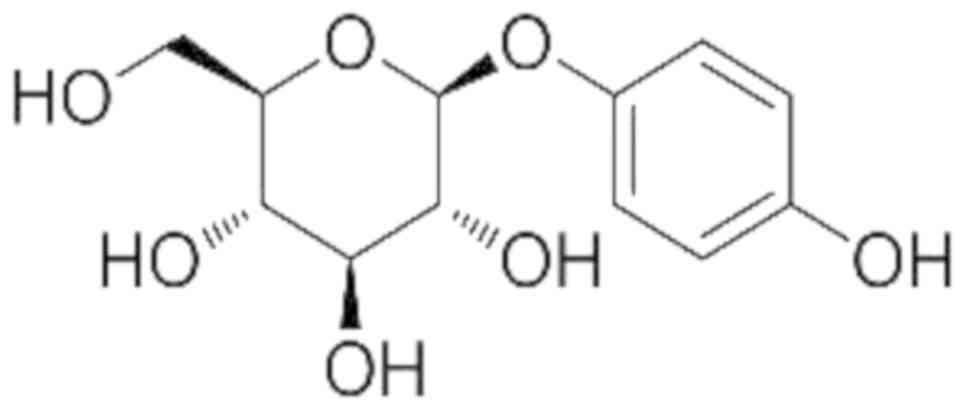
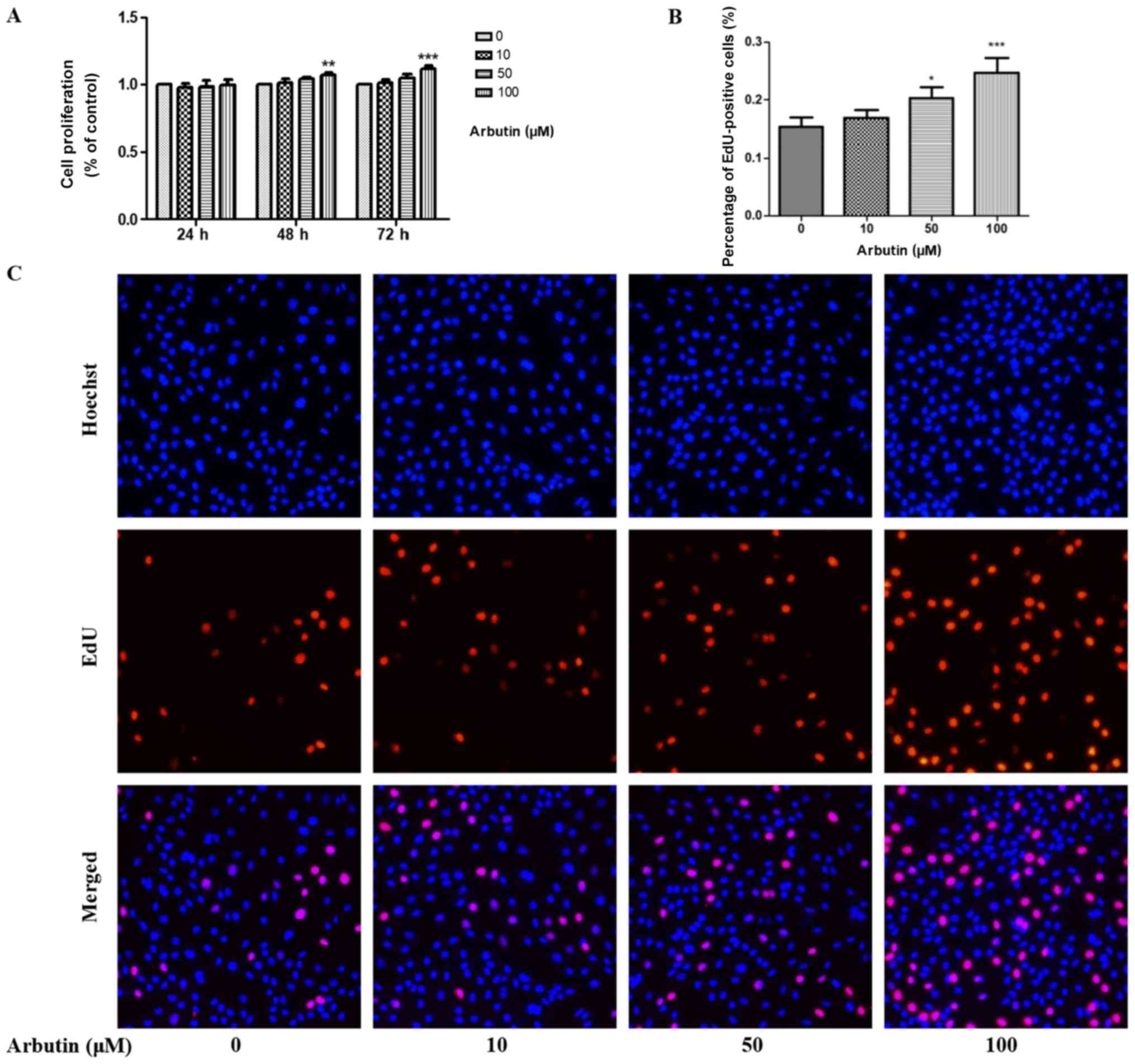
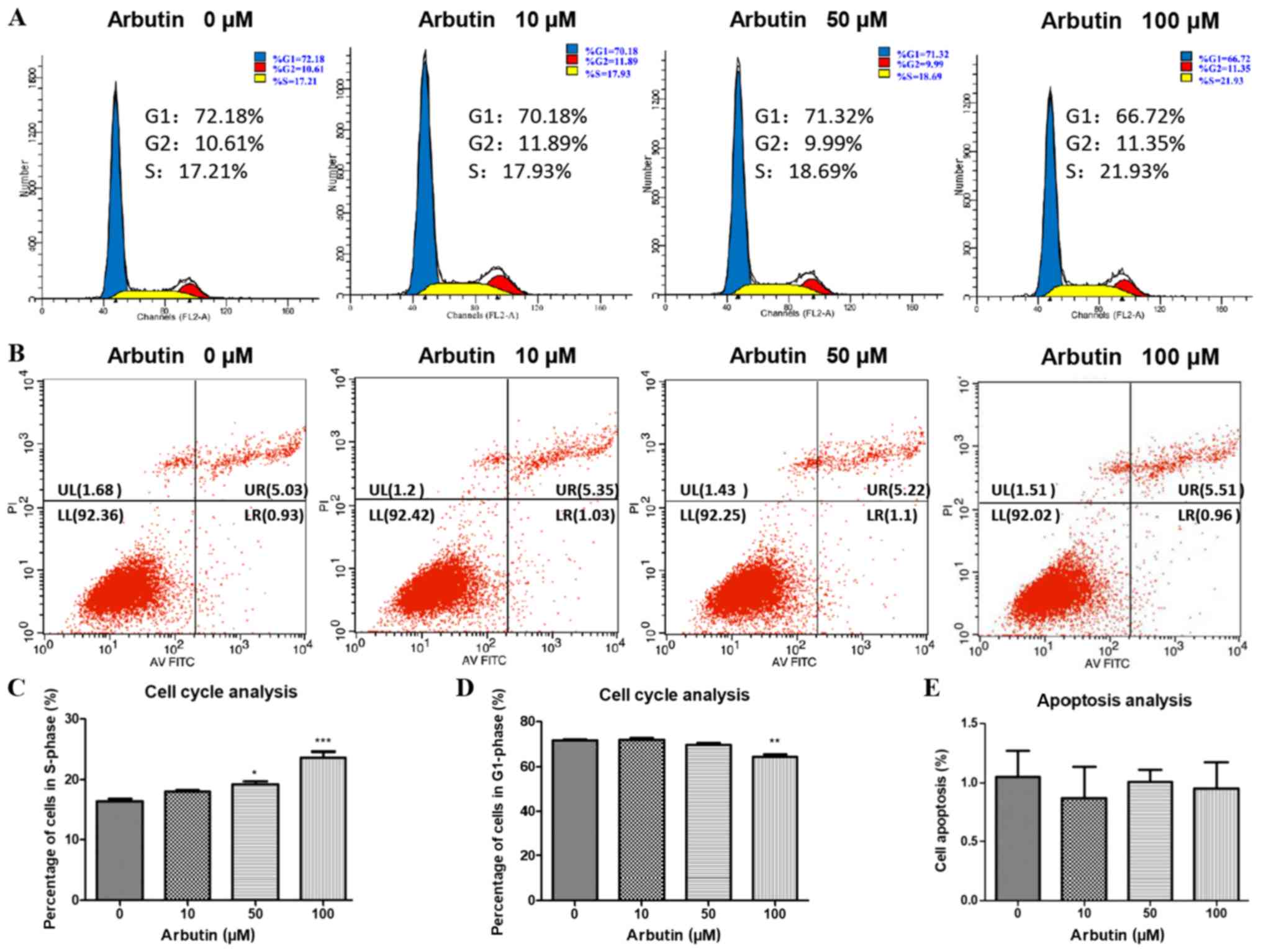
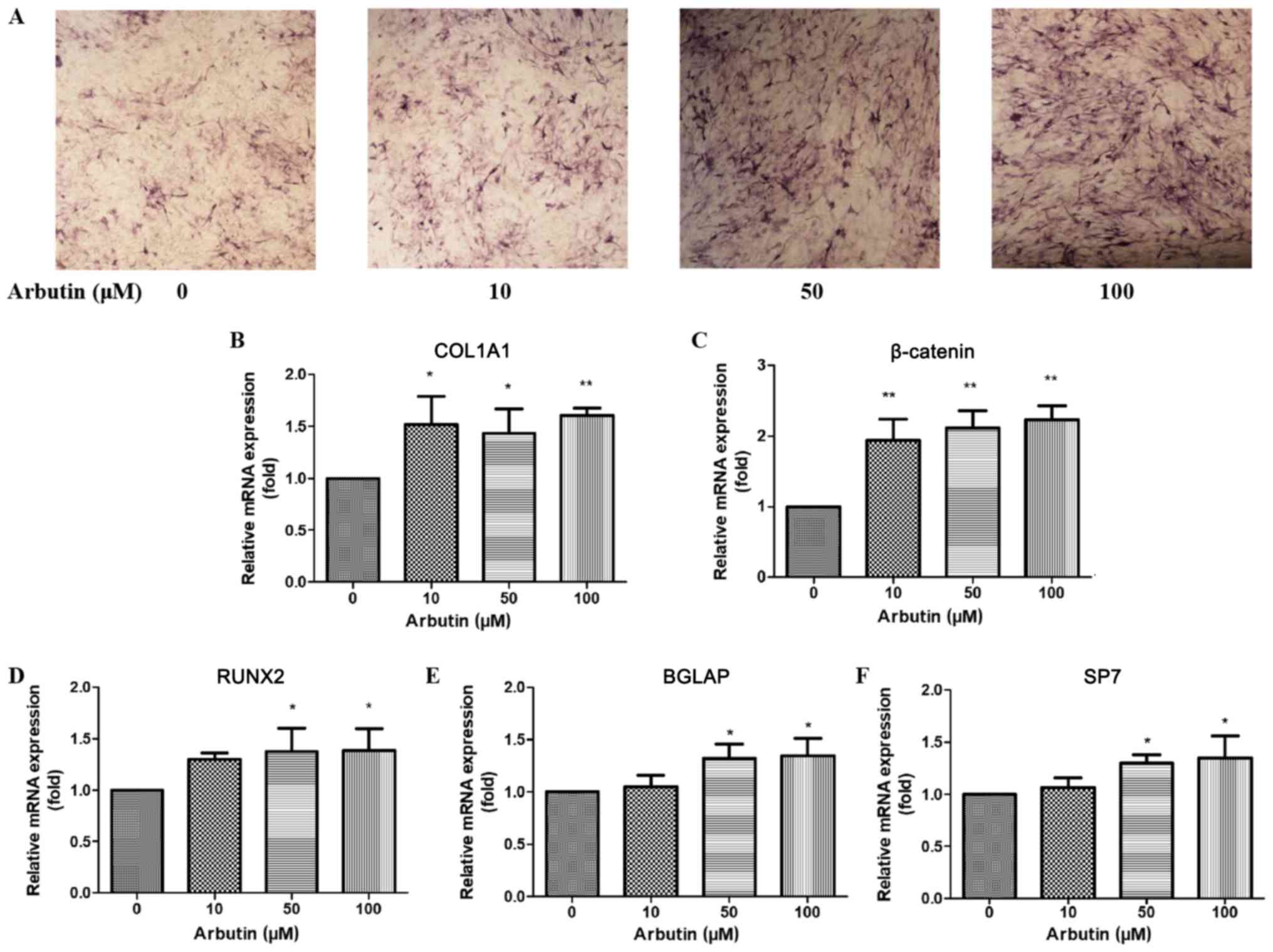
|
1
|
Das S and Crockett JC: Osteoporosis-a
current view of pharmacological prevention and treatment. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 7:435–448. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rachner TD, Khosla S and Hofbauer LC:
Osteoporosis: Now and the future. Lancet. 377:1276–1287. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hernlund E, Svedbom A, Ivergård M,
Compston J, Cooper C, Stenmark J, McCloskey EV, Jönsson B and Kanis
JA: Osteoporosis in the European Union: Medical management,
epidemiology and economic burden. A report prepared in
collaboration with the international osteoporosis foundation (IOF)
and the European federation of pharmaceutical industry associations
(EFPIA). Arch Osteoporos. 8:1362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cauley JA: Public health impact of
osteoporosis. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 68:1243–1251. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Manolagas SC and Jilka RL: Bone marrow,
cytokines, and bone remodeling. Emerging insights into the
pathophysiology of osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 332:305–311. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Baron R and Hesse E: Update on bone
anabolics in osteoporosis treatment: Rationale, current status, and
perspectives. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:311–325. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tang DZ, Hou W, Zhou Q, Zhang M, Holz J,
Sheu TJ, Li TF, Cheng SD, Shi Q, Harris SE, et al: Osthole
stimulates osteoblast differentiation and bone formation by
activation of beta-catenin-BMP signaling. J Bone Miner Res.
25:1234–1245. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Canalis E: Update in new anabolic
therapies for osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 95:1496–1504.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lamien-Meda A, Lukas B, Schmiderer C,
Franz C and Novak J: Validation of a quantitative assay of arbutin
using gas chromatography in Origanum majorana and
Arctostaphylos uva-ursi extracts. Phytochem Anal.
20:416–420. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lim YJ, Lee EH, Kang TH, Ha SK, Oh MS, Kim
SM, Yoon TJ, Kang C, Park JH and Kim SY: Inhibitory effects of
arbutin on melanin biosynthesis of alpha-melanocyte stimulating
hormone-induced hyperpigmentation in cultured brownish guinea pig
skin tissues. Arch Pharm Res. 32:367–373. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Maeda K and Fukuda M: Arbutin: Mechanism
of its depigmenting action in human melanocyte culture. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther. 276:765–769. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu LH, Li P, Zhao QL, Piao JL, Jiao YF,
Kadowaki M and Kondo T: Arbutin, an intracellular hydroxyl radical
scavenger, protects radiation-induced apoptosis in human lymphoma
U937 cells. Apoptosis. 19:1654–1663. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Omori A, Yoshimura Y, Deyama Y and Suzuki
K: Rosmarinic acid and arbutin suppress osteoclast differentiation
by inhibiting superoxide and NFATc1 downregulation in RAW 264.7
cells. Biomed Rep. 3:483–490. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Baron R and Kneissel M: WNT signaling in
bone homeostasis and disease: From human mutations to treatments.
Nat Med. 19:179–192. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Baron R and Rawadi G: Targeting the
Wnt/beta-catenin pathway to regulate bone formation in the adult
skeleton. Endocrinology. 148:2635–2643. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hoeppner LH, Secreto FJ and Westendorf JJ:
Wnt signaling as a therapeutic target for bone diseases. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 13:485–496. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Williams BO and Insogna KL: Where Wnts
went: The exploding field of Lrp5 and Lrp6 signaling in bone. J
Bone Miner Res. 24:171–178. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lin X, Xiong D, Peng YQ, Sheng ZF, Wu XY,
Wu XP, Wu F, Yuan LQ and Liao EY: Epidemiology and management of
osteoporosis in the People's Republic of China: Current
perspectives. Clin Interv Aging. 10:1017–1033. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Manolagas SC: Birth and death of bone
cells: Basic regulatory mechanisms and implications for the
pathogenesis and treatment of osteoporosis. Endocr Rev. 21:115–137.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu S, Fang T, Yang L, Chen Z, Mu S and Fu
Q: Gastrodin protects MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts from
dexamethasone-induced cellular dysfunction and promotes bone
formation via induction of the NRF2 signaling pathway. Int J Mol
Med. 41:2059–2069. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yun HM, Park KR, Quang TH, Oh H, Hong JT,
Kim YC and Kim EC: 2,4,5-Trimethoxyldalbergiquinol promotes
osteoblastic differentiation and mineralization via the BMP and
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cell Death Dis. 6:e18192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cosman F, Nieves JW and Dempster DW:
Treatment sequence matters: Anabolic and antiresorptive therapy for
osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res. 32:198–202. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Uihlein AV and Leder BZ: Anabolic
therapies for osteoporosis. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am.
41:507–525. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakamura T, Sugimoto T, Nakano T,
Kishimoto H, Ito M, Fukunaga M, Hagino H, Sone T, Yoshikawa H,
Nishizawa Y, et al: Randomized Teriparatide [human parathyroid
hormone (PTH) 1–34] Once-Weekly Efficacy Research (TOWER) trial for
examining the reduction in new vertebral fractures in subjects with
primary osteoporosis and high fracture risk. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 97:3097–3106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jurica K, Brčić Karačonji I, Mikolić A,
Milojković-Opsenica D, Benković V and Kopjar N: In vitro safety
assessment of the strawberry tree (Arbutus unedo L.) water
leaf extract and arbutin in human peripheral blood lymphocytes.
Cytotechnology. 70:1261–1278. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schindler G, Patzak U, Brinkhaus B, von
Niecieck A, Wittig J, Krähmer N, Glöckl I and Veit M: Urinary
excretion and metabolism of arbutin after oral administration of
Arctostaphylos uvae ursi extract as film-coated tablets and
aqueous solution in healthy humans. J Clin Pharmacol. 42:920–927.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Genovese C, Davinelli S, Mangano K,
Tempera G, Nicolosi D, Corsello S, Vergalito F, Tartaglia E,
Scapagnini G and Di Marco R: Effects of a new combination of plant
extracts plus d-mannose for the management of uncomplicated
recurrent urinary tract infections. J Chemother. 30:107–114. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee HJ and Kim KW: Anti-inflammatory
effects of arbutin in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial
cells. Inflamm Res. 61:817–825. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang L and Wang D, Zhang Y, Li J, Wu Z,
Wang Z and Wang D: Investigation of the pro-apoptotic effects of
arbutin and its acetylated derivative on murine melanoma cells. Int
J Mol Med. 41:1048–1054. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Marie PJ and Kassem M: Osteoblasts in
osteoporosis: Past, emerging, and future anabolic targets. Eur J
Endocrinol. 165:1–10. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Canalis E: Management of endocrine
disease: Novel anabolic treatments for osteoporosis. Eur J
Endocrinol. 178:R33–R44. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Weinreb M, Shinar D and Rodan GA:
Different pattern of alkaline phosphatase, osteopontin, and
osteocalcin expression in developing rat bone visualized by in situ
hybridization. J Bone Miner Res. 5:831–842. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim YJ, Lee MH, Wozney JM, Cho JY and Ryoo
HM: Bone morphogenetic protein-2-induced alkaline phosphatase
expression is stimulated by Dlx5 and repressed by Msx2. J Biol
Chem. 279:50773–50780. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
An J, Yang H, Zhang Q, Liu C, Zhao J,
Zhang L and Chen B: Natural products for treatment of osteoporosis:
The effects and mechanisms on promoting osteoblast-mediated bone
formation. Life Sci. 147:46–58. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kobayashi T and Kronenberg H: Minireview:
Transcriptional regulation in development of bone. Endocrinology.
146:1012–1017. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Alford AI, Golicz AZ, Cathey AL and Reddy
AB: Thrombospondin-2 facilitates assembly of a type-I collagen-rich
matrix in marrow stromal cells undergoing osteoblastic
differentiation. Connect Tissue Res. 54:275–282. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Neve A, Corrado A and Cantatore FP:
Osteocalcin: Skeletal and extra-skeletal effects. J Cell Physiol.
228:1149–1153. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang Y, Li YP, Paulson C, Shao JZ, Zhang
X, Wu M and Chen W: Wnt and the Wnt signaling pathway in bone
development and disease. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 19:379–407.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kramer I, Halleux C, Keller H, Pegurri M,
Gooi JH, Weber PB, Feng JQ, Bonewald LF and Kneissel M: Osteocyte
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is required for normal bone homeostasis.
Mol Cell Biol. 30:3071–3085. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ducy P, Schinke T and Karsenty G: The
osteoblast: A sophisticated fibroblast under central surveillance.
Science. 289:1501–1504. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Franceschi RT and Xiao G: Regulation of
the osteoblast-specific transcription factor, RUNX2: Responsiveness
to multiple signal transduction pathways. J Cell Biochem.
88:446–454. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gaur T, Lengner CJ, Hovhannisyan H, Bhat
RA, Bodine PV, Komm BS, Javed A, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Stein GS
and Lian JB: Canonical WNT signaling promotes osteogenesis by
directly stimulating Runx2 gene expression. J Biol Chem.
280:33132–33140. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kawano Y and Kypta R: Secreted antagonists
of the Wnt signalling pathway. J Cell Sci. 116:2627–2634. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Daoussis D and Andonopoulos AP: The
emerging role of Dickkopf-1 in bone biology: Is it the main switch
controlling bone and joint remodeling? Semin Arthritis Rheum.
41:170–177. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Taurin S, Sandbo N, Qin Y, Browning D and
Dulin NO: Phosphorylation of beta-catenin by cyclic AMP-dependent
protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 281:9971–9976. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|