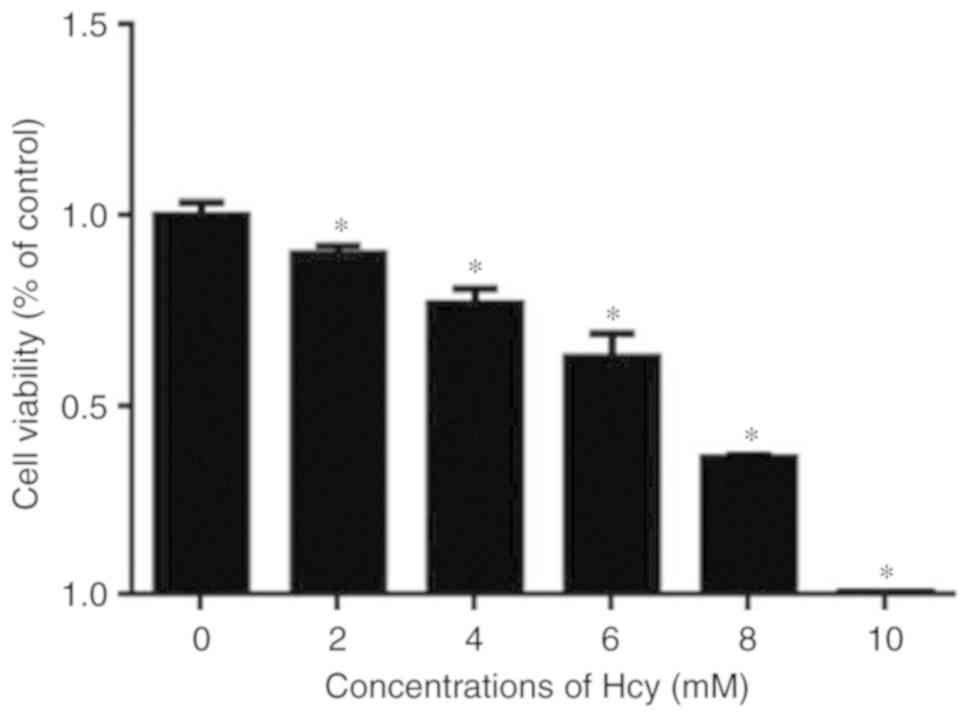
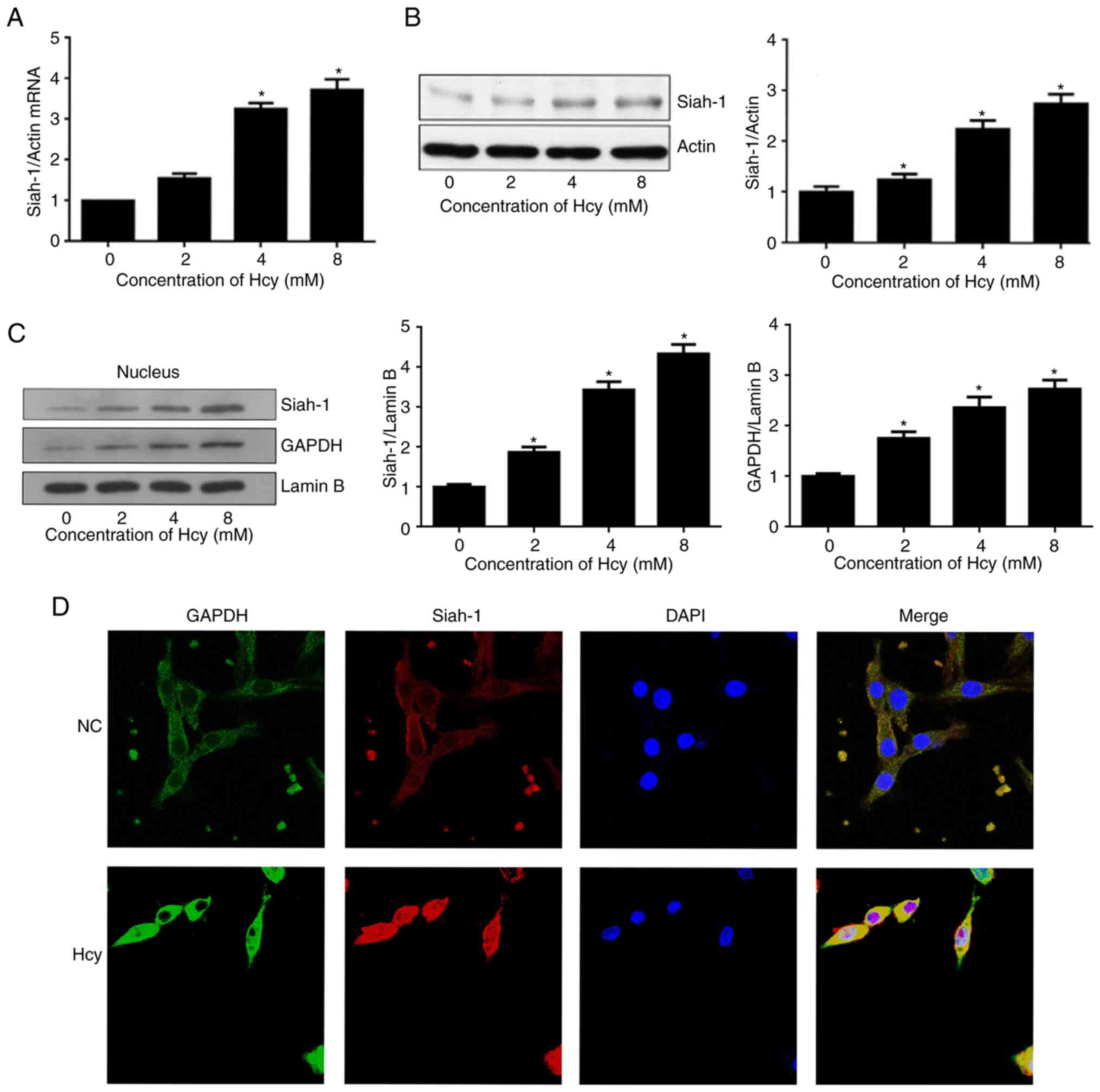
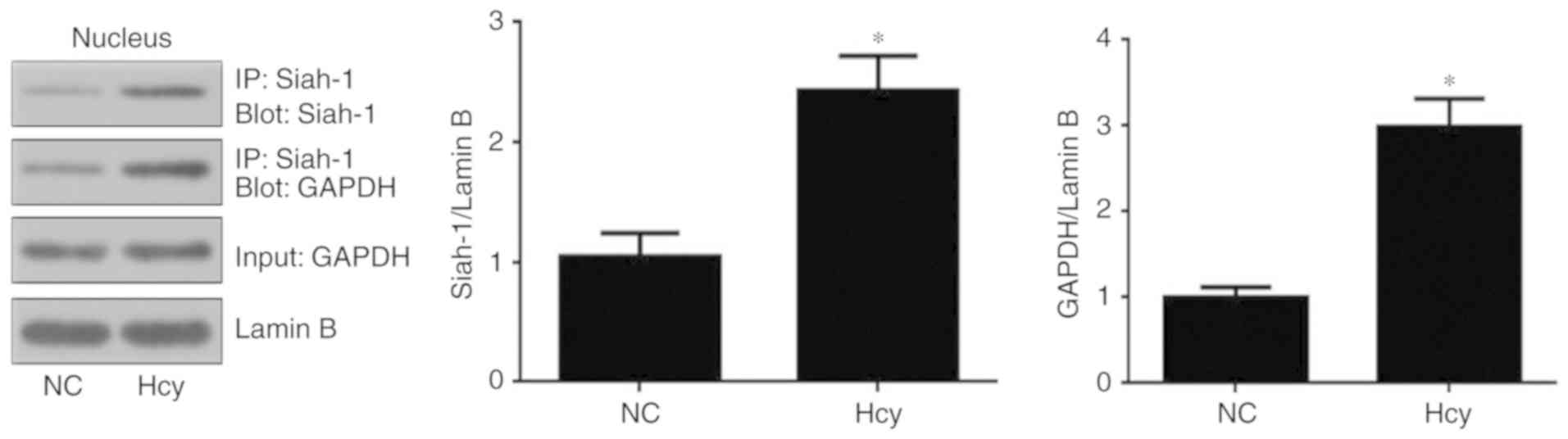
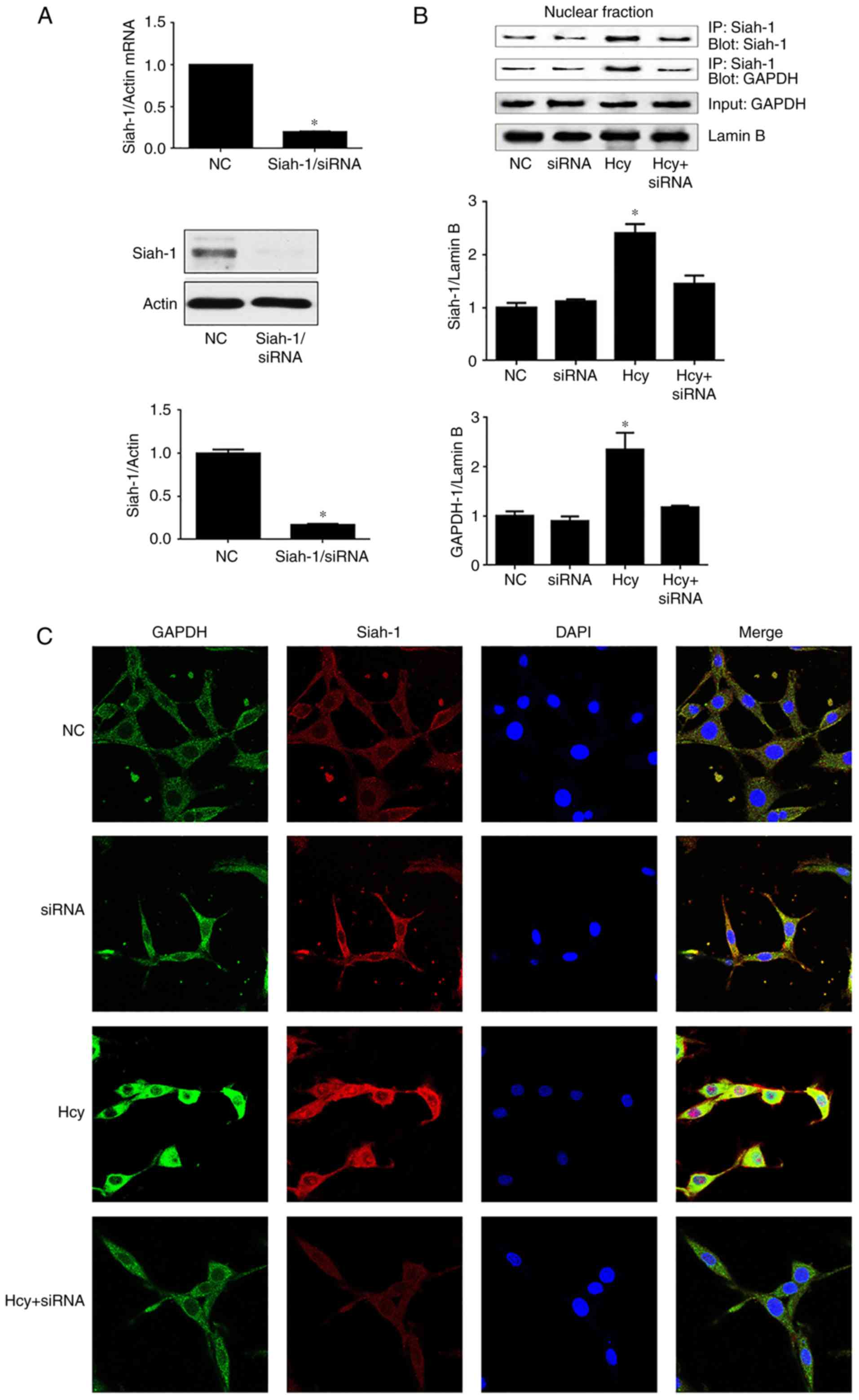
|
1
|
Kim H and Lee KJ: Serum homocysteine
levels are correlated with behavioral and psychological symptoms of
Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 10:1887–1896.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kamat PK, Vacek JC, Kalani A and Tyagi N:
Homocysteine induced cerebrovascular dysfunction: A link to
Alzheimer's disease etiology. Open Neurol J. 9:9–14. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sharma M, Tiwari M and Tiwari RK:
Hyperhomocysteinemia: Impact on neurodegenerative diseases. Basic
Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 117:287–296. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jin Y and Brennan L: Effects of
homocysteine on metabolic pathways in cultured astrocytes.
Neurochem Int. 52:1410–1415. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kruman II, Kumaravel TS, Lohani A,
Pedersen WA, Cutler RG, Kruman Y, Haughey N, Lee J, Evans M and
Mattson MP: Folic acid deficiency and homocysteine impair DNA
repair in hippocampal neurons and sensitize them to amyloid
toxicity in experimental models of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci.
22:1752–1762. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oldreive CE and Doherty GH: Neurotoxic
effects of homocysteine on cerebellar Purkinje neurons in vitro.
Neurosci Lett. 413:52–57. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Maler JM, Seifert W, Hüther G, Wiltfang J,
Rüther E, Kornhuber J and Bleich S: Homocysteine induces cell death
of rat astrocytes in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 347:85–88. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Škovierová H, Mahmood S, Blahovcová E,
Hatok J, Lehotský J and Murín R: Effect of homocysteine on survival
of human glial cells. Physiol Res. 64:747–754. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Turnquist C, Horikawa I, Foran E, Major
EO, Vojtesek B, Lane DP, Lu X, Harris BT and Harris CC: p53
isoforms regulate astrocyte-mediated neuroprotection and
neurodegeneration. Cell Death Differ. 23:1515–1528. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dallérac G and Rouach N: Astrocytes as new
targets to improve cognitive functions. Prog Neurobiol. 144:48–67.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hsu CC, Cheng CH, Hsu CL, Lee WJ, Huang SC
and Huang YC: Role of vitamin B6 status on antioxidant defenses,
glutathione, and related enzyme activities in mice with
homocysteine-induced oxidative stress. Food Nutr Res. 59:257022015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Itakura M, Nakajima H, Semi Y, Higashida
S, Azuma YT and Takeuchi T: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
dehydrogenase aggregation inhibitor peptide: A potential
therapeutic strategy against oxidative stress-induced cell death.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 467:373–376. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fang M, Jin A, Zhao Y and Liu X:
Homocysteine induces glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
acetylation and apoptosis in the neuroblastoma cell line Neuro2a.
Braz J Med Biol Res. 49:e45432016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ban R, Matsuzaki H, Akashi T, Sakashita G,
Taniguchi H, Park SY, Tanaka H, Furukawa K and Urano T: Mitotic
regulation of the stability of microtubule plus-end tracking
protein EB3 by ubiquitin ligase SIAH-1 and Aurora mitotic kinases.
J Biol Chem. 284:28367–28381. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Winter M, Sombroek D, Dauth I,
Moehlenbrink J, Scheuermann K, Crone J and Hofmann TG: Control of
HIPK2 stability by ubiquitin ligase Siah-1 and checkpoint kinases
ATM and ATR. Nat Cell Biol. 10:812–824. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu Z, Sproul A, Wang W, Kukekov N and
Greene LA: Siah1 interacts with the scaffold protein POSH to
promote JNK activation and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 281:303–312.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bruzzoni-Giovanelli H, Fernandez P, Veiga
L, Podgorniak MP, Powell DJ, Candeias MM, Mourah S, Calvo F and
Marín M: Distinct expression patterns of the E3 ligase SIAH-1 and
its partner Kid/KIF22 in normal tissues and in the breast tumoral
processes. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:102010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
House CM, Frew IJ, Huang HL, Wiche G,
Traficante N, Nice E, Catimel B and Bowtell DD: A binding motif for
Siah ubiquitin ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:3101–3106. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
House CM, Hancock NC, Möller A, Cromer BA,
Fedorov V, Bowtell DD, Parker MW and Polekhina G: Elucidation of
the substrate binding site of Siah ubiquitin ligase. Structure.
14:695–701. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
He HT, Fokas E, You A, Engenhart-Cabillic
R and An HX: Siah1 proteins enhance radiosensitivity of human
breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 10:4032010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hara MR, Agrawal N, Kim SF, Cascio MB,
Fujimuro M, Ozeki Y, Takahashi M, Cheah JH, Tankou SK, Hester LD,
et al: S-nitrosylated GAPDH initiates apoptotic cell death by
nuclear translocation following Siah1 binding. Nat Cell Biol.
7:665–674. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yego EC and Mohr S: siah-1 protein is
necessary for high glucose-induced glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
dehydrogenase nuclear accumulation and cell death in muller cells.
J Biol Chem. 285:3181–3190. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee JT, Wheeler TC, Li L and Chin LS:
Ubiquitination of alpha-synuclein by Siah-1 promotes
alpha-synuclein aggregation and apoptotic cell death. Hum Mol
Genet. 17:906–917. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kruman II, Culmsee C, Chan SL, Kruman Y,
Guo Z, Penix L and Mattson MP: Homocysteine elicits a DNA damage
response in neurons that promotes apoptosis and hypersensitivity to
excitotoxicity. J Neurosci. 20:6920–6926. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tawfik A and Smith SB: Increased ER stress
as a mechanism of retinal neurovasculopathy in mice with severe
hyperhomocysteinemia. Austin J Clin Ophthalmol.
1:10232014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ho PI, Ortiz D, Rogers E and Shea TB:
Multiple aspects of homocysteine neurotoxicity: Glutamate
excitotoxicity, kinase hyperactivation and DNA damage. J Neurosci
Res. 70:694–702. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Suarez S, McCollum GW, Jayagopal A and
Penn JS: High glucose-induced retinal pericyte apoptosis depends on
association of GAPDH and Siah1. J Biol Chem. 290:28311–28320. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sen N, Hara MR, Kornberg MD, Cascio MB,
Bae BI, Shahani N, Thomas B, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, Snyder SH and
Sawa A: Nitric oxide-induced nuclear GAPDH activates p300/CBP and
mediates apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 10:866–873. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kwon HJ, Rhim JH, Jang IS, Kim GE, Park SC
and Yeo EJ: Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase stimulates
the nuclear localization of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
dehydrogenase in human diploid fibroblasts. Exp Mol Med.
42:254–269. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao Y, Li Q, Jin A, Cui M and Liu X: E3
ubiquitin ligase Siah-1 downregulates synaptophysin expression
under high glucose and hypoxia. Am J Transl Res. 7:15–27.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Roperch JP, Lethrone F, Prieur S, Piouffre
L, Israeli D, Tuynder M, Nemani M, Pasturaud P, Gendron MC, Dausset
J, et al: SIAH-1 promotes apoptosis and tumor suppression through a
network involving the regulation of protein folding, unfolding, and
trafficking: Identification of common effectors with p53 and
p21(Waf1). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:8070–8073. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|