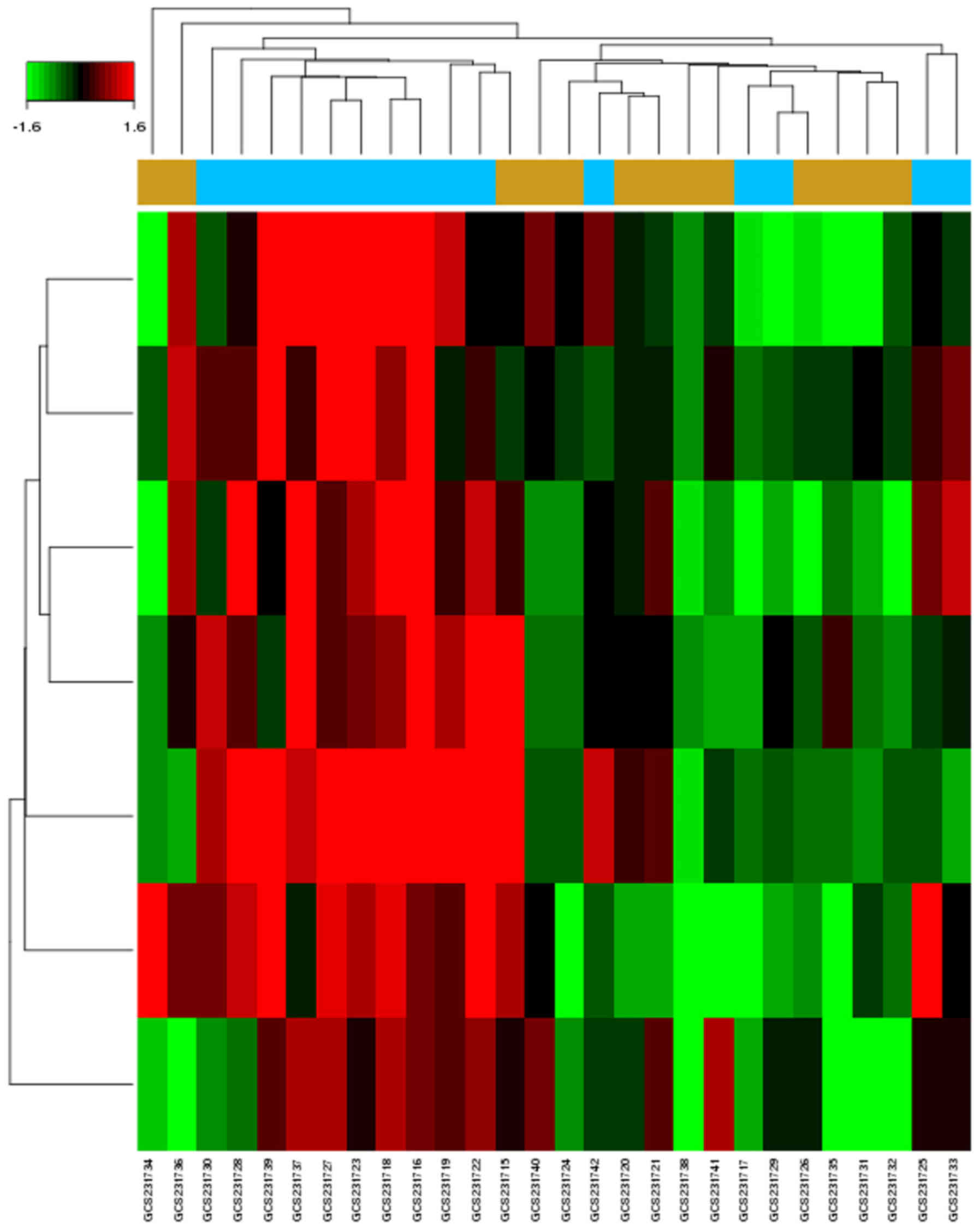
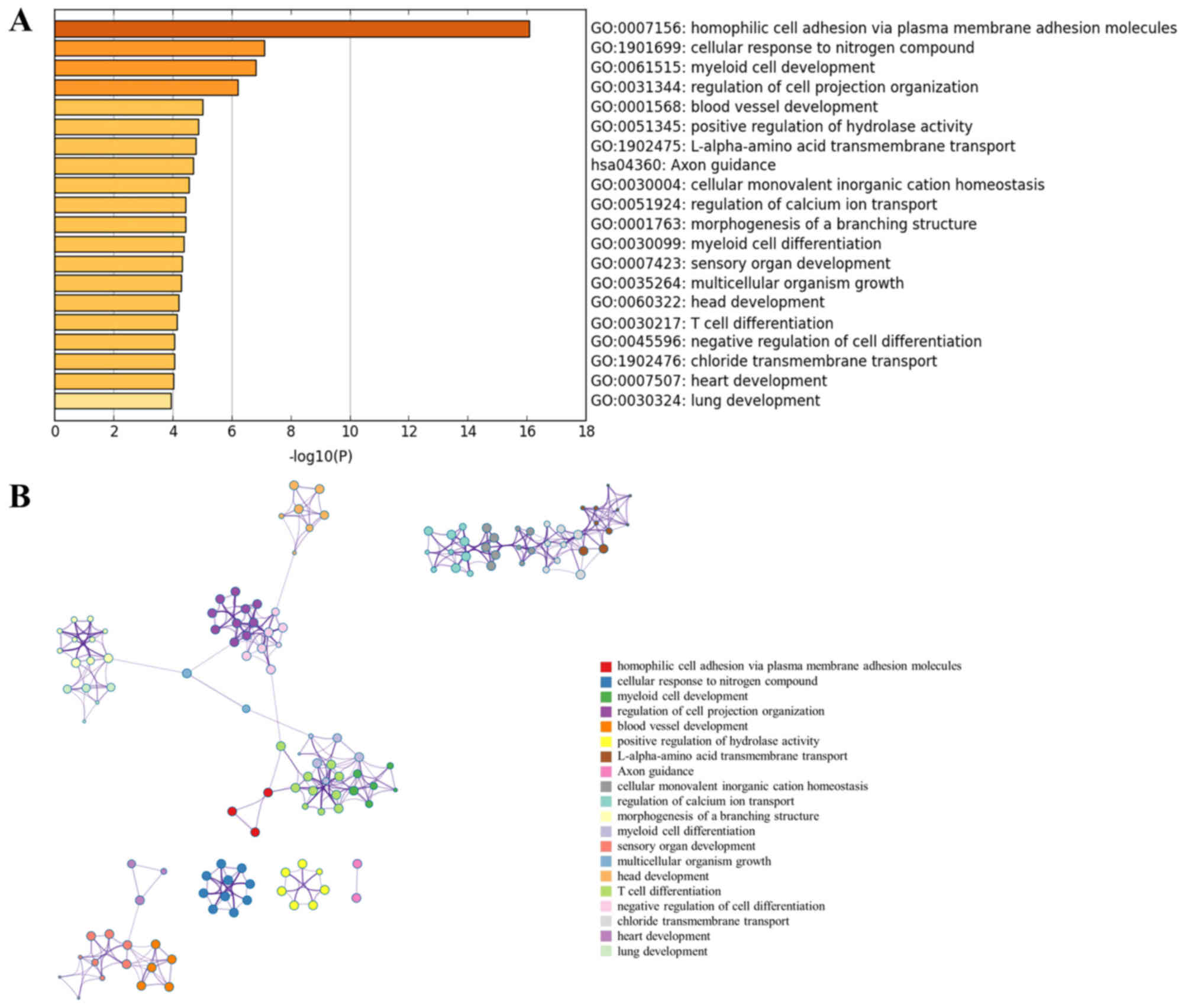
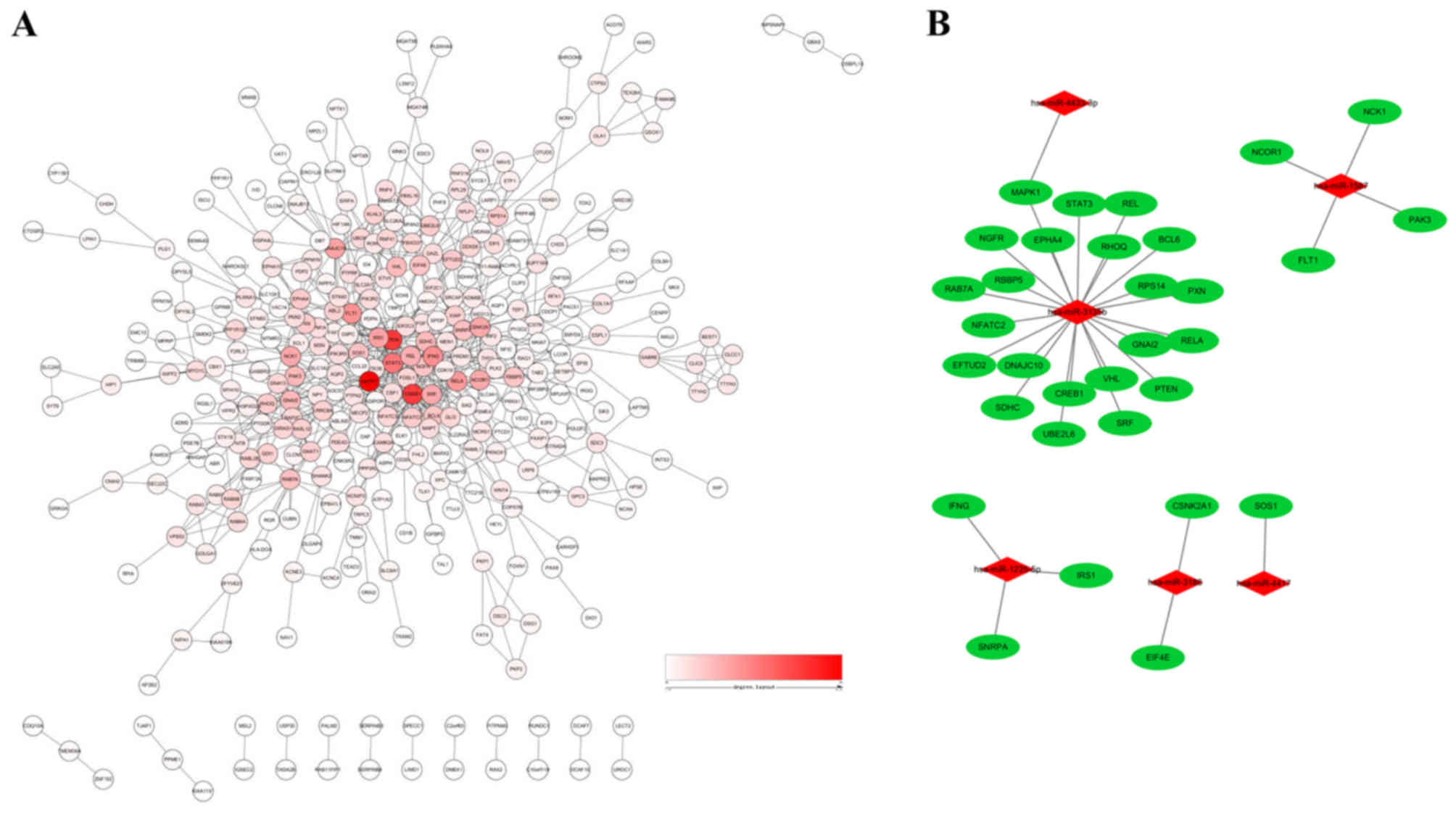
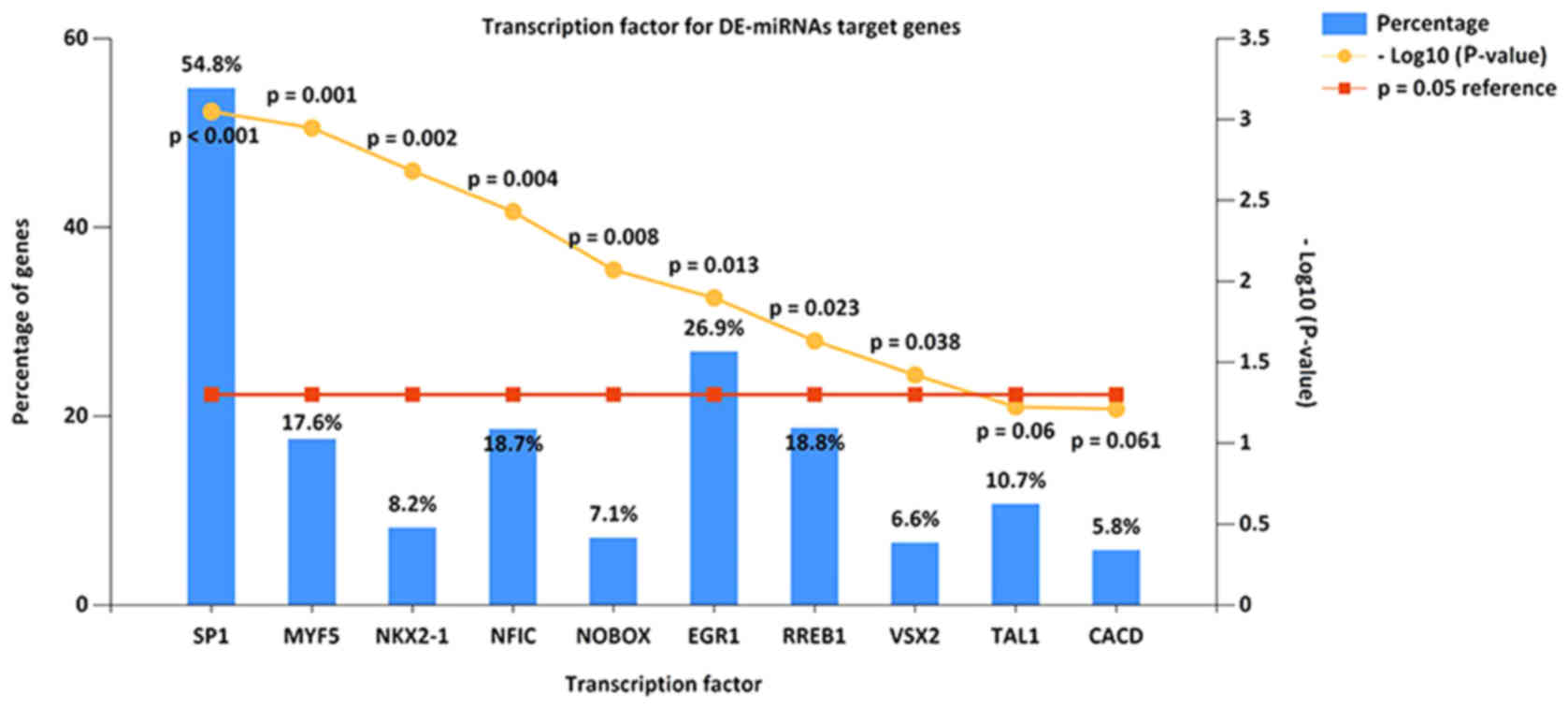
|
1
|
Franks S: Polycystic ovary syndrome. N
Engl J Med. 333:853–861. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lizneva D, Suturina L, Walker W, Brakta S,
Gavrilova-Jordan L and Azziz R: Criteria, prevalence, and
phenotypes of polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril. 106:6–15.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhao Y and Qiao J: Ethnic differences in
the phenotypic expression of polycystic ovary syndrome. Steroids.
78:755–760. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dumesic DA, Padmanabhan V and Abbott DH:
Polycystic ovary syndrome and oocyte developmental competence.
Obstet Gynecol Surv. 63:39–48. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nelson LR and Bulun SE: Estrogen
production and action. J Am Acad Dermatol 45 (3 Suppl). S116–S124.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Artimani T, Saidijam M, Aflatoonian R,
Amiri I, Ashrafi M, Shabab N, Mohammadpour N and Mehdizadeh M:
Estrogen and progesterone receptor subtype expression in granulosa
cells from women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Gynecol
Endocrinol. 31:379–383. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Haouzi D, Assou S, Monzo C, Vincens C,
Dechaud H and Hamamah S: Altered gene expression profile in cumulus
cells of mature MII oocytes from patients with polycystic ovary
syndrome. Hum Reprod. 27:3523–3530. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jansen E, Laven JS, Dommerholt HB, Polman
J, van Rijt C, van den Hurk C, Westland J, Mosselman S and Fauser
BC: Abnormal gene expression profiles in human ovaries from
polycystic ovary syndrome patients. Mol Endocrinol. 18:3050–3063.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Manneras-Holm L, Benrick A and
Stener-Victorin E: Gene expression in subcutaneous adipose tissue
differs in women with polycystic ovary syndrome and controls
matched pair-wise for age, body weight, and body mass index.
Adipocyte. 3:190–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sorensen AE, Wissing ML, Salö S, Englund
AL and Dalgaard LT: MicroRNAs related to polycystic ovary syndrome
(PCOS). Genes (Basel). 5:684–708. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wood JR, Ho CK, Nelson-Degrave VL,
McAllister JM and Strauss JF III: The molecular signature of
polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) theca cells defined by gene
expression profiling. J Reprod Immunol. 63:51–60. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Esteller M: Non-coding RNAs in human
disease. Nat Rev Genet. 12:861–874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rossi JJ: New hope for a microRNA therapy
for liver cancer. Cell. 137:990–992. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim YJ, Ku SY, Kim YY, Liu HC, Chi SW, Kim
SH, Choi YM, Kim JG and Moon SY: MicroRNAs transfected into
granulosa cells may regulate oocyte meiotic competence during in
vitro maturation of mouse follicles. Hum Reprod. 28:3050–3061.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu B, Zhang YW, Tong XH and Liu YS:
Characterization of microRNA profile in human cumulus granulosa
cells: Identification of microRNAs that regulate Notch signaling
and are associated with PCOS. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 404:26–36. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Imbar T and Eisenberg I: Regulatory role
of microRNAs in ovarian function. Fertil Steril. 101:1524–1530.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu J, Tu F, Yao W, Li X, Xie Z, Liu H, Li
Q and Pan Z: Conserved miR-26b enhances ovarian granulosa cell
apoptosis through HAS2-HA-CD44-Caspase-3 pathway by targeting HAS2.
Sci Rep. 6:211972016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou J, Liu J, Pan Z, Du X, Li X, Ma B,
Yao W, Li Q and Liu H: The let-7g microRNA promotes follicular
granulosa cell apoptosis by targeting transforming growth
factor-beta type 1 receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 409:103–112.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Carletti MZ and Christenson LK: MicroRNA
in the ovary and female reproductive tract. J Anim Sci 87 (14
Suppl). E29–E38. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen YH, Heneidi S, Lee JM, Layman LC,
Stepp DW, Gamboa GM, Chen BS, Chazenbalk G and Azziz R: miRNA-93
inhibits GLUT4 and is overexpressed in adipose tissue of polycystic
ovary syndrome patients and women with insulin resistance.
Diabetes. 62:2278–2286. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Long W, Zhao C, Ji C, Ding H, Cui Y, Guo
X, Shen R and Liu J: Characterization of serum microRNAs profile of
PCOS and identification of novel non-invasive biomarkers. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 33:1304–1315. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Roth LW, McCallie B, Alvero R, Schoolcraft
WB, Minjarez D and Katz-Jaffe MG: Altered microRNA and gene
expression in the follicular fluid of women with polycystic ovary
syndrome. J Assist Reprod Genet. 31:355–362. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Murri M, Insenser M, Fernandez-Duran E,
San-Millan JL and Escobar-Morreale HF: Effects of polycystic ovary
syndrome (PCOS), sex hormones, and obesity on circulating miRNA-21,
miRNA-27b, miRNA-103, and miRNA-155 expression. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 98:E1835–E1844. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shi L, Liu S, Zhao W and Shi J: miR-483-5p
and miR-486-5p are down-regulated in cumulus cells of metaphase II
oocytes from women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Reprod Biomed
Online. 31:565–572. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang L, Huang J, Li L, Chen Y, Chen X,
Zhao X and Yang D: MicroRNA-93 promotes ovarian granulosa cells
proliferation through targeting CDKN1A in polycystic ovarian
syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 100:E729–E738. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhu XL, Chen XF and Xu WL: miR-34a
regulates apoptosis of human ovarian granulosa cells. J Jiangsu
Univ (Med Ed). 26:470–474. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
27
|
He X and Zhang J: Why do hubs tend to be
essential in protein networks? PLoS Genet. 2:e882006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res 41
(Database Issue). D808–D815. 2013.
|
|
29
|
Pathan M, Keerthikumar S, Ang CS, Gangoda
L, Quek CY, Williamson NA, Mouradov D, Sieber OM, Simpson RJ, Salim
A, et al: FunRich: An open access standalone functional enrichment
and interaction network analysis tool. Proteomics. 15:2597–2601.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rotterdam ESHRE/ASRM-Sponsored PCOS
consensus workshop Group, : Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic
criteria and long-term health risks related to polycystic ovary
syndrome (PCOS). Hum Reprod. 19:41–47. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Azziz R, Carmina E, Dewailly D,
Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Escobar-Morreale HF, Futterweit W, Janssen
OE, Legro RS, Norman RJ, Taylor AE, et al: Positions statement:
Criteria for defining polycystic ovary syndrome as a predominantly
hyperandrogenic syndrome: An Androgen Excess Society guideline. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 91:4237–4245. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Escobar-Morreale HF, Luque-Ramirez M and
San Millan JL: The molecular-genetic basis of functional
hyperandrogenism and the polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocr Rev.
26:251–282. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Miska EA: How microRNAs control cell
division, differentiation and death. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
15:563–568. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Maalouf SW, Liu WS and Pate JL: MicroRNA
in ovarian function. Cell Tissue Res. 363:7–18. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xue Y, Lv J, Xu P, Gu L, Cao J, Xu L, Xue
K and Li Q: Identification of microRNAs and genes associated with
hyperandrogenism in the follicular fluid of women with polycystic
ovary syndrome. J Cell Biochem. 119:3913–3921. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jiang YC and Ma JX: The role of MiR-324-3p
in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) via targeting WNT2B. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:3286–3293. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Murri M, Insenser M, Fernandez-Duran E,
San-Millan JL, Luque-Ramirez M and Escobar-Morreale HF:
Non-targeted profiling of circulating microRNAs in women with
polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): Effects of obesity and sex
hormones. Metabolism. 86:49–60. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Arancio W, Calogero Amato M, Magliozzo M,
Pizzolanti G, Vesco R and Giordano C: Serum miRNAs in women
affected by hyperandrogenic polycystic ovary syndrome: The
potential role of miR-155 as a biomarker for monitoring the
estroprogestinic treatment. Gynecol Endocrinol. 34:704–708. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhong Z, Li F, Li Y, Qin S, Wen C, Fu Y
and Xiao Q: Inhibition of microRNA-19b promotes ovarian granulosa
cell proliferation by targeting IGF-1 in polycystic ovary syndrome.
Mol Med Rep. 17:4889–4898. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang M, Liu M, Sun J, Jia L, Ma S, Gao J,
Xu Y, Zhang H, Tsang SY and Li X: MicroRNA-27a-3p affects estradiol
and androgen imbalance by targeting Creb1 in the granulosa cells in
mouse polycytic ovary syndrome model. Reprod Biol. 17:295–304.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yao G, Yin M, Lian J, Tian H, Liu L, Li X
and Sun F: MicroRNA-224 is involved in transforming growth
factor-beta-mediated mouse granulosa cell proliferation and
granulosa cell function by targeting Smad4. Mol Endocrinol.
24:540–551. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Carletti MZ, Fiedler SD and Christenson
LK: MicroRNA 21 blocks apoptosis in mouse periovulatory granulosa
cells. Biol Reprod. 83:286–295. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yin M, Wang X, Yao G, Lü M, Liang M, Sun Y
and Sun F: Transactivation of micrornA-320 by microRNA-383
regulates granulosa cell functions by targeting E2F1 and SF-1
proteins. J Biol Chem. 289:18239–18257. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fiedler SD, Carletti MZ, Hong X and
Christenson LK: Hormonal regulation of MicroRNA expression in
periovulatory mouse mural granulosa cells. Biol Reprod.
79:1030–1037. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhou SJ, Deng YL, Liang HF, Jaoude JC and
Liu FY: Hepatitis B virus X protein promotes CREB-mediated
activation of miR-3188 and Notch signaling in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cell Death Differ. 24:1577–1587. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen X and Chen J: MiR-3188 regulates cell
proliferation, apoptosis, and migration in breast cancer by
targeting TUSC5 and regulating the p38 MAPK signaling pathway.
Oncol Res. 26:363–372. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhao M, Luo R, Liu Y, Gao L, Fu Z, Fu Q,
Luo X, Chen Y, Deng X, Liang Z, et al: miR-3188 regulates
nasopharyngeal carcinoma proliferation and chemosensitivity through
a FOXO1-modulated positive feedback loop with
mTOR-p-PI3K/AKT-c-JUN. Nat Commun. 7:113092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu W, Ling S, Sun W, Liu T, Li Y, Zhong
G, Zhao D, Zhang P, Song J, Jin X, et al: Circulating microRNAs
correlated with the level of coronary artery calcification in
symptomatic patients. Sci Rep. 5:160992015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Figueroa J, Phillips LM, Shahar T, Hossain
A, Gumin J, Kim H, Bean AJ, Calin GA, Fueyo J, Walters ET, et al:
Exosomes from Glioma-associated mesenchymal stem cells increase the
tumorigenicity of glioma stem-like cells via transfer of miR-1587.
Cancer Res. 77:5808–5819. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sun P, Zhang D, Huang H, Yu Y, Yang Z, Niu
Y and Liu J: MicroRNA-1225-5p acts as a tumor-suppressor in
laryngeal cancer via targeting CDC14B. Biol Chem. 400:237–246.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Fomicheva KA, Osip'yants AI, Knyazev EN,
Samatov TR and Shkurnikov MY: Detection of potential metastatic
prostate cancer circulating biomarkers by comparison of miRNA
profiles in DU145 cells and culture medium. Bull Exp Biol Med.
162:792–796. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Song L, Zhang W, Chang Z, Pan Y, Zong H,
Fan Q and Wang L: miR-4417 targets tripartite motif-containing 35
(TRIM35) and regulates pyruvate kinase muscle 2 (PKM2)
phosphorylation to promote proliferation and suppress apoptosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Med Sci Monit. 23:1741–1750. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Schreiner D and Weiner JA: Combinatorial
homophilic interaction between gamma-protocadherin multimers
greatly expands the molecular diversity of cell adhesion. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 107:14893–14898. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yagi T and Takeichi M: Cadherin
superfamily genes: Functions, genomic organization, and neurologic
diversity. Genes Dev. 14:1169–1180. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mah KM and Weiner JA: Regulation of Wnt
signaling by protocadherins. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 69:158–171. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Inan MS, Al-Hassan S, Ozand P and Coskun
S: Transcriptional profiling of granulosa cells from a patient with
recurrent empty follicle syndrome. Reprod Biomed Online.
13:481–491. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dickinson SE: Effect of pre-ovulatory
follicle size on oocyte transcript abundance in beef cows. Master's
Thesis University of Missouri-Columbia. 2016.
|
|
59
|
Mitchell LM, Kennedy CR and Hartshorne GM:
Expression of nitric oxide synthase and effect of substrate
manipulation of the nitric oxide pathway in mouse ovarian
follicles. Hum Reprod. 19:30–40. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Guo YX, Zhang GM, Yao XL, Tong R, Cheng
CY, Zhang TT, Wang ST, Yang H and Wang F: Effects of nitric oxide
on steroidogenesis and apoptosis in goat luteinized granulosa
cells. Theriogenology. 126:55–62. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Liu Z, Liu C, Hao C, Xue Q, Huang X, Zhang
N, Bao H and Qu Q: Aberrant expression of angiopoietin-like
proteins 1 and 2 in cumulus cells is potentially associated with
impaired oocyte developmental competence in polycystic ovary
syndrome. Gynecol Endocrinol. 32:557–561. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chen H, Guo JH, Lu YC, Ding GL, Yu MK,
Tsang LL, Fok KL, Liu XM, Zhang XH, Chung YW, et al: Impaired
CFTR-dependent amplification of FSH-stimulated estrogen production
in cystic fibrosis and PCOS. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:923–932.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Sun M, Sui Y, Li L, Su W, Hao F, Zhu Q, Di
W, Gao H and Ma T: Anoctamin 1 calcium-activated chloride channel
downregulates estrogen production in mouse ovarian granulosa cells.
Endocrinology. 155:2787–2796. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Li D, You Y, Bi FF, Zhang TN, Jiao J, Wang
TR, Zhou YM, Shen ZQ, Wang XX and Yang Q: Autophagy is activated in
the ovarian tissue of polycystic ovary syndrome. Reproduction.
155:85–92. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Cui Y, Sun Y, Hu S, Luo J, Li L, Li X, Yeh
S, Jin J and Chang C: Neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPCa)
increased the neighboring PCa chemoresistance via altering the
PTHrP/p38/Hsp27/androgen receptor (AR)/p21 signals. Oncogene.
35:6065–6076. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kupreeva M, Diane A, Lehner R, Watts R,
Ghosh M, Proctor S and Vine D: Effect of metformin and flutamide on
insulin, lipogenic and androgen-estrogen signaling and
cardiometabolic risk in a PCOS-prone rodent model. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 316:E16–E33. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Liu N, Ding D, Hao W, Yang F, Wu X, Wang
M, Xu X, Ju Z, Liu JP, Song Z, et al: hTERT promotes tumor
angiogenesis by activating VEGF via interactions with the Sp1
transcription factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:8693–8703. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Solomon SS, Majumdar G, Martinez-Hernandez
A and Raghow R: A critical role of Sp1 transcription factor in
regulating gene expression in response to insulin and other
hormones. Life Sci. 83:305–312. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Anjali G, Kaur S, Lakra R, Taneja J,
Kalsey GS, Nagendra A, Shrivastav TG, Devi MG, Malhotra N, Kriplani
A and Singh R: FSH stimulates IRS-2 expression in human granulosa
cells through cAMP/SP1, an inoperative FSH action in PCOS patients.
Cell Signal. 27:2452–2466. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|