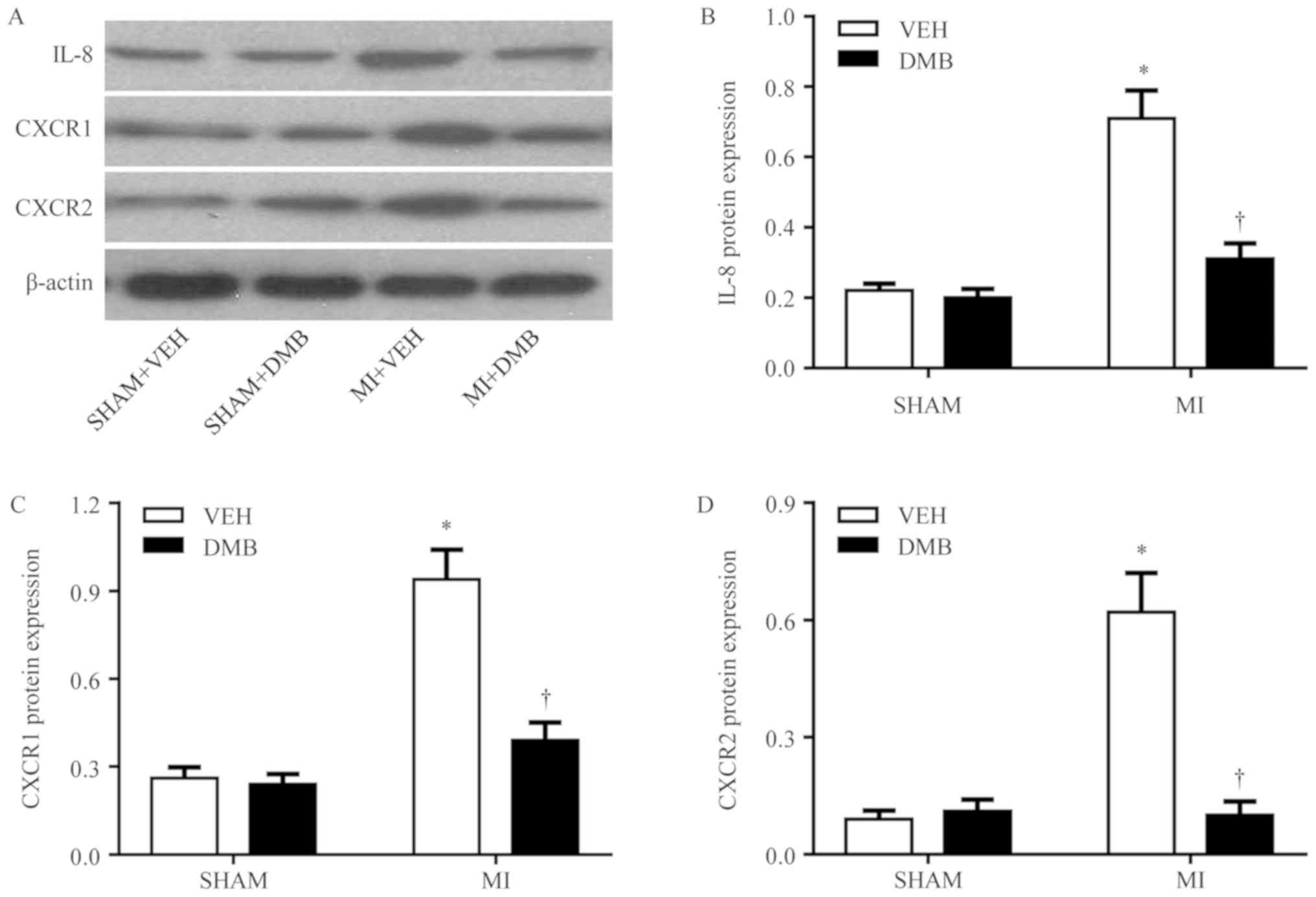
|
1
|
Hartman MH, Groot HE, Leach IM, Karper JC
and van der Harst P: Translational overview of cytokine inhibition
in acute myocardial infarction and chronic heart failure. Trends
Cardiovasc Med. 28:369–379. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Albert CL and Tang WH: Metabolic
biomarkers in heart failure. Heart Fail Clin. 14:109–118. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Subramaniam S and Fletcher C:
Trimethylamine N-oxide: Breathe new life. Br J Pharmacol.
175:1344–1353. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Velasquez MT, Ramezani A, Manal A and Raj
DS: Trimethylamine N-oxide: The good, the bad and the unknown.
Toxins (Basel). 8:E3262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kitai T, Kirsop J and Tang WH: Exploring
the microbiome in heart failure. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 13:103–109.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu KY, Xia GH, Lu JQ, Chen MX, Zhen X,
Wang S, You C, Nie J, Zhou HW and Yin J: Impaired renal function
and dysbiosis of gut microbiota contribute to increased
trimethylamine-N-oxide in chronic kidney disease patients. Sci Rep.
7:14452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Suzuki T, Heaney LM, Jones DJ and Ng LL:
Trimethylamine N-oxide and risk stratification after acute
myocardial infarction. Clin Chem. 63:420–428. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Organ CL, Otsuka H, Bhushan S, Wang Z,
Bradley J, Trivedi R, Polhemus DJ, Tang WH, Wu Y, Hazen SL and
Lefer DJ: Choline diet and its gut microbe-derived metabolite,
trimethylamine N-oxide, exacerbate pressure overload-induced heart
failure. Circ Heart Fail. 9:e0023142016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li Z, Wu Z, Yan J, Liu H, Liu Q, Deng Y,
Ou C and Chen M: Gut microbe-derived metabolite trimethylamine
N-oxide induces cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis. Lab Invest.
99:346–357. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen K, Zheng X, Feng M, Li D and Zhang H:
Gut microbiota-dependent metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide
contributes to cardiac dysfunction in western diet-induced obese
mice. Front Physiol. 8:1392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Westman PC, Lipinski MJ, Luger D, Waksman
R, Bonow RO, Wu E and Epstein SE: Inflammation as a driver of
adverse left ventricular remodeling after acute myocardial
infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 67:2050–2060. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shetelig C, Limalanathan S, Hoffmann P,
Seljeflot I, Gran JM, Eritsland J and Andersen GØ: Association of
IL-8 with infarct size and clinical outcomes in patients with
STEMI. J Am Coll Cardiol. 72:187–198. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zarrouk-Mahjoub S, Zaghdoudi M, Amira Z,
Chebi H, Khabouchi N, Finsterer J, Mechmeche R and Ghazouani E:
Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in post-infarction left
ventricular remodeling. Int J Cardiol. 221:632–636. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Apostolakis S, Vogiatzi K, Amanatidou V
and Spandidos DA: Interleukin 8 and cardiovascular disease.
Cardiovasc Res. 84:353–360. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li T, Chen Y, Gua C and Li X: Elevated
circulating trimethylamine N-oxide levels contribute to endothelial
dysfunction in aged rats through vascular inflammation and
Oxidative stress. Front Physiol. 8:3502017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pacher P, Liaudet L, Mabley JG, Cziráki A,
Haskó G and Szabó C: Beneficial effects of a novel ultrapotent
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor in murine models of heart
failure. Int J Mol Med. 17:369–375. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hua Y, Chen H, Zhao X, Liu M, Jin W, Yan
W, Wu Y, Tan Z, Fan H, Wu Y, et al: Alda1, an aldehyde
dehydrogenase-2 agonist, improves longterm survival in rats with
chronic heart failure following myocardial infarction. Mol Med Rep.
18:3159–3166. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ram R, Mickelsen DM, Theodoropoulos C and
Blaxall BC: New approaches in small animal echocardiography:
Imaging the sounds of silence. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
301:H1765–H1780. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Iliopoulou I, Mourouzis I, Lambrou GI,
Iliopoulou D, Koutsouris DD and Pantos C: Timedependent and
independent effects of thyroid hormone administration following
myocardial infarction in rats. Mol Med Rep. 18:864–876.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Morgan EE, Casabianca AB, Khouri SJ and
Kalinoski AL: In vivo assessment of arterial stiffness in the
isoflurane anesthetized spontaneously hypertensive rat. Cardiovasc
Ultrasound. 12:372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zambricki EA and Dalecy LG: Rat sex
differences in anesthesia. Comp Med. 54:49–53. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tang WH, Wang Z, Fan Y, Levison B, Hazen
JE, Donahue LM, Wu Y and Hazen SL: Prognostic value of elevated
levels of intestinal microbe-generated metabolite
trimethylamine-N-oxide in patients with heart failure: Refining the
gut hypothesis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 64:1908–1914. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Suzuki T, Heaney LM, Bhandari SS, Jones DJ
and Ng LL: Trimethylamine N-oxide and prognosis in acute heart
failure. Heart. 102:841–848. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu Z, Liu HY, Zhou H, Zhan Q, Lai W, Zeng
Q, Ren H and Xu D: Moderate-intensity exercise affects gut
microbiome composition and influences cardiac function in
myocardial infarction mice. Front Microbiol. 8:16872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Z, Roberts AB, Buffa JA, Levison BS,
Zhu W, Org E, Gu X, Huang Y, Zamanian-Daryoush M, Culley MK, et al:
Non-lethal inhibition of gut microbial trimethylamine Production
for the treatment of atherosclerosis. Cell. 163:1585–1595. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Roberts AB, Gu X, Buffa JA, Hurd AG, Wang
Z, Zhu W, Gupta N, Skye SM, Cody DB, Levison BS, et al: Development
of a gut microbe-targeted nonlethal therapeutic to inhibit
thrombosis potential. Nat Med. 24:1407–1417. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gong X, Zhou R and Li Q: Effects of
captopril and valsartan on ventricular remodeling and inflammatory
cytokines after interventional therapy for AMI. Exp Ther Med.
16:3579–3583. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Meng C, Guo Z, Li D, Li H, He J, Wen D and
Luo B: Preventive effect of hesperidin modulates inflammatory
responses and antioxidant status following acute myocardial
infarction through the expression of PPAR-γ and Bcl-2 in model
mice. Mol Med Rep. 17:1261–1268. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Na D, Aijie H, Bo L, Zhilin M and Long Y:
Gambogic acid exerts cardioprotective effects in a rat model of
acute myocardial infarction through inhibition of inflammation,
iNOS and NF-κB/p38 pathway. Exp Ther Med. 15:1742–1748.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lu L, Wei P, Cao Y, Zhang Q, Liu M, Liu
XD, Wang ZL and Zhang PY: Effect of total peony glucoside
pretreatment on NF-κB and ICAM-1 expression in myocardial tissue of
rat with myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Genet Mol Res.
15:2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Kukielka GL, Smith CW, LaRosa GJ, Manning
AM, Mendoza LH, Daly TJ, Hughes BJ, Youker KA, Hawkins HK, Michael
LH, et al: Interleukin-8 gene induction in the myocardium after
ischemia and reperfusion in vivo. J Clin Invest. 95:89–103. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Damås JK, Eiken HG, Oie E, Bjerkeli V,
Yndestad A, Ueland T, Tonnessen T, Geiran OR, Aass H, Simonsen S,
et al: Myocardial expression of CC- and CXC-chemokines and their
receptors in human end-stage heart failure. Cardiovasc Res.
47:778–787. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hu L, Cai N and Jia H: Pterostilbene
attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via the
phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase-protein kinase B signaling pathway.
Exp Ther Med. 14:5509–5514. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Boyle EM Jr, Kovacich JC, Hèbert CA, Canty
TG Jr, Chi E, Morgan EN, Pohlman TH and Verrier ED: Inhibition of
interleukin-8 blocks myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. J
Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 116:114–121. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wuyts WA, Vanaudenaerde BM, Dupont LJ, Van
Raemdonck DE, Demedts MG and Verleden GM: Interleukin-17-induced
interleukin-8 release in human airway smooth muscle cells: Role for
mitogen-activated kinases and nuclear factor-kappaB. J Heart Lung
Transplant. 24:875–881. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vanaudenaerde BM, Wuyts WA, Dupont LJ, Van
Raemdonck DE, Demedts MM and Verleden GM: Interleukin-17 stimulates
release of interleukin-8 by human airway smooth muscle cells in
vitro: A potential role for interleukin-17 and airway smooth muscle
cells in bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome. J Heart Lung
Transplant. 22:1280–1283. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tedesco D, Thapa M, Chin CY, Ge Y, Gong M,
Li J, Gumber S, Speck P, Elrod EJ, Burd EM, et al: Alterations in
intestinal microbiota lead to production of interleukin 17 by
intrahepatic γδ T-cell receptor-positive cells and pathogenesis of
cholestatic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 154:2178–2193. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|