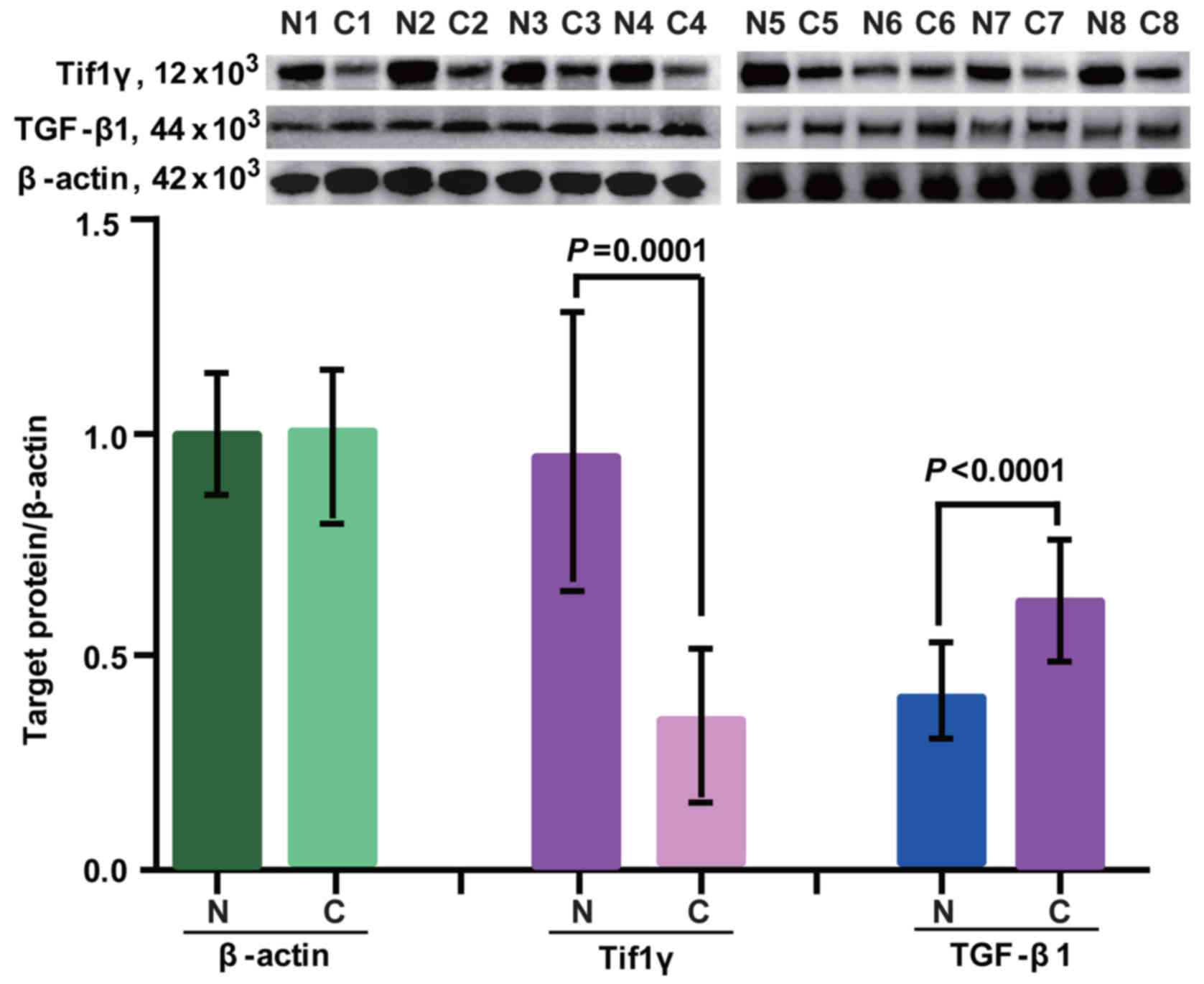
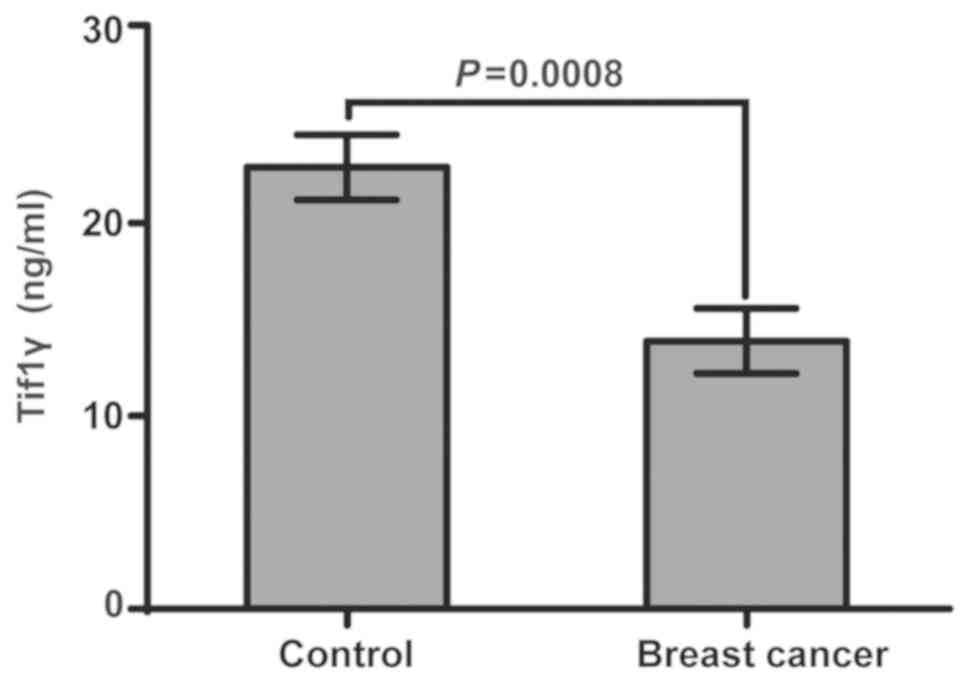
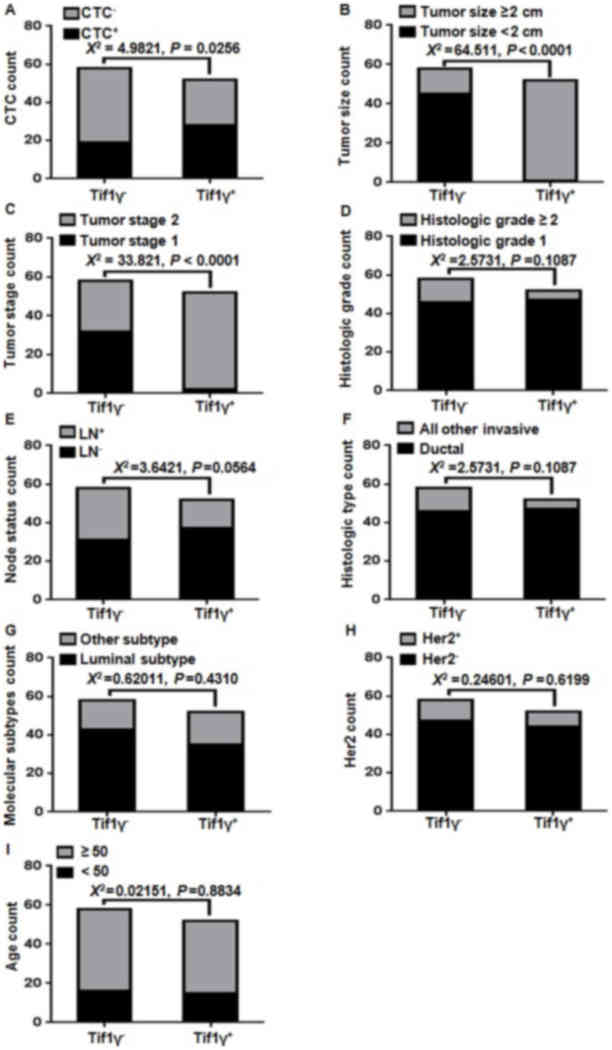
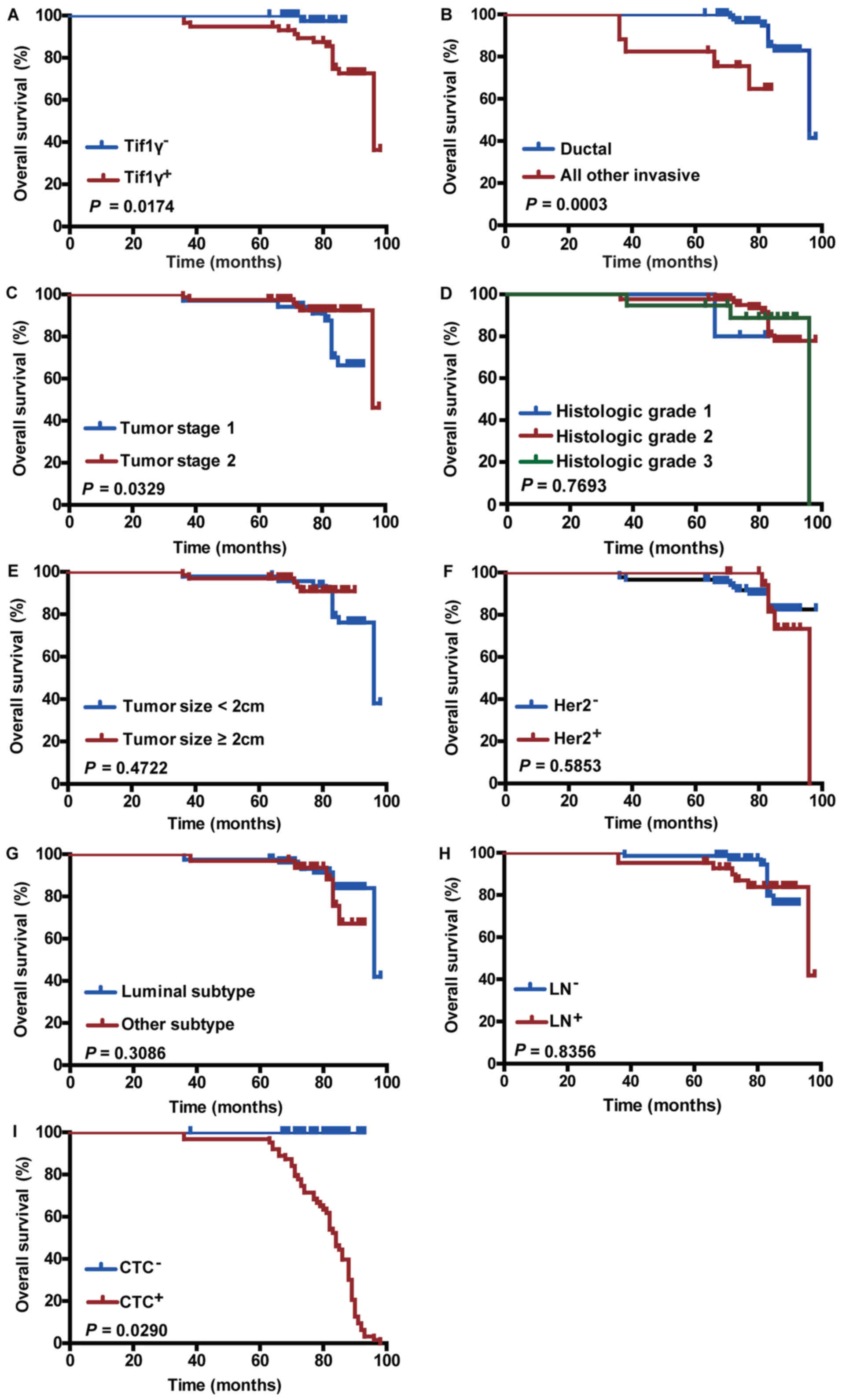
|
1
|
Herquel B, Ouararhni K and Davidson I: The
TIF1α-related TRIM cofactors couple chromatin modifications to
transcriptional regulation, signaling and tumor suppression.
Transcription. 2:231–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Venturini L, You J, Stadler M, Galien R,
Lallemand V, Koken MH, Mattei MG, Ganser A, Chambon P, Losson R and
de Thé H: TIF1gamma, a novel member of the transcriptional
intermediary factor 1 family. Oncogene. 18:1209–1217. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hatakeyama S: TRIM proteins and cancer.
Nat Rev Cancer. 11:792–804. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Herquel B, Ouararhni K, Khetchoumian K,
Ignat M, Teletin M, Mark M, Béchade G, Van Dorsselaer A,
Sanglier-Cianférani S, Hamiche A, et al: Transcription cofactors
TRIM24, TRIM28, and TRIM33 associate to form regulatory complexes
that suppress murine hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 108:8212–8217. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen T and Dent SY: Chromatin modifiers
and remodellers: Regulators of cellular differentiation. Nat Rev
Genet. 15:93–106. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xi Q, Wang Z, Zaromytidou AI, Zhang XH,
Chow-Tsang LF, Liu JX, Kim H, Barlas A, Manova-Todorova K,
Kaartinen V, et al: A poised chromatin platform for TGF-β access to
master regulators. Cell. 147:1511–1524. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Massagué J and Xi Q: TGF-β control of stem
cell differentiation genes. FEBS Lett. 586:1953–1958. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Heldin CH and Moustakas A: A new twist in
Smad signaling. Dev Cell. 10:685–686. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Moustakas A and Heldin CH: The regulation
of TGFbeta signal transduction. Development. 136:3699–3714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Heldin CH and Moustakas A: Role of Smads
in TGFβ signaling. Cell Tissue Res. 347:21–36. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Attisano L and Lee-Hoeflich ST: The Smads.
Genome Biol. 2:REVIEWS30102001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Smith AP, Verrecchia A, Fagà G, Doni M,
Perna D, Martinato F, Guccione E and Amati B: A positive role for
Myc in TGFbeta-induced Snail transcription and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene. 28:422–430. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Padgett RW: TGFbeta signaling pathways and
human diseases. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 18:247–259. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dupont S, Zacchigna L, Cordenonsi M,
Soligo S, Adorno M, Rugge M and Piccolo S: Germ-layer specification
and control of cell growth by ectodermin, a Smad4 ubiquitin ligase.
Cell. 121:87–99. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Morsut L, Yan KP, Enzo E, Aragona M,
Soligo SM, Wendling O, Mark M, Khetchoumian K, Bressan G, Chambon
P, et al: Negative control of Smad activity by ectodermin/Tif1gamma
patterns the mammalian embryo. Development. 137:2571–2578. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Agricola E, Randall RA, Gaarenstroom T,
Dupont S and Hill CS: Recruitment of TIF1g to Chromatin via Its PHD
finger-bromodomain activates its ubiquitin ligase and
transcriptional repressor activities. Mol Cell. 43:85–96. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kusy S, Gault N, Ferri F, Lewandowski D,
Barroca V, Jaracz-Ros A, Losson R and Romeo PH: Adult hematopoiesis
is regulated by TIF1γ, a repressor of TAL1 and PU.1 transcriptional
activity. Cell Stem Cell. 8:412–425. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bai RY, Koester C, Ouyang T, Hahn SA,
Hammerschmidt M, Peschel C and Duyster J: SMIF, a Smad4-interacting
protein that functions as a co-activator in TGFbeta signalling. Nat
Cell Biol. 4:181–190. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He W, Dorn DC, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst
P, Moore MA and Massagué J: Hematopoiesis controlled by distinct
TIF1gamma and Smad4 Branches of the TGFbeta Pathway. Cell.
125:929–941. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Aucagne R, Droin N, Paggetti J, Lagrange
B, Largeot A, Hammann A, Bataille A, Martin L, Yan KP, Fenaux P, et
al: Transcription intermediary factor 1γ is a tumor suppressor in
mouse and human chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. J Clin Invest.
121:2361–2370. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Emanuel PD: Juvenile myelomonocytic
leukemia and chronic myelomonocytic leukemia. Leukemia.
22:1335–1342. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Quéré R, Saint-Paul L, Carmignac V, Martin
RZ, Chrétien ML, Largeot A, Hammann A, Pais de Barros JP, Bastie JN
and Delva L: Tif1γ regulates the TGF-β1 receptor and promotes
physiological aging of hematopoietic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 111:10592–10597. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lindley LE and Briegel KJ: Generation of
mice with a conditional Lbh null allele. Genesis. 51:491–497. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou Y, You MJ, Young KH, Lin P, Lu G,
Medeiros LJ and Bueso-Ramos CE: Advances in the molecular
pathobiology of B-lymphoblastic leukemia. Hum Pathol. 43:1347–1362.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang E, Kawaoka S, Roe JS, Shi J, Hohmann
AF, Xu Y, Bhagwat AS, Suzuki Y and Kinney JB: The transcriptional
cofactor TRIM33 prevents apoptosis in B lymphoblastic leukemia by
deactivating a single enhancer. Elife. 4:e063772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yuan N, Song L, Zhang S, Lin W, Cao Y, Xu
F, Fang Y, Wang Z, Zhang H, Li X, et al: Bafilomycin A1 targets
both autophagy and apoptosis pathways in pediatric B-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica. 100:345–356. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jain S, Singhal S, Francis F, Hajdu C,
Wang JH, Suriawinata A, Wang YQ, Zhang M, Weinshel EH, Francois F,
et al: Association of overexpression of TIF1γ with colorectal
carcinogenesis and advanced colorectal adenocarcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 17:3994–4000. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jain S, Yu M, Singhal S, Francis F, Hajdu
C, Suriawinata S, Zhang M, Aladhamy N, Chiriboga L, Pan R, et al:
Overexpression of transcription intermediary factor 1 γ (TIF1γ) is
an early event in colorectal carcinogenesis and inversely related
to Smad4 inactivation in colorectal carcinoma. Lab Investig.
90:149A2010.
|
|
29
|
Fearon ER and Vogelstein B: A genetic
model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 61:759–767. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics: 2011. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E,
Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JW, Comber H, Forman D and
Bray F: Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe:
Estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer. 49:1374–1403.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sikov WM, Berry DA, Perou CM, Singh B,
Cirrincione CT, Tolaney SM, Kuzma CS, Pluard TJ, Somlo G, Port RT,
et al: Impact of the addition of carboplatin and/or bevacizumab to
neoadjuvant once-per-week paclitaxel followed by dose-dense
doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide on pathologic complete response
rates in stage II to III triple-negative breast cancer: CALGB 40603
(Alliance). J Clin Oncol. 33:13–21. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Desantis C, Ma J, Bryan L and Jemal A:
Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:52–62. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sharma P, Stecklein SR, Kimler BF, Sethi
G, Petroff BK, Phillips TA, Tawfik OW, Godwin AK and Jensen RA: The
prognostic value of BRCA1 promoter methylation in early stage
triple negative breast cancer. J Cancer Ther Res. 3:1–11. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Müller HM, Fiegl H, Widschwendter A and
Widschwendter M: Prognostic DNA methylation marker in serum of
cancer patients. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences.
pp44–49. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Duffy MJ: Serum tumor markers in breast
cancer: Are they of clinical value? Clin Chem. 52:345–351. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cai FF, Kohler C, Zhang B, Wang MH, Chen
WJ and Zhong XY: Epigenetic therapy for breast cancer. Int J Mol
Sci. 12:4465–4487. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sharma S, Kelly TK and Jones PA:
Epigenetics in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 31:27–36. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kumar R: Breast cancer tumor markers. J
Solid Tumors. 2:432012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Payne SJ, Bowen RL, Jones JL and Wells CA:
Predictive markers in breast cancer-the present. Histopathology.
52:82–90. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wakefield LM and Roberts AB: TGF-beta
signaling: Positive and negative effects on tumorigenesis. Curr
Opin Genet Dev. 12:22–29. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Giampieri S, Manning C, Hooper S, Jones L,
Hill CS and Sahai E: Localized and reversible TGFbeta signalling
switches breast cancer cells from cohesive to single cell motility.
Nat Cell Biol. 11:1287–1296. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ikushima H and Miyazono K: TGFbeta
signalling: A complex web in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:415–424. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Faure E, Heisterkamp N, Groffen J and
Kaartinen V: Differential expression of TGF-beta isoforms during
postlactational mammary gland involution. Cell Tissue Res.
300:89–95. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nguyen AV and Pollard JW: Transforming
growth factor beta3 induces cell death during the first stage of
mammary gland involution. Development. 127:3107–3118.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li M, Liu X, Robinson G, Bar-Peled U,
Wagner KU, Young WS, Hennighausen L and Furth PA: Mammary-derived
signals activate programmed cell death during the first stage of
mammary gland involution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:3425–3430.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bierie B, Gorska AE, Stover DG and Moses
HL: TGF-beta promotes cell death and suppresses lactation during
the second stage of mammary involution. J Cell Physiol. 219:57–68.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Panis C, Herrera AC, Victorino VJ, Aranome
AM and Cecchini R: Screening of circulating TGF-beta levels and its
clinicopathological significance in human breast cancer. Anticancer
Res. 33:737–742. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Paiva CE, Drigo SA, Rosa FE, Moraes Neto
FA, Caldeira JR, Soares FA, Domingues MA and Rogatto SR: Absence of
transforming growth factor-beta type II receptor is associated with
poorer prognosis in HER2-negative breast tumours. Ann Oncol.
21:734–740. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Richardsen E, Uglehus RD, Johnsen SH and
Busund LT: Immunohistochemical expression of epithelial and stromal
immunomodulatory signalling molecules is a prognostic indicator in
breast cancer. BMC Res Notes. 5:1102012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Desruisseau S, Palmari J, Giusti C, Romain
S, Martin PM and Berthois Y: Determination of TGFbeta1 protein
level in human primary breast cancers and its relationship with
survival. Br J Cancer. 94:239–246. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Koumoundourou D, Kassimatis T, Zolota V,
Tzorakoeleftherakis E, Ravazoula P, Vassiliou V, Kardamakis D and
Varakis J: Prognostic significance of TGFbeta-1 and pSmad2/3 in
breast cancer patients with T1-2,N0 tumours. Anticancer Res.
27:2613–2620. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Vincent DF, Yan KP, Treilleux I, Gay F,
Arfi V, Kaniewsky B, Marie JC, Lepinasse F, Martel S, Goddard-Leon
S, et al: Inactivation of TIF1gamma cooperates with Kras to induce
cystic tumors of the pancreas. PLoS Genet. 5:e10005752009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fattet L, Ay AS, Bonneau B, Jallades L,
Mikaelian I, Treilleux I, Gillet G, Hesling C and Rimokh R: TIF1γ
requires sumoylation to exert its repressive activity on TGFβ
signaling. J Cell Sci. 126:3713–3123. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mascle XH, Germain-Desprez D, Huynh P,
Estephan P and Aubry M: Sumoylation of the transcriptional
intermediary factor 1beta (TIF1beta), the Co-repressor of the KRAB
multifinger proteins, is required for its transcriptional activity
and is modulated by the KRAB domain. J Biol Chem. 282:10190–10202.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kretzschmar M, Doody J, Timokhina I and
Massagué J: A mechanism of repression of TGFbeta/Smad signaling by
oncogenic Ras. Genes Dev. 13:804–816. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wang L, Yang H, Lei Z, Zhao J, Chen Y,
Chen P, Li C, Zeng Y, Liu Z, Liu X and Zhang HT: Repression of
TIF1γ by SOX2 promotes TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 35:867–877.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mikaelian I, Malek M, Gadet R, Viallet J,
Garcia A, Girard-Gagnepain A, Hesling C, Gillet G, Gonzalo P,
Rimokh R and Billaud M: Genetic and pharmacologic inhibition of
mTORC1 promotes EMT by a TGF-β-independent mechanism. Cancer Res.
73:6621–6631. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hesling C, Fattet L, Teyre G, Jury D,
Gonzalo P, Lopez J, Vanbelle C, Morel AP, Gillet G, Mikaelian I and
Rimokh R: Antagonistic regulation of EMT by TIF1γ and Smad4 in
mammary epithelial cells. EMBO Rep. 12:665–672. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Hesling C, Lopez J, Fattet L, Gonzalo P,
Treilleux I, Blanchard D, Losson R, Goffin V, Pigat N, Puisieux A,
et al: Tif1γ is essential for the terminal differentiation of
mammary alveolar epithelial cells and for lactation through SMAD4
inhibition. Development. 140:167–175. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kassem L, Deygas M, Fattet L, Lopez J,
Goulvent T, Lavergne E, Chabaud S, Carrabin N, Chopin N, Bachelot
T, et al: TIF1γ interferes with TGFβ1/SMAD4 signaling to promote
poor outcome in operable breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer.
15:4532015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kim MY, Oskarsson T, Acharyya S, Nguyen
DX, Zhang XH, Norton L and Massagué J: Tumor self-seeding by
circulating cancer cells. Cell. 139:1315–1326. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Li P, Mao Z, Peng Z, Zhou L, Chen Y, Huang
PH, Truica CI, Drabick JJ, El-Deiry WS, Dao M, et al: Acoustic
separation of circulating tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:4970–4975. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Dive C and Brady G: SnapShot: Circulating
tumor cells. Cell. 168:P742–P742.e1. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Dawson SJ, Tsui DW, Murtaza M, Biggs H,
Rueda OM, Chin SF, Dunning MJ, Gale D, Forshew T, Mahler-Araujo B,
et al: Analysis of circulating tumor DNA to monitor metastatic
breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 368:1199–1209. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Scully OJ, Bay BH, Yip G and Yu Y: Breast
cancer metastasis. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 9:311–320.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kuo AH and Clarke MF: Identifying the
metastatic seeds of breast cancer. Nat Biotechnol. 31:504–505.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Cristofanilli M, Budd GT, Ellis MJ,
Stopeck A, Matera J, Miller MC, Reuben JM, Doyle GV, Allard WJ,
Terstappen LWMM and Hayes DF: Circulating tumor cells, disease
progression, and survival in metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J
Med. 351:781–791. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Giuliano M, Giordano A, Jackson S, Hess
KR, de Giorgi U, Mego M, Handy BC, Ueno NT, Alvarez RH, De
Laurentiis M, et al: Circulating tumor cells as prognostic and
predictive markers in metastatic breast cancer patients receiving
first-line systemic treatment. Breast Cancer Res. 13:R672011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Pierga JY, Bidard FC, Mathiot C, Brain E,
Delaloge S, Giachetti S, de Cremoux P, Salmon R, Vincent-Salomon A
and Marty M: Circulating tumor cell detection predicts early
metastatic relapse after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in large operable
and locally advanced breast cancer in a phase II randomized trial.
Clin Cancer Res. 14:7004–7010. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Bidard FC, Proudhon C and Pierga JY:
Circulating tumor cells in breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 10:418–430.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Pan X, Zeng SL, Yu D, Liang XL, Ji C, Pan
B, Cai J, Wang Y, Min Y, Fang W and Liao WQ: Variable domain of the
heavy chain of heavy-chain antibody of the Rv0733 antigen of
mycobacterium tuberculosis panned and identified from a nonimmune
llama VHH phage display library. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
9:2869–2878. 2016.
|
|
74
|
Lin XY, Cai FF, Wang MH, Pan X, Wang F,
Cai L, Cui RR, Chen S and Ewelina B: Mammalian sterile 20-like
kinase 1 expression and its prognostic significance in patients
with breast cancer. Oncology Lett. 14:5457–5463. 2017.
|
|
75
|
Chen B, Le W, Wang Y, Li Z, Wang D, Ren L,
Lin L, Cui S, Hu JJ, Hu Y, et al: Targeting negative surface
charges of cancer cells by multifunctional nanoprobes.
Theranostics. 6:1887–1898. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Banin Hirata BK, Oda JM, Losi Guembarovski
R, Ariza CB, de Oliveira CE and Watanabe MA: Molecular markers for
breast cancer: Prediction on tumor behavior. Dis Markers.
2014:5131582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Curtis C, Shah SP, Chin SF, Turashvili G,
Rueda OM, Dunning MJ, Speed D, Lynch AG, Samarajiwa S, Yuan Y, et
al: The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast
tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature. 486:346–352. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hah N, Danko CG, Core L, Waterfall JJ,
Siepel A, Lis JT and Kraus WL: A rapid, extensive, and transient
transcriptional response to estrogen signaling in breast cancer
cells. Cell. 145:622–634. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Xiong R, Zhao J, Gutgesell LM, Wang Y, Lee
S, Karumudi B, Zhao H, Lu Y, Tonetti DA and Thatcher GR: Novel
selective estrogen receptor downregulators (SERDs) developed
against treatment-resistant breast cancer. J Med Chem.
60:1325–1342. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Reis-Filho JS and Pusztai L: Gene
expression profiling in breast cancer: Classification,
prognostication, and prediction. Lancet. 378:1812–1823. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Assi HA, Khoury KE, Dbouk H, Khalil LE,
Mouhieddine TH and El Saghir NS: Epidemiology and prognosis of
breast cancer in young women. J Thorac Dis. 5 (Suppl 1):S2–S8.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Hefti MM, Hu R, Knoblauch NW, Collins LC,
Haibe-Kains B, Tamimi RM and Beck AH: Estrogen receptor
negative/progesterone receptor positive breast cancer is not a
reproducible subtype. Breast Cancer Res. 15:R682013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Cancer Research UK: Breast cancer
incidence statistics. Cancer Res UK. 2012.
|
|
84
|
Ban KA and Godellas CV: Epidemiology of
breast cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 23:409–422. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Cianfrocca M and Goldstein LJ: Prognostic
and predictive factors in early-stage breast cancer. Oncologist.
9:606–616. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M,
Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and
Bray F: GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer incidence and mortality
worldwide: IARC CancerBase. No. 11 [Internet]. Lyon: Fr Int Agency
Res Cancer. 11. http://globocan.iarc.f2013
|
|
87
|
Yoneda A, Lendorf ME, Couchman JR and
Multhaupt HA: Breast and ovarian cancers: A survey and possible
roles for the cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. J
Histochem Cytochem. 60:9–21. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Esteva FJ and Hortobagyi GN: Prognostic
molecular markers in early breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res.
6:109–118. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Prat A, Parker JS, Karginova O, Fan C,
Livasy C, Herschkowitz JI, He X and Perou CM: Phenotypic and
molecular characterization of the claudin-low intrinsic subtype of
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 12:R682010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Payne SJL, Bowen RL, Jones JL and Wells
CA: Predictive markers in breast cancer-the present.
Histopathology. 52:82–90. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Andrieux G, Fattet L, Le Borgne M, Rimokh
R and Théret N: Dynamic regulation of Tgf-B signaling by Tif1γ: A
computational approach. PLoS One. 7:e337612012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|