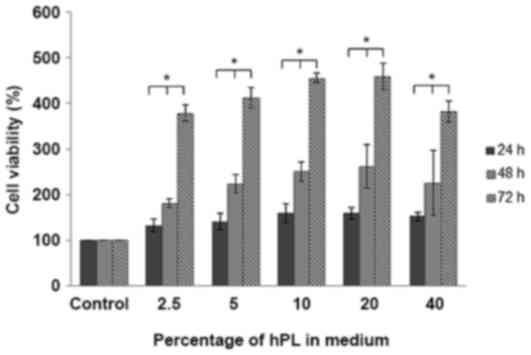
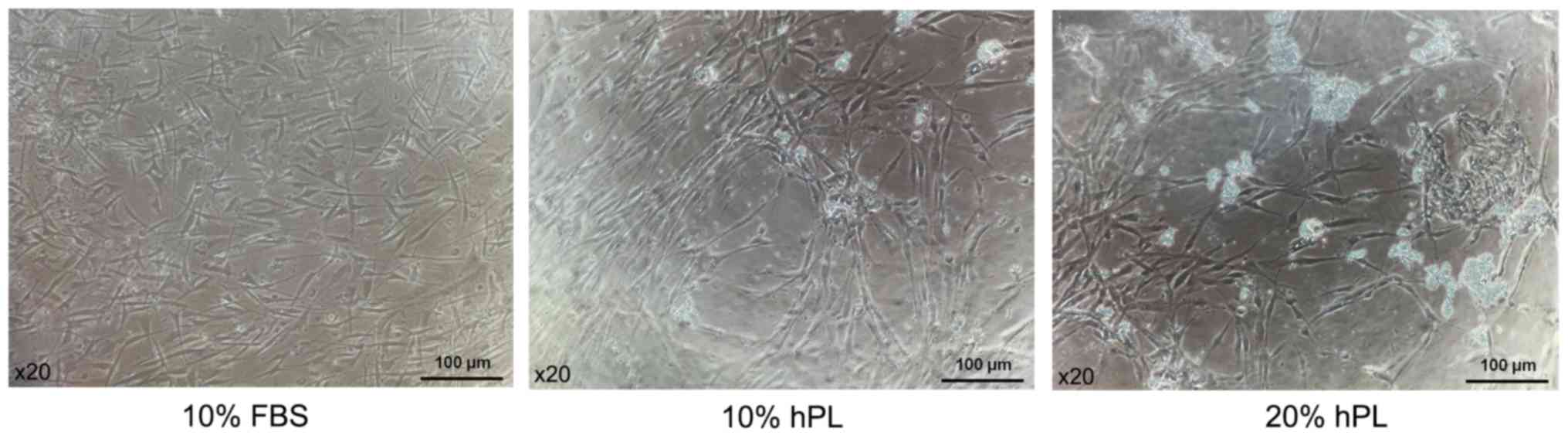
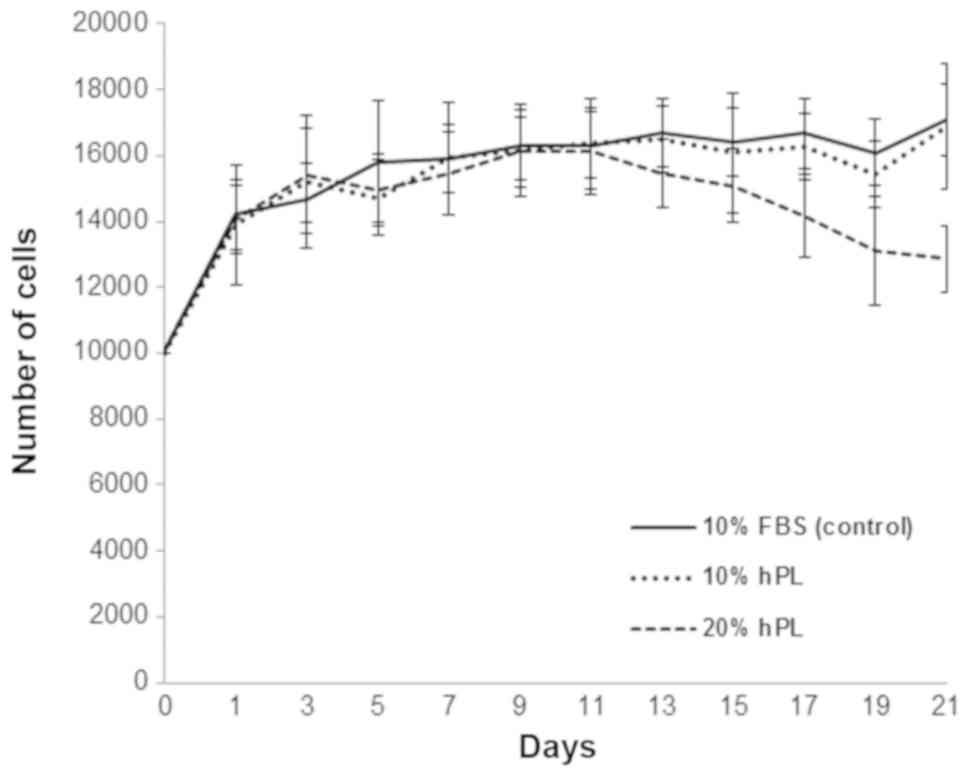
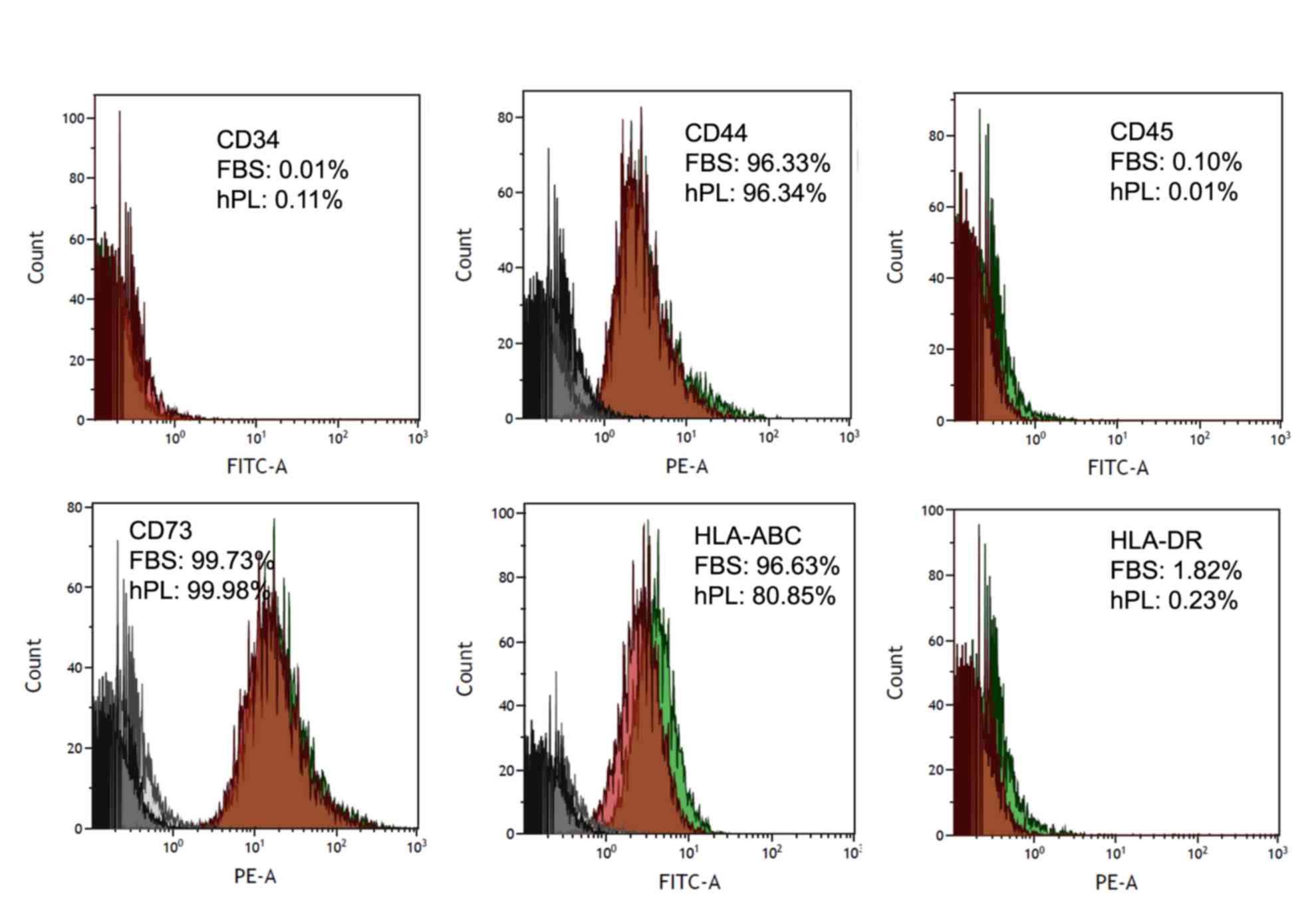
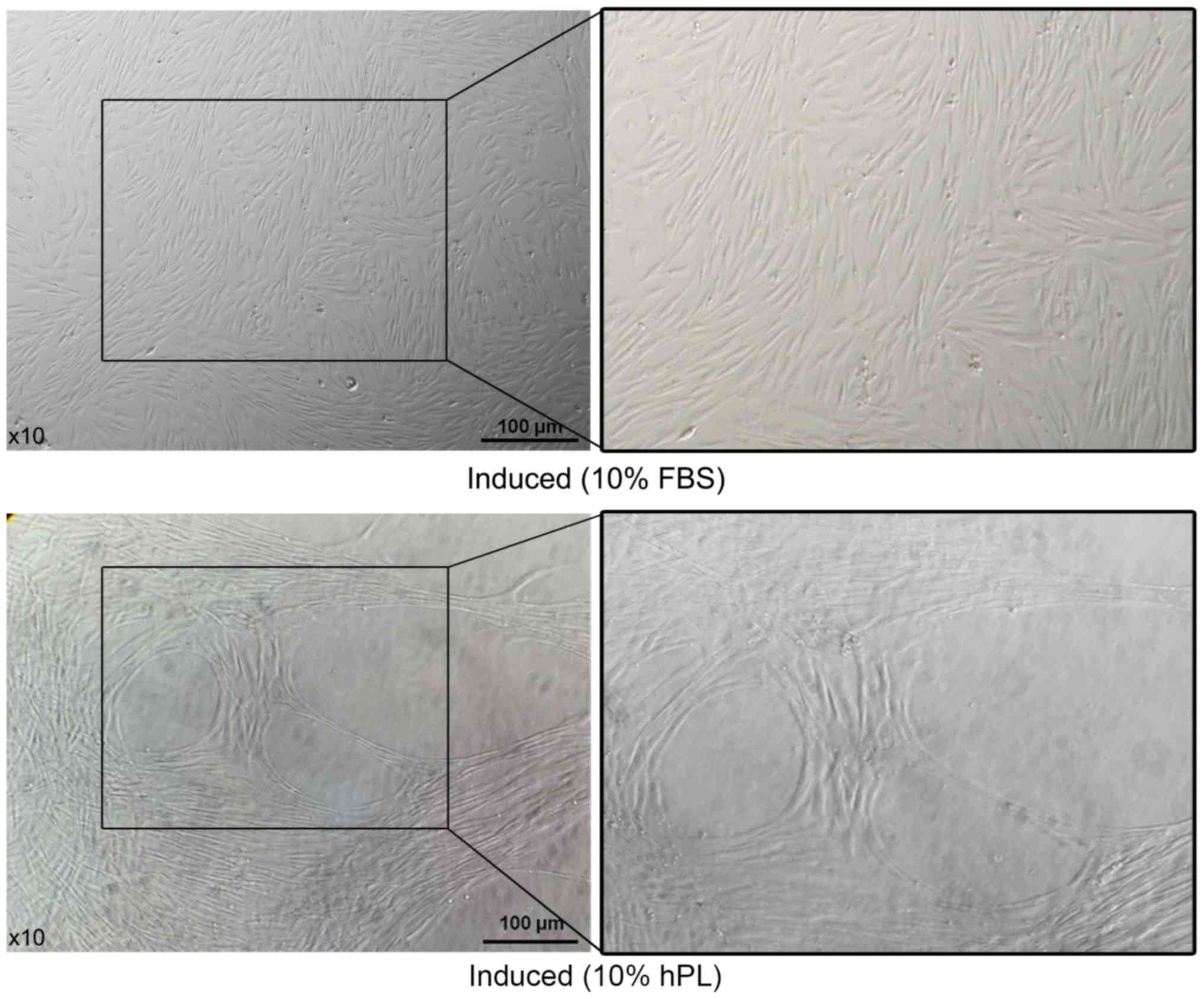
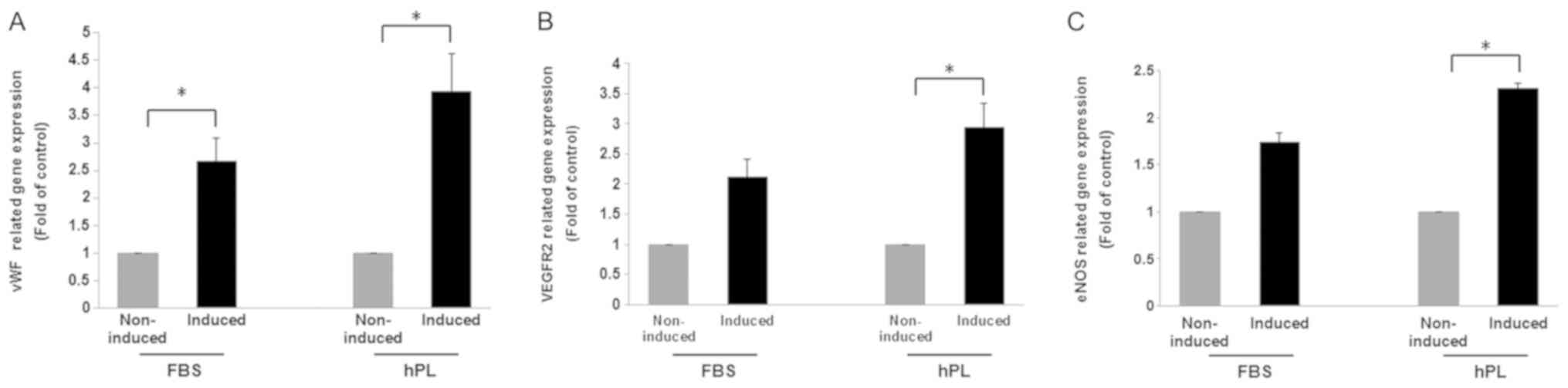
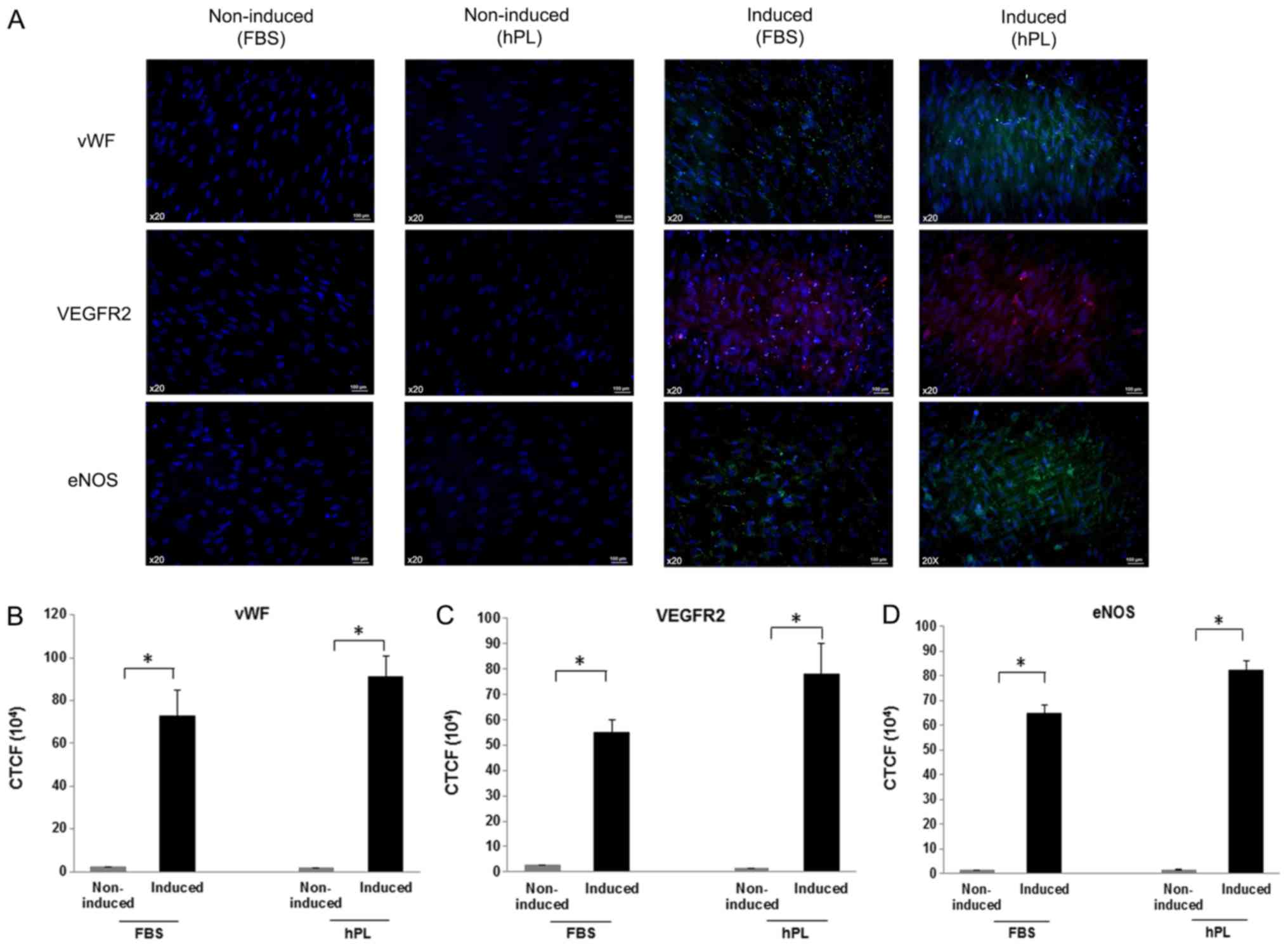
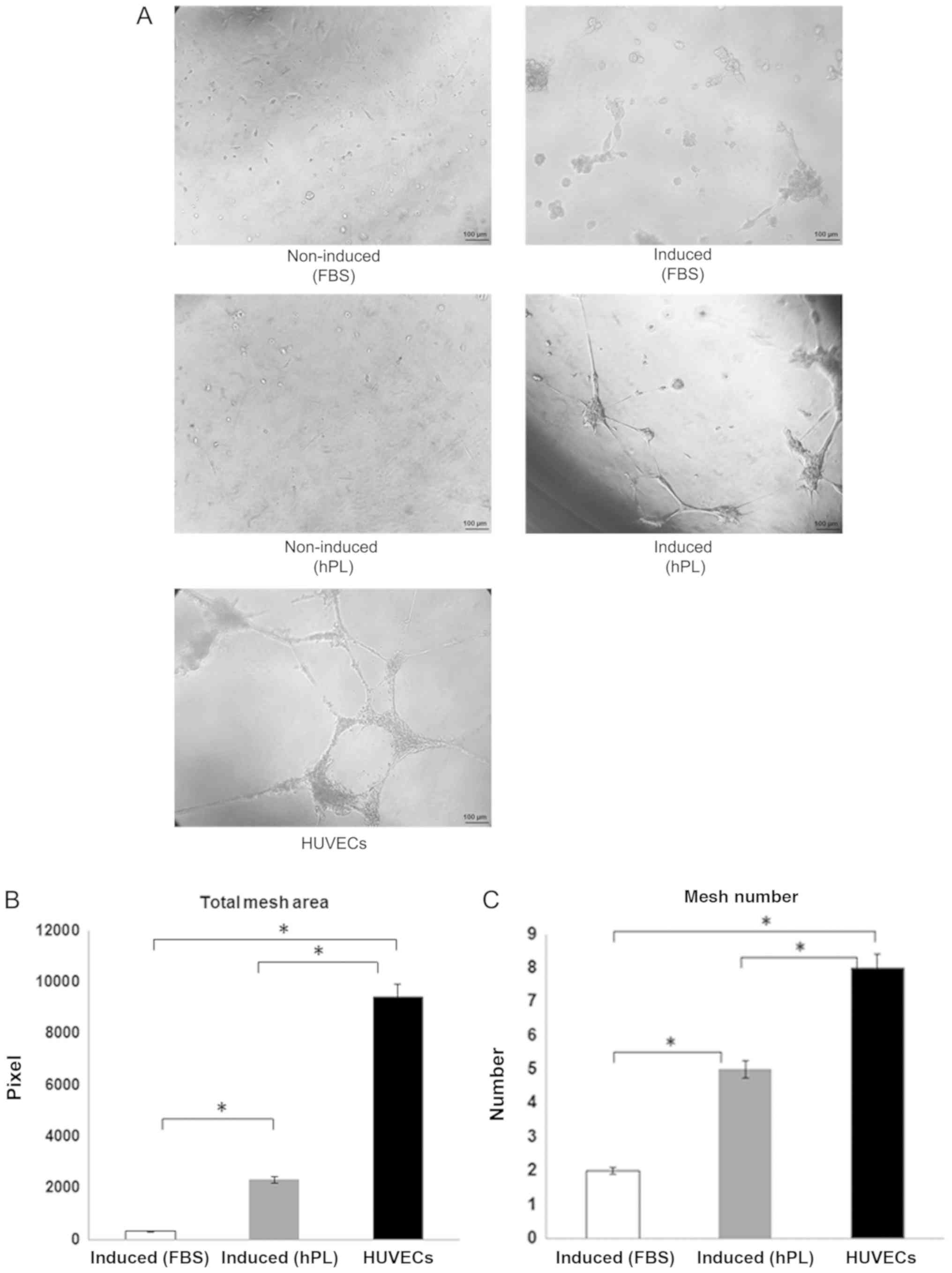
|
1
|
Cananzi M, Atala A and De Coppi P: Stem
cells derived from amniotic fluid: New potentials in regenerative
medicine. Reprod Biomed Online. 18 (Suppl 1):S17–S27. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Antonucci I, Stuppia L, Kaneko Y, Yu S,
Tajiri N, Bae EC, Chheda SH, Weinbren NL and Borlongan CV: Amniotic
fluid as a rich source of mesenchymal stromal cells for
transplantation therapy. Cell Transplant. 20:789–795. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhou J, Wang D, Liang T, Guo Q and Zhang
G: Amniotic fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Characteristics
and therapeutic applications. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 290:223–231.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wei X, Yang X, Han ZP, Qu FE, Shao L and
Shi YF: Mesenchymal stem cells: A new trend for cell therapy. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 34:747–754. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu JW, Dunoyer-Geindre S, Serre-Beinier
V, Mai G, Lambert JF, Fish RJ, Pernod G, Buehler L, Bounameaux H
and Kruithof EK: Characterization of endothelial-like cells derived
from human mesenchymal stem cells. J Thromb Haemost. 5:826–834.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lidong G, Shaoqing L, Yunfang W, Huimin Y,
Daqing L, Lijuan H, Cixian B, Fang Y and Xue N: In vitro
differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
into endothelial-like cells. Chin Sci Bull. 51:1863–1868. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Witzeneder K, Lindenmair A, Gabriela C,
Höllera K, Theißa D, Redlb H and Hennerbichler S: Human-derived
alternatives to fetal bovine serum in cell culture. Transfus Med
Hemother. 40:417–423. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rauch C, Feifel E, Amann EM, Spötl HP,
Schennach H, Pfaller W and Gstraunthaler G: Alternatives to the use
of fetal bovine serum: Human platelet lysates as a serum substitute
in cell culture media. ALTEX. 28:305–316. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hemeda H, Giebel B and Wagner W:
Evaluation of human platelet lysate versus fetal bovine serum for
culture of mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 16:170–180.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Naaijkens B, Niessen HW, Prins HJ, Krijnen
PA, Kokhuis TJ, de Jong N, Van Hinsbergh VW, Kamp O, Helder MN,
Musters RJ, et al: Human platelet lysate as a fetal bovine serum
substitute improves human adipose-derived stromal cell culture for
future cardiac repair applications. Cell Tissue Res. 348:119–130.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Antoninus AA, Widowati W, Wijaya L,
Agustina D, Puradisastra S, Sumitro SB, Widodo MA and Bachtiar I:
Human platelet lysate enhances the proliferation of Wharton's
jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biomarkers Genomic Med.
7:87–97. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bieback K, Hecker A, Kocaömer A, Lannert
H, Schallmoser K, Strunk D and Klüter H: Human alternatives to
fetal bovine serum for the expansion of mesenchymal stromal cells
from bone marrow. Stem Cells. 27:2331–2341. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Doucet C, Ernou I, Zhang Y, Llense JR,
Begot L, Holy X and Lataillade JJ: Platelet lysates promote
mesenchymal stem cell expansion: A safety substitute for animal
serum in cell-based therapy applications. J Cell Physiol.
205:228–236. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Avanzini MA, Bernardo ME, Cometa AM,
Perotti C, Zaffaroni N, Novara F, Visai L, Moretta A, Del Fante C,
Villa R, et al: Generation of mesenchymal stromal cells in the
presence of platelet lysate: A phenotypic and functional comparison
of umbilical cord blood- and bone marrow-derived progenitors.
Haematologica. 94:1649–1660. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Homayouni Moghadam F, Tayebi T, Moradi A,
Nadri H, Barzegar K and Eslami G: Treatment with platelet lysate
induces endothelial differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells under fluid shear stress. EXCLI J. 13:638–649.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Soltis RD, Hasz D, Morris MJ and Wilson
ID: The effect of heat inactivation of serum on aggregation of
immunoglobulins. Immunology. 36:37–45. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tancharoen W, Aungsuchawan S, Pothacharoen
P, Markmee R, Narakornsak S, Kieodee J, Boonma N and Tasuya W:
Differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from human amniotic fluid
to vascular endothelial cells. Acta Histochem. 119:113–121. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fei X, Jiang S, Zhang S, Li Y, Ge J, He B,
Goldstein S and Ruiz G: Isolation, culture, and identification of
amniotic fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 67:689–694. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Naskou MC, Sumner SM, Chocallo A,
Kemelmakher H, Thoresen M, Copland I, Galipeau J and Peroni JF:
Platelet lysate as a novel serum-free media supplement for the
culture of equine bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 9:752018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schallmoser K, Bartmann C, Rohde E,
Reinisch A, Kashofe K, Stadelmeyer E, Drexler C, Lanzer G, Linkesch
W and Strunk D: Human platelet lysate can replace fetal bovine
serum for clinical-scale expansion of functional mesenchymal
stromal cells. Transfusion. 47:1436–1446. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fekete N, Gadelorge M, Fürst D, Maurer C,
Dausend J, Fleury-Cappellesso S, Mailänder V, Lotfi R, Ignatius A,
Sensebé L, et al: Platelet lysate from whole blood-derived pooled
platelet concentrates and apheresis-derived platelet concentrates
for the isolation and expansion of human bone marrow mesenchymal
stromal cells: Production process, content and identifi cation of
active components. Cytotherapy. 14:540–554. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Burnouf T, Strunk D, Koh MB and
Schallmoser K: Human platelet lysate: Replacing fetal bovine serum
as a gold standard for human cell propagation? Biomaterials.
76:371–387. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lykov AP, Bondarenko NA, Surovtseva MA,
Kim II, Poveshchenko OV, Pokushalov EA and Konenkov VI: Comparative
effects of platelet-rich plasma, platelet lysate, and fetal calf
serum on mesenchymal stem cells. Bull Exp Biol Med. 163:757–760.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lohmann M, Walenda G, Hemeda H, Joussen S,
Drescher W, Jockenhoevel S, Hutschenreuter G, Zenke M and Wagner W:
Donor age of human platelet lysate affects proliferation and
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 7:e378392012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,
Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A,
Prockop DJ and Horwitz E: Minimal criteria for defining multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells. The international society for cellular
therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 8:315–317. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Narakornsak S, Poovachiranon N,
Peerapapong L, Pothacharoen P and Aungsuchawan S: Mesenchymal stem
cells differentiated into chondrocyte-Like cells. Acta Histochem.
118:418–429. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Laowanitwattana T, Aungsuchawan S,
Narakornsak S, Markmee R, Tancharoen W, Keawdee J, Boonma N, Tasuya
W, Peerapapong L, Pangjaidee N and Pothacharoen P: Osteoblastic
differentiation potential of human amniotic fluid-derived
mesenchymal stem cells in different culture conditions. Acta
Histochem. 120:701–712. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ben Azouna N, Jenhani F, Regaya Z,
Berraeis L, Ben Othman T, Ducrocq E and Domenech J: Phenotypical
and functional characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells from bone
marrow: Comparison of culture using different media supplemented
with human platelet lysate or fetal bovine serum. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 3:62012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim H, Prasain N, Vemula S, Ferkowicz MJ,
Yoshimoto M, Voytik-Harbin SL and Yoder MC: Human platelet lysate
improves human cord blood derived ECFC survival and vasculogenesis
in three dimensional (3D) collagen matrices. Microvasc Res.
101:72–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jazayeri M, Allameh A, Soleimani M,
Jazayeri SH, Kaviani S and Kazemnejad S: Capillary network
formation by endothelial cells differentiated from human bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Iran J Biotechnol. 6:29–35.
2008.
|
|
32
|
Gang EJ, Jeong JA, Han S, Yan Q, Jeon CJ
and Kim H: In vitro endothelial potential of human UC blood-derived
mesenchymal stem cells. Cytotherapy. 8:215–227. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Quirici N, Soligo D, Caneva L, Servida F,
Bossolasco P and Deliliers GL: Differentiation and expansion of
endothelial cells from human bone marrow CD133(+) cells. Br J
Haematol. 115:186–194. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fortunato TM, Beltrami C, Emanueli C, De
Bank PA and Pula G: Platelet lysate gel and endothelial progenitors
stimulate microvascular network formation in vitro: Tissue
engineering implications. Sci Rep. 6:253262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hofbauer P, Riedl S, Witzeneder K, Hildner
F, Wolbank S, Groeger M, Gabriel C, Redl H and Holnthoner W: Human
platelet lysate is a feasible candidate to replace fetal calf serum
as medium supplement for blood vascular and lymphatic endothelial
cells. Cytotherapy. 16:1238–1244. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Barsotti MC, Losi P, Briganti E,
Sanguinetti E, Magera A, Al Kayal TA, Feriani R, Di Stefano R and
Soldani G: Effect of platelet lysate on human cells involved in
different phases of wound healing. PLoS One. 8:e847532013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|