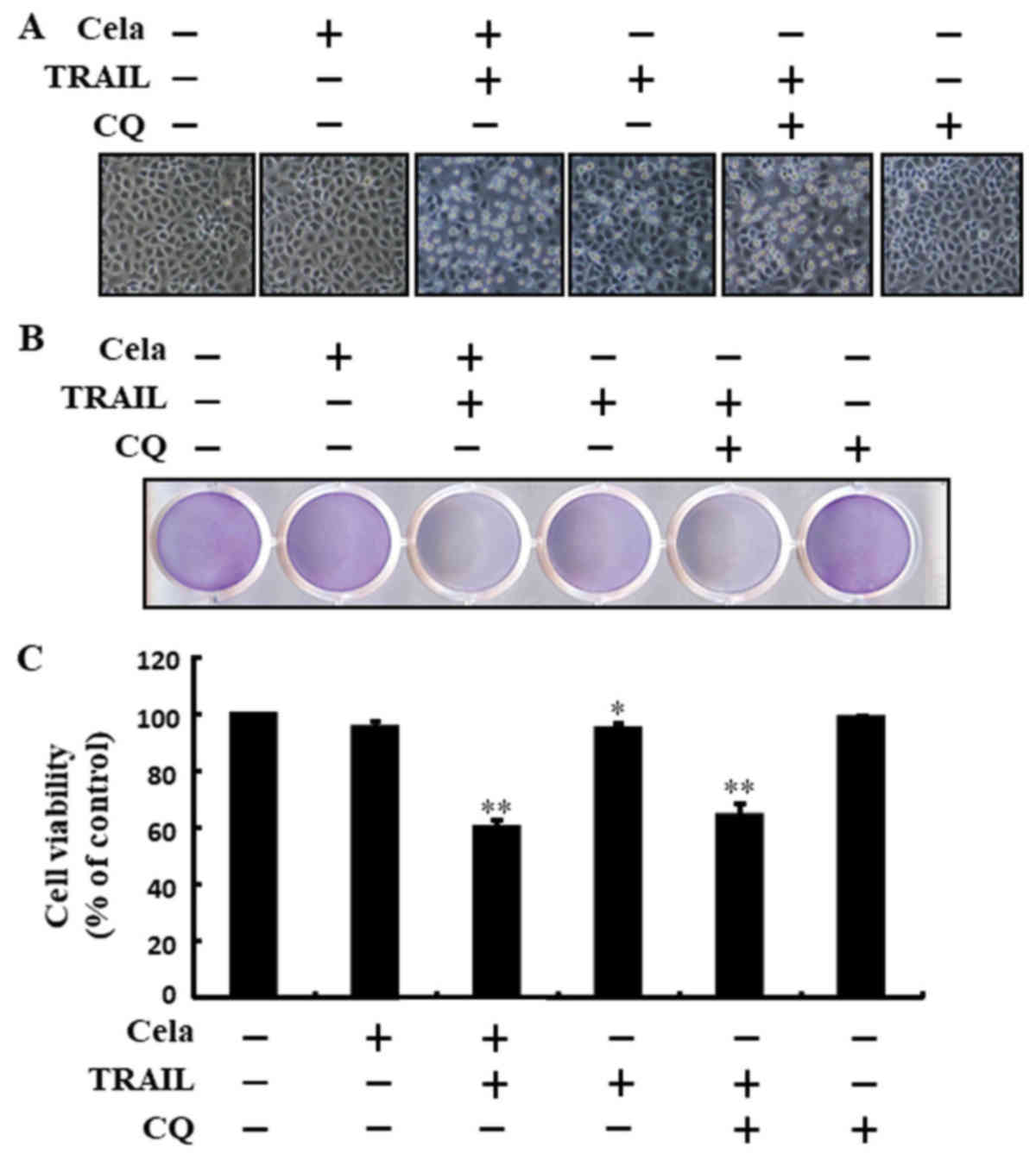
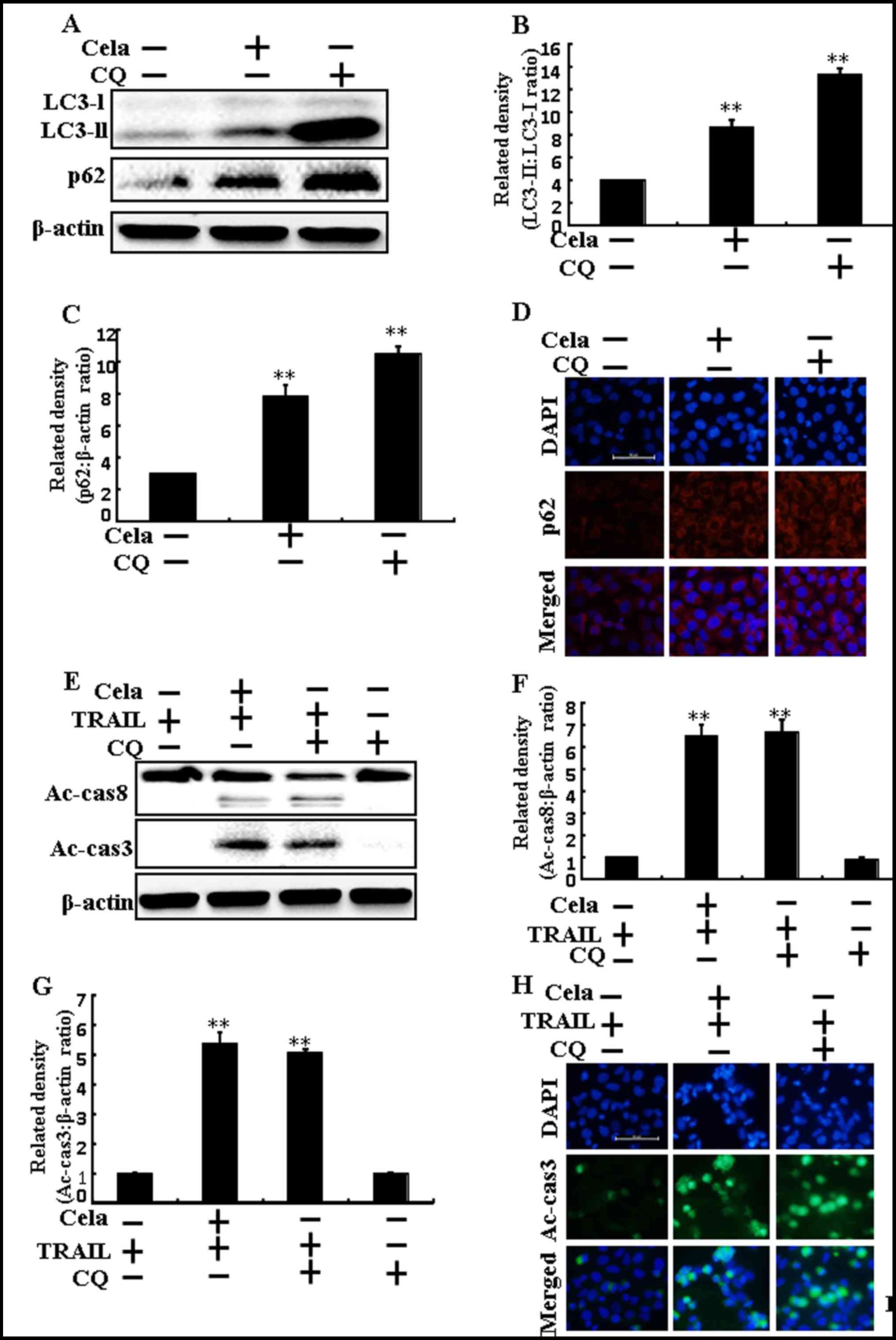
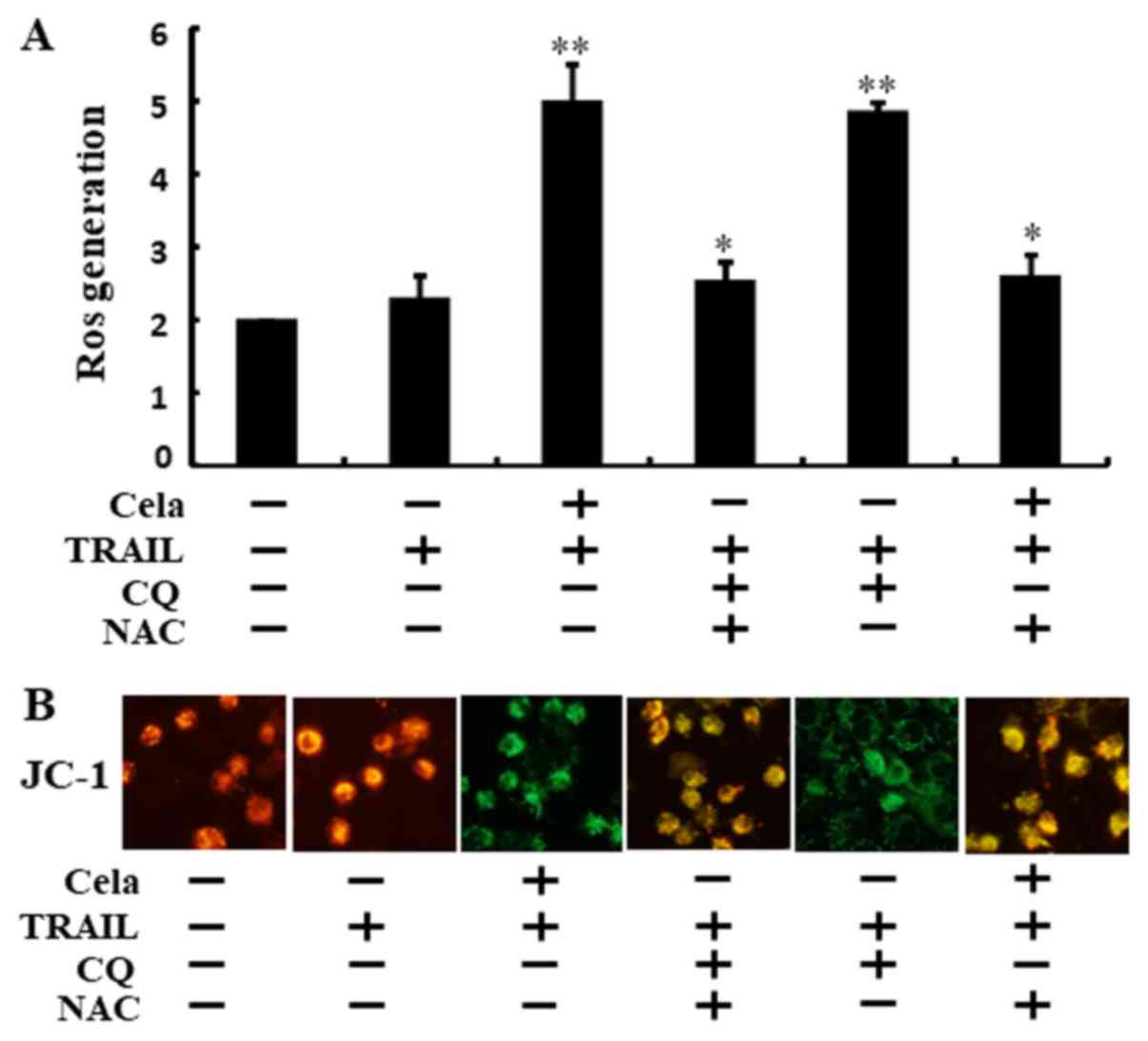
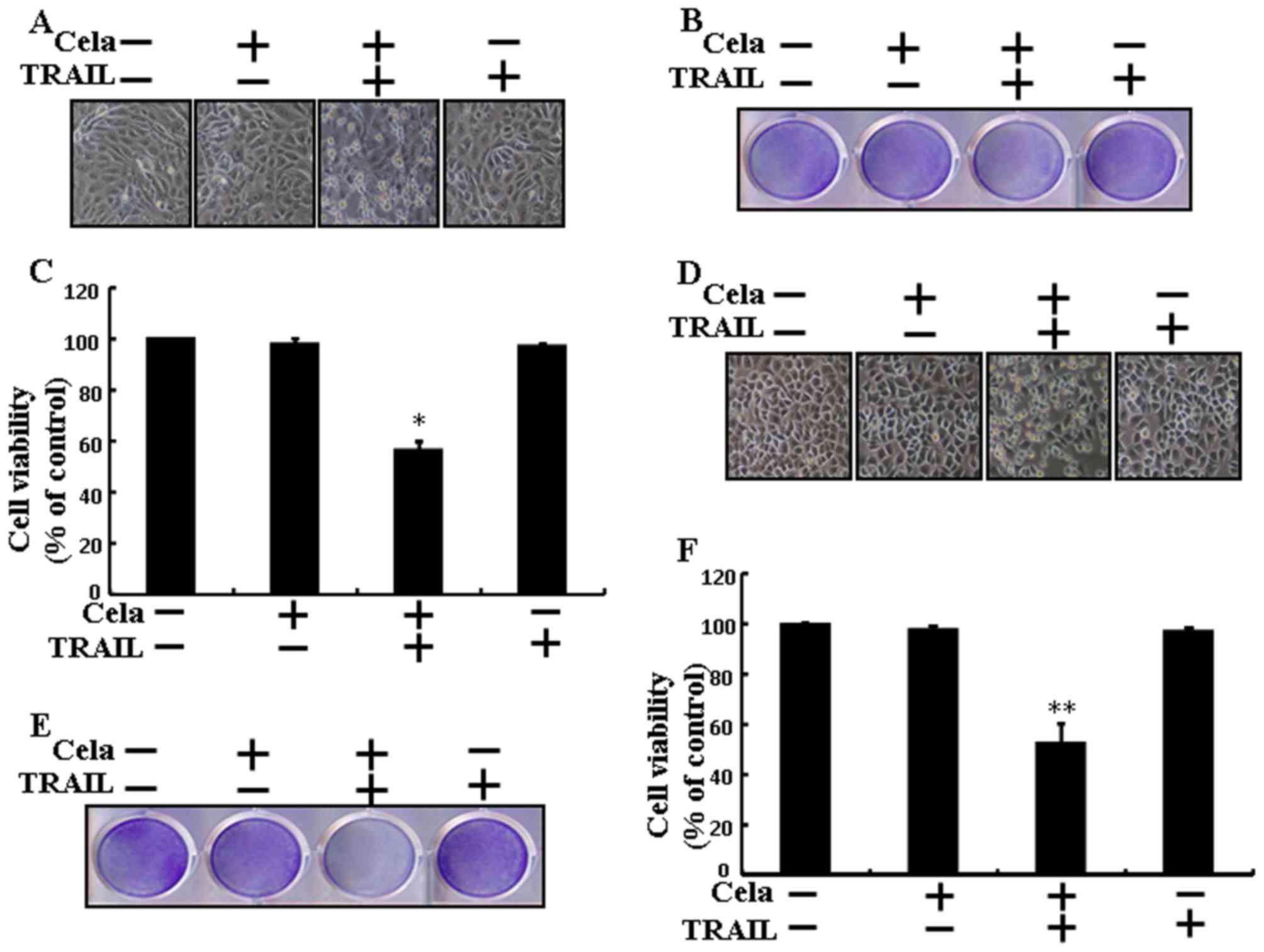
|
1
|
Garcia G and Odaimi M: Systemic
combination chemotherapy in elderly pancreatic cancer: A review. J
Gastrointest Cancer. 48:121–128. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sun W, Sanderson PE and Zheng W: Drug
combination therapy increases successful drug repositioning. Drug
Discov Today. 21:1189–1195. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aggarwal BB: Signalling pathways of the
TNF superfamily: A double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol. 3:745–756.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pitti RM, Marsters SA, Ruppert S, Donahue
CJ, Moore A and Ashkenazi A: Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2
ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family.
J Biol Chem. 271:12687–12690. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S,
Lawrence DA, Marsters SA, Blackie C, Chang L, McMurtrey AE, Hebert
A, et al: Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2
ligand. J Clin Invest. 104:155–162. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bellail AC, Qi L, Mulligan P, Chhabra V
and Hao C: TRAIL agonists on clinical trials for cancer therapy:
The promises and the challenges. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 4:34–41.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang S and El-Deiry WS: TRAIL and
apoptosis induction by TNF-family death receptors. Oncogene.
22:8628–8633. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gonzalvez F and Ashkenazi A: New insights
into apoptosis signaling by Apo2L/TRAIL. Oncogene. 29:4752–4765.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Johnstone RW, Frew AJ and Smyth MJ: The
TRAIL apoptotic pathway in cancer onset, progression and therapy.
Nat Rev Cancer. 8:782–798. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jin CY, Park C, Hwang HJ, Kim GY, Choi BT,
Kim WJ and Choi YH: Naringenin up-regulates the expression of death
receptor 5 and enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human lung
cancer A549 cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 55:300–309. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li H, Zhang YY, Huang XY, Sun YN, Jia YF
and Li D: Beneficial effect of tripterine on systemic lupus
erythematosus induced by active chromatin in BALB/c mice. Eur J
Pharmacol. 512:231–237. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu X, Wu Z, Xu C, Ren Y and Ge Y:
Observation on serum anti-double stranded DNA antibodies of
tripterine in systemic lupus erythematosus of (NZBxW)F1 mice. Ann
Rheum Dis. 62:377–378. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pinna GF, Fiorucci M, Reimund JM, Taquet
N, Arondel Y and Muller CD: Celastrol inhibits pro-inflammatory
cytokine secretion in Crohn's disease biopsies. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 322:778–786. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cleren C, Calingasan NY, Chen J and Beal
MF: Celastrol protects against MPTP- and 3-nitropropionic
acid-induced neurotoxicity. J Neurochem. 94:995–1004. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang H, Chen D, Cui QC, Yuan X and Dou QP:
Celastrol, a triterpene extracted from the Chinese ‘Thunder of God
Vine,’ is a potent proteasome inhibitor and suppresses human
prostate cancer growth in nude mice. Cancer Res. 66:4758–4765.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang T, Hamza A, Cao X, Wang B, Yu S,
Zhan CG and Sun D: A novel Hsp90 inhibitor to disrupt Hsp90/Cdc37
complex against pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:162–170. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nagase M, Oto J, Sugiyama S, Yube K,
Takaishi Y and Sakato N: Apoptosis induction in HL-60 cells and
inhibition of topoisomerase II by triterpene celastrol. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 67:1883–1887. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mizushima N: Autophagy: Process and
function. Genes Dev. 21:2861–2873. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H,
Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M,
Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy.
8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Todde V, Veenhuis M and van der Klei IJ:
Autophagy: Principles and significance in health and disease.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1792:3–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mizushima N and Komatsu M: Autophagy:
Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 147:728–741. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A,
Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, a
mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome
membranes after processing. EMBO J. 19:5720–5728. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tanida I, Minematsu-Ikeguchi N, Ueno T and
Kominami E: Lysosomal turnover, but not a cellular level, of
endogenous LC3 is a marker for autophagy. Autophagy. 1:84–91. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Apel A, Herr I, Schwarz H, Rodemann HP and
Mayer A: Blocked autophagy sensitizes resistant carcinoma cells to
radiation therapy. Cancer Res. 68:1485–1494. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Carew JS, Espitia CM, Esquivel JA II,
Mahalingam D, Kelly KR, Reddy G, Giles FJ and Nawrocki ST:
Lucanthone is a novel inhibitor of autophagy that induces cathepsin
D-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 286:6602–6613. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Boya P, Gonzalez-Polo RA, Casares N,
Perfettini JL, Dessen P, Larochette N, Métivier D, Meley D,
Souquere S, Yoshimori T, et al: Inhibition of macroautophagy
triggers apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 25:1025–1040. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Poole B and Ohkuma S: Effect of weak bases
on the intralysosomal pH in mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Cell
Biol. 90:665–669. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fan C, Wang W, Zhao B, Zhang S and Miao J:
Chloroquine inhibits cell growth and induces cell death in A549
lung cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem. 14:3218–3222. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang PD, Zhao YL, Deng XQ, Mao YQ, Shi W,
Tang QQ, Li ZG, Zheng YZ, Yang SY and Wei YQ: Antitumor and
antimetastatic activities of chloroquine diphosphate in a murine
model of breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 64:609–614. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yoon YH, Cho KS, Hwang JJ, Lee SJ, Choi JA
and Koh JY: Induction of lysosomal dilatation, arrested autophagy,
and cell death by chloroquine in cultured ARPE-19 cells. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 51:6030–6037. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kroemer G and Reed JC: Mitochondrial
control of cell death. Nat Med. 6:513–519. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lim ML, Minamikawa T and Nagley P: The
protonophore CCCP induces mitochondrial permeability transition
without cytochrome c release in human osteosarcoma cells. FEBS
Lett. 503:69–74. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Linsinger G, Wilhelm S, Wagner H and
Häcker G: Uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation can enhance a Fas
death signal. Mol Cell Biol. 19:3299–3311. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mlejnek P: Caspase-3 activity and carbonyl
cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone-induced apoptosis in HL-60. Altern
Lab Anim. 29:243–249. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nagata S: Apoptosis by death factor. Cell.
88:355–365. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Newmeyer DD and Ferguson-Miller S:
Mitochondria: Releasing power for life and unleashing the
machineries of death. Cell. 112:481–490. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zou ZZ, Nie PP, Li YW, Hou BX, Rui-Li, Shi
XP, Ma ZK, Han BW and Luo XY: Synergistic induction of apoptosis by
salinomycin and gefitinib through lysosomal and mitochondrial
dependent pathway overcomes gefitinib resistance in colorectal
cancer. Oncotarget. 8:22414–22432. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mi YJ, Geng GJ, Zou ZZ, Gao J, Luo XY, Liu
Y, Li N, Li CL, Chen YQ, Yu XY and Jiang J: Dihydroartemisinin
inhibits glucose uptake and cooperates with glycolysis inhibitor to
induce apoptosis in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. PLoS One.
10:e01204262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nazim UM, Moon JH, Lee YJ, Seol JW and
Park SY: PPARγ activation by troglitazone enhances human lung
cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via autophagy flux.
Oncotarget. 8:26819–26831. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Chuntharapai A,
Schow P, Kim KJ and Ashkenazi A: Apo2L/TRAIL-dependent recruitment
of endogenous FADD and caspase-8 to death receptors 4 and 5.
Immunity. 12:611–620. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Van Geelen CM, de Vries EG and de Jong S:
Lessons from TRAIL-resistance mechanisms in colorectal cancer
cells: Paving the road to patient-tailored therapy. Drug Resist
Updat. 7:345–358. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Srivastava RK: TRAIL/Apo-2L: Mechanisms
and clinical applications in cancer. Neoplasia. 3:535–546. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shankar S and Srivastava RK: Enhancement
of therapeutic potential of TRAIL by cancer chemotherapy and
irradiation: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Drug Resist
Updat. 7:139–156. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
LeBlanc H, Lawrence D, Varfolomeev E,
Totpal K, Morlan J, Schow P, Fong S, Schwall R, Sinicropi D and
Ashkenazi A: Tumor-cell resistance to death receptor-induced
apoptosis through mutational inactivation of the proapoptotic Bcl-2
homolog Bax. Nat Med. 8:274–281. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B,
Griffith TS, Kubin M, Chin W, Jones J, Woodward A, Le T, et al:
Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med. 5:157–163. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Abbas S, Bhoumik A, Dahl R, Vasile S,
Krajewski S, Cosford ND and Ronai ZA: Preclinical studies of
celastrol and acetyl isogambogic acid in melanoma. Clin Cancer Res.
13:6769–6778. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sethi G, Ahn KS, Pandey MK and Aggarwal
BB: Celastrol, a novel triterpene, potentiates TNF-induced
apoptosis and suppresses invasion of tumor cells by inhibiting
NF-kappaB-regulated gene products and TAK1-mediated NF-kappaB
activation. Blood. 109:2727–2735. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Klionsky DJ, Abeliovich H, Agostinis P,
Agrawal DK, Aliev G, Askew DS, Baba M, Baehrecke EH, Bahr BA,
Ballabio A, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of
assays for monitoring autophagy in higher eukaryotes. Autophagy.
4:151–175. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dimberg LY, Anderson CK, Camidge R,
Behbakht K, Thorburn A and Ford HL: On the TRAIL to successful
cancer therapy? Predicting and counteracting resistance against
TRAIL-based therapeutics. Oncogene. 32:1341–1350. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lee HW, Jang KS, Choi HJ, Jo A, Cheong JH
and Chun KH: Celastrol inhibits gastric cancer growth by induction
of apoptosis and autophagy. BMB Rep. 47:697–702. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang HS, Kim JY, Lee JH, Lee BW, Park KH,
Shim KH, Lee MK and Seo KI: Celastrol isolated from Tripterygium
regelii induces apoptosis through both caspase-dependent and
-independent pathways in human breast cancer cells. Food Chem
Toxicol. 49:527–532. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kannaiyan R, Manu KA, Chen L, Li F,
Rajendran P, Subramaniam A, Lam P, Kumar AP and Sethi G: Celastrol
inhibits tumor cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis through
the activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and suppression of PI3
K/Akt signaling pathways. Apoptosis. 16:1028–1041. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Saleem A, Dvorzhinski D, Santanam U,
Mathew R, Bray K, Stein M, White E and DiPaola RS: Effect of dual
inhibition of apoptosis and autophagy in prostate cancer. Prostate.
72:1374–1381. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang J, Tan X, Yang Q, Zeng X, Zhou Y, Luo
W, Lin X, Song L, Cai J, Wang T and Wu X: Inhibition of autophagy
promotes apoptosis and enhances anticancer efficacy of adriamycin
via augmented ROS generation in prostate cancer cells. Int J Bioch
Cell Biol. 77:80–90. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|