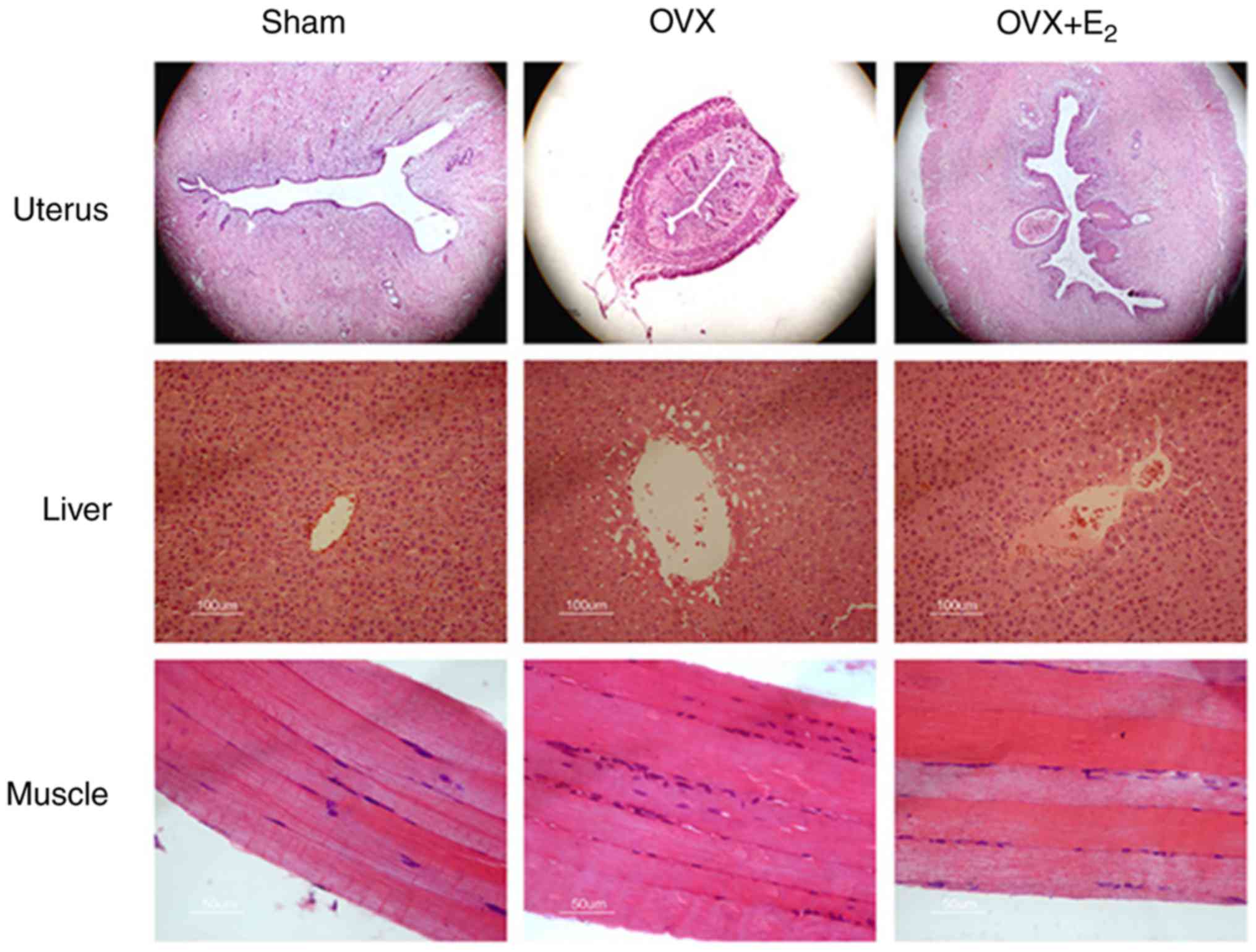
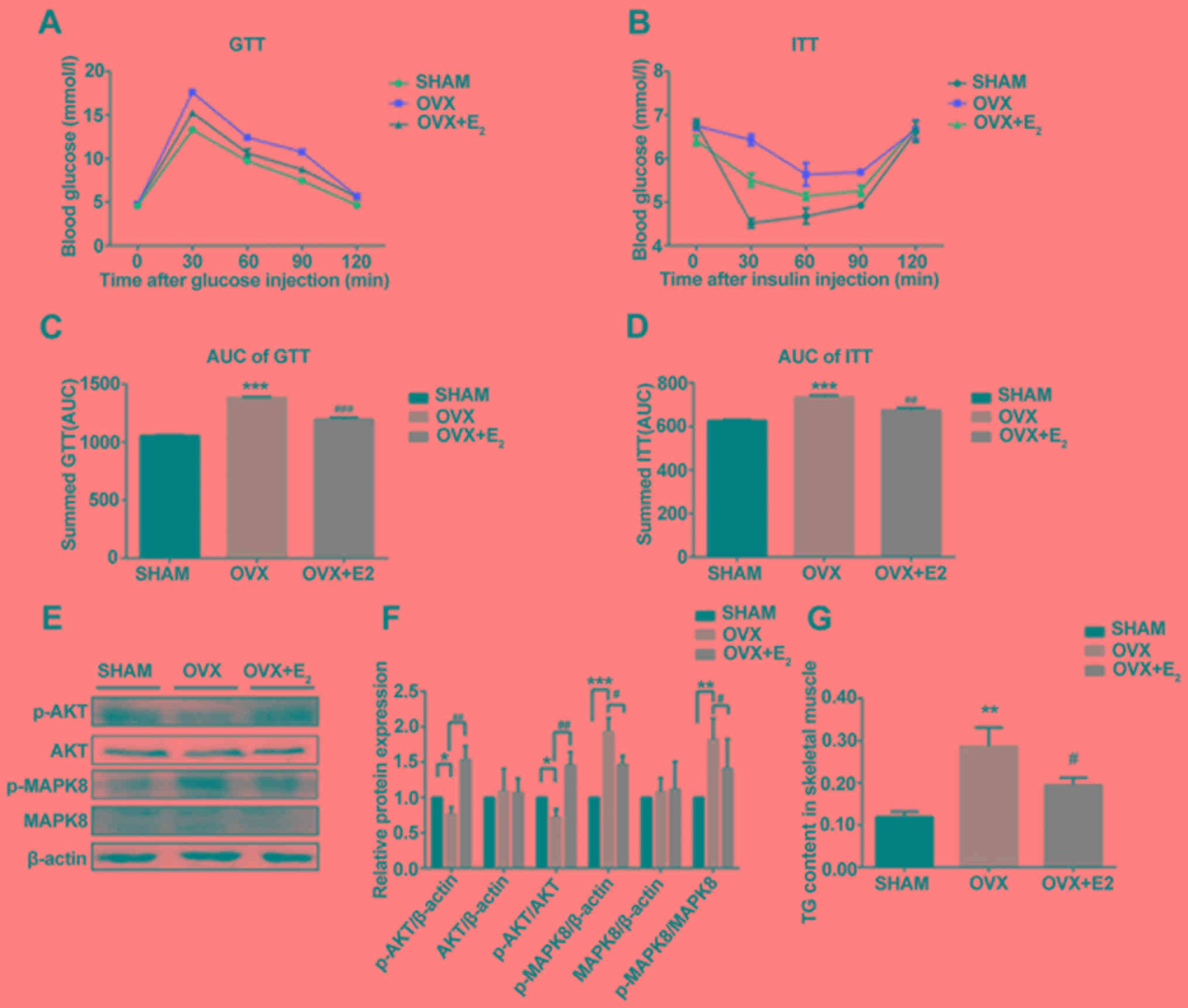
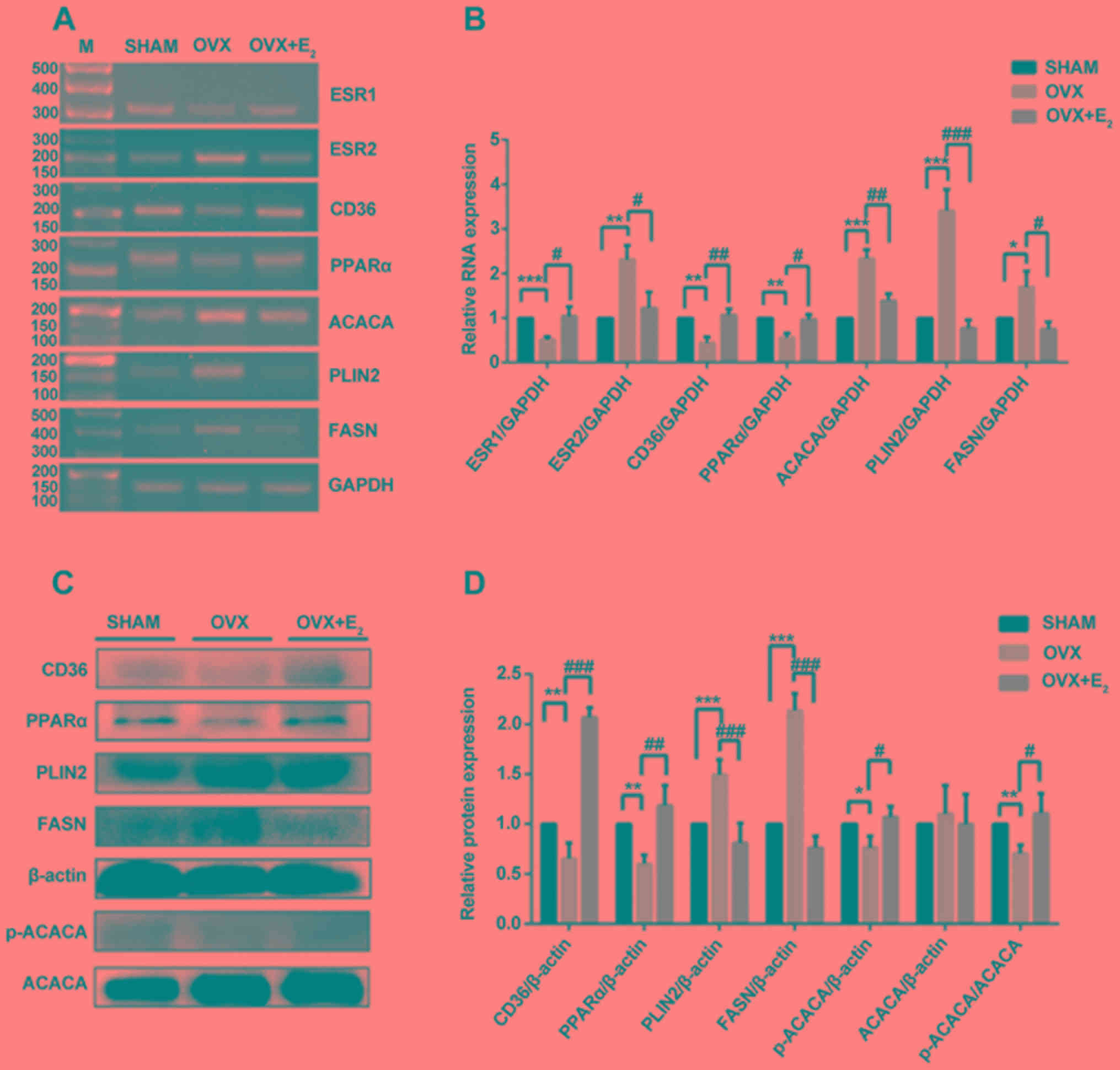
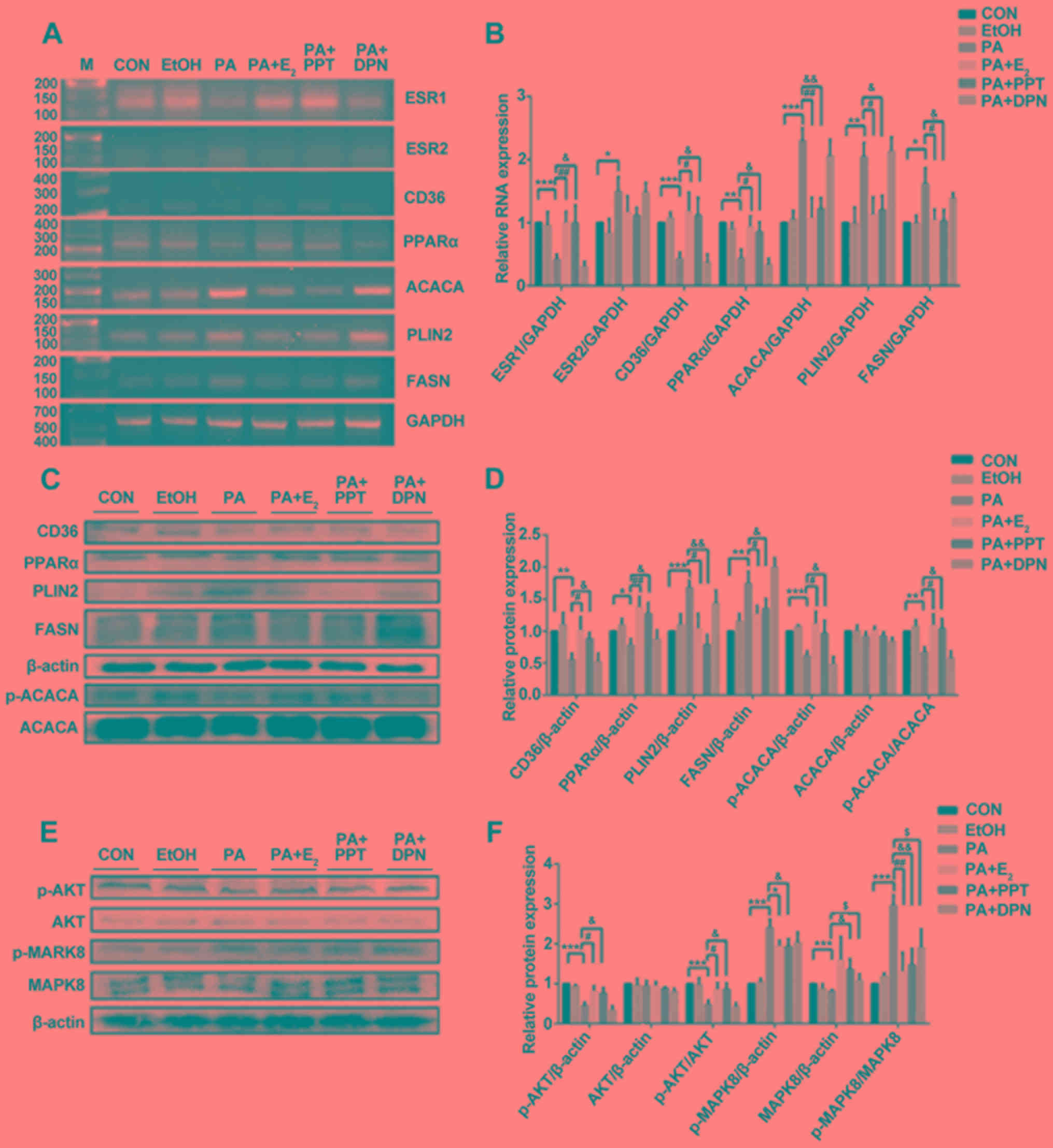
|
1
|
Endo K, Weng H, Naito Y, Sasaoka T,
Takahashi A, Fukushima Y and Iwai N: Classification of various
muscular tissues using miRNA profiling. Biomed Res. 34:289–299.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pierdominici M, Ortona E, Franconi F,
Caprio M, Straface E and Malorni W: Gender specific aspects of cell
death in the cardiovascular system. Curr Pharm Des. 17:1046–1055.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Welle S, Tawil R and Thornton CA:
Sex-related differences in gene expression in human skeletal
muscle. PLoS One. 3:e13852008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dewailly D, Robin G, Peigne M, Decanter C,
Pigny P and Catteau-Jonard S: Interactions between androgens, FSH,
anti-Müllerian hormone and estradiol during folliculogenesis in the
human normal and polycystic ovary. Hum Reprod Update. 22:709–724.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Galluzzo P, Rastelli C, Bulzomi P,
Acconcia F, Pallottini V and Marino M: 17beta-Estradiol regulates
the first steps of skeletal muscle cell differentiation via
ER-alpha-mediated signals. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
297:C1249–C1262. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sipilä S, Finni T and Kovanen V: Estrogen
influences on neuromuscular function in postmenopausal women.
Calcif Tissue Int. 96:222–233. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hevener AL, Clegg DJ and Mauvais-Jarvis F:
Impaired estrogen receptor action in the pathogenesis of the
metabolic syndrome. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 418:306–321. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tena-Sempere M: Neuroendocrinology in
2016: Neuroendocrine control of metabolism and reproduction. Nat
Rev Endocrinol. 13:67–68. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Martínez de Morentin PB, Lage R,
González-García I, Ruíz-Pino F, Martins L, Fernández-Mallo D,
Gallego R, Fernø J, Señarís R, Saha AK, et al: Pregnancy induces
resistance to the anorectic effect of hypothalamic malonyl-CoA and
the thermogenic effect of hypothalamic AMPK inhibition in female
rats. Endocrinology. 156:947–960. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mauvais-Jarvis F, Clegg DJ and Hevener AL:
The role of estrogens in control of energy balance and glucose
homeostasis. Endocr Rev. 34:309–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moran AL, Warren GL and Lowe DA: Removal
of ovarian hormones from mature mice detrimentally affects muscle
contractile function and myosin structural distribution. J Appl
Physiol (1985). 100:548–559. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Klinge CM: Estrogens regulate life and
death in mitochondria. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 49:307–324. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
López M and Tena-Sempere M: Estrogens and
the control of energy homeostasis: A brain perspective. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 26:411–421. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hamilton DJ, Minze LJ, Kumar T, Cao TN,
Lyon CJ, Geiger PC, Hsueh WA and Gupte AA: Estrogen receptor alpha
activation enhances mitochondrial function and systemic metabolism
in high-fat-fed ovariectomized mice. Physiol Rep. 4:e129132016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van Hall G: The physiological regulation
of skeletal muscle fatty acid supply and oxidation during
moderate-intensity exercise. Sports Med. 45 (Suppl 1):S23–S32.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kewalramani G, Bilan PJ and Klip A: Muscle
insulin resistance: Assault by lipids, cytokines and local
macrophages. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 13:382–390. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tepavcevic S, Koricanac G, Zakula Z,
Milosavljevic T, Stojiljkovic M and Isenovic ER: Interaction
between insulin and estradiol-17β in regulation of cardiac glucose
and free fatty acid transporters. Horm Metab Res. 43:524–530. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Stavinoha MA, RaySpellicy JW, Essop MF,
Graveleau C, Abel ED, Hart-Sailors ML, Mersmann HJ, Bray MS and
Young ME: Evidence for mitochondrial thioesterase 1 as a peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-alpha-regulated gene in cardiac and
skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 287:E888–E895.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mosti MP, Ericsson M, Erben RG, Schüler C,
Syversen U and Stunes AK: The PPARα agonist fenofibrate improves
the musculoskeletal effects of exercise in ovariectomized rats.
Endocrinology. 157:3924–3934. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gorres BK, Bomhoff GL, Morris JK and
Geiger PC: In vivo stimulation of oestrogen receptor α increases
insulin-stimulated skeletal muscle glucose uptake. J Physiol.
589:2041–2054. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
van de Heijning BJM, Oosting A, Kegler D
and van der Beek EM: An increased dietary supply of medium-chain
fatty acids during early weaning in rodents prevents excessive fat
accumulation in adulthood. Nutrients. 9:E6312017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Han LD, Xia JF, Liang QL, Wang Y, Wang YM,
Hu P, Li P and Luo GA: Plasma esterified and non-esterified fatty
acids metabolic profiling using gas-chromatography mass
spectrometry and its application in the study of diabetic mellitus
and diabetic nephropathy. Anal Chim Acta. 689:85–91. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tarchalski J, Guzik P and Wysocki H:
Correlation between the extent of coronary atherosclerosis and
lipid profile. Mol Cell Biochem. 246:25–30. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Salpeter SR, Walsh JM, Ormiston TM,
Greyber E, Buckley NS and Salpeter EE: Meta-analysis: Effect of
hormone-replacement therapy on components of the metabolic syndrome
in postmenopausal women. Diabetes Obes Metab. 8:538–554. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Manrique C, Lastra G, Habibi J, Mugerfeld
I, Garro M and Sowers JR: Loss of estrogen receptor signaling leads
to insulin resistance and obesity in young and adult female mice.
Cardiorenal Med. 2:200–210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Marchand GB, Carreau AM, Weisnagel SJ,
Bergeron J, Labrie F, Lemieux S and Tchernof A: Increased body fat
mass explains the positive association between circulating
estradiol and insulin resistance in postmenopausal women. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 314:E448–E456. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Manco M, Mingrone G, Greco AV, Capristo E,
Gniuli D, De Gaetano A and Gasbarrini G: Insulin resistance
directly correlates with increased saturated fatty acids in
skeletal muscle triglycerides. Metabolism. 49:220–224. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Strehlow K, Rotter S, Wassmann S, Adam O,
Grohé C, Laufs K, Böhm M and Nickenig G: Modulation of antioxidant
enzyme expression and function by estrogen. Circ Res. 93:170–177.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang L, Tepaamorndech S, Kirschke CP,
Newman JW, Keyes WR, Pedersen TL and Dumnil J: Aberrant fatty acid
metabolism in skeletal muscle contributes to insulin resistance in
zinc transporter 7 (znt7)-knockout mice. J Biol Chem.
293:7549–7563. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Weigt C, Hertrampf T, Kluxen FM, Flenker
U, Hülsemann F, Fritzemeier KH and Diel P: Molecular effects of ER
alpha- and beta-selective agonists on regulation of energy
homeostasis in obese female Wistar rats. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
377:147–158. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Duval C, Müller M and Kersten S: PPARalpha
and dyslipidemia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1771:961–971. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Minnaard R, Schrauwen P, Schaart G,
Jorgensen JA, Lenaers E, Mensink M and Hesselink MK: Adipocyte
differentiation-related protein and OXPAT in rat human skeletal
muscle: Involvement in lipid accumulation and type 2 diabetes
mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 94:4077–4085. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Velders M, Schleipen B, Fritzemeier KH,
Zierau O and Diel P: Selective estrogen receptor-β activation
stimulates skeletal muscle growth and regeneration. FASEB J.
26:1909–1920. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ribas V, Drew BG, Zhou Z, Phun J, Kalajian
NY, Soleymani T, Daraei P, Widjaja K, Wanagat J, de Aguiar Vallim
TQ, et al: Skeletal muscle action of estrogen receptor α is
critical for the maintenance of mitochondrial function and
metabolic homeostasis in females. Sci Transl Med. 8:334ra542016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ribas V, Nguyen MT, Henstridge DC, Nguyen
AK, Beaven SW, Watt MJ and Hevener AL: Impaired oxidative
metabolism and inflammation are associated with insulin resistance
in ERalpha-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
298:E304–E319. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Glatz JFC and Luiken JJFP: Dynamic role of
the transmembrane glycoprotein CD36 (SR-B2) in cellular fatty acid
uptake and utilization. J Lipid Res. 59:1084–1093. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|