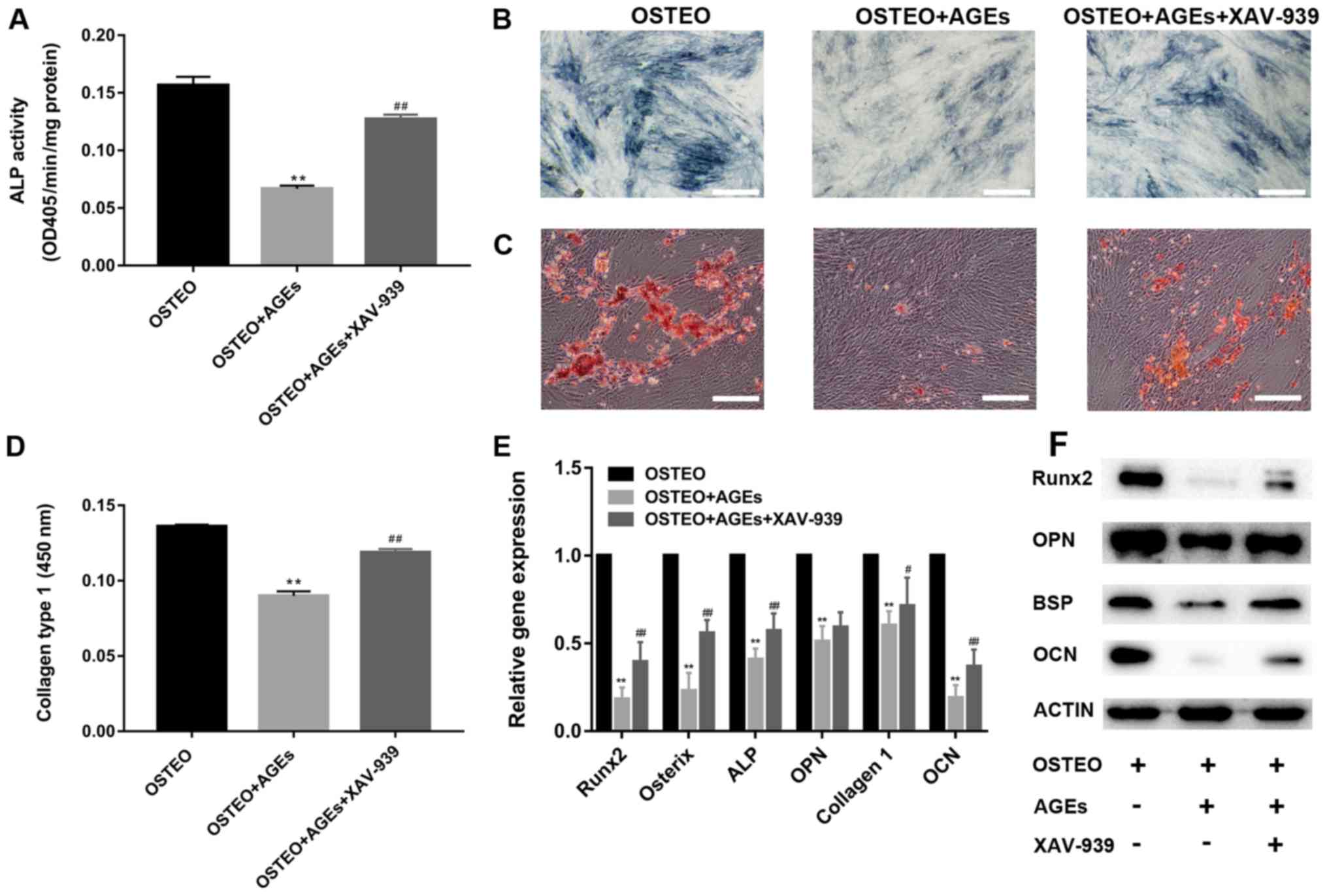
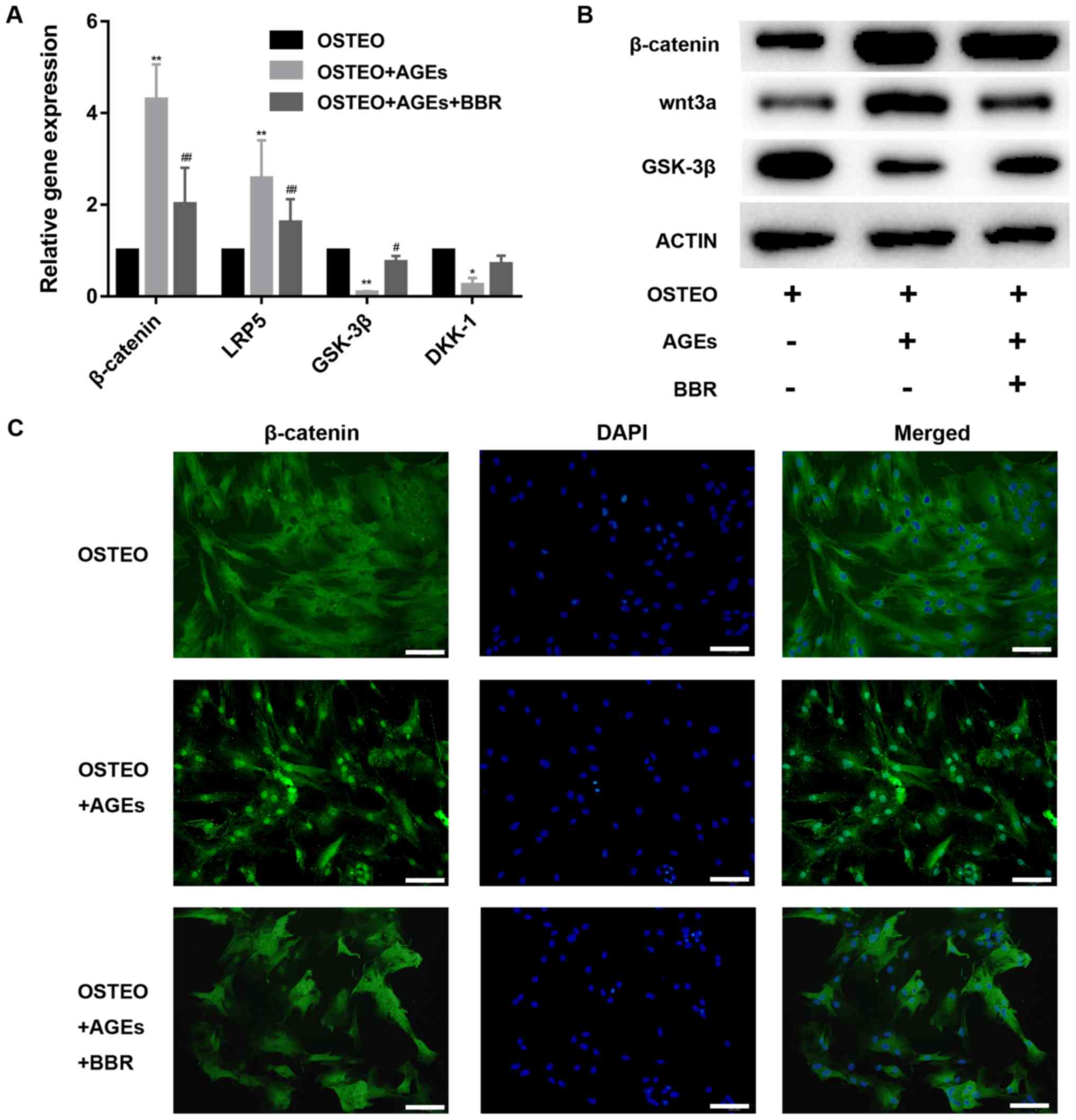
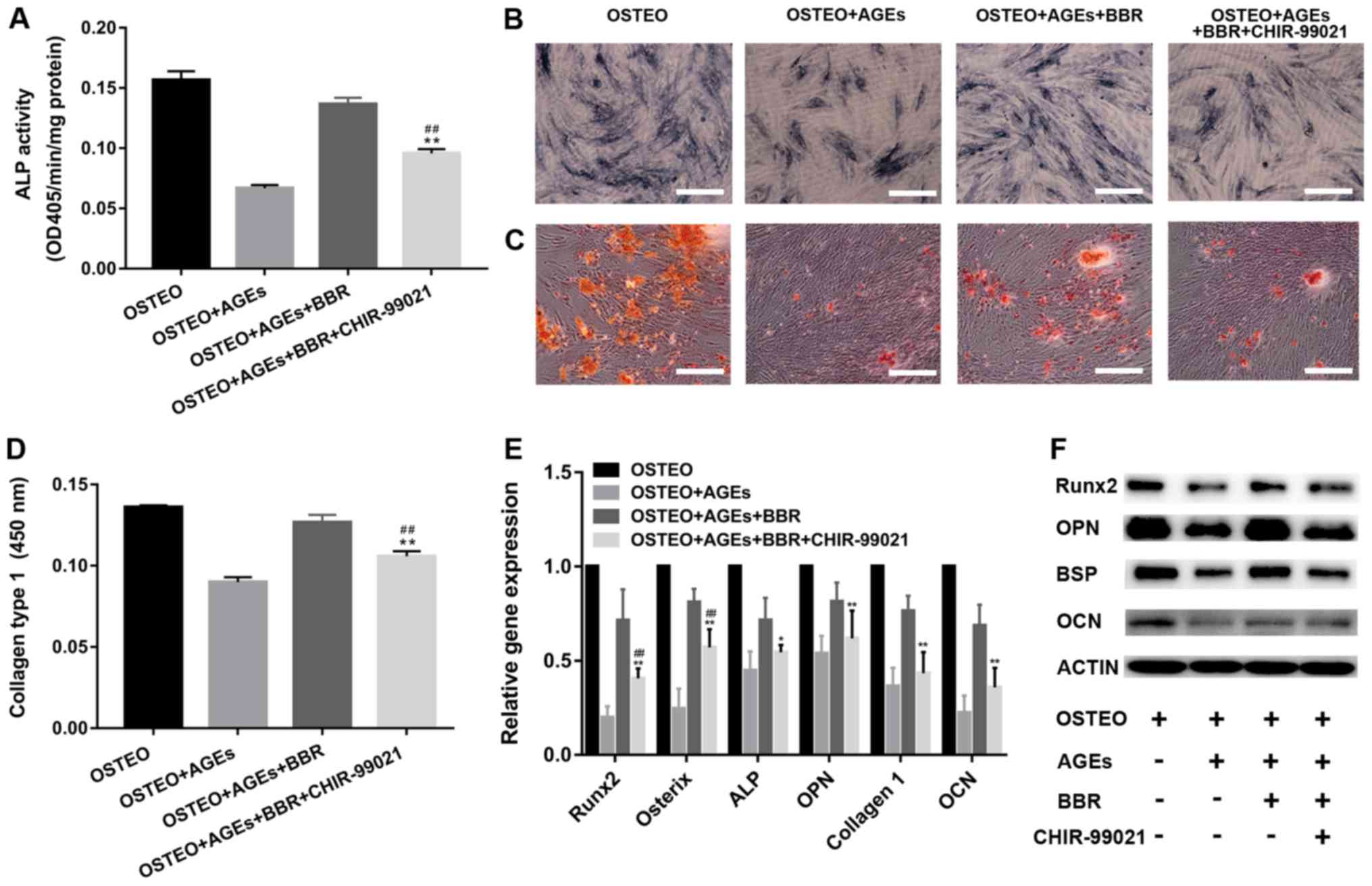
|
1
|
Preshaw PM, Alba AL, Herrera D, Jepsen S,
Konstantinidis A, Makrilakis K and Taylor R: Periodontitis and
diabetes: A two-way relationship. Diabetologia. 55:21–31. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Löe H: Periodontal disease. The sixth
complication of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 16:329–334. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu N, Shi S, Deng M, Tang L, Zhang G, Liu
N, Ding B, Liu W, Liu Y, Shi H, et al: High levels of β-catenin
signaling reduce osteogenic differentiation of stem cells in
inflammatory microenvironments through inhibition of the
noncanonical Wnt pathway. J Bone Miner Res. 26:2082–2095. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Poulsen MW, Hedegaard RV, Andersen JM, de
Courten B, Bügel S, Nielsen J, Skibsted LH and Dragsted LO:
Advanced glycation endproducts in food and their effects on health.
Food Chem Toxicol. 60:10–37. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gurav AN: Advanced glycation end products:
A link between periodontitis and diabetes mellitus? Curr Diabetes
Rev. 9:355–361. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zizzi A, Tirabassi G, Aspriello SD,
Piemontese M, Rubini C and Lucarini G: Gingival advanced glycation
end-products in diabetes mellitus-associated chronic periodontitis:
An immunohistochemical study. J Periodontal Res. 48:293–301. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bosshardt DD and Sculean A: Does
periodontal tissue regeneration really work? Periodontol 2000.
51:208–219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Reynolds MA, Kao RT, Camargo PM, Caton JG,
Clem DS, Fiorellini JP, Geisinger ML, Mills MP, Nares S and Nevins
ML: Periodontal regeneration-intrabony defects: A consensus report
from the AAP Regeneration Workshop. J Periodontol 86 (2 Suppl).
S105–S107. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bartold PM, Gronthos S, Ivanovski S,
Fisher A and Hutmacher DW: Tissue engineered periodontal products.
J Periodontal Res. 51:1–15. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cai C, Yuan GJ, Huang Y, Yang N, Chen X,
Wen L, Wang X, Zhang L and Ding Y: Estrogen-related receptor α is
involved in the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem
cells isolated from human periodontal ligaments. Int J Mol Med.
31:1195–1201. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Drake MT, Clarke BL and Khosla S:
Bisphosphonates: Mechanism of action and role in clinical practice.
Mayo Clin Proc. 83:1032–1045. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kuo YJ, Tsuang FY, Sun JS, Lin CH, Chen
CH, Li JY, Huang YC, Chen WY, Yeh CB and Shyu JF: Calcitonin
inhibits SDCP-induced osteoclast apoptosis and increases its
efficacy in a rat model of osteoporosis. PLoS One. 7:e402722012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kong W, Wei J, Abidi P, Lin M, Inaba S, Li
C, Wang Y, Wang Z, Si S, Pan H, et al: Berberine is a novel
cholesterol-lowering drug working through a unique mechanism
distinct from statins. Nat Med. 10:1344–1351. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stermitz FR, Lorenz P, Tawara JN, Zenewicz
LA and Lewis K: Synergy in a medicinal plant: Antimicrobial action
of berberine potentiated by 5′-methoxyhydnocarpin, a multidrug pump
inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:1433–1437. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang J, Yin J, Gao H, Xu L, Wang Y, Xu L
and Li M: Berberine improves insulin sensitivity by inhibiting fat
store and adjusting adipokines profile in human preadipocytes and
metabolic syndrome patients. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2012:3638452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Logan CY and Nusse R: The Wnt signaling
pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
20:781–810. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Reya T and Clevers H: Wnt signalling in
stem cells and cancer. Nature. 434:843–850. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Krishnan V, Bryant HU and Macdougald OA:
Regulation of bone mass by Wnt signaling. J Clin Invest.
116:1202–1209. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Holmen SL, Zylstra CR, Mukherjee A, Sigler
RE, Faugere MC, Bouxsein ML, Deng L, Clemens TL and Williams BO:
Essential role of beta-catenin in postnatal bone acquisition. J
Biol Chem. 280:21162–21168. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Miller JR: The Wnts. Genome Biol.
3:REVIEWS30012002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rawadi G, Vayssière B, Dunn F, Baron R and
Roman-Roman S: BMP-2 controls alkaline phosphatase expression and
osteoblast mineralization by a Wnt autocrine loop. J Bone Miner
Res. 18:1842–1853. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
de Boer J, Siddappa R, Gaspar C, van
Apeldoorn A, Fodde R and van Blitterswijk C: Wnt signaling inhibits
osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Bone.
34:818–826. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Boland GM, Perkins G, Hall DJ and Tuan RS:
Wnt 3a promotes proliferation and suppresses osteogenic
differentiation of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell
Biochem. 93:1210–1230. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
van der Horst G, van der Werf SM,
Farih-Sips H, van Bezooijen RL, Löwik CW and Karperien M:
Downregulation of Wnt signaling by increased expression of
Dickkopf-1 and −2 is a prerequisite for late-stage osteoblast
differentiation of KS483 cells. J Bone Miner Res. 20:1867–1877.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang M, Zhang W, Xu S, Peng L, Wang Z, Liu
H, Fang Q, Deng T, Men X and Lou J: TRB3 mediates advanced
glycation end product-induced apoptosis of pancreatic β-cells
through the protein kinase C β pathway. Int J Mol Med. 40:130–136.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang H, Shan Y, Wu Y, Xu C, Yu X, Zhao J,
Yan J and Shang W: Berberine suppresses LPS-induced inflammation
through modulating Sirt1/NF-κB signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells.
Int Immunopharmacol. 52:93–100. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bennett CN, Ross SE, Longo KA, Bajnok L,
Hemati N, Johnson KW, Harrison SD and MacDougald OA: Regulation of
Wnt signaling during adipogenesis. J Biol Chem. 277:30998–31004.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liccardo D, Cannavo A, Spagnuolo G,
Ferrara N, Cittadini A, Rengo C and Rengo G: Periodontal disease: A
risk factor for diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Int J Mol Sci.
20(pii): E14142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gheorghita D, Eördegh G, Nagy F and Antal
M: Periodontal disease, a risk factor for atherosclerotic
cardiovascular disease. Orv Hetil. 160:419–425. 2019.(In
Hungarian). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Du J, Shan Z, Ma P, Wang S and Fan Z:
Allogeneic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for
periodontal regeneration. J Dent Res. 93:183–188. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chamila Prageeth Pandula PK, Samaranayake
LP, Jin LJ and Zhang C: Periodontal ligament stem cells: An update
and perspectives. J Investig Clin Dent. 5:81–90. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Trubiani O, Di Primio R, Traini T,
Pizzicannella J, Scarano A, Piattelli A and Caputi S: Morphological
and cytofluorimetric analysis of adult mesenchymal stem cells
expanded ex vivo from periodontal ligament. Int J Immunopathol
Pharmacol. 18:213–221. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Morsczeck C and Reichert TE: Dental stem
cells in tooth regeneration and repair in the future. Expert Opin
Biol Ther. 18:187–196. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
An K and Liu H: Survival of bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells and periodontal ligament stem cells in cell
sheets. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 49:682–687. 2014.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yao S, Zhao W, Ou Q, Liang L, Lin X and
Wang Y: MicroRNA-214 suppresses osteogenic differentiation of human
periodontal ligament stem cells by targeting ATF4. Stem Cells Int.
2017:30286472017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ji K, Liu Y, Lu W, Yang F, Yu J, Wang X,
Ma Q, Yang Z, Wen L and Xuan K: Periodontal tissue engineering with
stem cells from the periodontal ligament of human retained
deciduous teeth. J Periodontal Res. 48:105–116. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Borgnakke WS, Ylöstalo PV, Taylor GW and
Genco RJ: Effect of periodontal disease on diabetes: Systematic
review of epidemiologic observational evidence. J Clin Periodontol.
40 (Suppl 14):S135–S152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Friedewald VE, Kornman KS, Beck JD, Genco
R, Goldfine A, Libby P, Offenbacher S, Ridker PM, Van Dyke TE,
Roberts WC, et al: The American journal of cardiology and journal
of periodontology editors' consensus: Periodontitis and
atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 104:59–68.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vlassara H and Uribarri J: Advanced
glycation end products (AGE) and diabetes: Cause, effect, or both?
Curr Diab Rep. 14:4532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu D, Xu J, Liu O, Fan Z, Liu Y, Wang F,
Ding G, Wei F, Zhang C and Wang S: Mesenchymal stem cells derived
from inflamed periodontal ligaments exhibit impaired
immunomodulation. J Clin Periodontol. 39:1174–1182. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu Q, Hu CH, Zhou CH, Cui XX, Yang K,
Deng C, Xia JJ, Wu Y, Liu LC and Jin Y: DKK1 rescues osteogenic
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from periodontal
ligaments of patients with diabetes mellitus induced periodontitis.
Sci Rep. 5:131422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kume S, Kato S, Yamagishi S, Inagaki Y,
Ueda S, Arima N, Okawa T, Kojiro M and Nagata K: Advanced glycation
end-products attenuate human mesenchymal stem cells and prevent
cognate differentiation into adipose tissue, cartilage, and bone. J
Bone Miner Res. 20:1647–1658. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pandey MK, Sung B, Kunnumakkara AB, Sethi
G, Chaturvedi MM and Aggarwal BB: Berberine modifies cysteine 179
of IkappaBalpha kinase, suppresses nuclear factor-kappaB-regulated
antiapoptotic gene products, and potentiates apoptosis. Cancer Res.
68:5370–5379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Singh T, Vaid M, Katiyar N, Sharma S and
Katiyar SK: Berberine, an isoquinoline alkaloid, inhibits melanoma
cancer cell migration by reducing the expressions of
cyclooxygenase-2, prostaglandin E2 and prostaglandin
E2 receptors. Carcinogenesis. 32:86–92. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hu JP, Nishishita K, Sakai E, Yoshida H,
Kato Y, Tsukuba T and Okamoto K: Berberine inhibits RANKL-induced
osteoclast formation and survival through suppressing the NF-kappaB
and Akt pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 580:70–79. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yang W and Ma B: A mini-review: The
therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells and relevant
signaling factors. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. Sep 12–2018.(Epub ahead
of print). doi: 10.2174/1574888X13666180912141228.
|
|
48
|
Moon RT, Kohn AD, De Ferrari GV and Kaykas
A: WNT and beta-catenin signalling: Diseases and therapies. Nat Rev
Genet. 5:691–701. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Aberle H, Bauer A, Stappert J, Kispert A
and Kemler R: beta-catenin is a target for the ubiquitin-proteasome
pathway. EMBO J. 16:3797–3804. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lee HW, Suh JH, Kim HN, Kim AY, Park SY,
Shin CS, Choi JY and Kim JB: Berberine promotes osteoblast
differentiation by Runx2 activation with p38 MAPK. J Bone Miner
Res. 23:1227–1237. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Huang SM, Mishina YM, Liu S, Cheung A,
Stegmeier F, Michaud GA, Charlat O, Wiellette E, Zhang Y, Wiessner
S, et al: Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt
signalling. Nature. 461:614–620. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bulut-Karslioglu A, Biechele S, Jin H,
Macrae TA, Hejna M, Gertsenstein M, Song JS and Ramalho-Santos M:
Inhibition of mTOR induces a paused pluripotent state. Nature.
540:119–123. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Han J, Wu Q, Xia Y, Wagner MB and Xu C:
Cell alignment induced by anisotropic electrospun fibrous scaffolds
alone has limited effect on cardiomyocyte maturation. Stem Cell
Res. 16:740–750. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Staines KA, MacRae VE and Farquharson C:
The importance of the SIBLING family of proteins on skeletal
mineralisation and bone remodelling. J Endocrinol. 214:241–255.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Neve A, Corrado A and Cantatore FP:
Osteocalcin: Skeletal and extra-skeletal effects. J Cell Physiol.
228:1149–1153. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kruger TE, Miller AH, Godwin AK and Wang
J: Bone sialoprotein and osteopontin in bone metastasis of
osteotropic cancers. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 89:330–341. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|