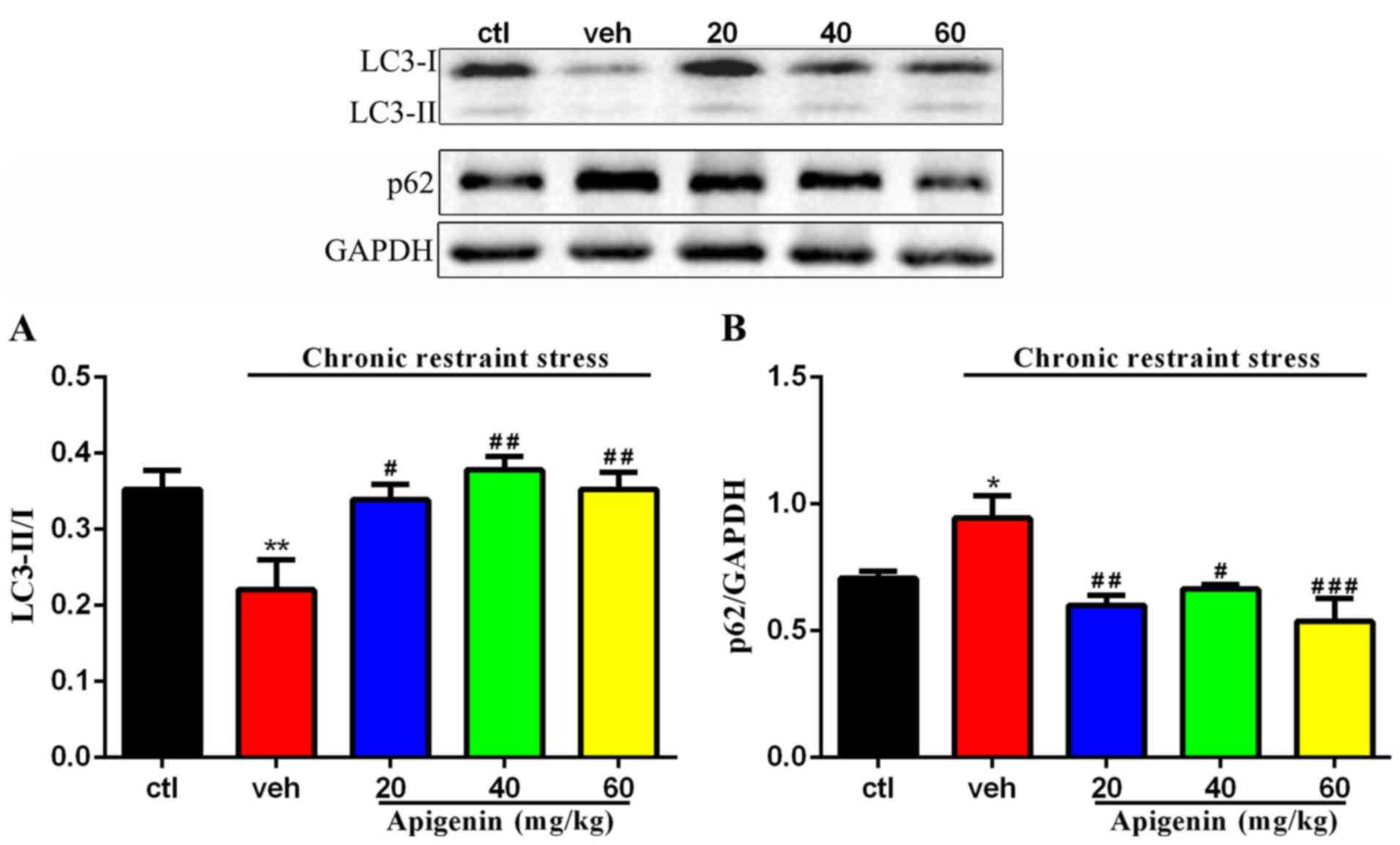
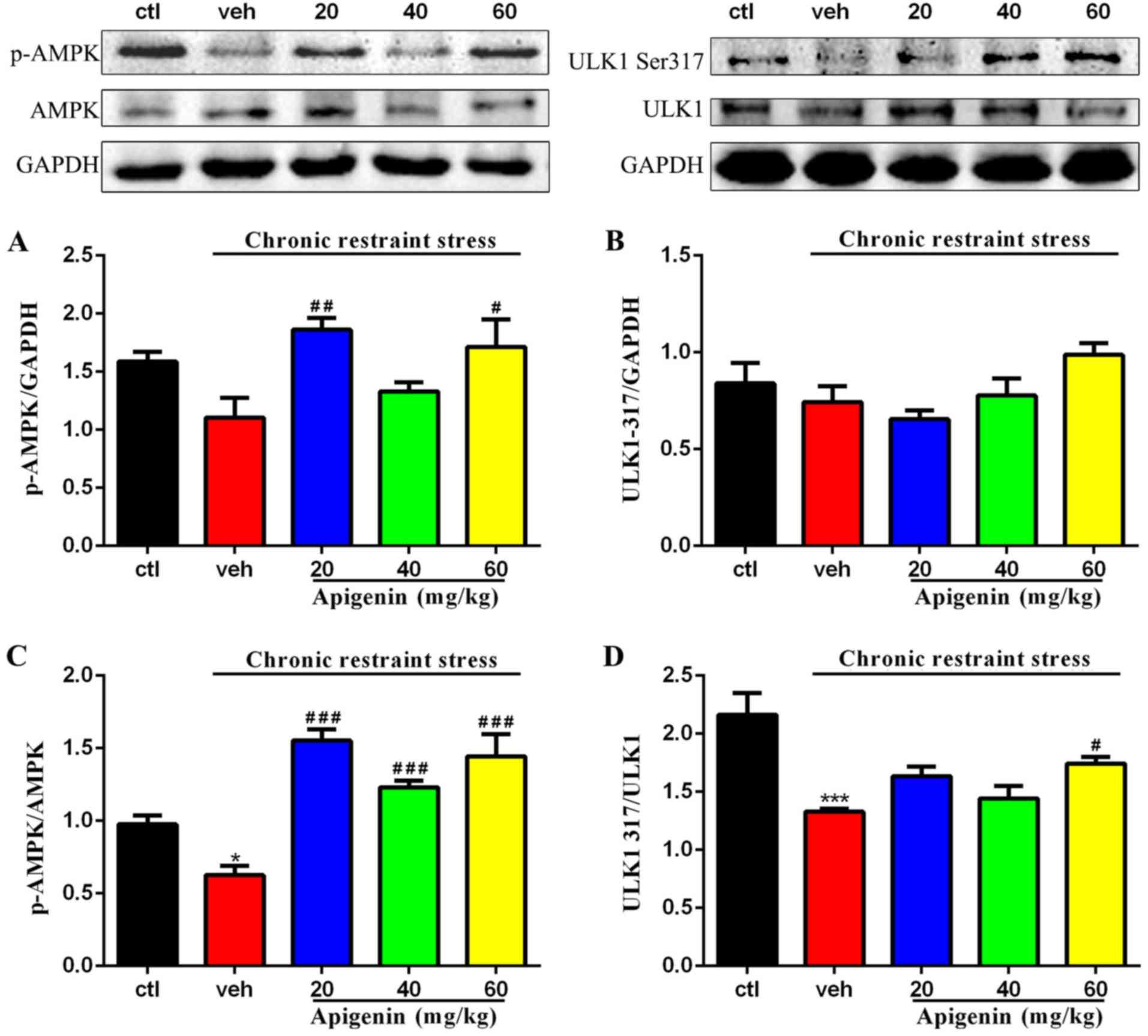
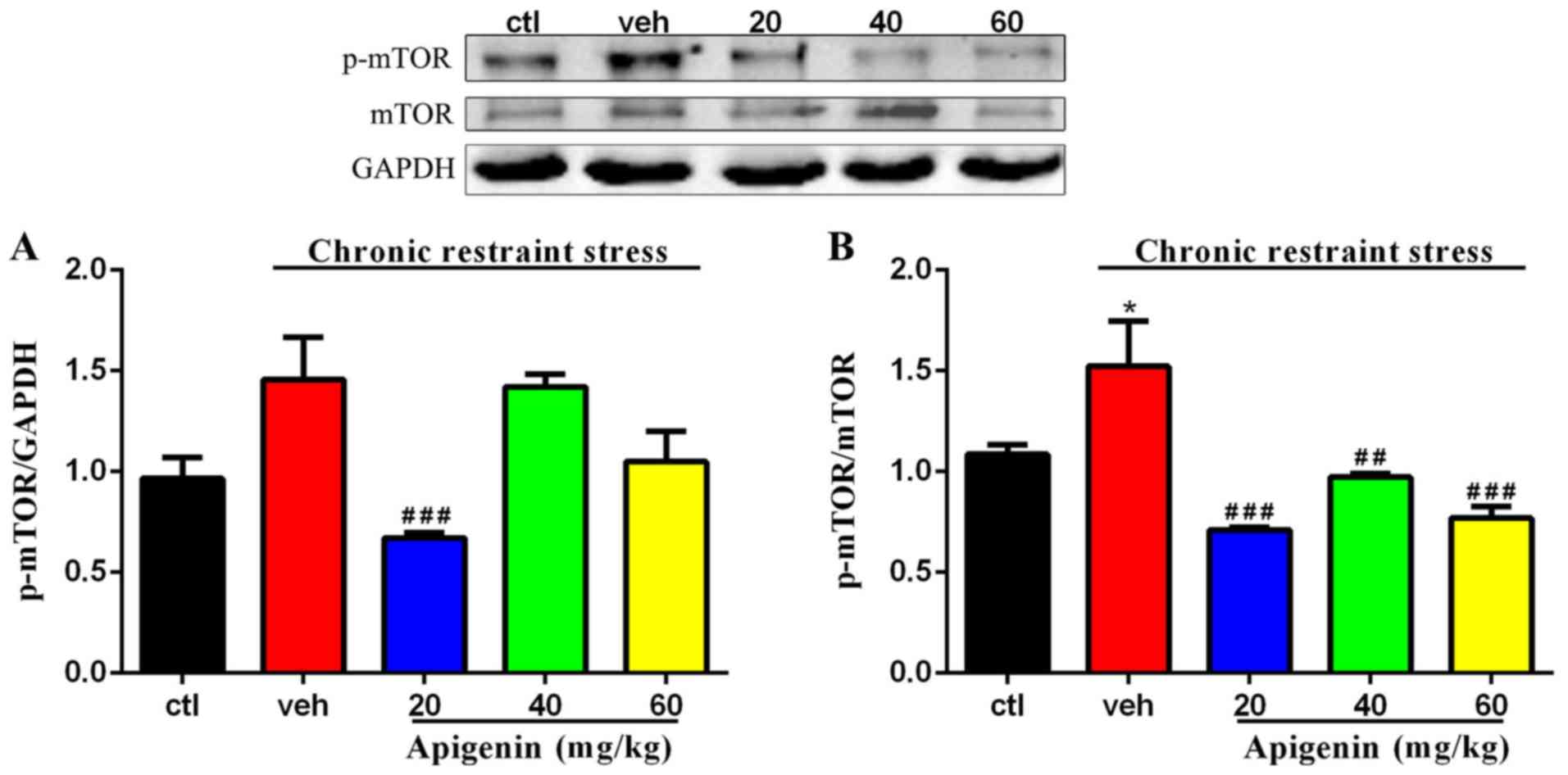
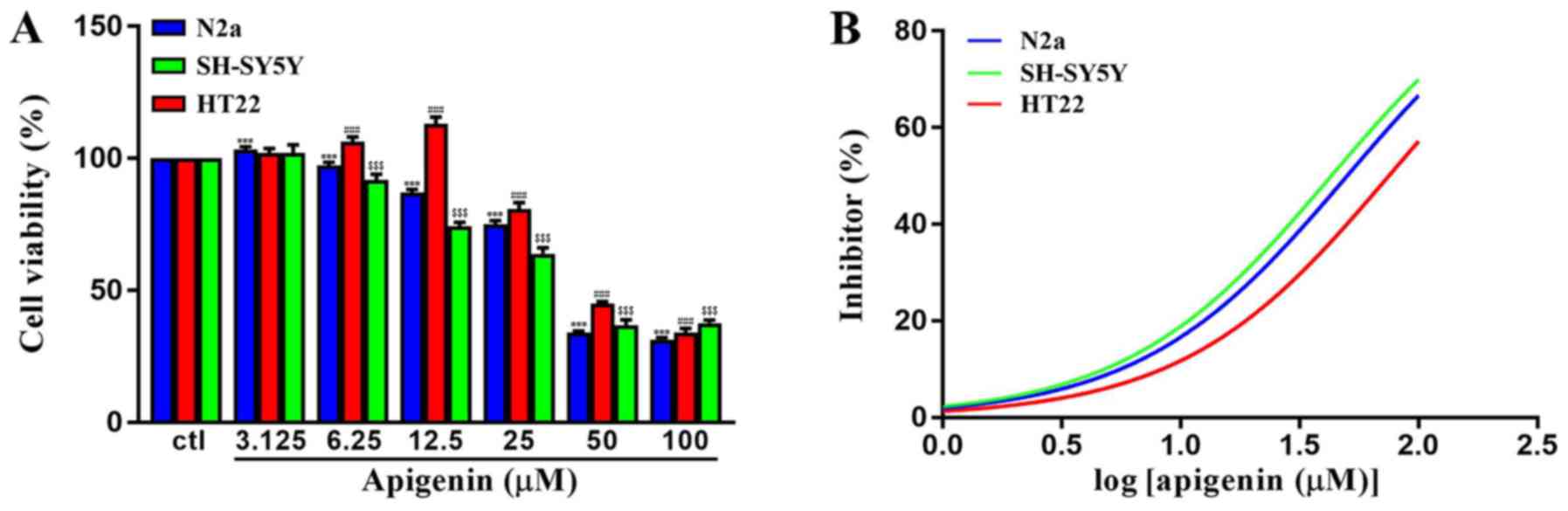
|
1
|
Steel N, Ford JA, Newton JN, Davis ACJ,
Vos T, Naghavi M, Glenn S, Hughes A, Dalton AM, Stockton D, et al:
Changes in health in the countries of the UK and 150 English local
authority areas 1990-2016: A systematic analysis for the Global
Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 392:1647–1661. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ogbo FA, Mathsyaraja S, Koti RK, Perz J
and Page A: The burden of depressive disorders in South Asia,
1990–2016: Findings from the global burden of disease study. BMC
Psychiatry. 18:3332018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Castellano S, Ventimiglia A, Salomone S,
Ventimiglia A, De Vivo S, Signorelli MS, Bellelli E, Santagati M,
Cantarella RA, Fazio E, et al: Selective serotonin reuptake
inhibitors and serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors
improve cognitive function in partial responders depressed
patients: Results from a prospective observational cohort study.
CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 15:1290–1298. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vaswani M, Linda FK and Ramesh S: Role of
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in psychiatric disorders: A
comprehensive review. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry.
27:85–102. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stahl SM: Mechanism of action of serotonin
selective reuptake inhibitors. Serotonin receptors and pathways
mediate therapeutic effects and side effects. J Affect Disord.
51:215–235. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nørr L, Bennedsen B, Fedder J and Larsen
ER: Use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors reduces
fertility in men. Andrology. 4:389–394. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li YJ and Li YM: Gestational exposure to
selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and offspring psychiatric
disorders: Need for further investigation. J Am Acad Child Adolesc
Psychiatry. 55:7262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Charney DS, Grothe DR, Smith SL, Brady KT,
Kaltsounis-Puckett J, Wright CW, Laird LK and Rush AJ: Overview of
psychiatric disorders and the role of newer antidepressants. J Clin
Psychiatry. 63 (Suppl 1):S3–S9. 2002.
|
|
9
|
Barros GO, Woodard SL and Nikolov ZL:
Phenolics removal from transgenic Lemna minor extracts expressing
mAb and impact on mAb production cost. Biotechnol Prog. 27:410–418.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tan GF, Ma J, Zhang XY, Xu ZS and Xiong
AS: AgFNS overexpression increase apigenin and decrease
anthocyanins in petioles of transgenic celery. Plant Sci.
263:31–38. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nabavi SF, Khan H, D'Onofrio G, Šamec D,
Shirooie S, Dehpour AR, Argüelles S, Habtemariam S and Sobarzo-
Sanchez E: Apigenin as neuroprotective agent: Of mice and men.
Pharmacol Res. 128:359–365. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li F, Lang F, Zhang H, Xu L, Wang Y, Zhai
C and Hao E: Apigenin alleviates endotoxin-induced myocardial
toxicity by modulating inflammation, oxidative stress, and
autophagy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:23028962017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Soyman Z, Kelekçi S, Sal V, Şevket O,
Bayindir N and Uzun H: Effects of Apigenin on experimental
Ischemia/Reperfusion injury in the rat ovary. Balkan Med J.
34:444–449. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li R, Wang X, Qin T, Qu R and Ma S:
Apigenin ameliorates chronic mild stress-induced depressive
behavior by inhibiting interleukin-1β production and NLRP3
inflammasome activation in the rat brain. Behav Brain Res.
296:318–325. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Weng L, Guo X, Li Y, Yang X and Han Y:
Apigenin reverses depression-like behavior induced by chronic
corticosterone treatment in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 774:50–54. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tan X, Du X, Jiang Y, Botchway BOA, Hu Z
and Fang M: Inhibition of autophagy in microglia alters
Depressive-like behavior via BDNF pathway in postpartum depression.
Front Psychiatry. 9:4342018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Anding AL and Baehrecke EH: Autophagy in
cell life and cell death. Curr Top Dev Biol. 114:67–91. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Muller S, Brun S, René F, de Séze J,
Loeffler JP and Jeltsch-David H: Autophagy in neuroinflammatory
diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 16:856–874. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Salmani JMM, Zhang XP, Jacob JA and Chen
BA: Apigenin's anticancer properties andmolecular mechanisms of
action: Recent advances and future prospectives. Chin J Nat Med.
15:321–329. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang J, Pi C and Wang G: Inhibition of
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway by apigenin induces apoptosis and autophagy
in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother.
103:699–707. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang Z, Huang X, Wang Q, Jiang R, Sun G,
Xu Y and Wu Q: Extract of Euryale ferox Salisb exerts
antidepressant effects and regulates autophagy through the
adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase-UNC-51-like kinase
1 pathway. IUBMB Life. 70:300–309. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang X, Wu H, Jiang R, Sun G, Shen J, Ma
M, Ma C, Zhang S, Huang Z, Wu Q, et al: The antidepressant effects
of a-tocopherol are related to activation of autophagy via the
AMPK/mTOR pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 833:1–7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim YR, Park BK, Kim YH, Shim I, Kang IC
and Lee MY: Antidepressant Effect of Fraxinus rhynchophylla hance
extract in a mouse model of chronic Stress-induced depression.
Biomed Res Int. 2018:82495632018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xue W, Wang W, Gong T, Zhang H, Tao W, Xue
L, Sun Y, Wang F and Chen G: PKA-CREB-BDNF signaling regulated long
lasting antidepressant activities of Yueju but not ketamine. Sci
Rep. 6:263312016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Castagné V, Moser P, Roux S and Porsolt
RD: Rodent models of depression: Forced swim and tail suspension
behavioral despair tests in rats and mice. Curr Protoc Neurosc:
Chapter 8: Unit 8.10A. 2011.doi: 10.1002/0471142301.ns0810as55.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang S, Xu S, Duan H, Zhu Z, Yang Z, Cao
J, Zhao Y, Huang Z, Wu Q and Duan J: A novel, highly-water-soluble
apigenin derivative provides neuroprotection following ischemia in
male rats by regulating the ERK/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Eur J Pharmacol.
855:208–215. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang J, Chao L, Liu X, Shi Y, Zhang C,
Kong L and Li R: The potential application of strategic released
apigenin from polymeric carrier in pulmonary fibrosis. Exp Lung
Res. 43:359–369. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bauer D, Redmon N, Mazzio E and Soliman
KF: Apigenin inhibits TNFα/IL-1α-induced CCL2 release through
IKBK-epsilon signaling in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells.
PLoS One. 12:e01755582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ai XY, Qin Y, Liu HJ, Cui ZH, Li M, Yang
JH, Zhong WL, Liu YR, Chen S, Sun T, et al: Apigenin inhibits
colonic inflammation and tumorigenesis by suppressing STAT3-NF-κB
signaling. Oncotarget. 8:100216–100226. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Han Y, Zhang T, Su J, Zhao Y, ChenchenWan
g and Li X: Apigenin attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal
apoptosis in early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage.
J Clin Neurosci. 40:157–162. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang T, Su J, Guo B, Wang K, Li X and
Liang G: Apigenin protects blood-brain barrier and ameliorates
early brain injury by inhibiting TLR4-mediated inflammatory pathway
in subarachnoid hemorrhage rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 28:79–87.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hernandez ME, Martinez-Mota L, Salinas C,
Marquez-Velasco R, Hernandez-Chan NG, Morales-Montor J, Pérez-Tapia
M, Streber ML, Granados-Camacho I, Becerril E, et al: Chronic
stress induces structural alterations in splenic lymphoid tissue
that are associated with changes in corticosterone levels in
wistar-kyoto rats. Biomed Res Int. 2013:8687422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pang Q, Zhang H, Chen Z, Wu Y, Bai M, Liu
Y, Zhao Y, Tu F, Liu C and Chen X: Role of caveolin-1/vascular
endothelial growth factor pathway in basic fibroblast growth
factor-induced angiogenesis and neurogenesis after treadmill
training following focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res.
1663:9–19. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang Q, Wang X, Bai X, Xie Y, Zhang T, Bo
S and Chen X: Resveratrol reversed chronic restraint stress-induced
impaired cognitive function in rats. Mol Med Rep. 16:2095–2100.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gassen NC, Hartmann J, Zschocke J, Stepan
J, Hafner K, Zellner A, Kirmeier T, Kollmannsberger L, Wagner KV,
Dedic N, et al: Association of FKBP51 with priming of autophagy
pathways and mediation of antidepressant treatment response:
Evidence in cells, mice, and humans. PLoS Med. 11:e10017552014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Alcocer-Gomez E, Casas-Barquero N,
Williams MR, Romero-Guillena SL, Cañadas-Lozano D, Bullón P,
Sánchez-Alcazar JA, Navarro-Pando JM and Cordero MD:
Antidepressants induce autophagy dependent-NLRP3-inflammasome
inhibition in Major depressive disorder. Pharmacol Res.
121:114–121. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Q, Liu Y and Sun M: Autophagy and
Alzheimer's disease. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 37:377–388. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Karabiyik C, Lee MJ and Rubinsztein DC:
Autophagy impairment in Parkinson's disease. Essays Biochem.
61:711–720. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jia J and Le W: Molecular network of
neuronal autophagy in the pathophysiology and treatment of
depression. Neurosci Bull. 31:427–434. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huang R and Liu W: Identifying an
essential role of nuclear LC3 for autophagy. Autophagy. 11:852–853.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dunlop EA and Tee AR: mTOR and autophagy:
A dynamic relationship governed by nutrients and energy. Semin Cell
Dev Biol. 36:121–129. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B and Guan KL:
AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of
Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 13:132–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rabanal-Ruiz Y, Otten EG and Korolchuk VI:
mTORC1 as the main gateway to autophagy. Essays Biochem.
61:565–584. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xu S, Li L, Li M, Zhang M, Ju M, Chen X
and Gu H: Impact on autophagy and Ultraviolet B induced responses
of treatment with the MTOR inhibitors rapamycin, everolimus, Torin
1, and pp242 in human keratinocytes. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017:59306392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hau AM, Greenwood JA, Löhr CV, Serrill JD,
Proteau PJ, Ganley IG, McPhail KL and Ishmael JE: Coibamide A
induces mTOR-independent autophagy and cell death in human
glioblastoma cells. PLoS One. 8:e652502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|