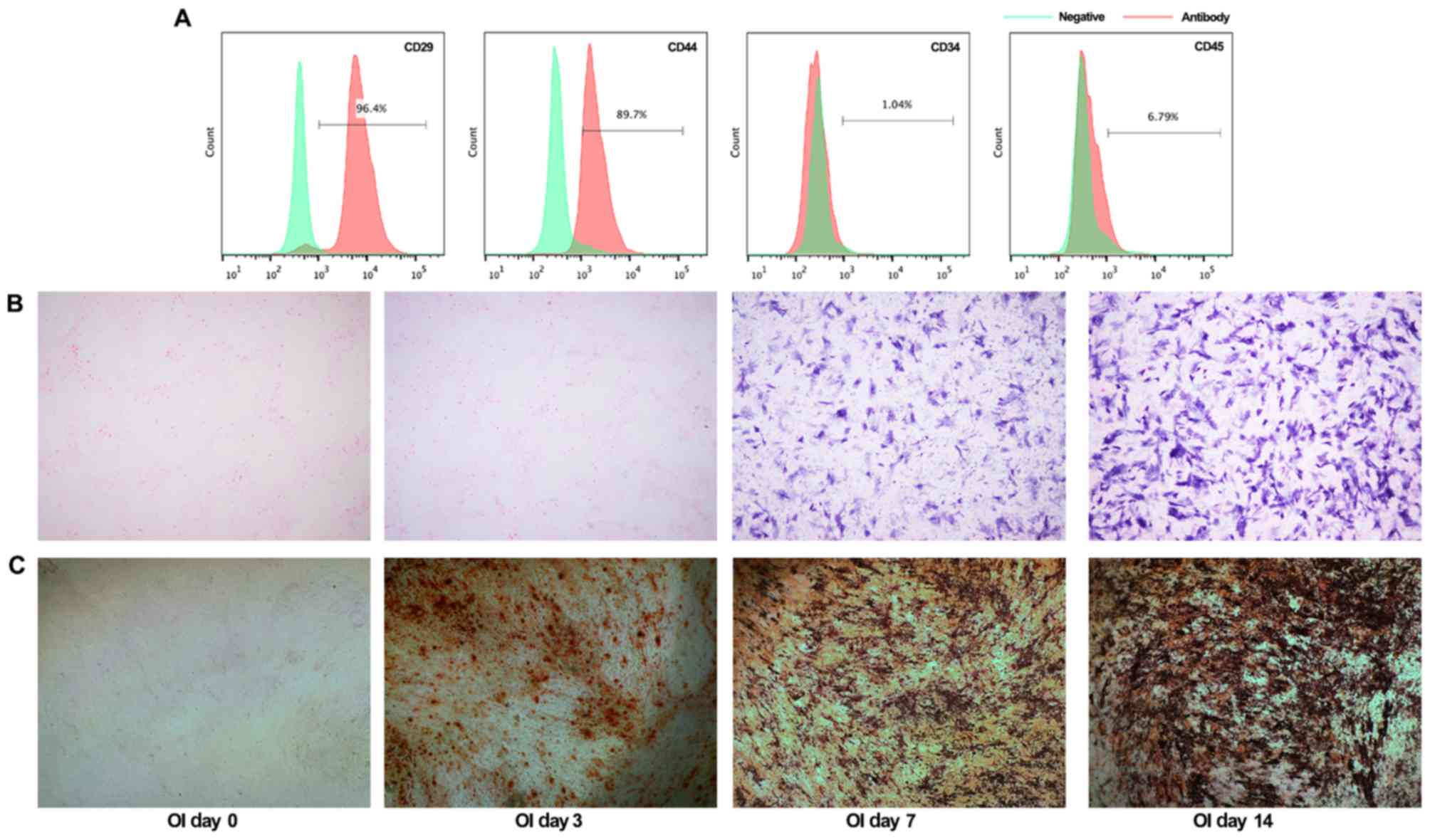
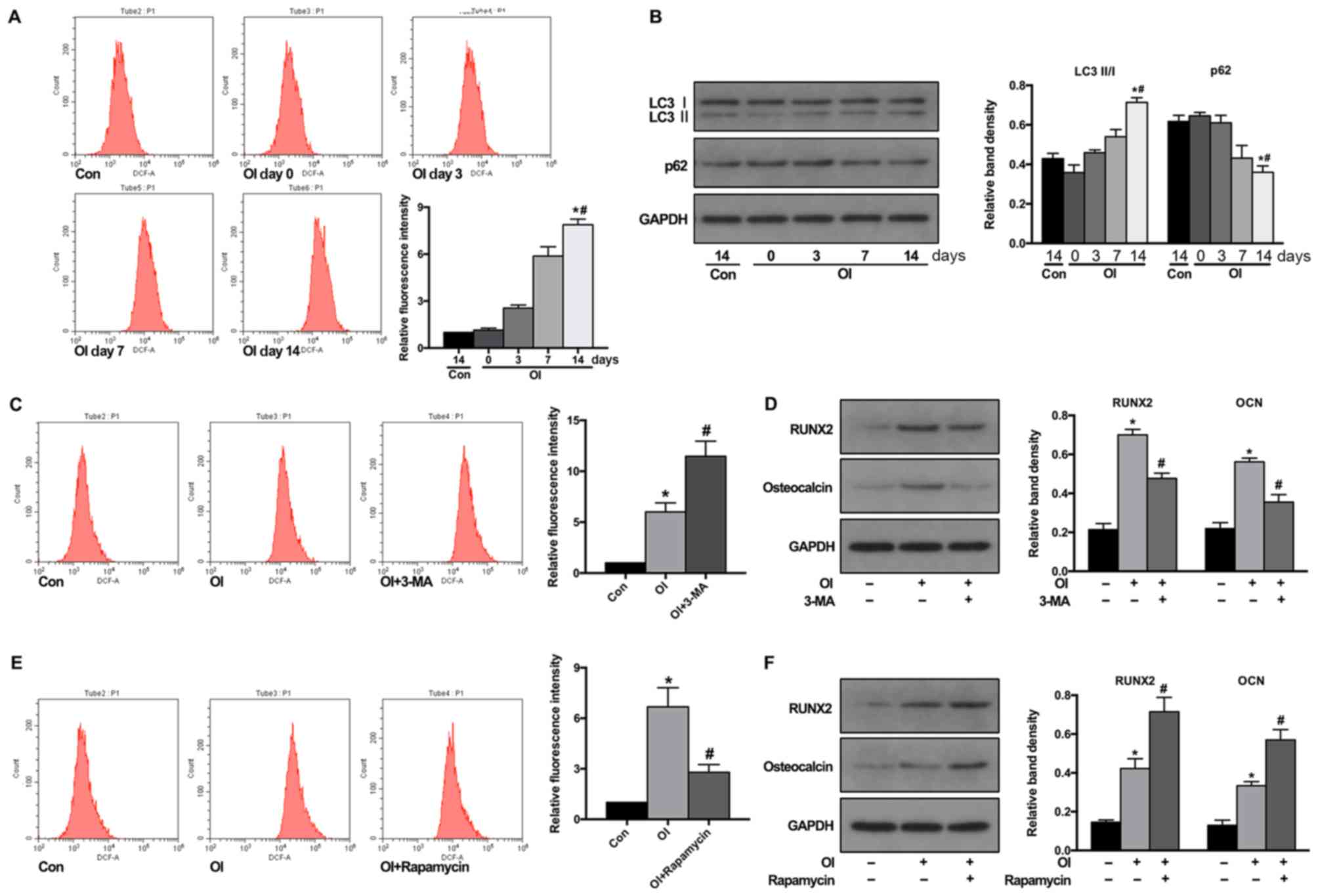
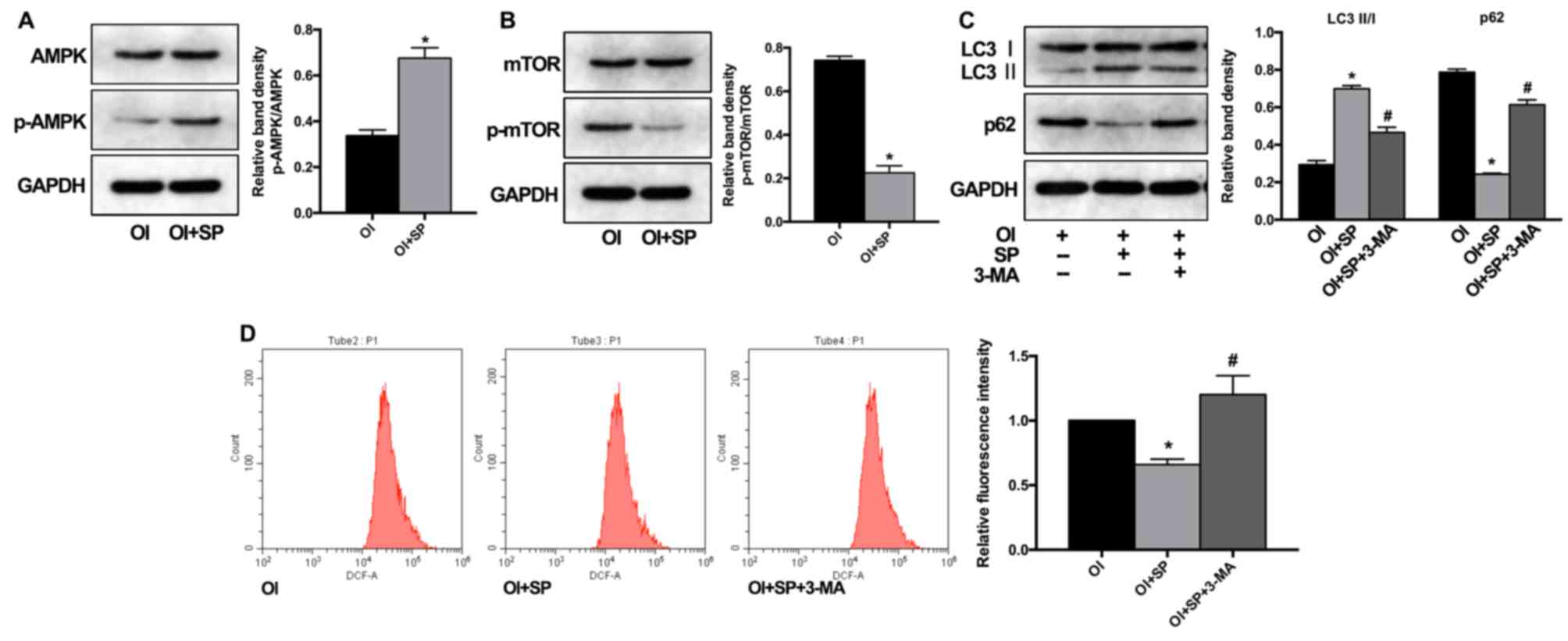
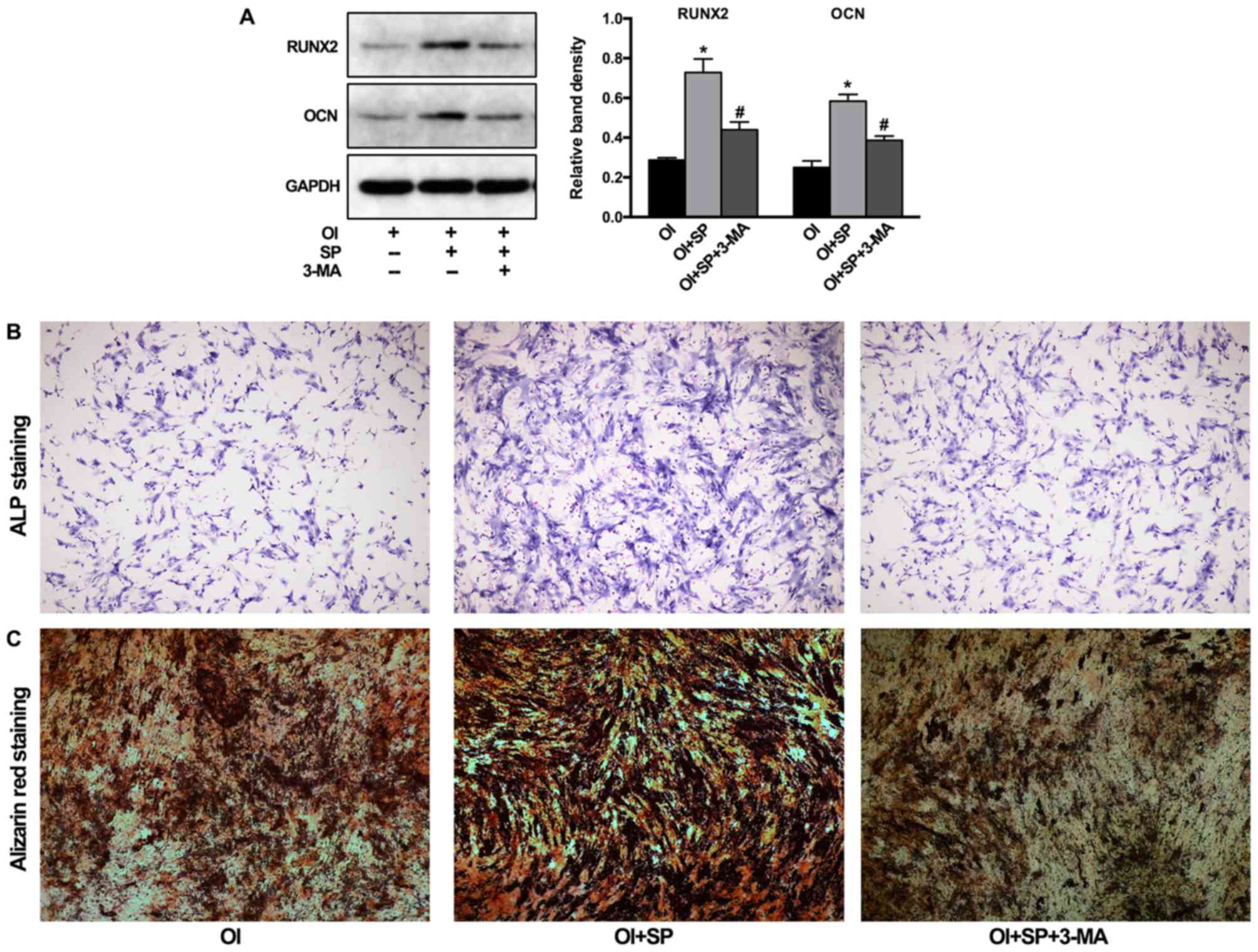
|
1
|
Petite H, Viateau V, Bensaïd W, Meunier A,
de Pollak C, Bourguignon M, Oudina K, Sedel L and Guillemin G:
Tissue-engineered bone regeneration. Nat Biotechnol. 18:959–963.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pobloth AM, Checa S, Razi H, Petersen A,
Weaver JC, Schmidt-Bleek K, Windolf M, Tatai AÁ, Roth CP, Schaser
KD, et al: Mechanobiologically optimized 3D titanium-mesh scaffolds
enhance bone regeneration in critical segmental defects in sheep.
Sci Transl Med. 10(pii): eaam88282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ho-Shui-Ling A, Bolander J, Rustom LE,
Johnson AW, Luyten FP and Picart C: Bone regeneration strategies:
Engineered scaffolds, bioactive molecules and stem cells current
stage and future perspectives. Biomaterials. 180:143–162. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Marolt D, Knezevic M and Novakovic GV:
Bone tissue engineering with human stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther.
1:102010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Man Z, Yin L, Shao Z, Zhang X, Hu X, Zhu
J, Dai L, Huang H, Yuan L, Zhou C, et al: The effects of
co-delivery of BMSC-affinity peptide and rhTGF-beta1 from coaxial
electrospun scaffolds on chondrogenic differentiation.
Biomaterials. 35:5250–5260. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cai S, Tsui YP, Tam KW, Shea GK, Chang RS,
Ao Q, Shum DK and Chan YS: Directed differentiation of human bone
marrow stromal cells to Fate-committed schwann cells. Stem Cell
Reports. 9:1097–1108. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen W, Shen X, Hu Y, Xu K, Ran Q, Yu Y,
Dai L, Yuan Z, Huang L, Shen T and Cai K: Surface functionalization
of titanium implants with chitosan-catechol conjugate for
suppression of ROS-induced cells damage and improvement of
osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 114:82–96. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Z, Yuan X, Fernandes G, Dziak R,
Ionita CN, Li C, Wang C and Yang S: The combination of nano-calcium
sulfate/platelet rich plasma gel scaffold with BMP2 gene-modified
mesenchymal stem cells promotes bone regeneration in rat
critical-sized calvarial defects. Stem Cell Res Ther. 8:1222017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li J, Zhang J, Chen Y, Kawazoe N and Chen
G: TEMPO-conjugated gold nanoparticles for reactive oxygen species
scavenging and regulation of stem cell differentiation. ACS Appl
Mater Interfaces. 9:35683–35692. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kumar Y, Biswas T, Thacker G, Kanaujiya
JK, Kumar S, Shukla A, Khan K, Sanyal S, Chattopadhyay N,
Bandyopadhyay A and Trivedi AK: BMP signaling-driven osteogenesis
is critically dependent on Prdx-1 expression-mediated maintenance
of chondrocyte prehypetrophy. Free Radic Biol Med. 118:1–12. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dioufa N, Schally AV, Chatzistamou I,
Moustou E, Block NL, Owens GK, Papavassiliou AG and Kiaris H:
Acceleration of wound healing by growth hormone-releasing hormone
and its agonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:18611–18615. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lim JE, Chung E and Son Y: A neuropeptide,
Substance-P, directly induces tissue-repairing M2 like macrophages
by activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway even in the presence of
IFNγ. Sci Rep. 7:94172017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Oh TS, Cho H, Cho JH, Yu SW and Kim EK:
Hypothalamic AMPK-induced autophagy increases food intake by
regulating NPY and POMC expression. Autophagy. 12:2009–2025. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Aveleira CA, Botelho M, Carmo-Silva S,
Pascoal JF, Ferreira-Marques M, Nóbrega C, Cortes L, Valero J,
Sousa-Ferreira L, Álvaro AR, et al: Neuropeptide Y stimulates
autophagy in hypothalamic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:E1642–E1651. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Atashi F, Modarressi A and Pepper MS: The
role of reactive oxygen species in mesenchymal stem cell adipogenic
and osteogenic differentiation: A review. Stem Cells Dev.
24:1150–1163. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hong HS and Son Y: Substance P ameliorates
collagen II-induced arthritis in mice via suppression of the
inflammatory response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 453:179–184.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim SJ, Kim JE, Kim SH, Kim SJ, Jeon SJ,
Kim SH and Jung Y: Therapeutic effects of neuropeptide substance P
coupled with self-assembled peptide nanofibers on the progression
of osteoarthritis in a rat model. Biomaterials. 74:119–130. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang L, Di G, Qi X, Qu M, Wang Y, Duan H,
Danielson P, Xie L and Zhou Q: Substance P promotes diabetic
corneal epithelial wound healing through molecular mechanisms
mediated via the neurokinin-1 receptor. Diabetes. 63:4262–4274.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin
MJ, Abeliovich H, Acevedo Arozena A, Adachi H, Adams CM, Adams PD,
Adeli K, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays
for monitoring autophagy 3rd edition). Autophagy. 12:1–222. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Roffi A, Krishnakumar GS, Gostynska N, Kon
E, Candrian C and Filardo G: The role of Three-dimensional
scaffolds in treating long bone defects: Evidence from preclinical
and clinical Literature-A systematic review. Biomed Res Int.
2017:80741782017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tormos KV, Anso E, Hamanaka RB, Eisenbart
J, Joseph J, Kalyanaraman B and Chandel NS: Mitochondrial complex
III ROS regulate adipocyte differentiation. Cell Metab. 14:537–544.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang K, Zhang T, Dong Q, Nice EC, Huang C
and Wei Y: Redox homeostasis: The linchpin in stem cell
self-renewal and differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 4:e5372013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen H, Liu X, Chen H, Cao J, Zhang L, Hu
X and Wang J: Role of SIRT1 and AMPK in mesenchymal stem cells
differentiation. Ageing Res Rev. 13:55–64. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen CT, Shih YR, Kuo TK, Lee OK and Wei
YH: Coordinated changes of mitochondrial biogenesis and antioxidant
enzymes during osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem
cells. Stem Cells. 26:960–968. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang S, Liu Y and Liang Q: Low-dose
dexamethasone affects osteoblast viability by inducing autophagy
via intracellular ROS. Mol Med Rep. 17:4307–4316. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shen C, Cai GQ, Peng JP and Chen XD:
Autophagy protects chondrocytes from glucocorticoids-induced
apoptosis via ROS/Akt/FOXO3 signaling. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
23:2279–2287. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang L, Zhao X, Wei BY, Liu Y, Ma XY, Wang
J, Cao PC, Zhang Y, Yan YB, Lei W and Feng YF: Insulin improves
osteogenesis of titanium implants under diabetic conditions by
inhibiting reactive oxygen species overproduction via the PI3K-Akt
pathway. Biochimie. 108:85–93. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Reikvam H, Brenner AK, Hagen KM, Liseth K,
Skrede S, Hatfield KJ and Bruserud Ø: The cytokine-mediated
crosstalk between primary human acute myeloid cells and mesenchymal
stem cells alters the local cytokine network and the global gene
expression profile of the mesenchymal cells. Stem Cell Res.
15:530–541. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gómez-Puerto MC, Verhagen LP, Braat AK,
Lam EW, Coffer PJ and Lorenowicz MJ: Activation of autophagy by
FOXO3 regulates redox homeostasis during osteogenic
differentiation. Autophagy. 12:1804–1816. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim H, Lee YD, Kim HJ, Lee ZH and Kim HH:
SOD2 and Sirt3 control osteoclastogenesis by regulating
mitochondrial ROS. J Bone Miner Res. 32:397–406. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Y, Chen G, Yan J, Chen X, He F, Zhu
C, Zhang J, Lin J, Pan G, Yu J, et al: Upregulation of SIRT1 by
kartogenin enhances antioxidant functions and promotes osteogenesis
in human mesenchymal stem cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018:13681422018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liao L, Su X, Yang X, Hu C, Li B, Lv Y,
Shuai Y, Jing H, Deng Z and Jin Y: TNF-α inhibits FoxO1 by
upregulating miR-705 to aggravate oxidative damage in bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells during osteoporosis. Stem
Cells. 34:1054–1067. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Abnosi MH and Yari S: The toxic effect of
gallic acid on biochemical factors, viability and proliferation of
rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells was compensated by boric
acid. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 48:246–253. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fu S, Mei G, Wang Z, Zou ZL, Liu S, Pei
GX, Bi L and Jin D: Neuropeptide substance P improves osteoblastic
and angiogenic differentiation capacity of bone marrow stem cells
in vitro. Biomed Res Int. 2014:5960232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Galluzzi L, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Levine B,
Green DR and Kroemer G: Pharmaological modulation of autophagy:
Therapeutic potential and persisting obstacles. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 16:487–511. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|