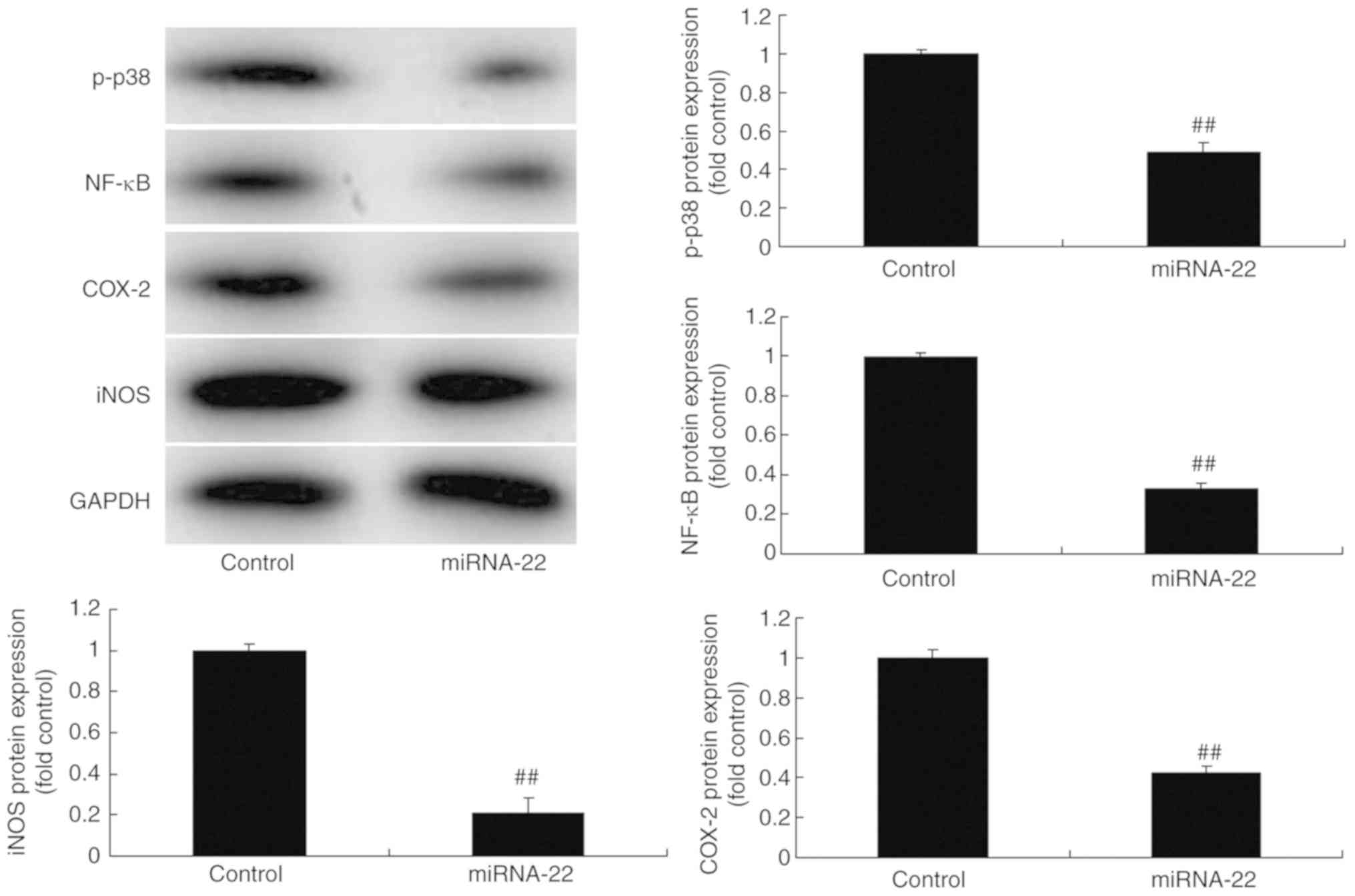
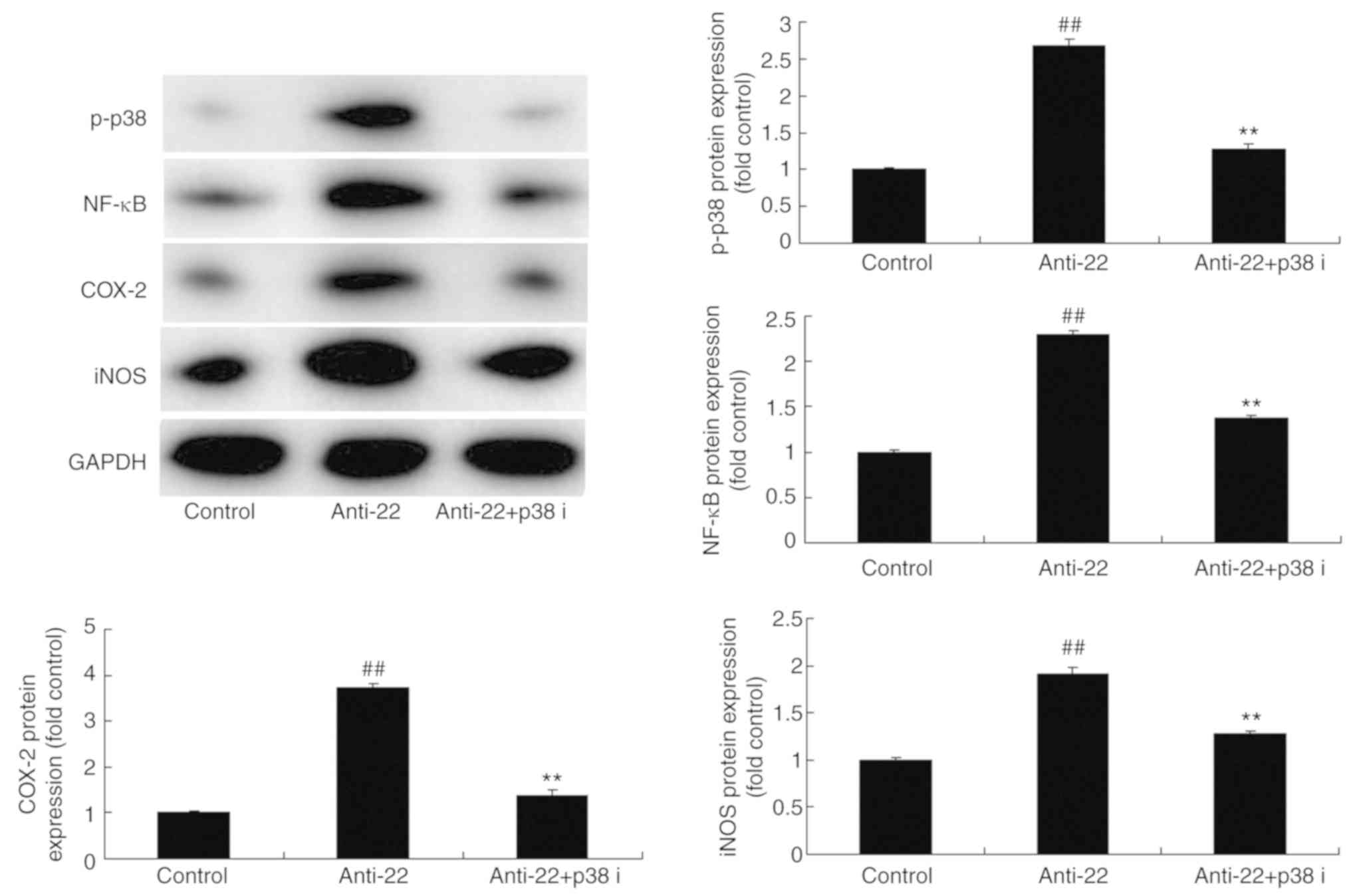
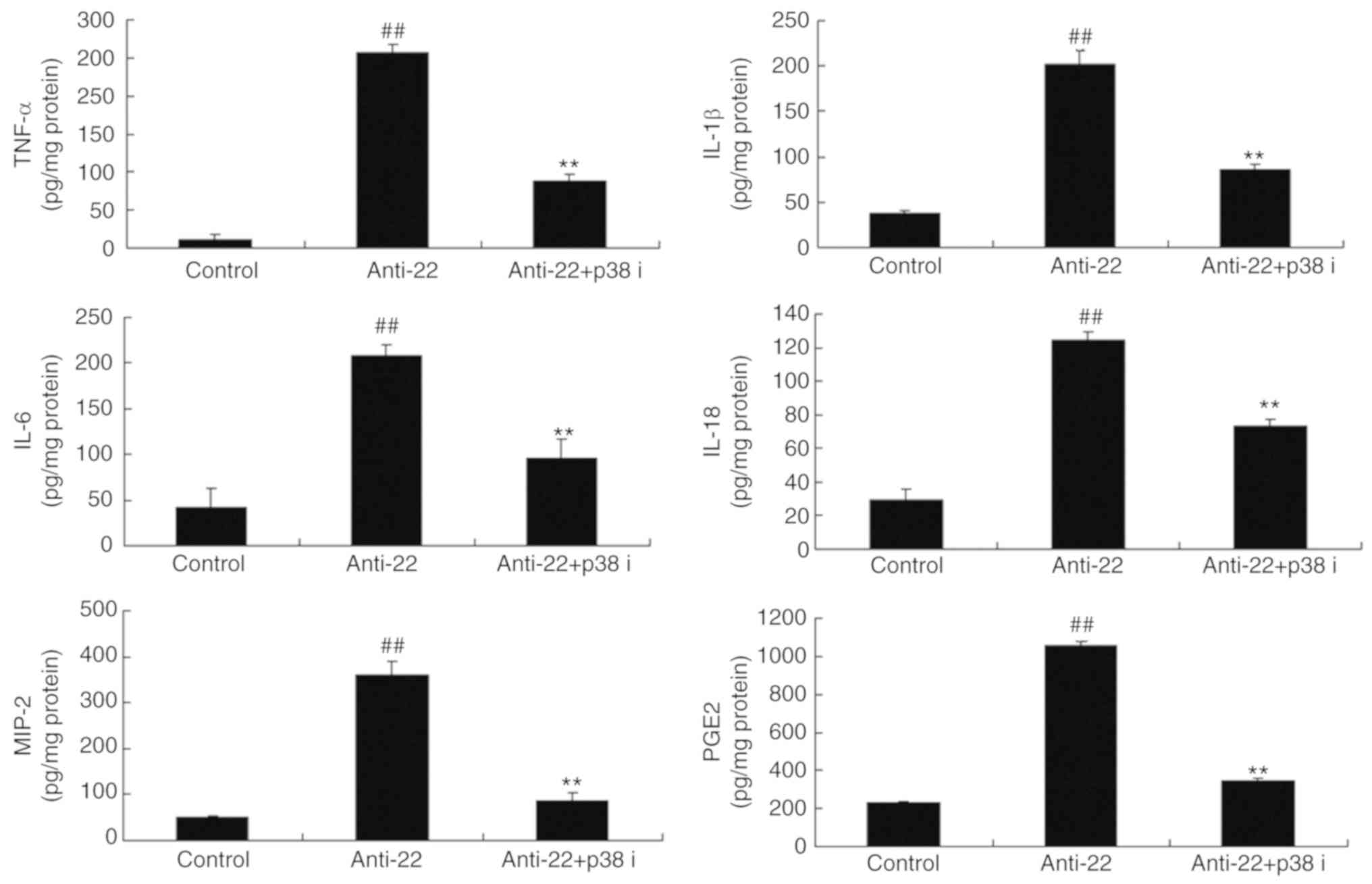
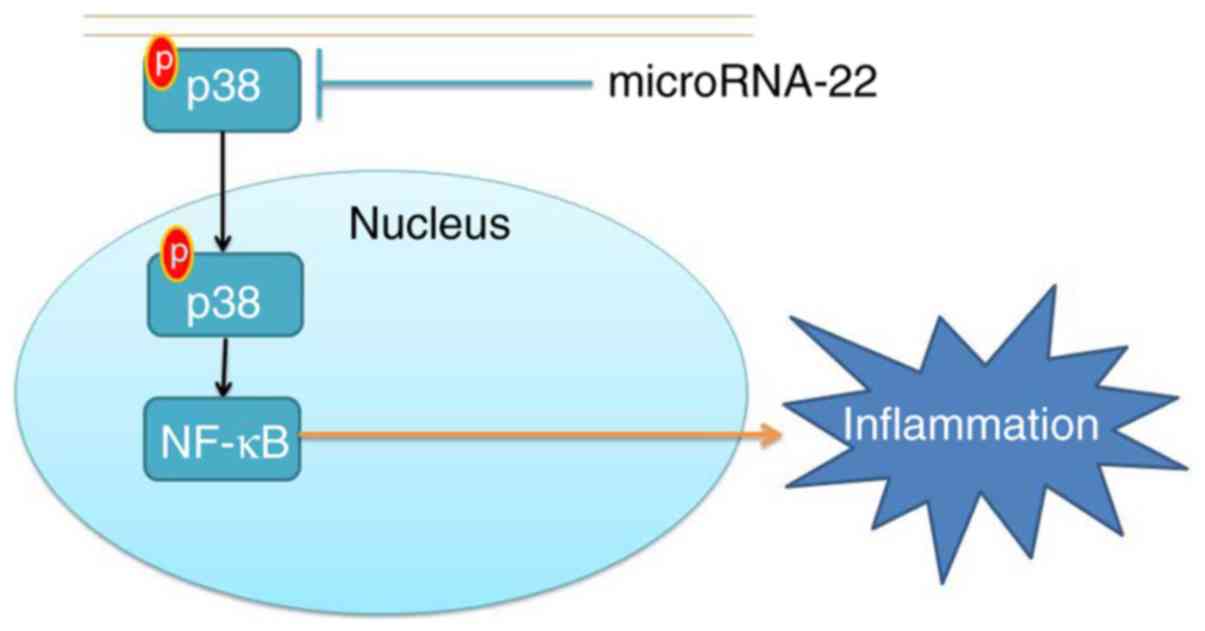
|
1
|
Luo F, Liu J, Yan T and Miao M:
Salidroside alleviates cigarette smoke-induced COPD in mice. Biomed
Pharmacother. 86:155–161. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhao Y, Peng R, Zhao W, Liu Q, Guo Y, Zhao
S and Xu D: Zhibitai and low-dose atorvastatin reduce blood lipids
and inflammation in patients with coronary artery disease. Medicine
(Baltimore). 96:e61042017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sun P, Song SZ, Jiang S, Li X, Yao YL, Wu
YL, Lian LH and Nan JX: Salidroside regulates inflammatory response
in raw 264.7 macrophages via TLR4/TAK1 and ameliorates inflammation
in alcohol binge drinking-induced liver injury. Molecules.
21:E14902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mello EA, Cohen LG, Monteiro Dos Anjos S,
Conti J, Andrade KN, Tovar Moll F, Marins T, Fernandes CA,
Rodrigues W Jr and Conforto AB: Increase in short-interval
intracortical facilitation of the motor cortex after low-frequency
repetitive magnetic stimulation of the unaffected hemisphere in the
subacute phase after stroke. Neural Plast. 2015:4073202015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Blesneag AV, Slavoaca DF, Popa L, Stan AD,
Jemna N, Isai Moldovan F and Mureșanu F: Low-frequency rTMS in
patients with subacute ischemic stroke: Clinical evaluation of
short and long-term outcomes and neurophysiological assessment of
cortical excitability. J Med Life. 8:378–387. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Koh GC, Yen SC, Tay A, Cheong A, Ng YS, De
Silva DA, Png C, Caves K, Koh K, Kumar Y, et al: Singapore
tele-technology aided rehabilitation in stroke (STARS) trial:
Protocol of a randomized clinical trial on tele-rehabilitation for
stroke patients. BMC Neurol. 15:1612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Piaggesi A, Sambataro M, Nicoletti C,
Goretti C, Lacopi E and Coppelli A: Safety and effectiveness of
therapeutic magnetic resonance in diabetic foot ulcers: A
prospective randomised controlled trial. J Wound Care. 25:704–711.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu ZR, Ran XW, Xian Y, Yan XD, Yuan GY, Mu
SM, Shen JF, Zhang BS, Gan WJ and Wang J: Ertapenem versus
piperacillin/tazobactam for diabetic foot infections in China: A
Phase 3, multicentre, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled,
non-inferiority trial. J Antimicrob Chemother. 71:1688–1696. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
You HJ, Han SK and Rhie JW: Randomised
controlled clinical trial for autologous fibroblast-hyaluronic acid
complex in treating diabetic foot ulcers. J Wound Care. 23:521–522,
524, 526–530. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Amoli MM, Hasani-Ranjbar S, Roohipour N,
Sayahpour FA, Amiri P, Zahedi P, Mehrab-Mohseni M, Heshmat R,
Larijani B and Tavakkoly-Bazzaz J: VEGF gene polymorphism
association with diabetic foot ulcer. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
93:215–219. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Drela E, Kulwas A, Jundzill W, Góralczyk
B, Boinska J, Drewniak W, Gadomska G and Rość D: VEGF-A and PDGF-BB
- angiogenic factors and the stage of diabetic foot syndrome
advancement. Endokrynol Pol. 65:306–312. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang F, Ren Y, Liu P, Ren Y and Wang D:
Expression of TGF-beta1 and miRNA-145 in patients with diabetic
foot ulcers. Exp Ther Med. 11:2011–2014. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Madhyastha R, Madhyastha H, Nakajima Y,
Omura S and Maruyama M: MicroRNA signature in diabetic wound
healing: Promotive role of miR-21 in fibroblast migration. Int
Wound J. 9:355–361. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Agh F, Mohammadzadeh Honarvar N, Djalali
M, Nematipour E, Gholamhoseini S, Zarei M, Ansari S and Javanbakht
MH: Omega-3 fatty acid could increase one of myokines in male
patients with coronary artery disease: A randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. Arch Iran Med. 20:28–33. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Q, Du GQ, Zhu ZT, Zhang C, Sun XW, Liu
JJ, Li X, Wang YS and Du WJ: Identification of apoptosis-related
microRNAs and their target genes in myocardial infarction
post-transplantation with skeletal myoblasts. J Transl Med.
13:2702015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Iekushi K, Seeger F, Assmus B, Zeiher AM
and Dimmeler S: Regulation of cardiac microRNAs by bone marrow
mononuclear cell therapy in myocardial infarction. Circulation.
125:1765–1773. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Salic K and De Windt LJ: MicroRNAs as
biomarkers for myocardial infarction. Curr Atheroscler Rep.
14:193–200. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jovicic A, Zaldivar Jolissaint JF, Moser
R, Silva Santos Mde F and Luthi-Carter R: MicroRNA-22 (miR-22)
overexpression is neuroprotective via general anti-apoptotic
effects and may also target specific Huntington's disease-related
mechanisms. PLoS One. 8:e542222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao J, Mou Y, Bernstock JD, Klimanis D,
Wang S, Spatz M, Maric D, Johnson K, Klinman DM, Li X, et al:
Synthetic oligodeoxynucleotides containing multiple telemeric
TTAGGG motifs suppress inflammasome activity in macrophages
subjected to oxygen and glucose deprivation and reduce ischemic
brain injury in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. PLoS
One. 10:e01407722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ha TS, Hong EJ and Han GD: Diabetic
conditions downregulate the expression of CD2AP in podocytes via
PI3-K/Akt signalling. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 31:50–60. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kandhare AD, Ghosh P and Bodhankar SL:
Naringin, a flavanone glycoside, promotes angiogenesis and inhibits
endothelial apoptosis through modulation of inflammatory and growth
factor expression in diabetic foot ulcer in rats. Chem Biol
Interact. 219:101–112. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang J, Chen L, Ding J, et al:
Cardioprotective effect of miRNA-22 on hypoxia/reoxygenation
induced cardiomyocyte injury in neonatal rats. Gene. 579:17–22.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim SH, Kim HJ and Kim CW: GLCCI1 is a
novel component associated with the PI3K signaling pathway in
podocyte foot processes. Exp Mol Med. 48:e2332016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Blume PA, Walters J, Payne W, Ayala J and
Lantis J: Comparison of negative pressure wound therapy using
vacuum-assisted closure with advanced moist wound therapy in the
treatment of diabetic foot ulcers: A multicenter randomized
controlled trial. Diabetes Care. 31:631–636. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Morley S, Griffiths J, Philips G, Moseley
H, O'Grady C, Mellish K, Lankester CL, Faris B, Young RJ, Brown SB
and Rhodes LE: Phase IIa randomized, placebo-controlled study of
antimicrobial photodynamic therapy in bacterially colonized,
chronic leg ulcers and diabetic foot ulcers: A new approach to
antimicrobial therapy. Br J Dermatol. 168:617–624. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fan P, He L, Hu N, et al: Effect of
1,25-(OH)2D3 on Proliferation of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes and
Expressions of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines through Regulating
MicroRNA-22 in a Rat Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 42:145–155. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liang L, Stone RC, Stojadinovic O, Ramirez
H, Pastar I, Maione AG, Smith A, Yanez V, Veves A, Kirsner RS, et
al: Integrative analysis of miRNA and mRNA paired expression
profiling of primary fibroblast derived from diabetic foot ulcers
reveals multiple impaired cellular functions. Wound Repair Regen.
24:943–953. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang J, Sun XJ, Chen J, Hu ZW, Wang L, Gu
DM and Wang AP: Increasing the miR-126 expression in the peripheral
blood of patients with diabetic foot ulcers treated with maggot
debridement therapy. J Diabetes Complications. 31:241–244. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Isner JM, Ropper A and Hirst K: VEGF gene
transfer for diabetic neuropathy. Hum Gene Ther. 12:1593–1594.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Laurents DV, Gorman PM, Guo M, Rico M,
Chakrabartty A and Bruix M: Alzheimer's Abeta40 studied by NMR at
low pH reveals that sodium 4,4-dimethyl-4-silapentane-1-sulfonate
(DSS) binds and promotes beta-ball oligomerization. J Biol Chem.
280:3675–3685. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liang X, Liu Y, Mei S, et al: MicroRNA-22
impairs anti-tumor ability of dendritic cells by targeting p38.
PLoS One. 10:e01215102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|