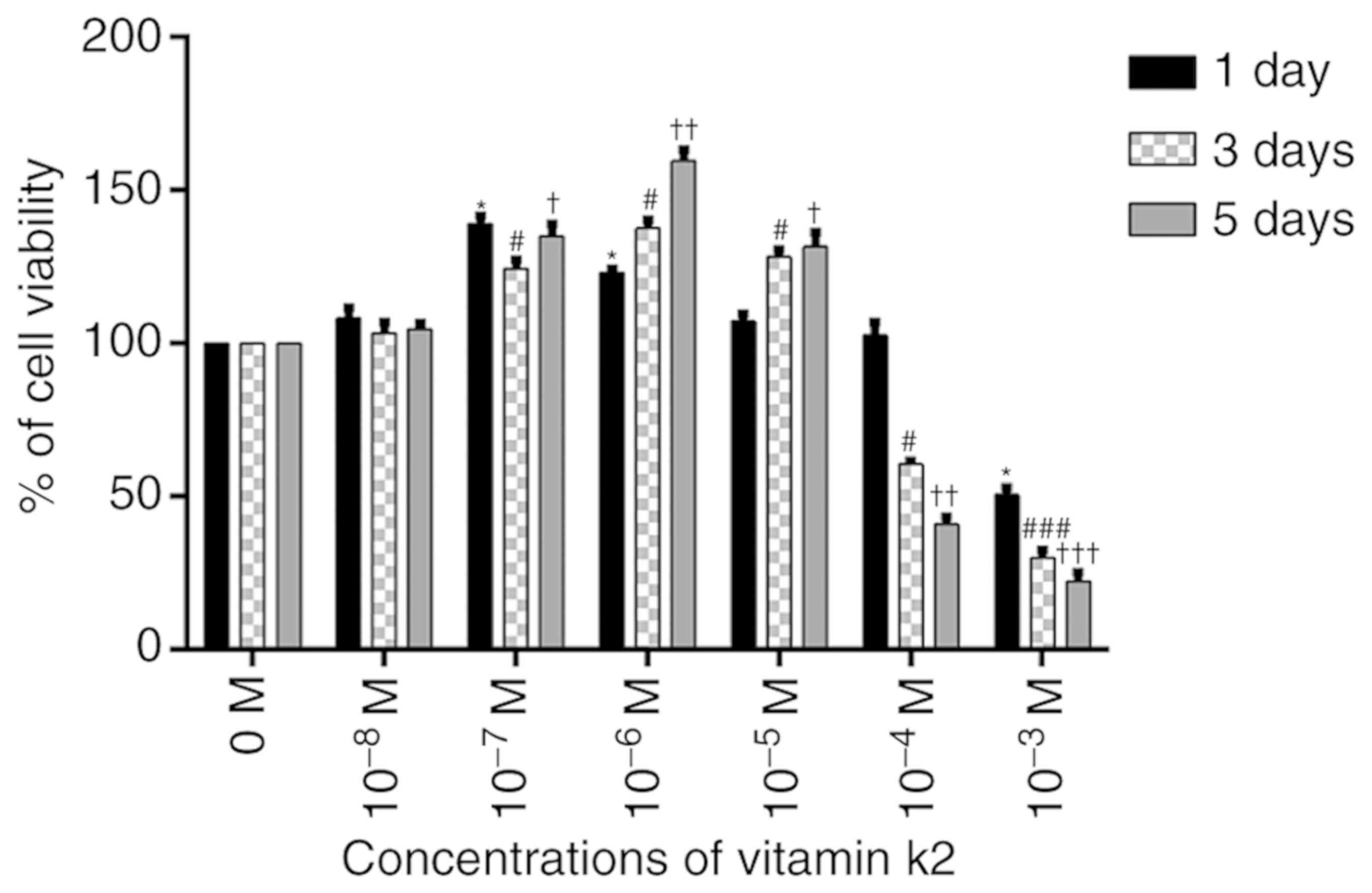
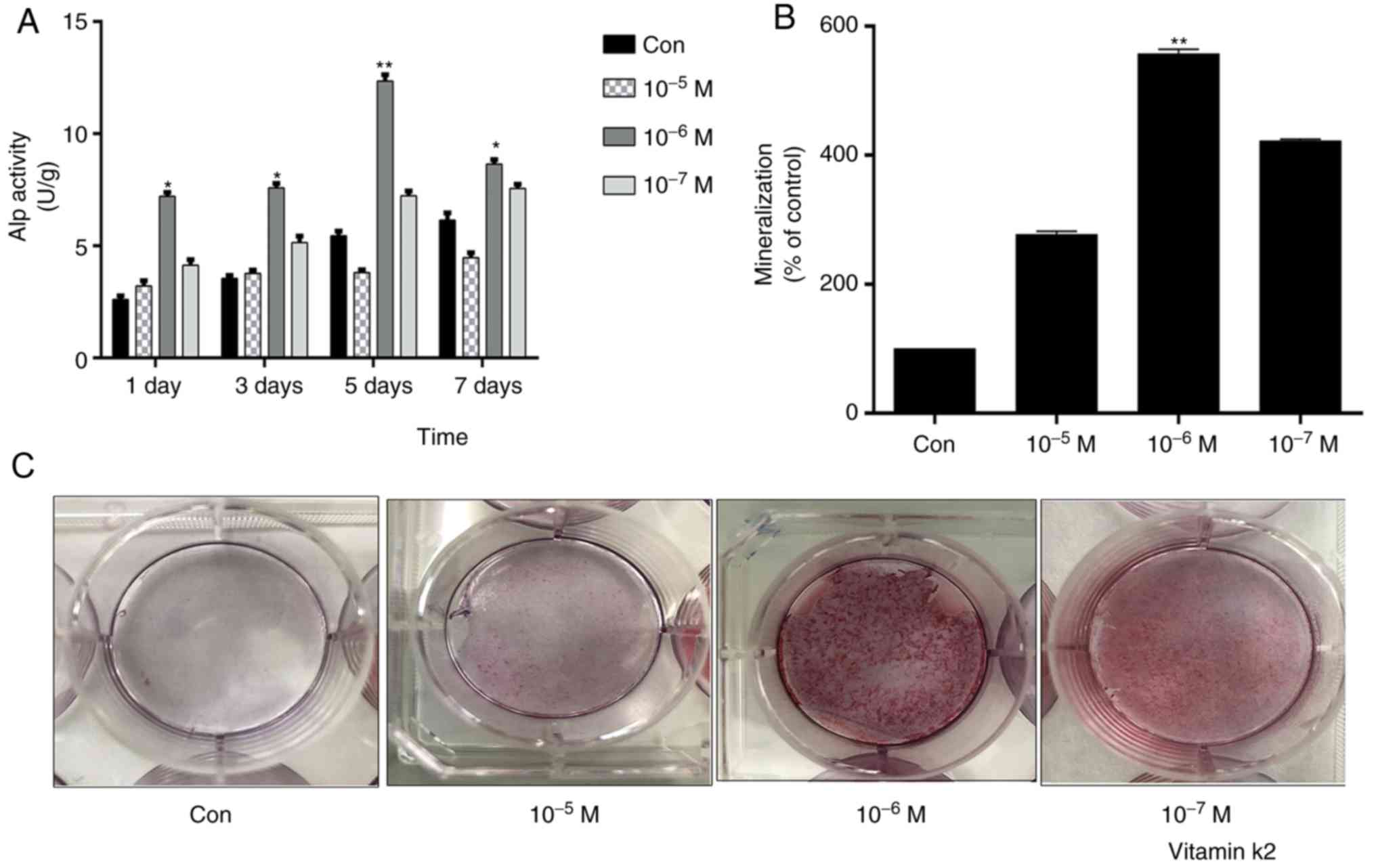
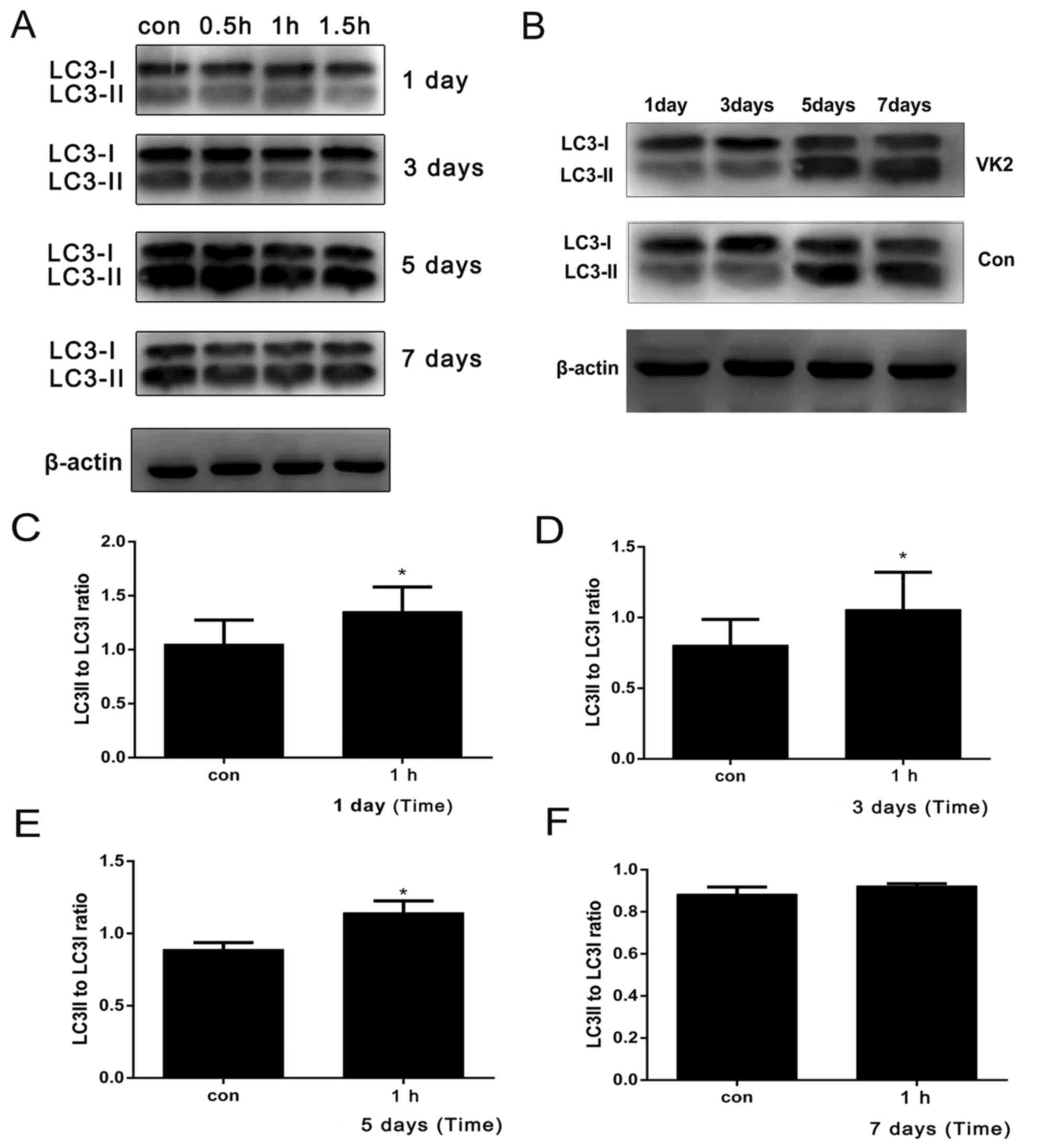
|
1
|
Tella SH and Gallagher JC: Prevention and
treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 142:155–170. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Glaser DL and Kaplan FS: Osteoporosis.
Definition and clinical presentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 22 (24
Suppl):12S–16S. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Edwards MH, Dennison EM, Aihie Sayer A,
Fielding R and Cooper C: Osteoporosis and sarcopenia in older age.
Bone. 80:126–130. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Diab DL and Watts NB: Postmenopausal
osteoporosis. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 20:501–509. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Clarke BL: Anti-sclerostin antibodies:
Utility in treatment of osteoporosis. Maturitas. 78:199–204. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Levine JP: Identification, diagnosis, and
prevention of osteoporosis. Am J Manag Care. 17 (Suppl
6):S170–S176. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Palermo A, Tuccinardi D, D'Onofrio L,
Watanabe M, Maggi D, Maurizi AR, Greto V, Buzzetti R, Napoli N,
Pozzilli P and Manfrini S: Vitamin K and osteoporosis: Myth or
reality? Metabolism. 70:57–71. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nelsestuen GL, Zytkovicz TH and Howard JB:
The mode of action of vitamin K. Identification of
gamma-carboxyglutamic acid as a component of prothrombin. J Biol
Chem. 249:6347–6350. 1974.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stenflo J, Fernlund P, Egan W and
Roepstorff P: Vitamin K dependent modifications of glutamic acid
residues in prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 71:2730–2733.
1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Berkner KL: The vitamin K-dependent
carboxylase. Annu Rev Nutr. 25:127–149. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hauschka PV, Lian JB and Gallop PM: Direct
identification of the calcium-binding amino acid,
gamma-carboxyglutamate, in mineralized tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 72:3925–3929. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Coutu DL, Wu JH, Monette A, Rivard GE,
Blostein MD and Galipeau J: Periostin, a member of a novel family
of vitamin K-dependent proteins, is expressed by mesenchymal
stromal cells. J Biol Chem. 283:17991–18001. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rubinacci A: Expanding the functional
spectrum of vitamin K in bone. Focus on: ‘Vitamin K promotes
mineralization, osteoblast to osteocyte transition, and an
anti-catabolic phenotype by {gamma}-carboxylation-dependent and
-independent mechanisms’. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
297:C1336–1338. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Atkins GJ, Welldon KJ, Wijenayaka AR,
Bonewald LF and Findlay DM: Vitamin K promotes mineralization,
osteoblast-to-osteocyte transition, and an anticatabolic phenotype
by {gamma}-carboxylation-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Am
J Physiol Cell Physiol. 297:C1358–1367. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pierrefite-Carle V, Santucci-Darmanin S,
Breuil V, Camuzard O and Carle GF: Autophagy in bone: Self-eating
to stay in balance. Ageing Res Rev. 24:206–217. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Parzych KR and Klionsky DJ: An overview of
autophagy: Morphology, mechanism, and regulation. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 20:460–473. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
White E, Mehnert JM and Chan CS:
Autophagy, Metabolism, and Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:5037–5046.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mizushima N and Levine B: Autophagy in
mammalian development and differentiation. Nat Cell Biol.
12:823–830. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamaguchi M: The role of regucalcin in
bone homeostasis: Involvement as a novel cytokine. Integr Biol
(Camb). 6:258–266. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Raouf A and Seth A: Ets transcription
factors and targets in osteogenesis. Oncogene. 19:6455–6463. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yamaguchi M and Weitzmann MN: Vitamin K2
stimulates osteoblastogenesis and suppresses osteoclastogenesis by
suppressing NF-κB activation. Int J Mol Med. 27:3–14.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ichikawa T, Horie-Inoue K, Ikeda K,
Blumberg B and Inoue S: Vitamin K2 induces phosphorylation of
protein kinase A and expression of novel target genes in
osteoblastic cells. J Mol Endocrinol. 39:239–247. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang YL, Yin JH, Ding H, Zhang W, Zhang
CQ and Gao YS: Protective effect of VK2 on glucocorticoid-treated
MC3T3-E1 cells. Int J Mol Med. 39:160–166. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nollet M, Santucci-Darmanin S, Breuil V,
Al-Sahlanee R, Cros C, Topi M, Momier D, Samson M, Pagnotta S,
Cailleteau L, et al: Autophagy in osteoblasts is involved in
mineralization and bone homeostasis. Autophagy. 10:1965–1977. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen K, Yang YH, Jiang SD and Jiang LS:
Decreased activity of osteocyte autophagy with aging may contribute
to the bone loss in senile population. Histochem Cell Biol.
142:285–295. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pan F, Liu XG, Guo YF, Chen Y, Dong SS,
Qiu C, Zhang ZX, Zhou Q, Yang TL, Guo Y, et al: The
regulation-of-autophagy pathway may influence Chinese stature
variation: Evidence from elder adults. J Hum Genet. 55:441–447.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jilka RL, Weinstein RS, Parfitt AM and
Manolagas SC: Quantifying osteoblast and osteocyte apoptosis:
Challenges and rewards. J Bone Miner Res. 22:1492–1501. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li L, Tan J, Miao Y, Lei P and Zhang Q:
ROS and Autophagy: Interactions and molecular regulatory
mechanisms. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 35:615–621. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu F, Fang F, Yuan H, Yang D, Chen Y,
Williams L, Goldstein SA, Krebsbach PH and Guan JL: Suppression of
autophagy by FIP200 deletion leads to osteopenia in mice through
the inhibition of osteoblast terminal differentiation. J Bone Miner
Res. 28:2414–2430. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xi G, Rosen CJ and Clemmons DR: IGF-I and
IGFBP-2 stimulate AMPK activation and autophagy, which are required
for osteoblast differentiation. Endocrinology. 157:268–281. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chang KH, Sengupta A, Nayak RC, Duran A,
Lee SJ, Pratt RG, Wellendorf AM, Hill SE, Watkins M, Gonzalez-Nieto
D, et al: p62 is required for stem cell/progenitor retention
through inhibition of IKK/NF-kB/Ccl4 signaling at the bone marrow
macrophage-osteoblast niche. Cell Rep. 9:2084–2097. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu Y, Huang L, Hao B, Li H, Zhu S, Wang
Q, Li R, Xu Y and Zhang X: Use of an osteoblast overload damage
model to probe the effect of icariin on the proliferation,
differentiation and mineralization of MC3T3-E1 cells through the
Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem.
41:1605–1615. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim EC, Kim TH, Jung JH, Hong SO and Lee
DW: Enhanced osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 on
rhBMP-2-immobilized titanium via click reaction. Carbohydr Polym.
103:170–178. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
He Y, Wang S, Mu J, Dai L, Zhang Z, Sun Y,
Shi W and Ge D: Synthesis of polypyrrole nanowires with positive
effect on MC3T3-E1 cell functions through electrical stimulation.
Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 71:43–50. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mu W and Wang Z, Ma C, Jiang Y, Zhang N,
Hu K, Li L and Wang Z: Metformin promotes the proliferation and
differentiation of murine preosteoblast by regulating the
expression of sirt6 and oct4. Pharmacol Res. 129:462–474. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|