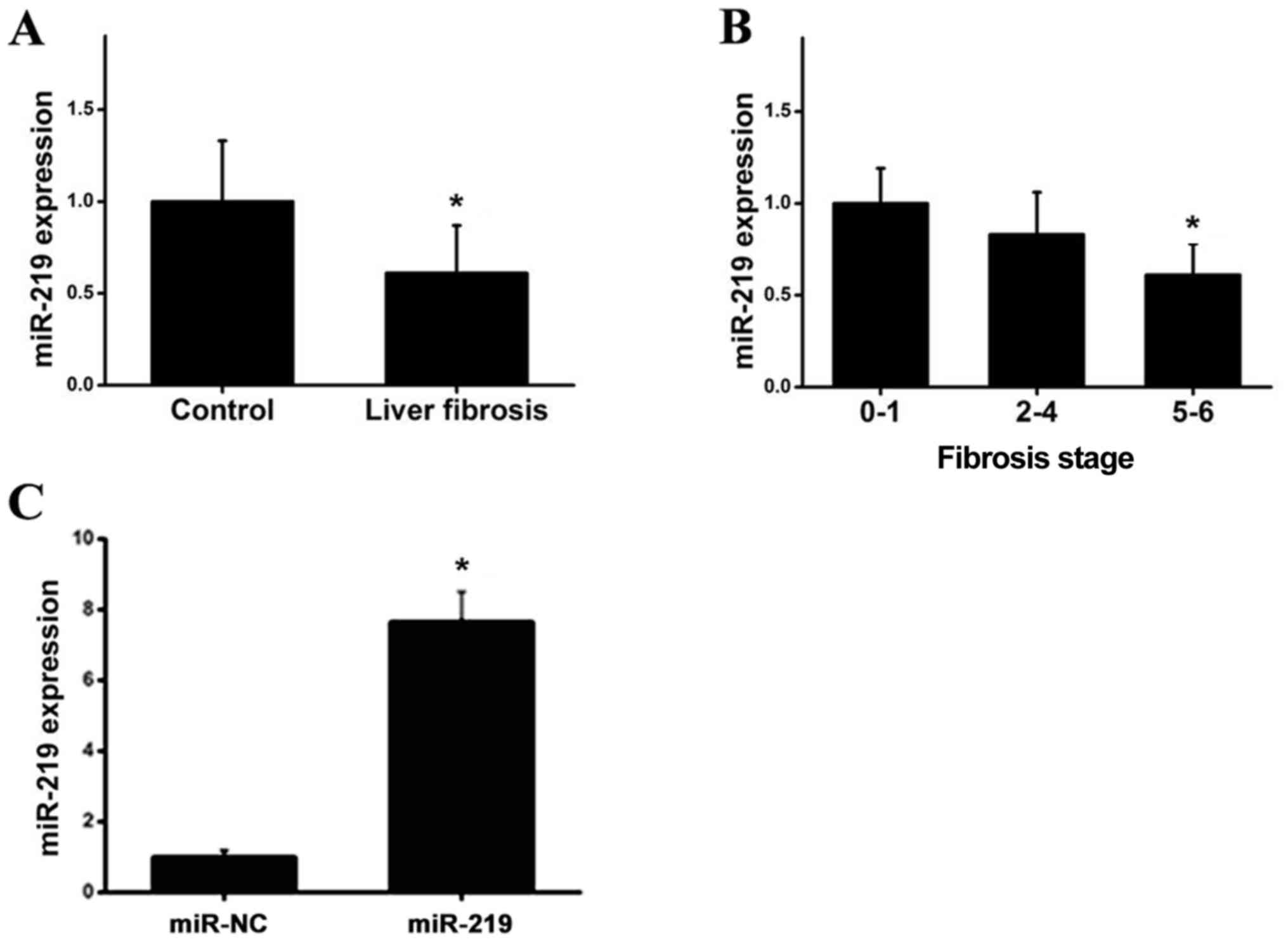
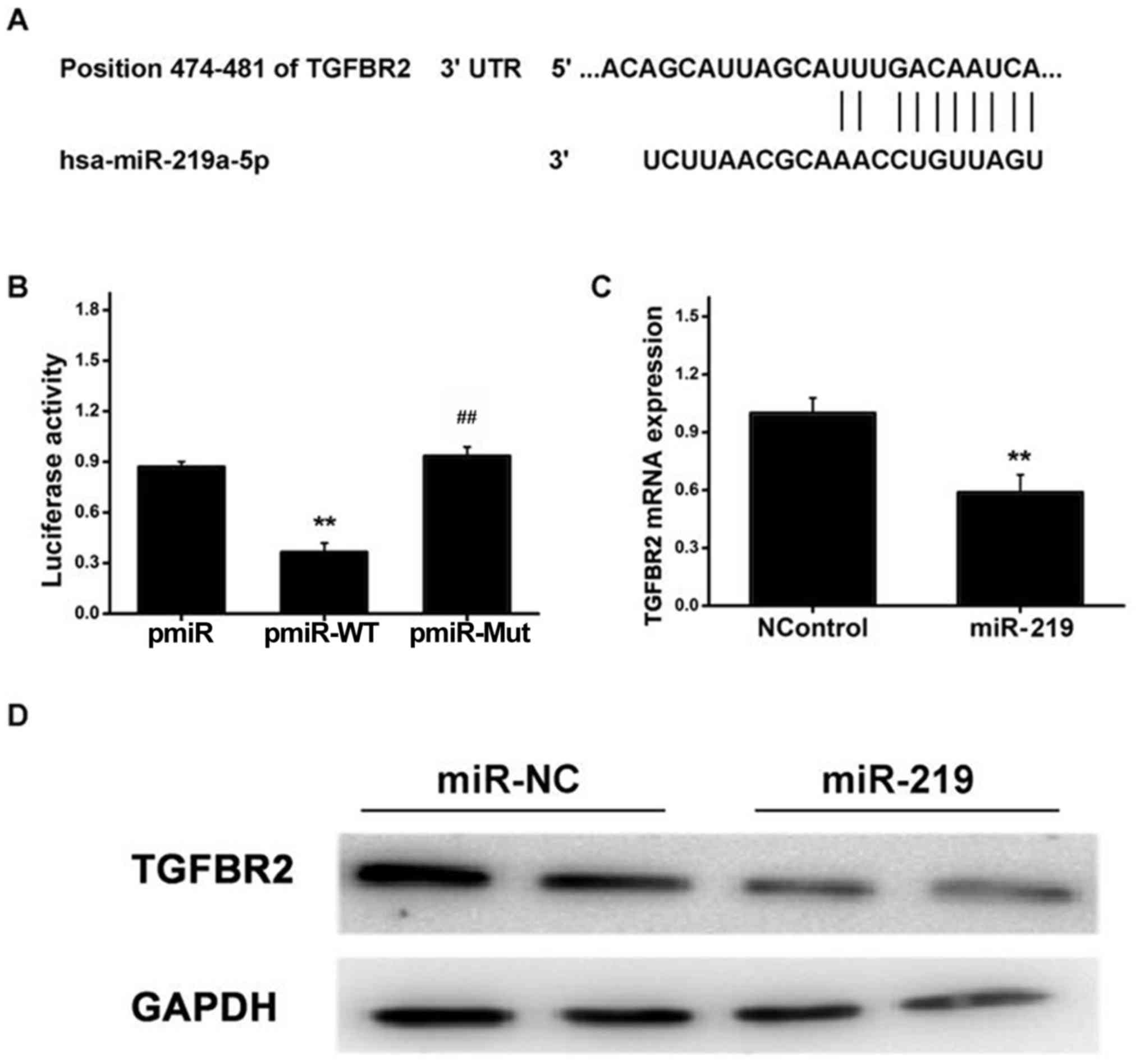
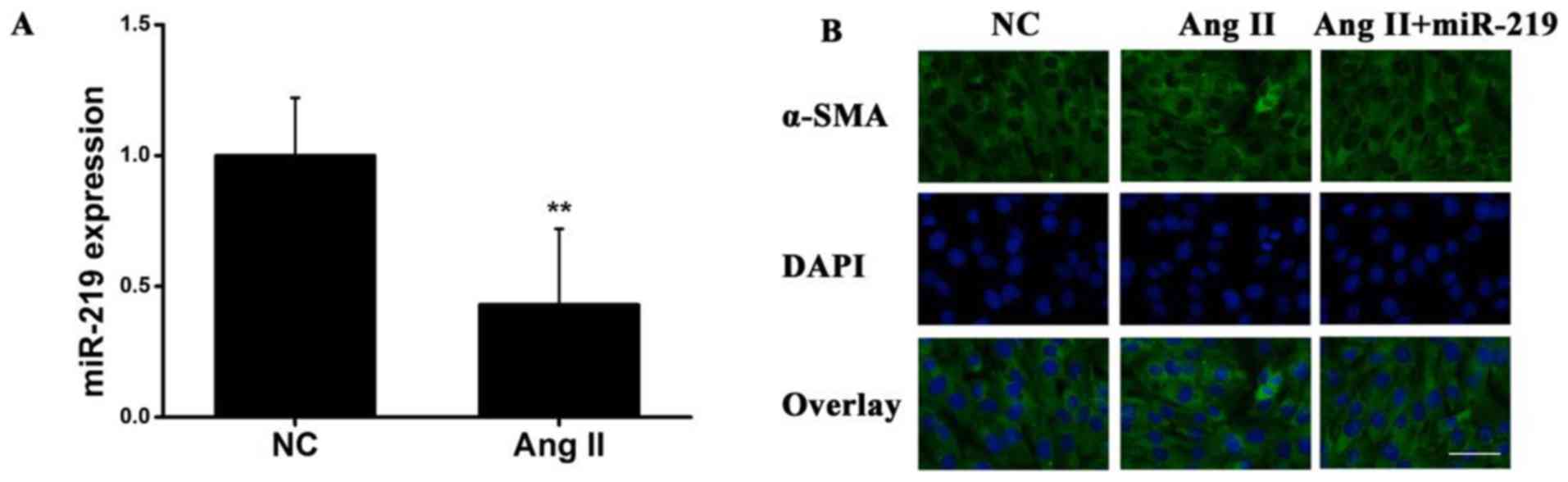
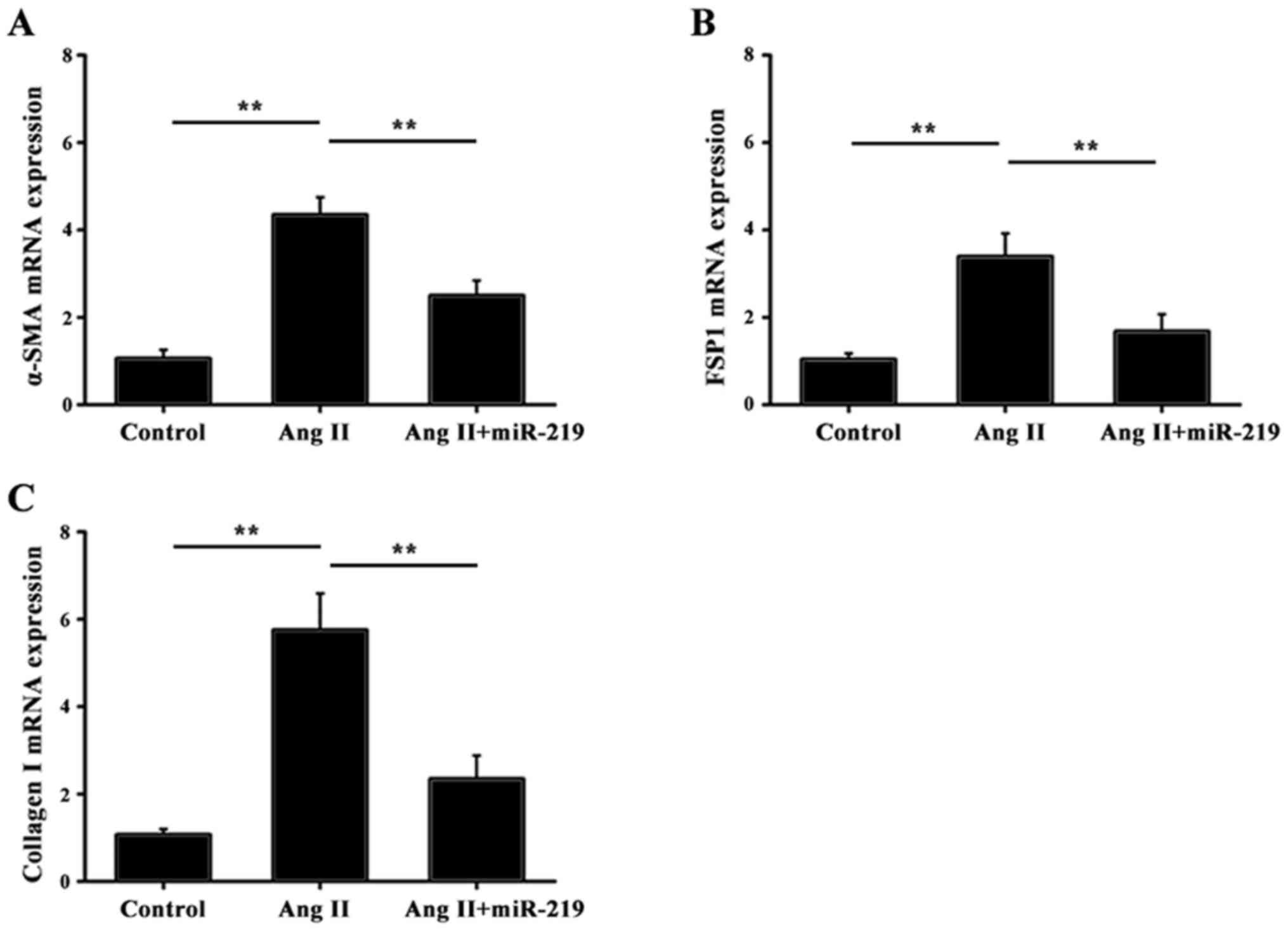
|
1
|
Roderburg C, Urban GW, Bettermann K, Vucur
M, Zimmermann H, Schmidt S, Janssen J, Koppe C, Knolle P, Castoldi
M, et al: Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human
and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 53:209–218. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Elsharkawy AM, Oakley F and Mann DA: The
role and regulation of hepatic stellate cell apoptosis in reversal
of liver fibrosis. Apoptosis. 10:927–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Piscaglia F, Dudás J, Knittel T, et al:
Expression of ECM proteins fibulin-1 and −2 in acute and chronic
liver disease and in cultured rat liver cells. Cell Tissue Res.
337:449–462. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yuan Y, Han Q, Li S, Tian Z and Zhang J:
Wnt2b attenuates HSCs activation and liver fibrosis through
negative regulating TLR4 signaling. Sci Rep. 7:39522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Henderson N and Iredale J: Liver fibrosis:
Cellular mechanisms of progression and resolution. Clin Sci (Lond).
112:265–280. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
He Y, Huang C, Zhang SP, Sun X, Long XR
and Li J: The potential of microRNAs in liver fibrosis. Cell
Signal. 24:2268–2272. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kakino S, Ohki T..Nakayama H, Yuan X,
Otabe S, Hashinaga T, Wada N, Kurita Y, Tanaka K, Hara K, et al:
Pivotal role of TNF-α in the development and progression of
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a murine model. Horm Metab Res.
50:80–87. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ogawa S, Ochi T, Shimada H, Inagaki K,
Fujita I, Nii A, Moffat MA, Katragadda M, Violand BN, Arch RH and
Masferrer JL: Anti-PDGF-B monoclonal antibody reduces liver
fibrosis development. Hepatol Res. 40:1128–1141. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Czochra P, Klopcic B, Meyer E, Herkel J,
Garcia-Lazaro JF, Thieringer F, Schirmacher P, Biesterfeld S, Galle
PR, Lohse AW and Kanzler S: Liver fibrosis induced by hepatic
overexpression of PDGF-B in transgenic mice. J Hepatol. 45:419–428.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ueberham E, Lã WR, Ueberham U, Schönig K,
Bujard H and Gebhardt R: Conditional tetracycline-regulated
expression of TGF-beta1 in liver of transgenic mice leads to
reversible intermediary fibrosis. Hepatology. 37:1067–1078. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
George J, Roulot D, Koteliansky VE and
Bissell DM: In vivo inhibition of rat stellate cell activation by
soluble transforming growth factor beta type II receptor: A
potential new therapy for hepatic fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
96:12719–12724. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kato M and Natarajan R: MicroRNAs in
diabetic nephropathy: Functions, biomarkers, and therapeutic
targets. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1353. 72–88. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhong X, Chung AC, Chen HY, Dong Y, Meng
XM, Li R, Yang W, Hou FF and Lan HY: miR-21 is a key therapeutic
target for renal injury in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes.
Diabetologia. 56:663–674. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang Y, He Y and Li J: MicroRNA-21: A
central regulator of fibrotic diseases via various targets. Curr
Pharm Des. 21:2236–2242. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zavadil J, Narasimhan M, Blumenberg M and
Schneider RJ: Transforming growth factor-beta and microRNA: mRNA
regulatory networks in epithelial plasticity. Cells Tissues Organs.
185:157–161. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wen M, Men R, Liu X and Yang L:
Involvement of miR-30c in hepatic stellate cell activation through
the repression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Life Sci.
155:21–28. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hyun J, Choi SS, Diehl AM and Jung Y:
Potential role of Hedgehog signaling and microRNA-29 in liver
fibrosis of IKKβ-deficient mouse. J Mol Histol. 45:103–112. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Venugopal SK, Jiang J, Kim TH, Li Y, Wang
SS, Torok NJ, Wu J and Zern MA: Liver fibrosis causes
downregulation of miRNA-150 and miRNA-194 in hepatic stellate
cells, and their overexpression causes decreased stellate cell
activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 298:G101–G106.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hartung T: Comparative analysis of the
revised directive 2010/63/EU for the protection of laboratory
animals with its predecessor 86/609/EEC-a t4 report. ALTEX.
27:285–303. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Müllenbach R, Fund N, Hall R, Dooley S and
Lammert F: Genotype to phenotype: Modelling the impact of natural
TGFbR2 expression variation on fibrosis initiation in vivo. Z
Gastroenterol. 49:2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang Y, Zhou X, Long YI, Peng S, Zhang Q
and Mantian MI: Dihydromyricetin attenuates activation of hepatic
stellate cells through TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway. J Third Mil
Med Univ. 40:282–289. 2018.
|
|
23
|
García-Sánchez O, López-Hernández FJ and
López-Novoa JM: An integrative view on the role of TGF-beta in the
progressive tubular deletion associated with chronic kidney
disease. Kidney Int. 77:950–955. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Border WA and Noble NA: Transforming
growth factor beta in tissue fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 331:1286–1292.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ning ZW, Luo XY, Wang GZ, Li Y, Pan MX,
Yang RQ, Ling XG, Huang S, Ma XX, Jin SY, et al: MicroRNA-21
mediates angiotensin II-induced liver fibrosis by activating NLRP3
Inflammasome/IL-1β axis via targeting Smad7 and Spry1. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 27:1–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Simms R, Coward WR, Pang L and Knox AJ;
Carol Feghali-Bostwick, : Identification of the sources of lung
myofibroblasts using FSP1 And ±-SMA As markers in idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 181:A11172010.
|
|
27
|
Ding H, Yang Q, Wang Z, et al: Effects of
sulfotanshinone IIA sodium on murine renal interstitial fibrosis
and CTGF level. Immunol J. 27:398–397. 2011.
|
|
28
|
Gressner AM and Weiskirchen R: Modern
pathogenetic concepts of liver fibrosis suggest stellate cells and
TGF-beta as major players and therapeutic targets. J Cell Mol Med.
10:76–99. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kota J, Chivukula RR, O'Donnell KA,
Wentzel EA, Montgomery CL, Hwang HW, Chang TC, Vivekanandan P,
Torbenson M, Clark KR, et al: Therapeutic microRNA delivery
suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell.
137:1005–1017. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lei H, Zou D, Li Z, Luo M, Dong L, Wang B,
Yin H, Ma Y, Liu C, Wang F, et al: MicroRNA-219-2-3p functions as a
tumor suppressor in gastric cancer and is regulated by DNA
methylation. PLoS One. 8:e603692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang N, Lin J, Ruan J, Su N, Qing R, Liu
F, He B, Lv C, Zheng D and Luo R: MiR-219-5p inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by targeting
glypican-3. FEBS Lett. 586:884–891. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wong TS, Liu XB, Wong YH, Ng RW, Yuen AP
and Wei WI: Mature miR-184 as potential oncogenic microRNA of
squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2588–2592.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Siddesha JM, Valente AJ, Yoshida T,
Sakamuri SS, Delafontaine P, Iba H, Noda M and Chandrasekar B:
Docosahexaenoic acid reverses angiotensin II-induced RECK
suppression and cardiac fibroblast migration. Cell Signal.
26:933–941. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dugas JC, Cuellar TL, Scholze A, Ason B,
Ibrahim A, Emery B, Zamanian JL, Foo LC, McManus MT and Barres BA:
Dicer1 and miR-219 are required for normal oligodendrocyte
differentiation and myelination. Neuron. 65:597–611. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xia Y, Jin X, Yan J, Entman ML and Wang Y:
CXCR6 plays a critical role in angiotensin II-induced renal injury
and fibrosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:1422–1428. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Maegdefessel L, Azuma J, Toh R, Deng A,
Merk DR, Raiesdana A, Leeper NJ, Raaz U, Schoelmerich AM, McConnell
MV, et al: MicroRNA-21 blocks abdominal aortic aneurysm development
and nicotine-augmented expansion. Sci Transl Med. 4:122ra222012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ning Q and Jiang X: Angiotensin II
upregulated the expression of microRNA-224 but not microRNA-21 in
adult rat cardiac fibroblasts. Biomed Rep. 1:776–780. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lorenzen JM, Schauerte C, Hübner A,
Kölling M, Martino F, Scherf K, Batkai S, Zimmer K, Foinquinos A,
Kaucsar T, et al: Osteopontin is indispensible for AP1-mediated
angiotensin II-related miR-21 transcription during cardiac
fibrosis. Eur Heart J. 36:2184–2196. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tian XF, Ji FJ, Zang HL and Cao H:
Activation of the miR-34a/SIRT1/p53 signaling pathway contributes
to the progress of liver fibrosis via inducing apoptosis in
hepatocytes but not in HSCs. PLoS One. 11:e01586572016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Santibañez JF, Quintanilla M and Bernabeu
C: TGF-β/TGF-β receptor system and its role in physiological and
pathological conditions. Clin Sci (Lond). 121:233–251. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu Y: Epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in renal fibrogenesis: Pathologic significance,
molecular mechanism, and therapeutic intervention. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 15:1–12. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|