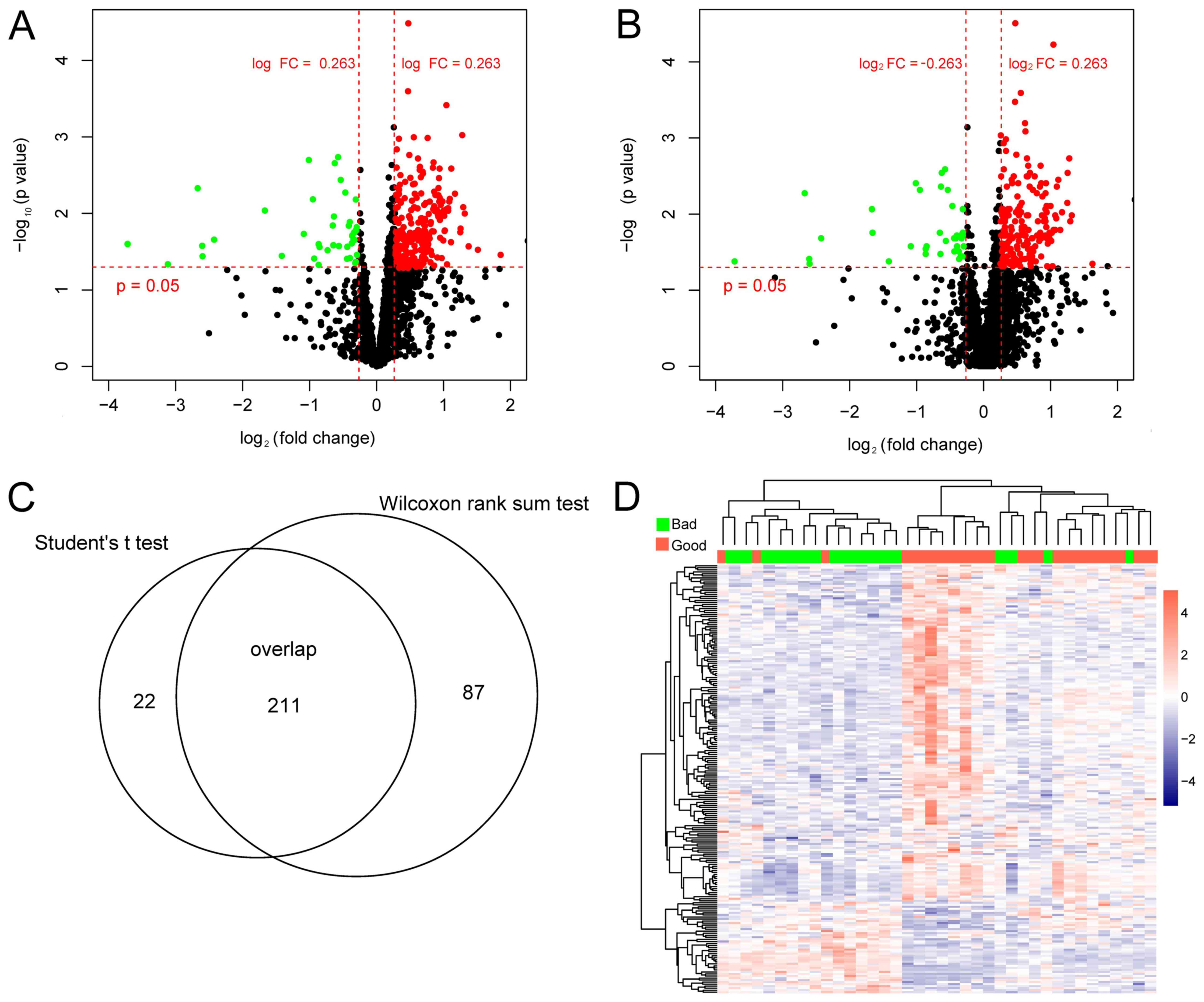
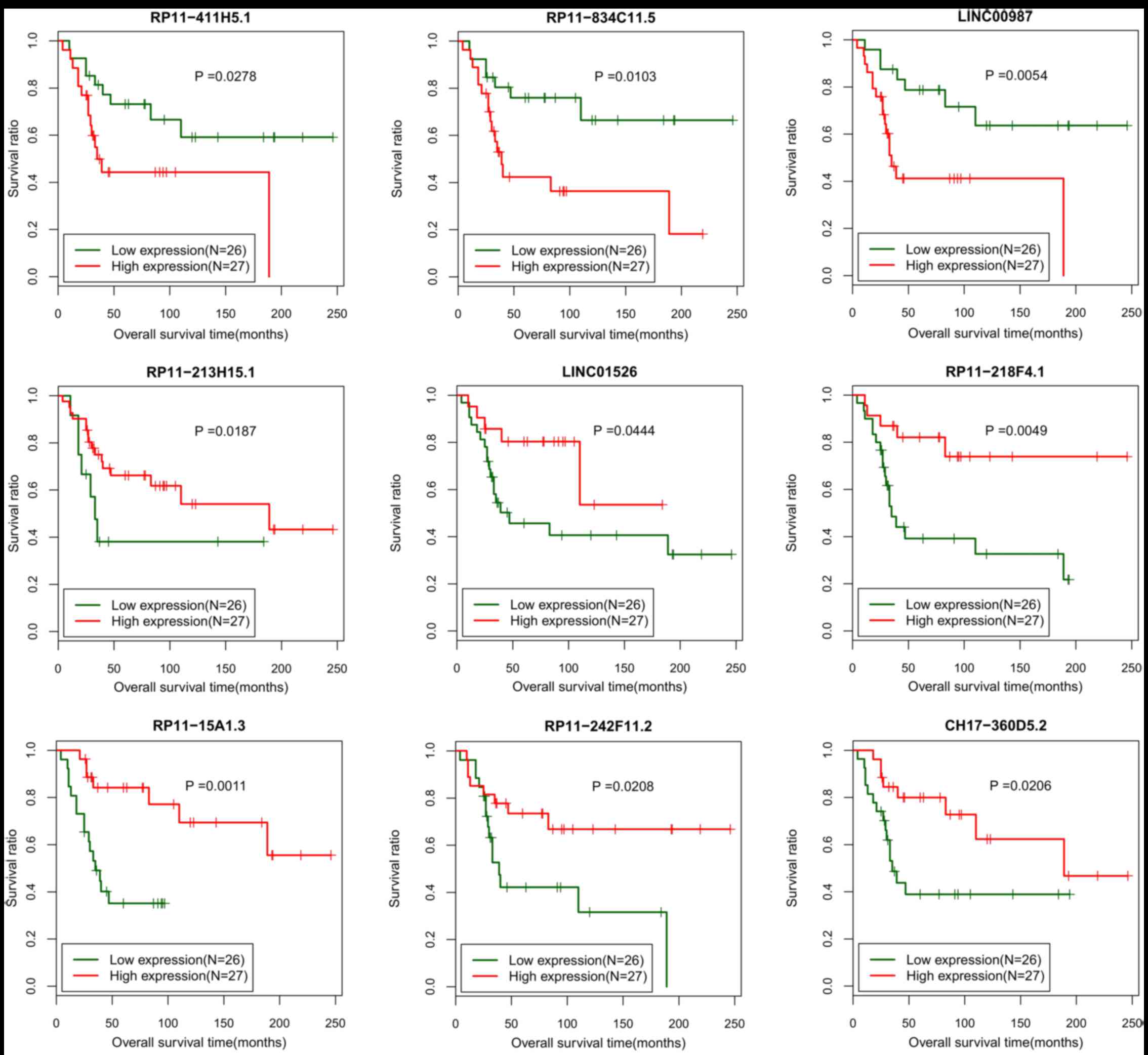
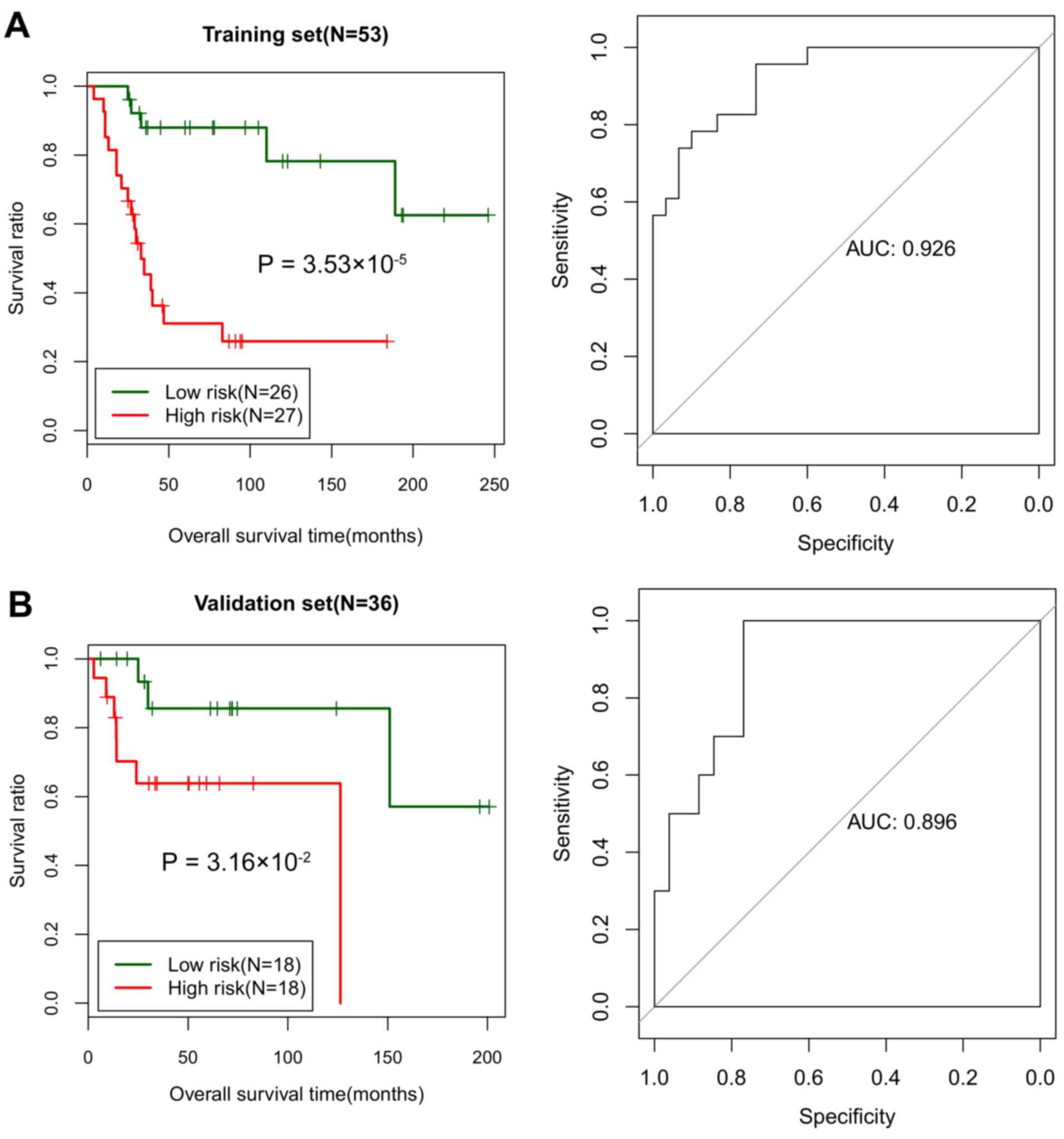
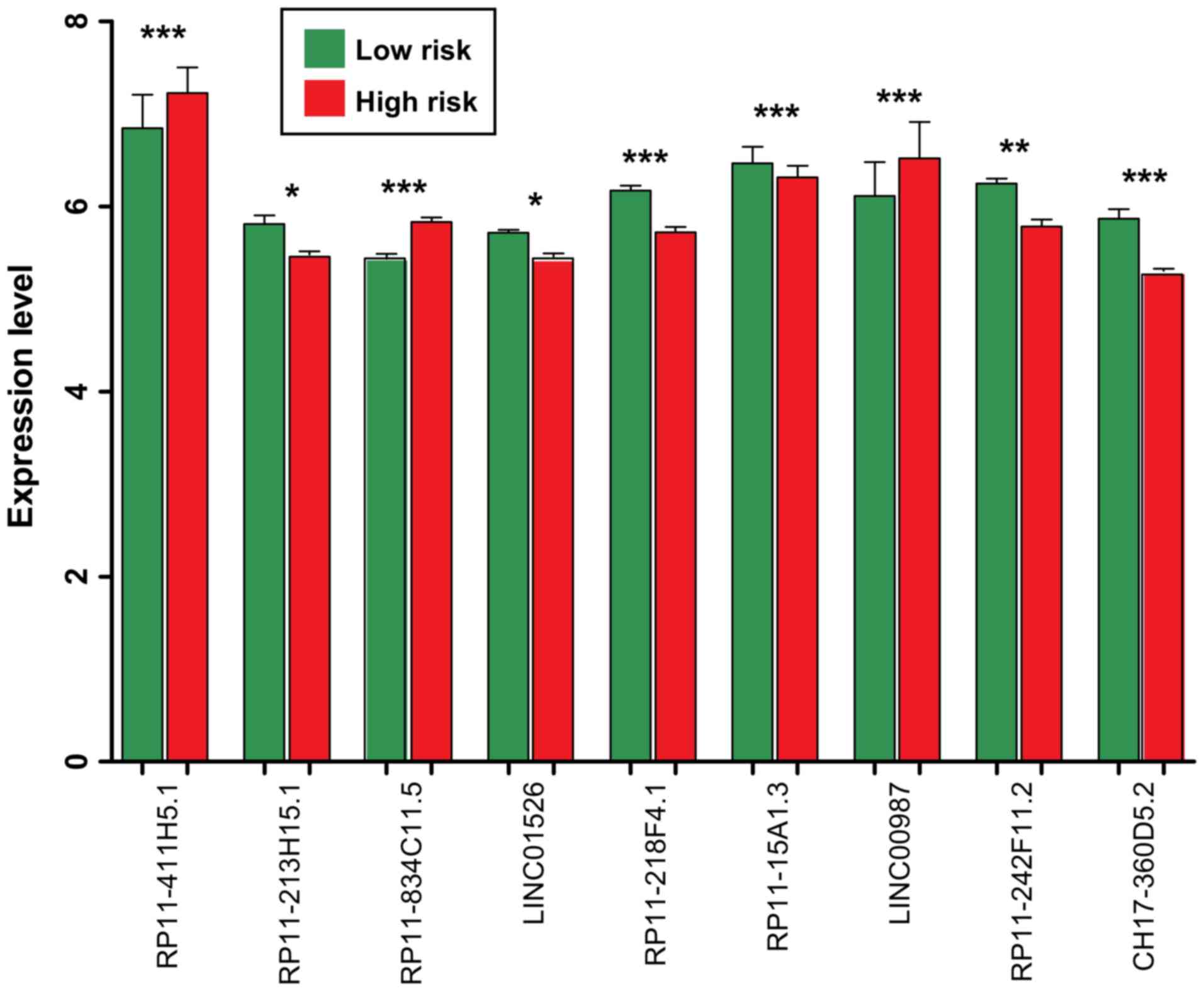
|
1
|
Duchman KR, Gao Y and Miller BJ:
Prognostic factors for survival in patients with high-grade
osteosarcoma using the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results
(SEER) program database. Cancer Epidemiol. 39:593–599. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ and Savage SA:
Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004: Data
from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results Program.
Cancer. 115:1531–1543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang W, Li X, Meng FB, Wang ZX, Zhao RT
and Yang CY: Effects of the long non-coding RNA HOST2 on the
proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of human
osteosarcoma cells. Cellular Physiol Biochem. 43:320–330. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Whelan J, McTiernan A, Cooper N, Wong YK,
Francis M, Vernon S and Strauss SJ: Incidence and survival of
malignant bone sarcomas in England 1979–2007. Int J Cancer.
131:E508–E517. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The epidemiology
of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 152:3–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fellenberg J, Bernd L, Delling G, Witte D
and Zahlten-Hinguranage A: Prognostic significance of
drug-regulated genes in high-grade osteosarcoma. Mod Pathol.
20:1085–1094. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Allison DC, Carney SC, Ahlmann ER,
Hendifar A, Chawla S, Fedenko A, Angeles C and Menendez LR: A
meta-analysis of osteosarcoma outcomes in the modern medical era.
Sarcoma. 2012:7048722012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jandura A and Krause HM: The new RNA
world: Growing evidence for long noncoding RNA functionality.
Trends Genet. 33:665–675. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li X, Wu Z, Fu X and Han W: Long noncoding
RNAs: Insights from biological features and functions to diseases.
Med Res Rev. 33:517–553. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guttman M and Rinn JL: Modular regulatory
principles of large non-coding RNAs. Nature. 482:339–346. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cheetham SW, Gruhl F, Mattick JS and
Dinger ME: Long noncoding RNAs and the genetics of cancer. Br J
Cancer. 108:2419–2425. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ji P, Diederichs S, Wang W, Böing S,
Metzger R, Schneider PM, Tidow N, Brandt B, Buerger H, Bulk E, et
al: MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin beta4 predict
metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncogene. 22:8031–8041. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang Z, Zhou L, Wu LM, Lai MC, Xie HY,
Zhang F and Zheng SS: Overexpression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR
predicts tumor recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma patients
following liver transplantation. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:1243–1250.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xie CH, Cao YM, Huang Y, Shi QW, Guo JH,
Fan ZW, Li JG, Chen BW and Wu BY: Long non-coding RNA TUG1
contributes to tumorigenesis of human osteosarcoma by sponging
miR-9-5p and regulating POU2F1 expression. Tumour Biol.
37:15031–15041. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Peng ZQ, Lu RB, Xiao DM and Xiao ZM:
Increased expression of the lncRNA BANCR and its prognostic
significance in human osteosarcoma. Genet Mol Res. 15:2016.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Wang P, Wang Y, Hang B, Zou X and Mao JH:
A novel gene expression-based prognostic scoring system to predict
survival in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 7:55343–55351.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bland JM and Altman DG: The logrank test.
BMJ. 328:10732004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Adler P, Kolde R, Kull M, Tkachenko A,
Peterson H, Reimand J and Vilo J: Mining for coexpression across
hundreds of datasets using novel rank aggregation and visualization
methods. Genome Biol. 10:R1392009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kolde R, Laur S, Adler P and Vilo J:
Robust rank aggregation for gene list integration and
meta-analysis. Bioinformatics. 28:573–580. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: Limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Phipson B, Lee S, Majewski IJ, Alexander
WS and Smyth GK: Robust hyperparameter estimation protects against
hypervariable genes and improves power to detect differential
expression. Ann Appl Stat. 10:946–963. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin X, Wells DE, Kimberling WJ and Kumar
S: Human NDUFB9 gene: Genomic organization and a possible candidate
gene associated with deafness disorder mapped to chromosome 8q13.
Hum Hered. 49:75–80. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ishikawa K, Takenaga K, Akimoto M,
Koshikawa N, Yamaguchi A, Imanishi H, Nakada K, Honma Y and Hayashi
J: ROS-generating mitochondrial DNA mutations can regulate tumor
cell metastasis. Science. 320:661–664. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Santidrian AF, Matsunoyagi A, Ritland M,
Seo BB, LeBoeuf SE, Gay LJ, Yagi T and Felding-Habermann B:
Mitochondrial complex I activity and NAD+/NADH balance
regulate breast cancer progression. J Clin Invest. 123:1068–1081.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Burk D and Schade AL: On respiratory
impairment in cancer cells. Science. 124:267–272. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Heiden MGV and Thompson CB: Understanding
the warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell
proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang Z, Li J, Du S, Tang Y, Huang L, Xiao
L and Tong P: FKBP14 overexpression contributes to osteosarcoma
carcinogenesis and indicates poor survival outcome. Oncotarget.
7:39872–39884. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu X, Liao W, Yuan Q, Ou Y and Huang J:
TTK activates Akt and promotes proliferation and migration of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncotarget. 6:34309–34320.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dong Z, Sun K, Luan Y, Chen Y, Wang W, Liu
D, Cheng C, Xiong F and Xi Y: Expression and clinical significance
of threonine and tyrosine protein kinase (TTK) in osteosarcoma.
Translational Cancer Res. 6:285–292. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gentric G, Maillet V, Paradis V, Couton D,
L'Hermitte A, Panasyuk G, Fromenty B, Celton-Morizur S and
Desdouets C: Oxidative stress promotes pathologic polyploidization
in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Invest. 125:981–992.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guo C, Wu G, Chin JL, Bauman G, Moussa M,
Wang F, Greenberg NM, Taylor SS and Xuan JW: Bub1 up-regulation and
hyperphosphorylation promote malignant transformation in SV40
Tag–Induced transgenic mouse models. Cancer Res.
66:7132006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Seyfried TN and Huysentruyt LC: On the
origin of cancer metastasis. Crit Rev Oncog. 18:43–73. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Guan X: Cancer metastases: Challenges and
opportunities. Acta Pharm Sin B. 5:402–418. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wells A, Grahovac J, Wheeler S, Ma B and
Lauffenburger D: Targeting tumor cell motility as a strategy
against invasion and metastasis. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 34:283–289.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Recher C, Ysebaert L, Beyne-Rauzy O,
Mansat-De Mas V, Ruidavets JB, Cariven P, Demur C, Payrastre B,
Laurent G, et al: Expression of focal adhesion kinase in acute
myeloid leukemia is associated with enhanced blast migration,
increased cellularity, and poor prognosis. Cancer Res.
64:3191–3197. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hu C, Chen X, Wen J, Gong L, Liu Z, Wang
J, Liang J, Hu F, Zhou Q, Wei L, et al: Antitumor effect of focal
adhesion kinase inhibitor PF562271 against human osteosarcoma in
vitro and in vivo. Cancer Sci. 108:1347–1356. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jiang WG, Ye L, Ji K, Ruge F, Wu Y, Gao Y,
Ji J and Mason MD: Antitumour effects of Yangzheng Xiaoji in human
osteosarcoma: The pivotal role of focal adhesion kinase signalling.
Oncol Rep. 30:1405–1413. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|