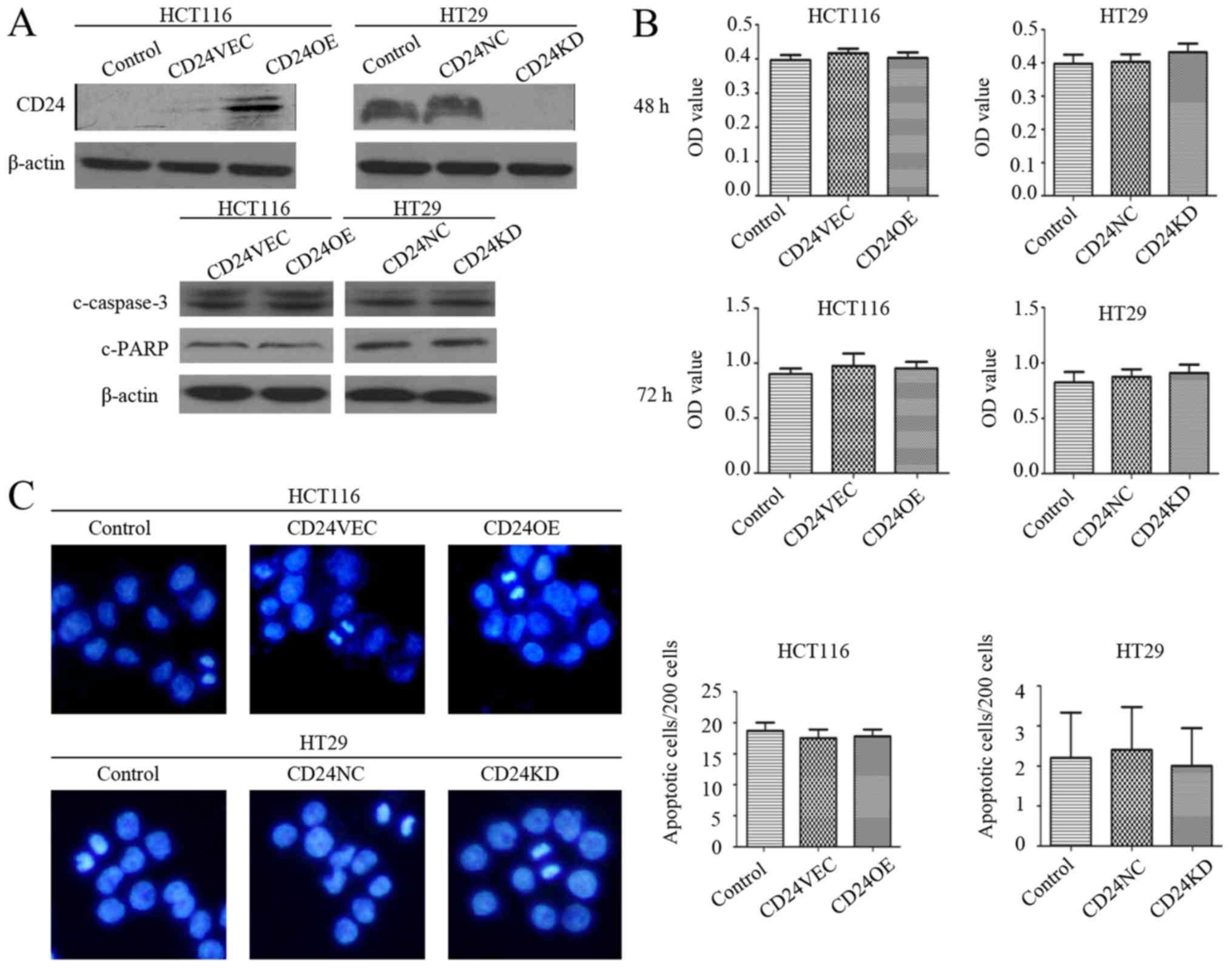
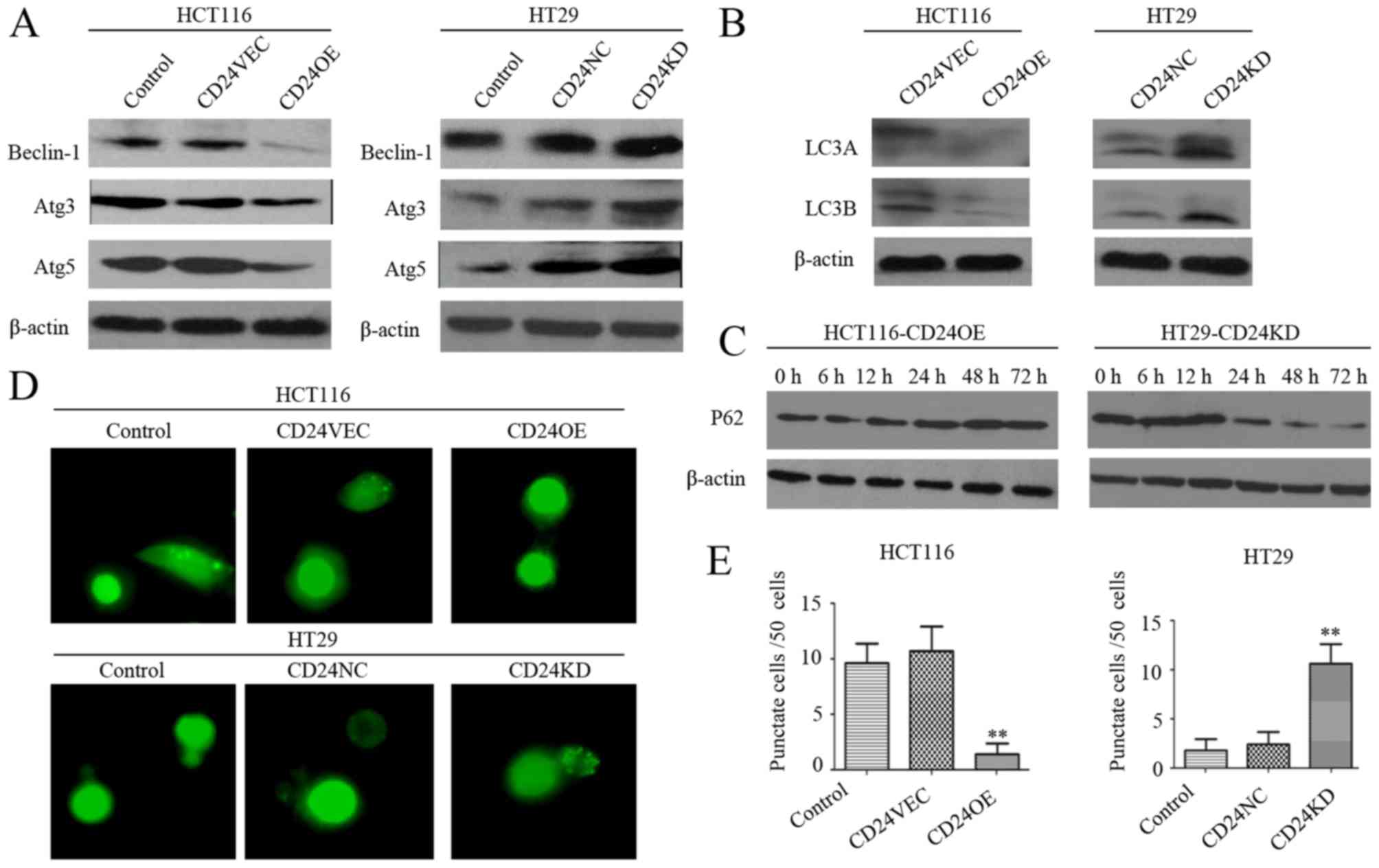
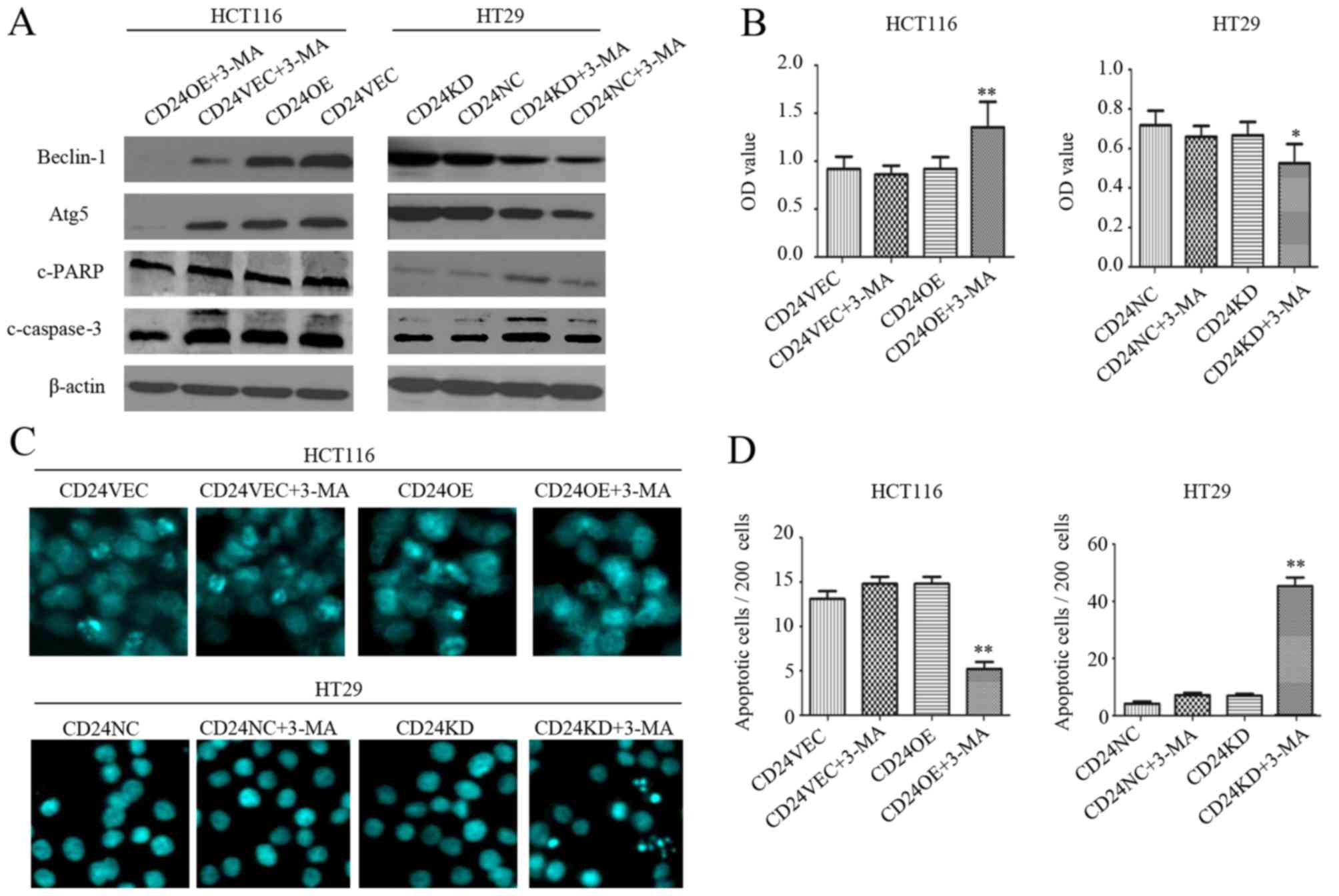
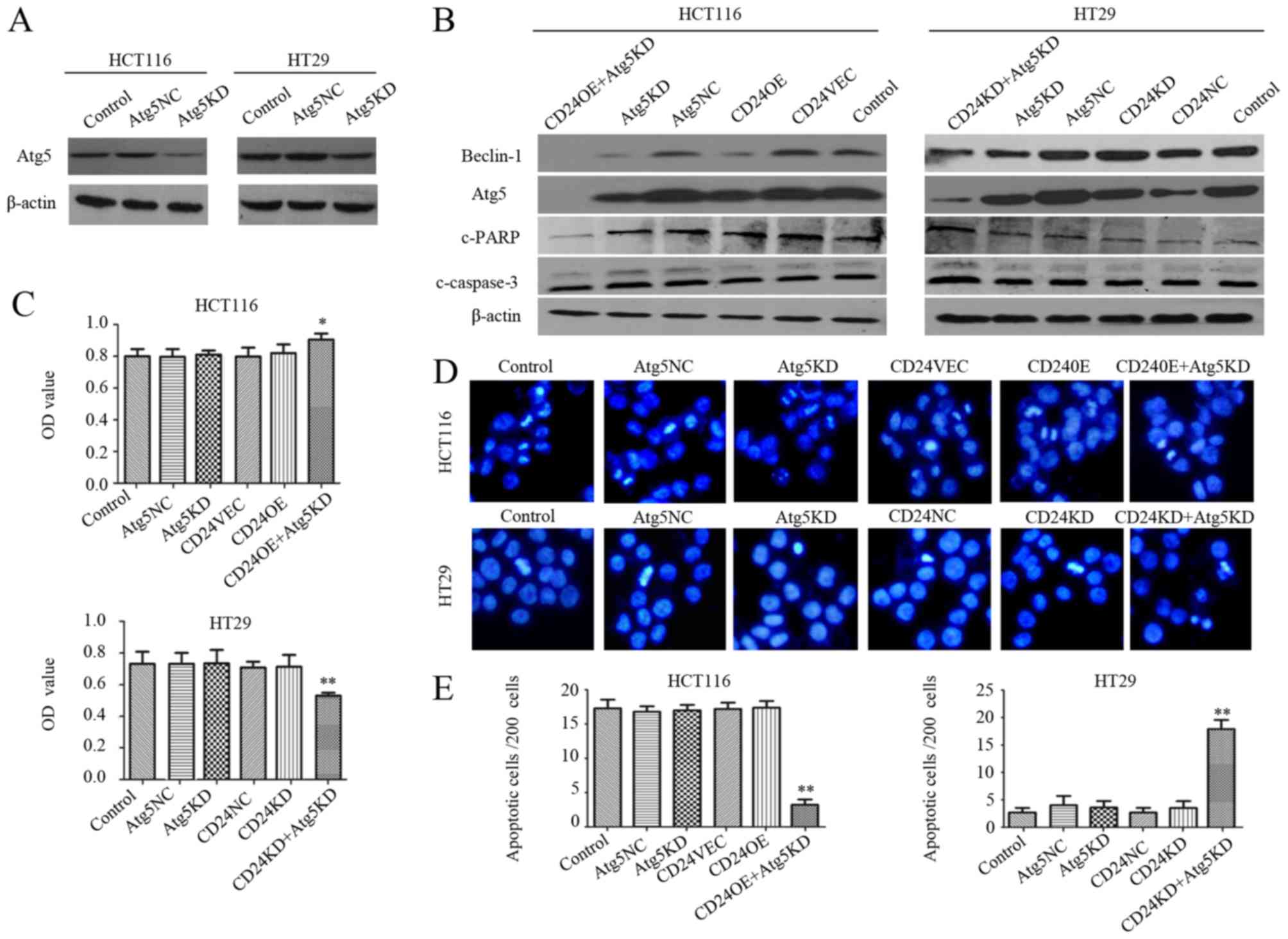
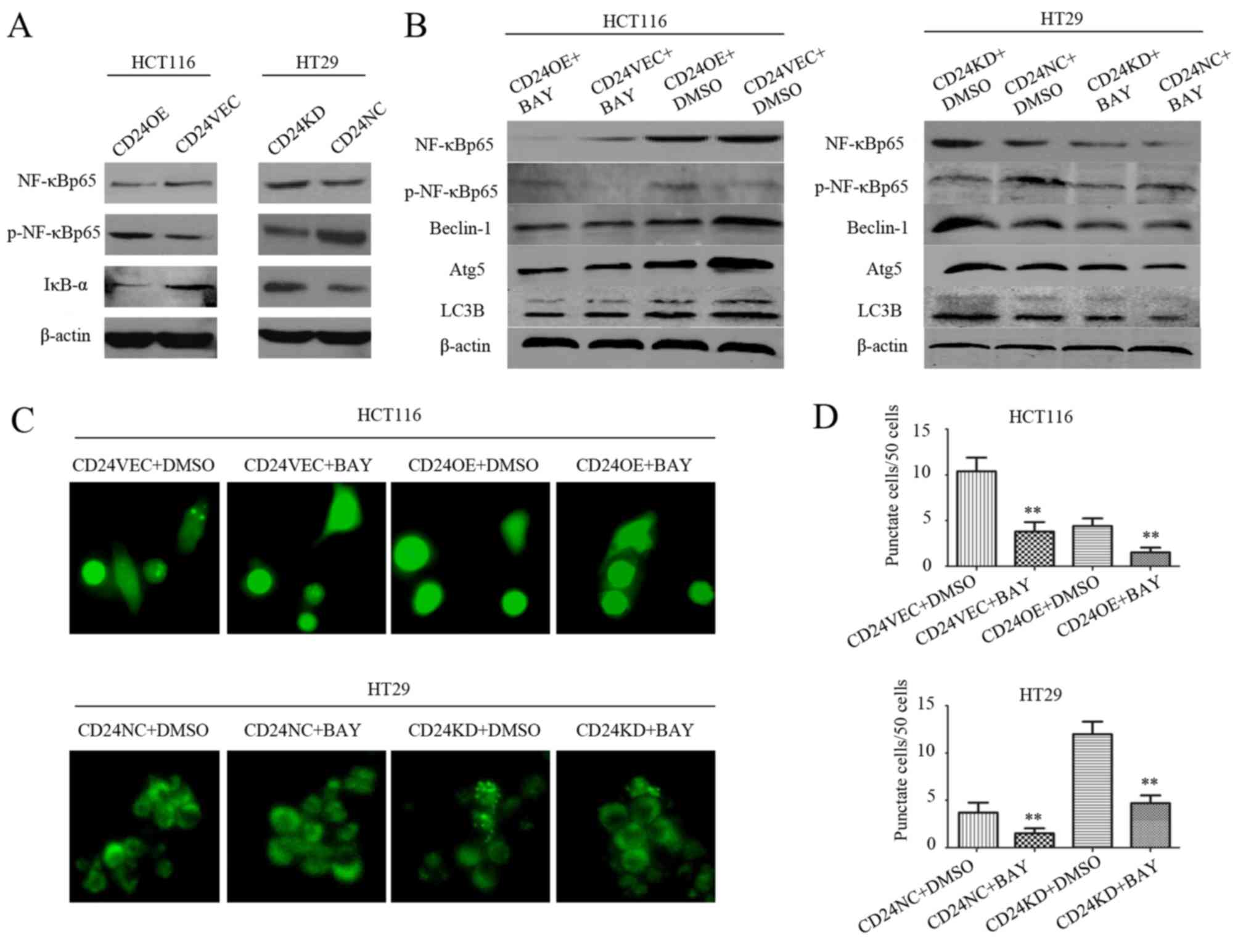
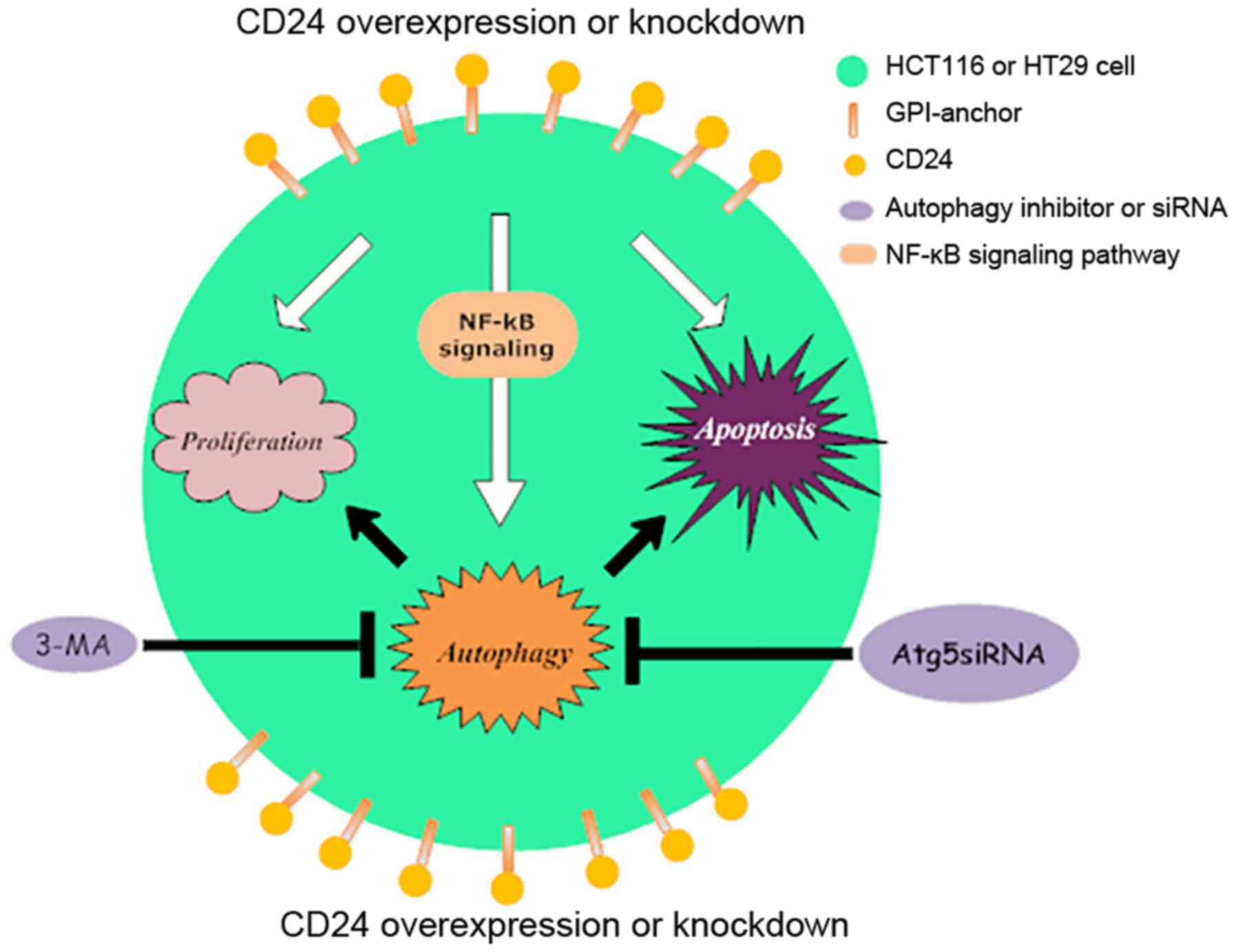
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kuipers EJ, Grady WM, Lieberman D,
Seufferlein T, Sung JJ, Boelens PG, van de Velde CJ and Watanabe T:
Colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 1:150652015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kerr D: Clinical development of gene
therapy for colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:615–622. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kuipers EJ, Rösch T and Bretthauer M:
Colorectal cancer screening-optimizing current strategies and new
directions. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 10:130–142. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Palta M, Czito BG and Willett CG:
Colorectal cancer: Adjuvant chemotherapy for rectal cancer-an
unresolved issue. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 11:182–184. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kristiansen G, Sammar M and Altevogt P:
Tumour biological aspects of CD24, a mucin-like adhesion molecule.
J Mol Histol. 35:255–262. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eyvazi S, Kazemi B, Dastmalchi S and
Bandehpour M: Involvement of CD24 in multiple cancer related
pathways makes it an interesting new target for cancer therapy.
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 18:328–336. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sagiv E, Memeo L, Karin A, Kazanov D,
Jacob-Hirsch J, Mansukhani M, Rechavi G, Hibshoosh H and Arber N:
CD24 is a new oncogene, early at the multistep process of
colorectal cancer carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 131:630–639.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee JH, Kim SH, Lee ES and Kim YS: CD24
overexpression in cancer development and progression: A
meta-analysis. Oncol Rep. 22:1149–1156. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lim SC: CD24 and human carcinoma: Tumor
biological aspects. Biomed Pharmacother. 59 (Suppl 2):S351–S354.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang JL, Guo CR, Su WY, Chen YX, Xu J and
Fang JY: CD24 overexpression related to lymph node invasion and
poor prognosis of colorectal cancer. Clin Lab. 64:497–505. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Weichert W, Denkert C, Burkhardt M,
Gansukh T, Bellach J, Altevogt P, Dietel M and Kristiansen G:
Cytoplasmic CD24 expression in colorectal cancer independently
correlates with shortened patient survival. Clin Cancer Res.
11:6574–6581. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Duex JE, Owens C, Chauca-Diaz A, Dancik
GM, Vanderlinden LA, Ghosh D, Leivo MZ, Hansel DE and Theodorescu
D: Nuclear CD24 drives tumor growth and is predictive of poor
patient prognosis. Cancer Res. 77:4858–4867. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shapira S, Shapira A, Starr A, Kazanov D,
Kraus S, Benhar I and Arber N: An immunoconjugate of anti-CD24 and
pseudomonas exotoxin selectively kills human colorectal tumors in
mice. Gastroenterology. 140:935–946. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sagiv E, Starr A, Rozovski U, Khosravi R,
Altevogt P, Wang T and Arber N: Targeting CD24 for treatment of
colorectal and pancreatic cancer by monoclonal antibodies or small
interfering RNA. Cancer Res. 68:2803–2812. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ahmed MA, Jackson D, Seth R, Robins A,
Lobo DN, Tomlinson IP and Ilyas M: CD24 is upregulated in
inflammatory bowel disease and stimulates cell motility and colony
formation. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 16:795–803. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mizushima N and Komatsu M: Autophagy:
Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 147:728–741. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lozy F and Karantza V: Autophagy and
cancer cell metabolism. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 23:395–401. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen N and Karantza-Wadsworth V: Role and
regulation of autophagy in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1793:1516–1523. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rikiishi H: Novel insights into the
interplay between apoptosis and autophagy. Int J Cell Biol.
2012:3176452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tschan MP and Simon HU: The role of
autophagy in anticancer therapy: Promises and uncertainties. J
Intern Med. 268:410–418. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tsujimoto Y and Shimizu S: Another way to
die: Autophagic programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ. 12 (Suppl
2):S1528–S1534. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cecconi F and Levine B: The role of
autophagy in mammalian development: Cell makeover rather than cell
death. Dev Cell. 15:344–357. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Paillas S, Causse A, Marzi L, de Medina P,
Poirot M, Denis V, Vezzio-Vie N, Espert L, Arzouk H, Coquelle A, et
al: MAPK14/p38α confers irinotecan resistance to TP53-defective
cells by inducing survival autophagy. Autophagy. 8:1098–1112. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H,
Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M,
Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy.
8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Selvakumaran M, Amaravadi RK, Vasilevskaya
IA and O'Dwyer PJ: Autophagy inhibition sensitizes colon cancer
cells to antiangiogenic and cytotoxic therapy. Clin Cancer Res.
19:2995–3007. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Petiot A, Ogier-Denis E, Blommaart EF,
Meijer AJ and Codogno P: Distinct classes of phosphatidylinositol
3′-kinases are involved in signaling pathways that control
macroautophagy in HT-29 cells. J Biol Chem. 275:992–998. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li J, Hou N, Faried A, Tsutsumi S and
Kuwano H: Inhibition of autophagy augments 5-fluorouracil
chemotherapy in human colon cancer in vitro and in vivo model. Eur
J Cancer. 46:1900–1909. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li J, Hou N, Faried A, Tsutsumi S,
Takeuchi T and Kuwano H: Inhibition of autophagy by 3-MA enhances
the effect of 5-FU-induced apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Ann
Surg Oncol. 16:761–771. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Trocoli A and Djavaheri-Mergny M: The
complex interplay between autophagy and NF-κB signaling pathways in
cancer cells. Am J Cancer Res. 1:629–649. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bassères DS and Baldwin AS: Nuclear
factor-kappaB and inhibitor of kappaB kinase pathways in oncogenic
initiation and progression. Oncogene. 25:6817–6830. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Keeratichamroen S, Leelawat K, Thongtawee
T, Narong S, Aegem U, Tujinda S, Praditphol N and Tohtong R:
Expression of CD24 in cholangiocarcinoma cells is associated with
disease progression and reduced patient survival. Int J Oncol.
39:873–881. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Luo JL, Kamata H and Karin M:
IKK/NF-kappaB signaling: Balancing life and death-a new approach to
cancer therapy. J Clin Invest. 115:2625–2632. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hoffmann A, Natoli G and Ghosh G:
Transcriptional regulation via the NF-kappaB signaling module.
Oncogene. 25:6706–6716. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Haskill S, Beg AA, Tompkins SM, Morris JS,
Yurochko AD, Sampson-Johannes A, Mondal K, Ralph P and Baldwin AS
Jr: Characterization of an immediate-early gene induced in adherent
monocytes that encodes I kappa B-like activity. Cell. 65:1281–1289.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Thompson JE, Phillips RJ,
Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P and Ghosh S: I kappa B-beta regulates
the persistent response in a biphasic activation of NF-kappa B.
Cell. 80:573–582. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Whiteside ST, Epinat JC, Rice NR and
Israël A: I kappa B epsilon, a novel member of the I kappa B
family, controls RelA and cRel NF-kappa B activity. EMBO J.
16:1413–1426. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Senftleben U, Cao Y, Xiao G, Greten FR,
Krähn G, Bonizzi G, Chen Y, Hu Y, Fong A, Sun SC and Karin M:
Activation by IKKalpha of a second, evolutionary conserved,
NF-kappa B signaling pathway. Science. 293:1495–1499. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xiao G, Harhaj EW and Sun SC:
NF-kappaB-inducing kinase regulates the processing of NF-kappaB2
p100. Mol Cell. 7:401–409. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Shared principles
in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 132:344–362. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang X, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Liang Y, Xiang C,
Zhou H, Zhang H, Zhang Q, Qing H, Jiang B, et al: CD24 promoted
cancer cell angiogenesis via Hsp90-mediated STAT3/VEGF signaling
pathway in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 7:55663–55676.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Nivon M, Richet E, Codogno P, Arrigo AP
and Kretz-Remy C: Autophagy activation by NFkappaB is essential for
cell survival after heat shock. Autophagy. 5:766–783. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ju JH, Jang K, Lee KM, Kim M, Kim J, Yi
JY, Noh DY and Shin I: CD24 enhances DNA damage-induced apoptosis
by modulating NF-κB signaling in CD44-expressing breast cancer
cells. Carcinogenesis. 32:1474–1483. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kristiansen G, Pilarsky C, Pervan J,
Sturzebecher B, Stephan C, Jung K, Loening S, Rosenthal A and
Dietel M: CD24 expression is a significant predictor of PSA relapse
and poor prognosis in low grade or organ confined prostate cancer.
Prostate. 58:183–192. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sagiv E, Kazanov D and Arber N: CD24 plays
an important role in the carcinogenesis process of the pancreas.
Biomed Pharmacother. 60:280–284. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Comb WC, Cogswell P, Sitcheran R and
Baldwin AS: IKK-dependent, NF-κB-independent control of autophagic
gene expression. Oncogene. 30:1727–1732. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Criollo A, Senovilla L, Authier H, Maiuri
MC, Morselli E, Vitale I, Kepp O, Tasdemir E, Galluzzi L, Shen S,
et al: The IKK complex contributes to the induction of autophagy.
EMBO J. 29:619–631. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Djavaheri-Mergny M, Amelotti M, Mathieu J,
Besançon F, Bauvy C, Souquère S, Pierron G and Codogno P: NF-kappaB
activation represses tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced autophagy.
J Biol Chem. 281:30373–30382. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Djavaheri-Mergny M and Codogno P:
Autophagy joins the game to regulate NF-kappaB signaling pathways.
Cell Res. 17:576–577. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Huett A, Goel G and Xavier RJ: A systems
biology viewpoint on autophagy in health and disease. Curr Opin
Gastroenterol. 26:302–309. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang W, Wang X, Peng L, Deng Q, Liang Y,
Qing H and Jiang B: CD24-dependent MAPK pathway activation is
required for colorectal cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Sci.
101:112–119. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xiao G: Autophagy and NF-kappaB: Fight for
fate. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 18:233–243. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Smith SC, Oxford G, Wu Z, Nitz MD, Conaway
M, Frierson HF, Hampton G and Theodorescu D: The
metastasis-associated gene CD24 is regulated by Ral GTPase and is a
mediator of cell proliferation and survival in human cancer. Cancer
Res. 66:1917–1922. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Su M, Mei Y and Sinha S: Role of the
crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis in cancer. J Oncol.
2013:1027352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yang SY and Winslet MC: Dual role of
autophagy in colon cancer cell survival. Ann Surg Oncol. 18 (Suppl
3):S2392011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zheng HY, Zhang XY, Wang XF and Sun BC:
Autophagy enhances the aggressiveness of human colorectal cancer
cells and their ability to adapt to apoptotic stimulus. Cancer Biol
Med. 9:105–110. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sato K, Tsuchihara K, Fujii S, Sugiyama M,
Goya T, Atomi Y, Ueno T, Ochiai A and Esumi H: Autophagy is
activated in colorectal cancer cells and contributes to the
tolerance to nutrient deprivation. Cancer Res. 67:9677–9684. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Sasaki K, Tsuno NH, Sunami E, Tsurita G,
Kawai K, Okaji Y, Nishikawa T, Shuno Y, Hongo K, Hiyoshi M, et al:
Chloroquine potentiates the anti-cancer effect of 5-fluorouracil on
colon cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 10:3702010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Singh P, Godbole M, Rao G, Annarao S,
Mitra K, Roy R, Ingle A, Agarwal G and Tiwari S: Inhibition of
autophagy stimulate molecular iodine-induced apoptosis in hormone
independent breast tumors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 415:181–186.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Guo XL, Li D, Hu F, Song JR, Zhang SS,
Deng WJ, Sun K, Zhao QD, Xie XQ, Song YJ, et al: Targeting
autophagy potentiates chemotherapy-induced apoptosis and
proliferation inhibition in hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Lett.
320:171–179. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ghosh S, Tergaonkar V, Rothlin CV, Correa
RG, Bottero V, Bist P, Verma IM and Hunter T: Essential role of
tuberous sclerosis genes TSC1 and TSC2 in NF-kappaB activation and
cell survival. Cancer Cell. 10:215–226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Copetti T, Bertoli C, Dalla E, Demarchi F
and Schneider C: p65/RelA modulates BECN1 transcription and
autophagy. Mol Cell Biol. 29:2594–2608. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|