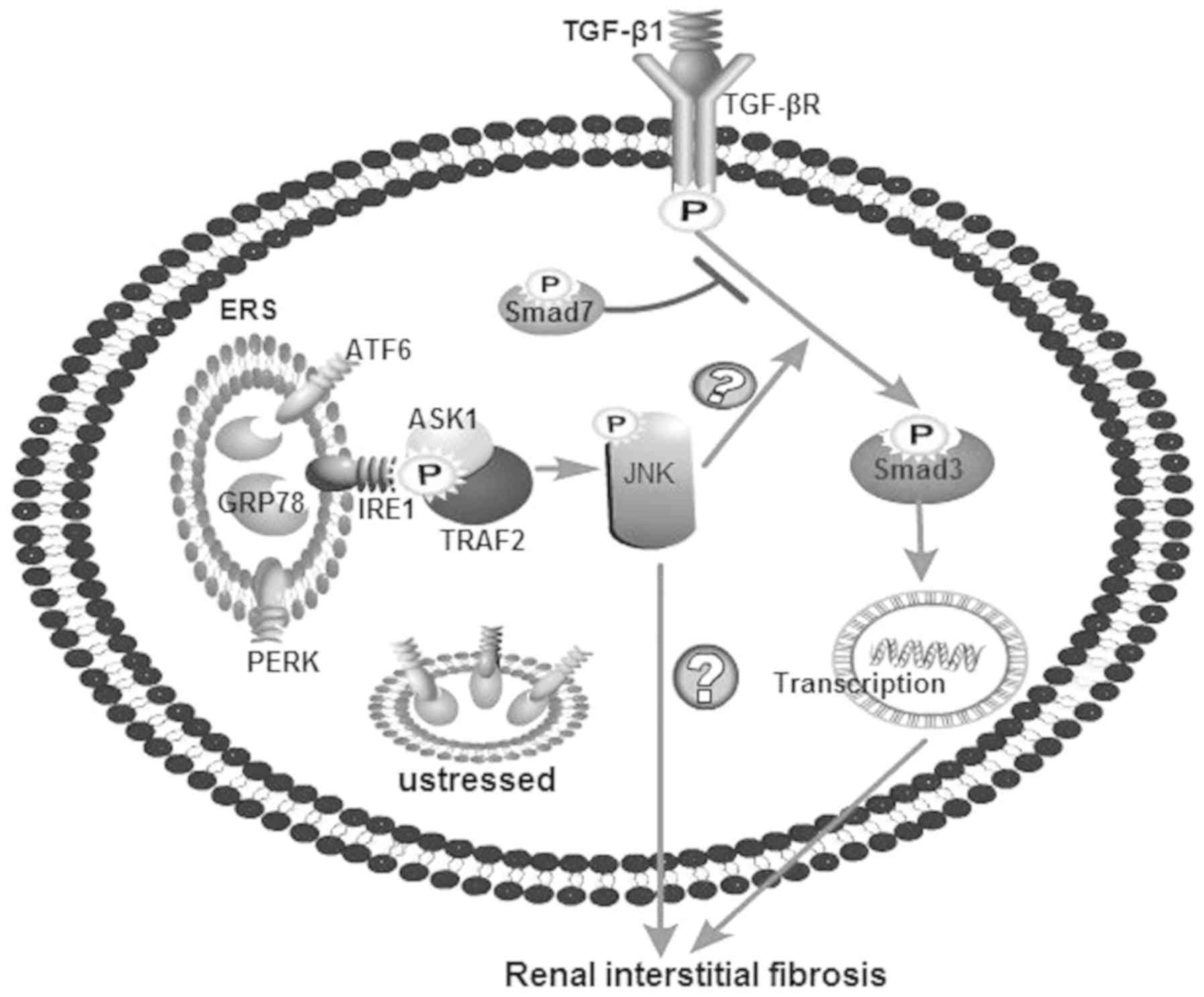
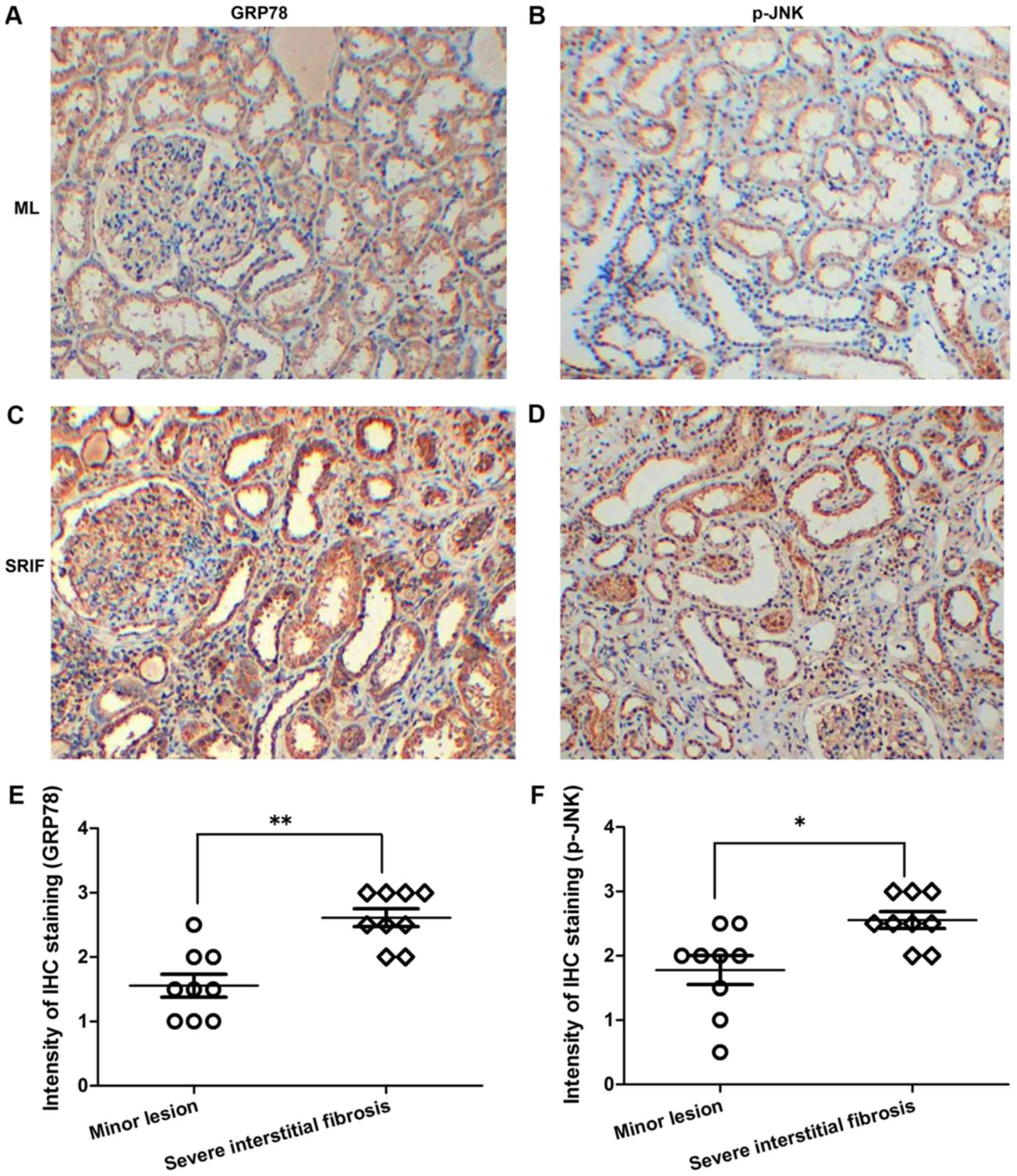
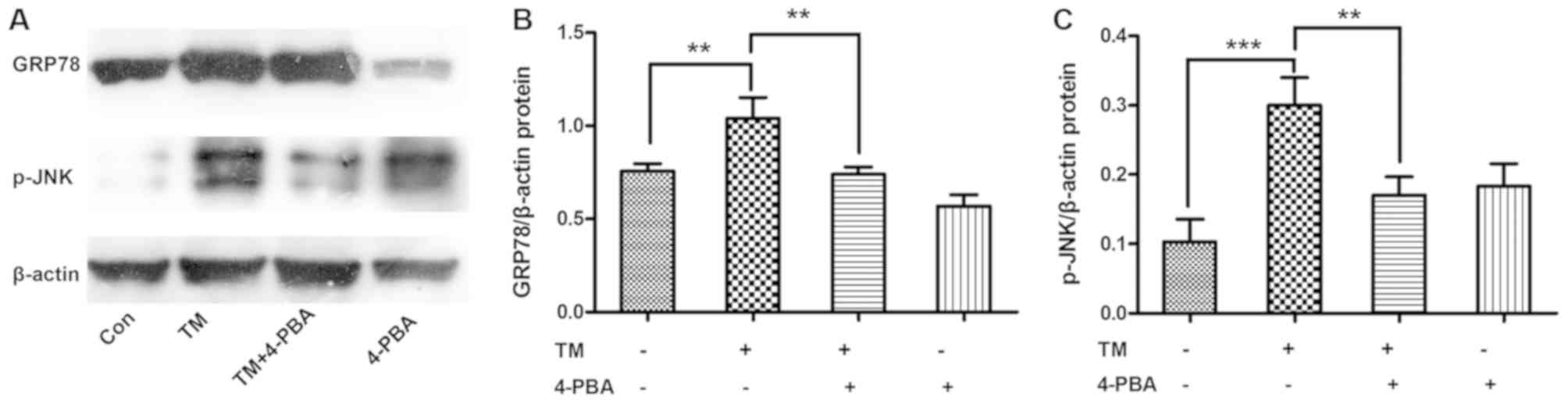
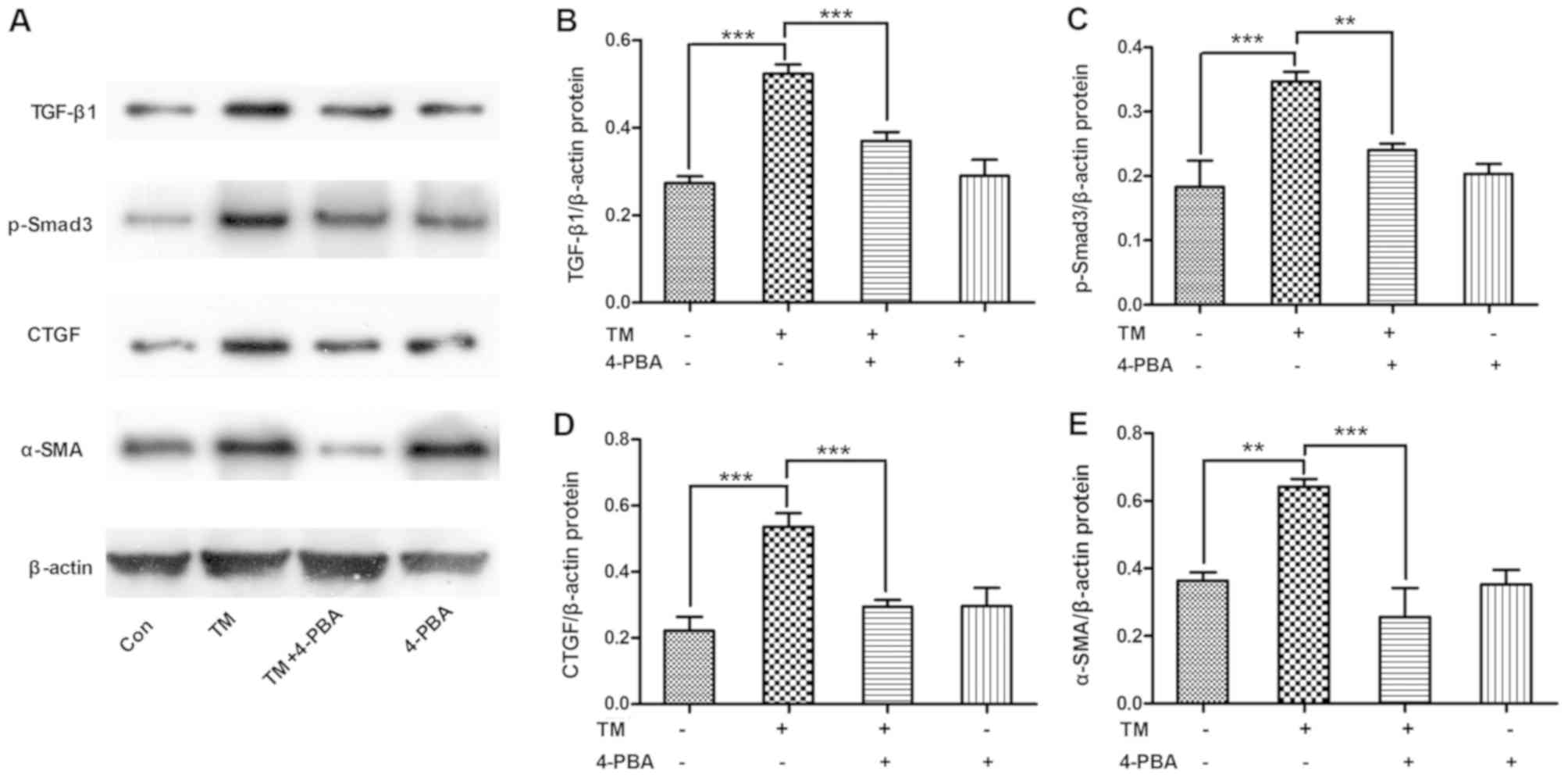
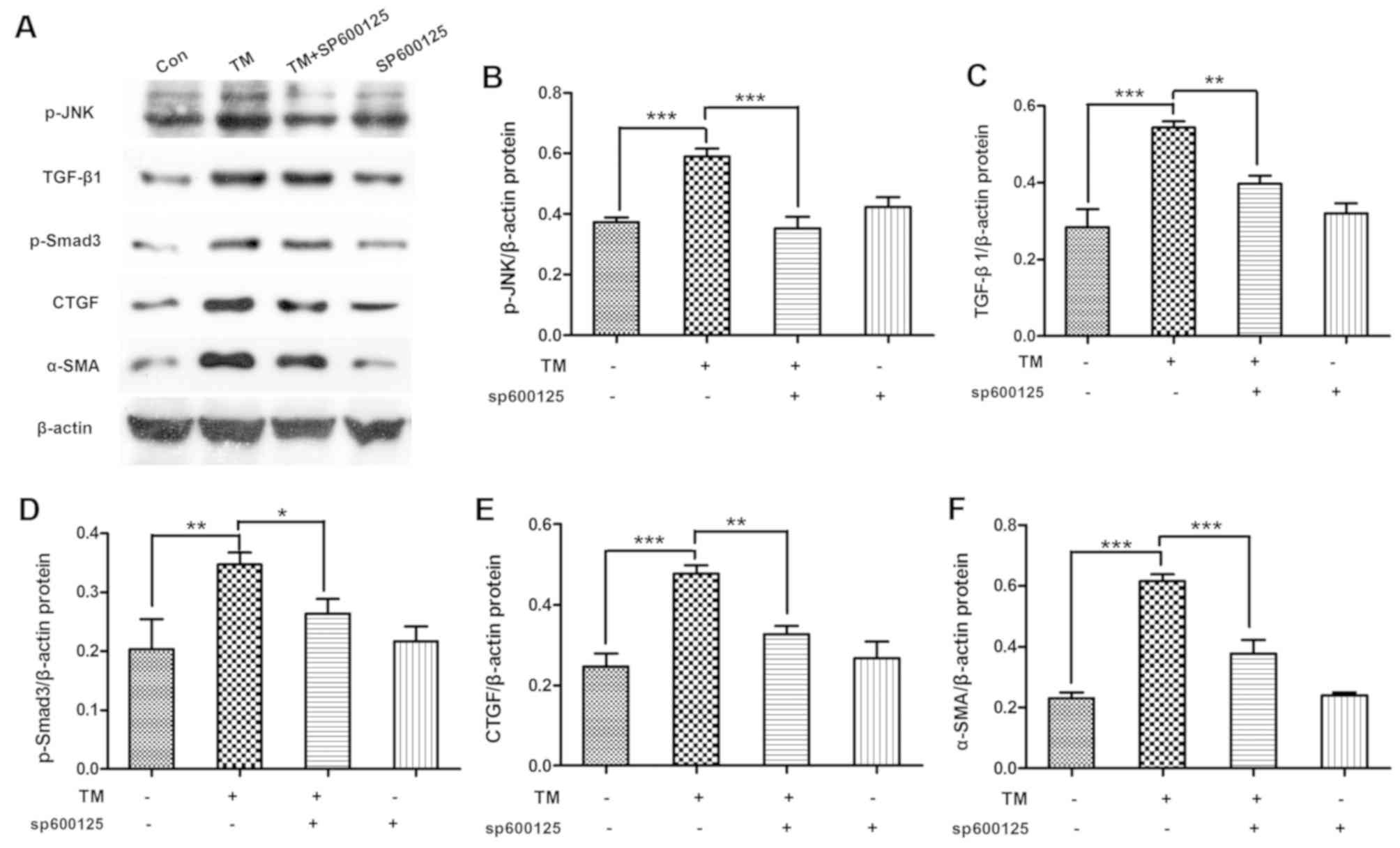
|
1
|
Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K, Li Z,
Naicker S, Plattner B, Saran R, Wang AY and Yang CW: Chronic kidney
disease: Global dimension and perspectives. Lancet. 382:260–272.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Collister D, Ferguson T, Komenda P and
Tangri N: The patterns, risk factors, and prediction of progression
in chronic kidney disease: A narrative review. Semin Nephrol.
36:273–282. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Boor P, Ostendorf T and Floege J: Renal
fibrosis: Novel insights into mechanisms and therapeutic targets.
Nat Rev Nephrol. 6:643–656. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chiang CK, Hsu SP, Wu CT, Huang JW, Cheng
HT, Chang YW, Hung KY, Wu KD and Liu SH: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress implicated in the development of renal fibrosis. Mol Med.
17:1295–1305. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Piret SE, Olinger E, Reed AAC, Nesbit MA,
Hough TA, Bentley L, Devuyst O, Cox RD and Thakker RV: A mouse
model for inherited renal fibrosis associated with endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Dis Model Mech. 10:773–786. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ke B, Zhu N, Luo F, Xu Y and Fang X:
Targeted inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress: New hope for
renal fibrosis (Review). Mol Med Rep. 16:1014–1020. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dickhout JG and Krepinsky JC: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and renal disease. Antioxid Redox Signal.
11:2341–2352. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Inagi R, Ishimoto Y and Nangaku M:
Proteostasis in endoplasmic reticulum-new mechanisms in kidney
disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 10:369–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee H, Noh JY, Oh Y, Kim Y, Chang JW,
Chung CW, Lee ST, Kim M, Ryu H and Jung YK: IRE1 plays an essential
role in ER stress-mediated aggregation of mutant hunting in via the
inhibition of autophagy flux. Hum Mol Genet. 21:101–114. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zheng QY, Li PP, Jin FS, Yao C, Zhang GH,
Zang T and Ai X: Ursolic acid induces ER stress response to
activate ASK1-JNK signaling and induce apoptosis in human bladder
cancer T24 cells. Cell Signal. 25:206–213. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Davis RJ: Signal transduction by the JNK
group of MAP kinases. Cell. 103:239–252. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hocevar BA, Brown TL and Howe PH: TGF-beta
induces fibronectin synthesis through a c-Jun N-terminal
kinase-dependent, Smad4-independent pathway. EMBO J. 18:1345–1356.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Utsugi M, Dobashi K, Ishizuka T, Masubuchi
K, Shimizu Y, Nakazawa T and Mori M: C-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase
mediates expression of connective tissue growth factor induced by
transforming growth factor-beta1 in human lung fibroblasts. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 28:754–761. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ma FY, Flanc RS, Tesch GH, Han Y, Atkins
RC, Bennett BL, Friedman GC, Fan JH and Nikolic-Paterson DJ: A
pathogenic role for c-Jun amino-terminal kinase signaling in renal
fibrosis and tubular cell apoptosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 18:472–484.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Q, Mao H, Nie J, Chen W, Yang Q, Dong
X and Yu X: Transforming growth factor {beta}1 induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by activating the JNK-Smad3
pathway in rat peritoneal mesothelial cells. Perit Dial Int. 3
(Suppl 28):S88–S95. 2008.
|
|
16
|
Liu SH, Yang CC, Chan DC, Wu CT, Chen LP,
Huang JW, Hung KY and Chiang CK: Chemical chaperon 4-phenylbutyrate
protects against the endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated renal
fibrosis in vivo and in vitro. Oncotarget. 7:22116–22127.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
National Kidney Foundation: K/DOQI
clinical practice guidelinesfor chronic kidney disease: Evaluation,
classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 39 (Suppl
1):S1–S266. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Churg J, Bernstein J and Glassock RJ:
Renal Disease: Classification and atlas of glomerular diseases.
2nd. Igaku-Shoin Ltd.; Tokyo: 1995
|
|
19
|
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL,
Castro AF III, Feldman HI, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Greene
T, et al: A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate.
Ann Intern Med. 150:604–612. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chang JW, Kim H, Baek CH, Lee RB, Yang WS
and Lee SK: Up-regulation of SIRT1 reduces endoplasmic reticulum
stress and renal fibrosis. Nephron. 133:116–128. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu S, Wang Y, Jin J, Guan C, Li M, Xi C,
Ouyang Z, Chen M, Qiu Y, Huang M and Huang Z: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress mediates aristolochic acid I-induced apoptosis in human
renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Toxicol In Vitro.
26:663–671. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hirai Y, Iyoda M, Shibata T, Kuno Y,
Kawaguchi M, Hizawa N, Matsumoto K, Wada Y, Kokubu F and Akizawa T:
IL-17A stimulates granulocyte colony-stimulating factor production
via ERK1/2 but not p38 or JNK in human renal proximal tubular
epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 302:F244–F250. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hewitson TD: Renal tubulointerstitial
fibrosis: Common but never simple. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
296:F1239–F1244. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Q, Usinger W, Nichols B, Gray J, Xu
L, Seeley TW, Brenner M, Guo G, Zhang W, Oliver N, et al:
Cooperative interaction of CTGF and TGF-β in animal models of
fibrotic disease. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 4:42011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yeh YC, Wei WC, Wang YK, Lin SC, Sung JM
and Tang MJ: Transforming growth factor-{beta}1 induces
Smad3-dependent {beta}1 integrin gene expression in
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition during chronic
tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 177:1743–1754. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Meng XM, Huang XR, Xiao J, Chung AC, Qin
W, Chen HY and Lan HY: Disruption of Smad4 impairs TGF-β/Smad3 and
Smad7 transcriptional regulation during renal inflammation and
fibrosis in vivo and in vitro. Kidney Int. 81:266–279. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lan HY: Diverse roles of TGF-β/Smads in
renal fibrosis and inflammation. Int J Biol Sci. 7:1056–1067. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Meng XM, Huang XR, Chung AC, Qin W, Shao
X, Igarashi P, Ju W, Bottinger EP and Lan HY: Smad2 protects
against TGF-beta/Smad3-mediated renal fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol.
21:1477–1487. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Grotendorst GR: Connective tissue growth
factor: A mediator of TGF-beta action on fibroblasts. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 8:171–179. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yokoi H, Sugawara A, Mukoyama M, Mori K,
Makino H, Suganami T, Nagae T, Yahata K, Fujinaga Y, Tanaka I and
Nakao K: Role of connective tissue growth factor in profibrotic
action of transforming growth factor-beta: A potential target for
preventing renal fibrosis. Am J Kidney Dis 38 (4 Suppl 1).
S134–S138. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Grande MT and Lopez-Novoa JM: Fibroblast
activation and myofibroblast generation in obstructive nephropathy.
Nat Rev Nephrol. 5:319–328. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao X, Fu J, Xu A, Yu L, Zhu J, Dai R, Su
B, Luo T, Li N, Qin W, et al: Gankyrin drives malignant
transformation of chronic liver damage-mediated fibrosis via the
Rac1/JNK pathway. Cell Death Dis. 6:e17512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bulut G, Kurdoglu Z, Dönmez YB, Kurdoglu M
and Erten R: Effects of jnk inhibitor on inflammation and fibrosis
in the ovary tissue of a rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:8774–8785. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|