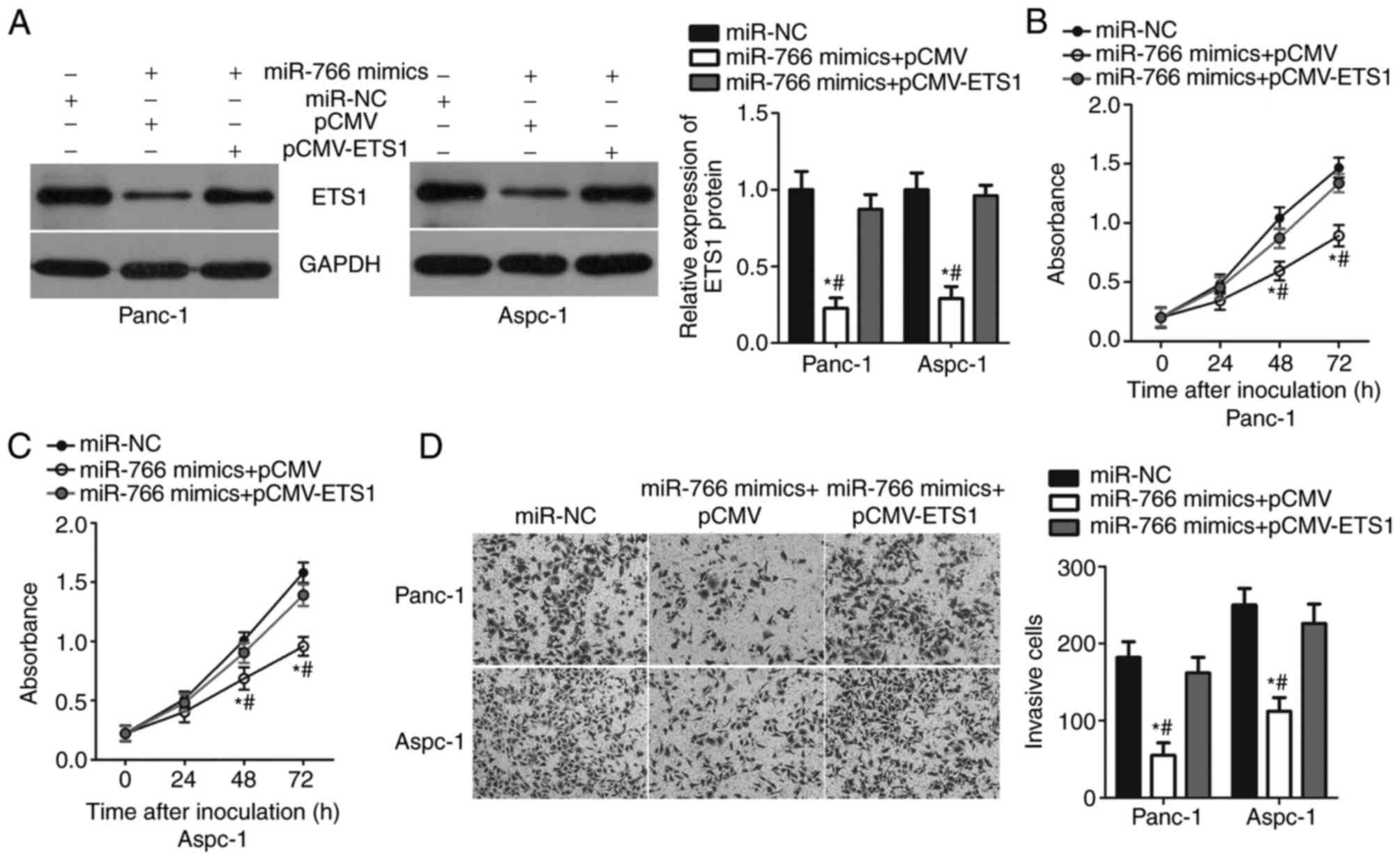
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Modolell I, Guarner L and Malagelada JR:
Vagaries of clinical presentation of pancreatic and biliary tract
cancer. Ann Oncol. 10 Suppl 4:S82–S84. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hidalgo M: Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J
Med. 362:1605–1617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Winter JM, Brennan MF, Tang LH, D'Angelica
MI, Dematteo RP, Fong Y, Klimstra DS, Jarnagin WR and Allen PJ:
Survival after resection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Results from
a single institution over three decades. Ann Surg Oncol.
19:169–175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cho K, Ishiwata T, Uchida E, Nakazawa N,
Korc M, Naito Z and Tajiri T: Enhanced expression of keratinocyte
growth factor and its receptor correlates with venous invasion in
pancreatic cancer. Am J Pathol. 170:1964–1974. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cleary SP, Gryfe R, Guindi M, Greig P,
Smith L, Mackenzie R, Strasberg S, Hanna S, Taylor B, Langer B and
Gallinger S: Prognostic factors in resected pancreatic
adenocarcinoma: Analysis of actual 5-year survivors. J Am Coll
Surg. 198:722–731. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Galasso M, Sandhu SK and Volinia S:
MicroRNA expression signatures in solid malignancies. Cancer J.
18:238–243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhu W, Wang Y, Zhang D, Yu X and Leng X:
MiR-7-5p functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting SOX18 in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
497:963–970. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xiong J, Wang D, Wei A, Ke N, Wang Y, Tang
J, He S, Hu W and Liu X: MicroRNA-410-3p attenuates gemcitabine
resistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by inhibiting
HMGB1-mediated autophagy. Oncotarget. 8:107500–107512. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu Z, Zhou L, Ding G and Cao L:
Overexpressions of miR-212 are associated with poor prognosis of
patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biomark.
18:35–39. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fan Y, Shi C, Li T and Kuang T:
microRNA-454 shows anti-angiogenic and anti-metastatic activity in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by targeting LRP6. Am J Cancer
Res. 7:139–147. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chang JC and Kundranda M: Novel diagnostic
and predictive biomarkers in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Int J Mol
Sci. 18:E6672017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Diab M, Muqbil I, Mohammad RM, Azmi AS and
Philip PA: The role of microRNAs in the diagnosis and treatment of
pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Clin Med. 5:E592016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Song B, Zhang C, Li G, Jin G and Liu C:
MiR-940 inhibited pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma growth by
targeting MyD88. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:1167–1177. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Keklikoglou I, Hosaka K, Bender C, Bott A,
Koerner C, Mitra D, Will R, Woerner A, Muenstermann E, Wilhelm H,
et al: MicroRNA-206 functions as a pleiotropic modulator of cell
proliferation, invasion and lymphangiogenesis in pancreatic
adenocarcinoma by targeting ANXA2 and KRAS genes. Oncogene.
34:4867–4878. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang R, Leng H, Huang J, Du Y, Wang Y,
Zang W, Chen X and Zhao G: miR-337 regulates the proliferation and
invasion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by targeting HOXB7.
Diagn Pathol. 9:1712014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen C, Xue S, Zhang J, Chen W, Gong D and
Zheng J, Ma J, Xue W, Chen Y, Zhai W and Zheng J:
DNA-methylation-mediated repression of miR-766-3p promotes cell
proliferation via targeting SF2 expression in renal cell carcinoma.
Int J Cancer. 141:1867–1878. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li YC, Li CF, Chen LB, Li DD, Yang L, Jin
JP and Zhang B: MicroRNA-766 targeting regulation of SOX6
expression promoted cell proliferation of human colorectal cancer.
Onco Targets Ther. 8:2981–2988. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li X, Shi Y, Yin Z, Xue X and Zhou B: An
eight-miRNA signature as a potential biomarker for predicting
survival in lung adenocarcinoma. J Transl Med. 12:1592014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park JY, Helm J, Coppola D, Kim D, Malafa
M and Kim SJ: MicroRNAs in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. World
J Gastroenterol. 17:817–827. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mardin WA and Mees ST: MicroRNAs: Novel
diagnostic and therapeutic tools for pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma? Ann Surg Oncol. 16:3183–3189. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Frampton AE, Krell J, Jacob J, Stebbing J,
Jiao LR and Castellano L: microRNAs as markers of survival and
chemoresistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 11:1837–1842. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oh K and Lee DS: In vivo validation
of metastasis-regulating microRNA-766 in human triple-negative
breast cancer cells. Lab Anim Res. 33:256–263. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Afgar A, Fard-Esfahani P, Mehrtash A,
Azadmanesh K, Khodarahmi F, Ghadir M and Teimoori-Toolabi L:
MiR-339 and especially miR-766 reactivate the expression of tumor
suppressor genes in colorectal cancer cell lines through DNA
methyltransferase 3B gene inhibition. Cancer Biol Ther.
17:1126–1138. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dittmer J: The role of the transcription
factor Ets1 in carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 35:20–38. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ito T, Nakayama T, Ito M, Naito S,
Kanematsu T and Sekine I: Expression of the ets-1 proto-oncogene in
human pancreatic carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 11:209–215. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lefter LP, Dima S, Sunamura M, Furukawa T,
Sato Y, Abe M, Chivu M, Popescu I and Horii A: Transcriptional
silencing of ETS-1 efficiently suppresses angiogenesis of
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 16:137–148. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Khanna A, Mahalingam K, Chakrabarti D and
Periyasamy G: Ets-1 expression and gemcitabine chemoresistance in
pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 16:101–113. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li C, Wang Z, Chen Y, Zhou M, Zhang H,
Chen R, Shi F, Wang C and Rui Z: Transcriptional silencing of ETS-1
abrogates epithelial-mesenchymal transition resulting in reduced
motility of pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 33:559–565. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li Z, Lin P, Gao C, Peng C, Liu S, Gao H,
Wang B, Wang J, Niu J and Niu W: Integrin β6 acts as an unfavorable
prognostic indicator and promotes cellular malignant behaviors via
ERK-ETS1 pathway in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). Tumour
Biol. 37:5117–5131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Christopher AF, Kaur RP, Kaur G, Kaur A,
Gupta V and Bansal P: MicroRNA therapeutics: Discovering novel
targets and developing specific therapy. Perspect Clin Res.
7:68–74. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|