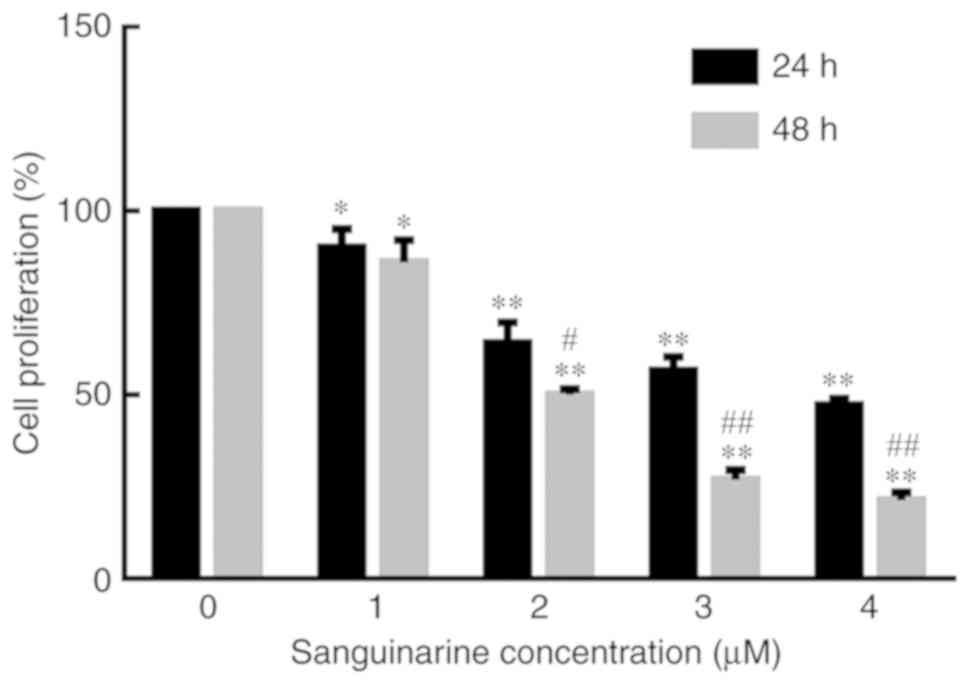
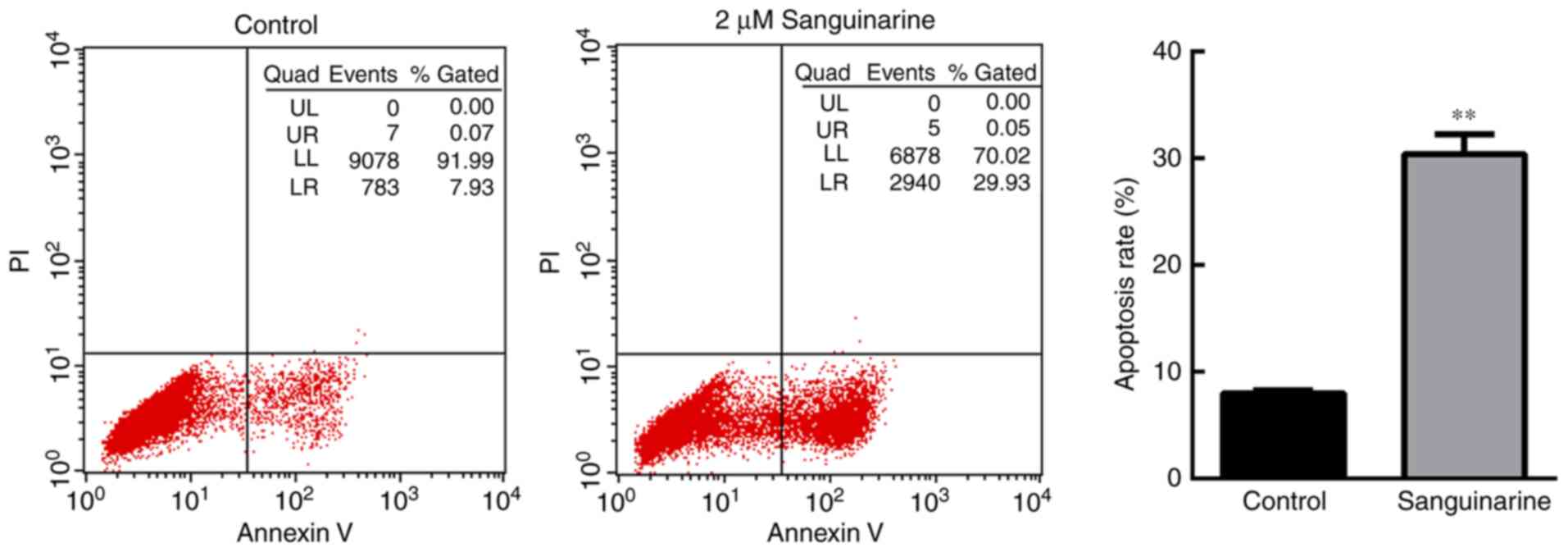
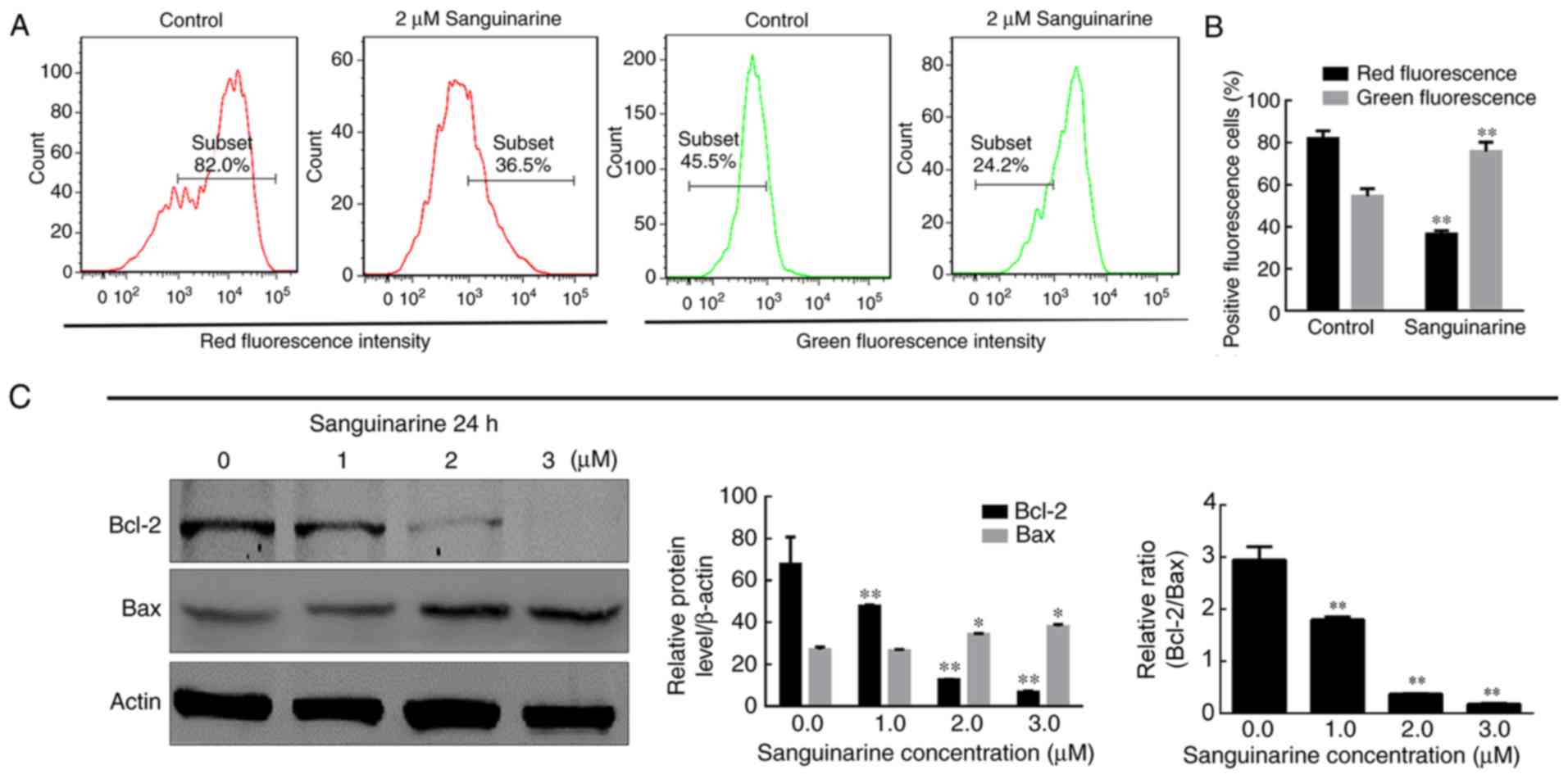
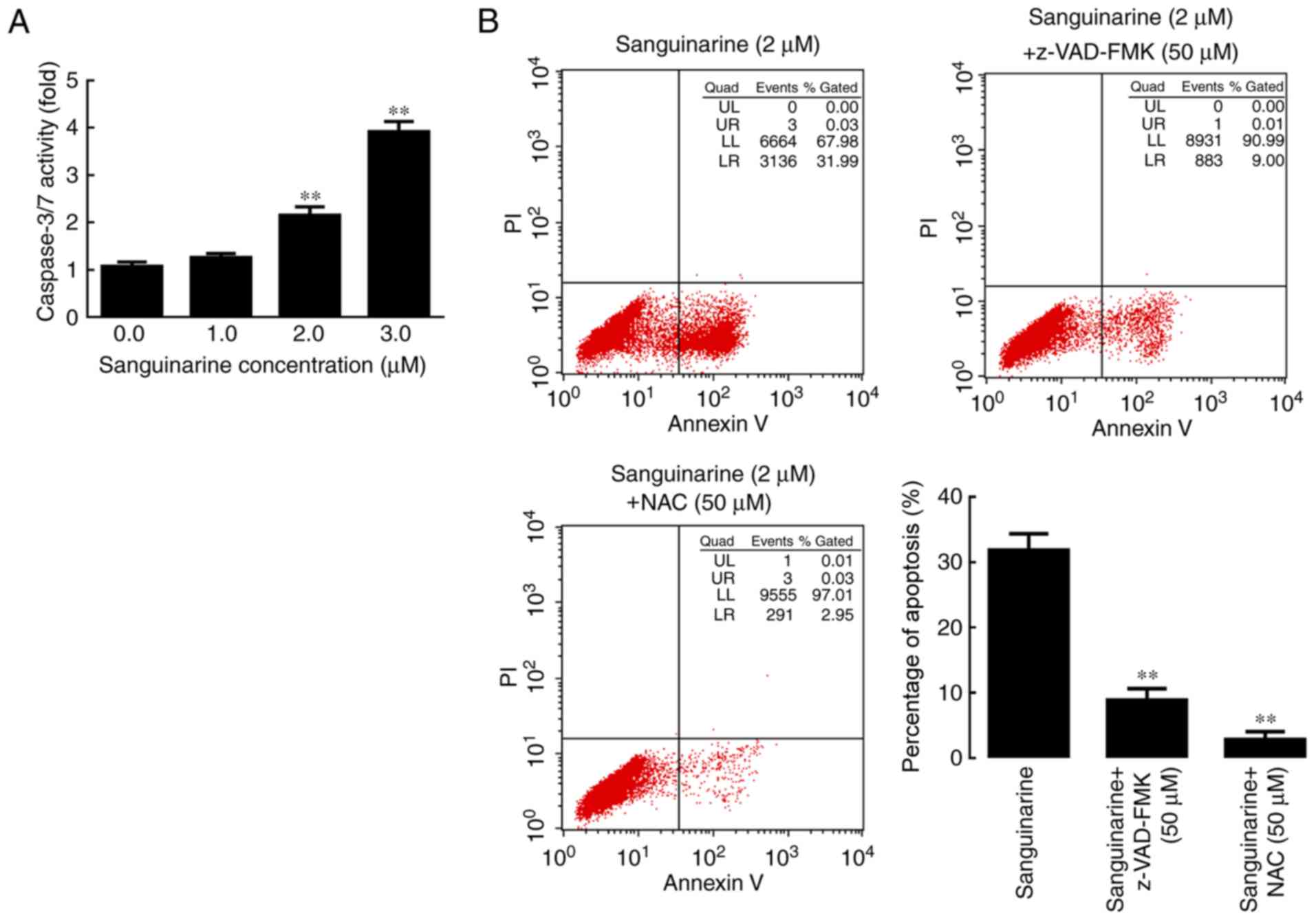
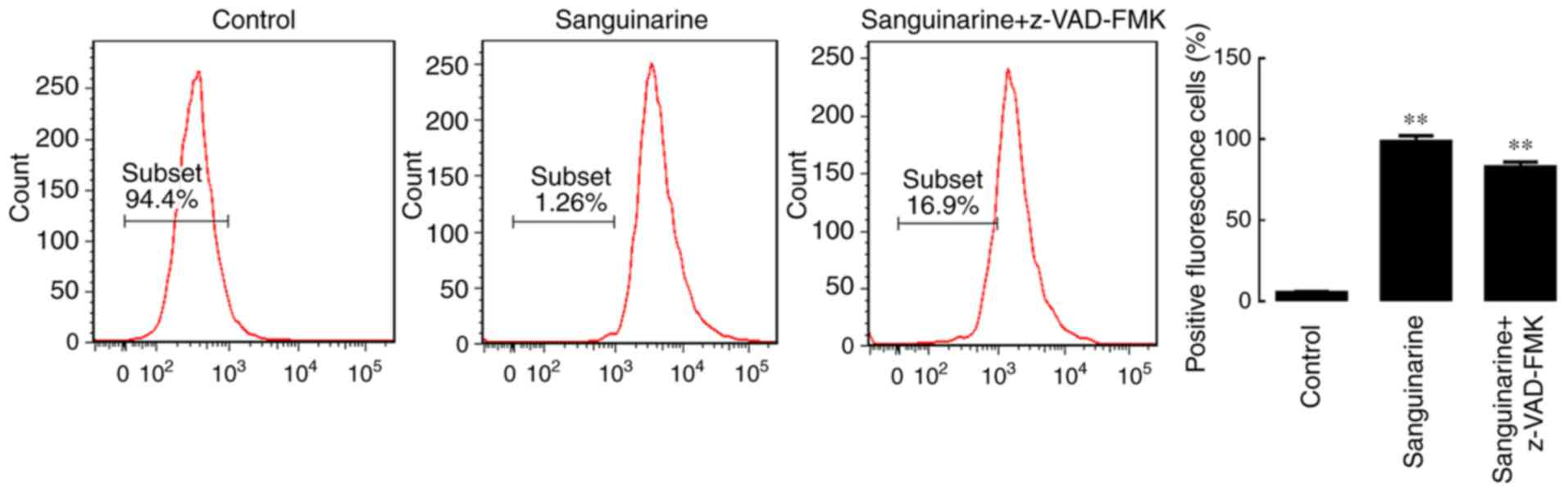
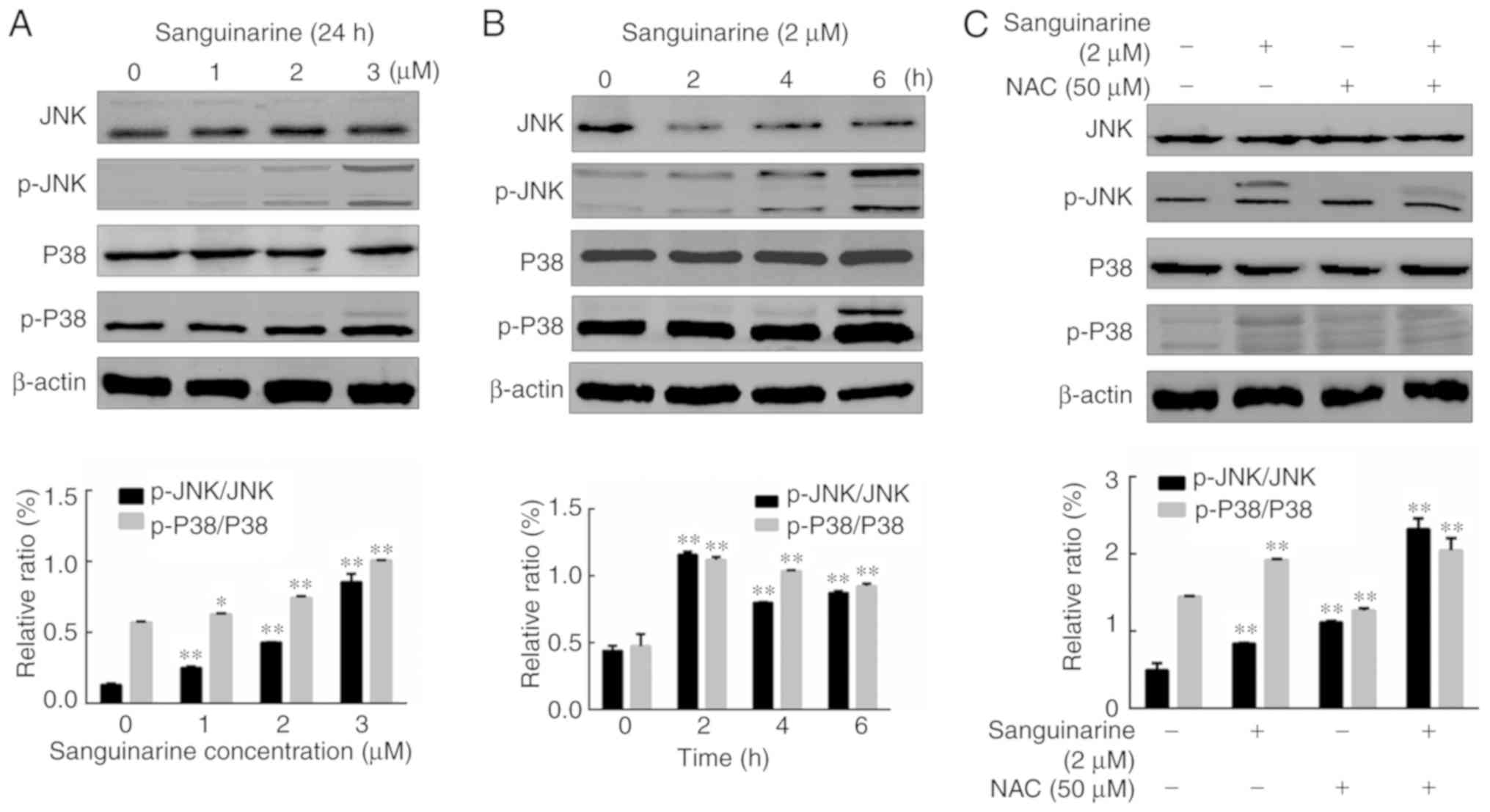
|
1
|
Chang KC and Petrash JM: Aldose reductase
mediates transforming growth factor β2 (TGF-β2)-induced migration
and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of lens-derived epithelial
cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 56:4198–4210. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Meacock WR, Spalton DJ, Boyce J and
Marshall J: The effect of posterior capsule opacification on visual
function. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 44:4665–4669. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fernandez V, Fragoso MA, Billotte C, Lamar
P, Orozco MA, Dubovy S, Willcox M and Parel JM: Efficacy of various
drugs in the prevention of posterior capsule opacification:
Experimental study of rabbit eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg.
30:2598–2605. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jiang YX, Lu Y, Liu TJ, Yang J, Chen Y and
Fang YW: Using HSV-TK/GCV suicide gene therapy to inhibit lens
epithelial cell proliferation for treatment of posterior capsular
opacification. Mol Vis. 17:291–299. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rönbeck M, Zetterström C, Wejde G and
Kugelberg M: Comparison of posterior capsule opacification
development with 3 intraocular lens types: Five-year prospective
study. J Cataract Refract Surg. 35:1935–1940. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang WR, Zhang Y and Tang X: Shikonin
inhibits the proliferation of human lens epithelial cells by
inducing apoptosis through ROS and caspase-dependent pathway.
Molecules. 19:7785–7797. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Laster LL and Lobene RR: New perspectives
on Sanguinaria clinicals: Individual toothpaste and oral rinse
testing. J Can Dent Assoc. 56 (Suppl 7):S19–S30. 1990.
|
|
8
|
Miao F, Yang XJ, Zhou L, Hu HJ, Zheng F,
Ding XD, Sun DM, Zhou CD and Sun W: Structural modification of
sanguinarine and chelerythrine and their antibacterial activity.
Nat Prod Res. 25:863–875. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Slaninová I, Pěnčíková K, Urbanová J,
Slanina J and Táborská E: Antitumour activities of sanguinarine and
related alkaloids. Phytochem Rev. 13:51–68. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gaziano R, Moroni G, Buè C, Miele MT,
Sinibaldi-Vallebona P and Pica F: Antitumor effects of the
benzophenanthridine alkaloid sanguinarine: Evidence and
perspectives. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 8:30–39. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Godowski KC: Antimicrobial action of
sanguinarine. J Clin Den. 1:96–101. 1989.
|
|
12
|
Achkar IW, Mraiche F, Mohammad RM and
Uddin S: Anticancer potential of sanguinarine for various human
malignancies. Future Med Chem. 9:933–950. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Q, Dai P, Bao H, Liang P, Wang W,
Xing A and Sun J: Anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects of
sanguinarine following cerebral ischemia in rats. Exp Ther Med.
13:263–268. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kalogris C, Garulli C, Pietrella L,
Gambini V, Pucciarelli S, Lucci C, Tilio M, Zabaleta ME, Bartolacci
C, Andreani C, et al: Sanguinarine suppresses basal-like breast
cancer growth through dihydrofolate reductase inhibition. Biochem
Pharmacol. 90:226–234. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kuttikrishnan S, Siveen KS, Prabhu KS,
Khan AQ, Akhtar S, Mateo JM, Merhi M, Taha R, Omri HE, Mraiche F,
et al: Sanguinarine suppresses growth and induces apoptosis in
childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 6:1–13.
2018.
|
|
16
|
Gong X, Chen Z, Han Q, Chen C, Jing L, Liu
Y, Zhao L, Yao X and Sun X: Sanguinarine triggers intrinsic
apoptosis to suppress colorectal cancer growth through
disassociation between STRAP and MELK. BMC Cancer. 18:5782018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vogt A, Tamewitz A, Skoko J, Sikorski RP,
Giuliano KA and Lazo JS: The benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloid,
sanguinarine, is a selective, cell-active inhibitor of
mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1. J Biol Chem.
280:19078–19086. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee TK, Park C, Jeong SJ, Jeong MJ, Kim
GY, Kim WJ and Choi YH: Sanguinarine induces apoptosis of human
oral squamous cell carcinoma KB cells via inactivation of the
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Drug Dev Res. 77:227–240. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang J, Fang Z, Wu J, Yin X, Fang Y, Zhao
F, Zhu S and Li Y: Construction and application of a lung cancer
stem cell model: Antitumor drug screening and molecular mechanism
of the inhibitory effects of sanguinarine. Tumour Biol.
37:13871–13883. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Meng YY, Liu Y, Hu ZF, Zhang Y, Ni J, Ma
ZG, Liao HH, Wu QQ and Tang QZ: Sanguinarine attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and apoptosis by inhibiting
the TLR4/NF-κB pathway in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Curr Med Sci.
38:204–211. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nguyen KC, Willmore WG and Tayabali AF:
Cadmium telluride quantum dots cause oxidative stress leading to
extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2
cells. Toxicology. 306:114–123. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang DS, Li YY, Chen XJ, Li YJ, Liu ZY,
Xie WJ and Sun ZL: BCL2 promotor methylation and miR-15a/16-1
upregulation is associated with sanguinarine-induced apoptotic
death in rat HSC-T6 cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 127:135–144. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He D, Ma X, Chen Y, Cai Y, Ru X, Bruce IC,
Xia Q, Shi G and Jin J: Luteolin inhibits pyrogallol-induced
apoptosis through the extracellular signal-regulated kinase
signaling pathway. FEBS J. 279:1834–1843. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hsu PC, Huang YT, Tsai ML, Wang YJ, Lin JK
and Pan MH: Induction of apoptosis by shikonin through coordinative
modulation of the Bcl-2 family, p27, and p53, release of cytochrome
c, and sequential activation of caspases in human colorectal
carcinoma cells. J Agric Food Chem. 52:6330–6337. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pradelli LA, Bénéteau M and Ricci JE:
Mitochondrial control of caspase-dependent and -independent cell
death. Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:1589–1597. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lakhani SA, Masud A, Kuida K, Porter GA
Jr, Booth CJ, Mehal WZ, Inayat I and Flavell RA: Caspases 3 and 7:
Key mediators of mitochondrial events of apoptosis. Science.
311:847–851. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zorov DB, Juhaszova M and Sollott SJ:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS
release. Physiol Rev. 94:909–950. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fonseca-Silva F, Inacio JD,
Canto-Cavalheiro MM and Almeida-Amaral EE: Reactive oxygen species
production and mitochondrial dysfunction contribute to quercetin
induced death in leishmania amazonensis. PLoS One. 6:e146662011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sui X, Kong N, Ye L, Han W, Zhou J, Zhang
Q, He C and Pan H: p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of
apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents.
Cancer Lett. 344:174–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang SY, Stem MS, Oren G, Shtein R and
Lichter PR: Patient-centered and visual quality outcomes of premium
cataract surgery: A systematic review. Eur J Ophthalmol.
27:387–401. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Awasthi N, Guo S and Wagner BJ: Posterior
capsular opacification: A problem reduced but not yet eradicated.
Arch Ophthalmol. 127:555–562. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Poyton RO, Ball KA and Castello PR:
Mitochondrial generation of free radicals and hypoxic signaling.
Trends Endocrinol Metab. 20:332–340. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ricci JE, Gottlieb RA and Green DR:
Caspase-mediated loss of mitochondrial function and generation of
reactive oxygen species during apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 160:65–75.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Park SY, Kim DY, Kang JK, Park G and Choi
YW: Involvement of activation of the Nrf2/ARE pathway in protection
against 6-OHDA-induced SH-SY5Y cell death by α-iso-cubebenol.
Neurotoxicology. 44:160–168. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schumacker PT: Reactive oxygen species in
cancer cells: Live by the sword, die by the sword. Cancer Cell.
10:175–176. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang B, Xie QY, Quan Y, Pan XM and Liao
DF: Reactive oxygen species induce cell death via Akt signaling in
rat osteoblast-like cell line ROS 17/2.8. Toxicol Ind Health.
31:1236–1242. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zubair H, Khan HY, Sohail A, Azim S, Ullah
MF, Ahmad A, Sarkar FH and Hadi SM: Redox cycling of endogenous
copper by thymoquinone leads to ROS-mediated DNA breakage and
consequent cell death: Putative anticancer mechanism of
antioxidants. Cell Death Dis. 4:e6602013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jeong SY and Seol DW: The role of
mitochondria in apoptosis. BMB Rep. 41:11–22. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kocic G, Tomovic K, Kocic H, Sokolovic D,
Djordjevic B, Stojanovic S, Arsic I and Smelcerovic A:
Antioxidative, membrane protective and antiapoptotic effects of
melatonin, in silico study of physico-chemical profile and
efficiency of nanoliposome delivery compared to betaine. RSC Adv.
7:1271–1281. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhou J and Tang XC: Huperzine A attenuates
apoptosis and mitochondria-dependent caspase-3 in rat cortical
neurons. FEBS Lett. 526:21–25. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yuyama K, Yamamoto H, Nishizaki I, Kato T,
Sora I and Yamamoto T: Caspase-independent cell death by low
concentrations of nitric oxide in PC12 cells: Involvement of
cytochrome C oxidase inhibition and the production of reactive
oxygen species in mitochondria. J Neurosci Res. 73:351–363. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhu JJ, Xu YQ, He JH, Yu HP, Huang CJ, Gao
JM, Dong QX, Xuan YX and Li CQ: Human cardiotoxic drugs delivered
by soaking and microinjection induce cardiovascular toxicity in
zebrafish. J Appl Toxicol. 34:139–148. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chao JI, Su WC and Liu HF: Baicalein
induces cancer cell death and proliferation retardation by the
inhibition of CDC2 kinase and survivin associated with opposite
role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and AKT. Mol Cancer
Ther. 6:3039–3048. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
He XQ, Chen R, Yang P, Li AP, Zhou JW and
Liu QZ: Biphasic effect of arsenite on cell proliferation and
apoptosis is associated with the activation of JNK and ERK1/2 in
human embryo lung fibroblast cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
220:18–24. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|