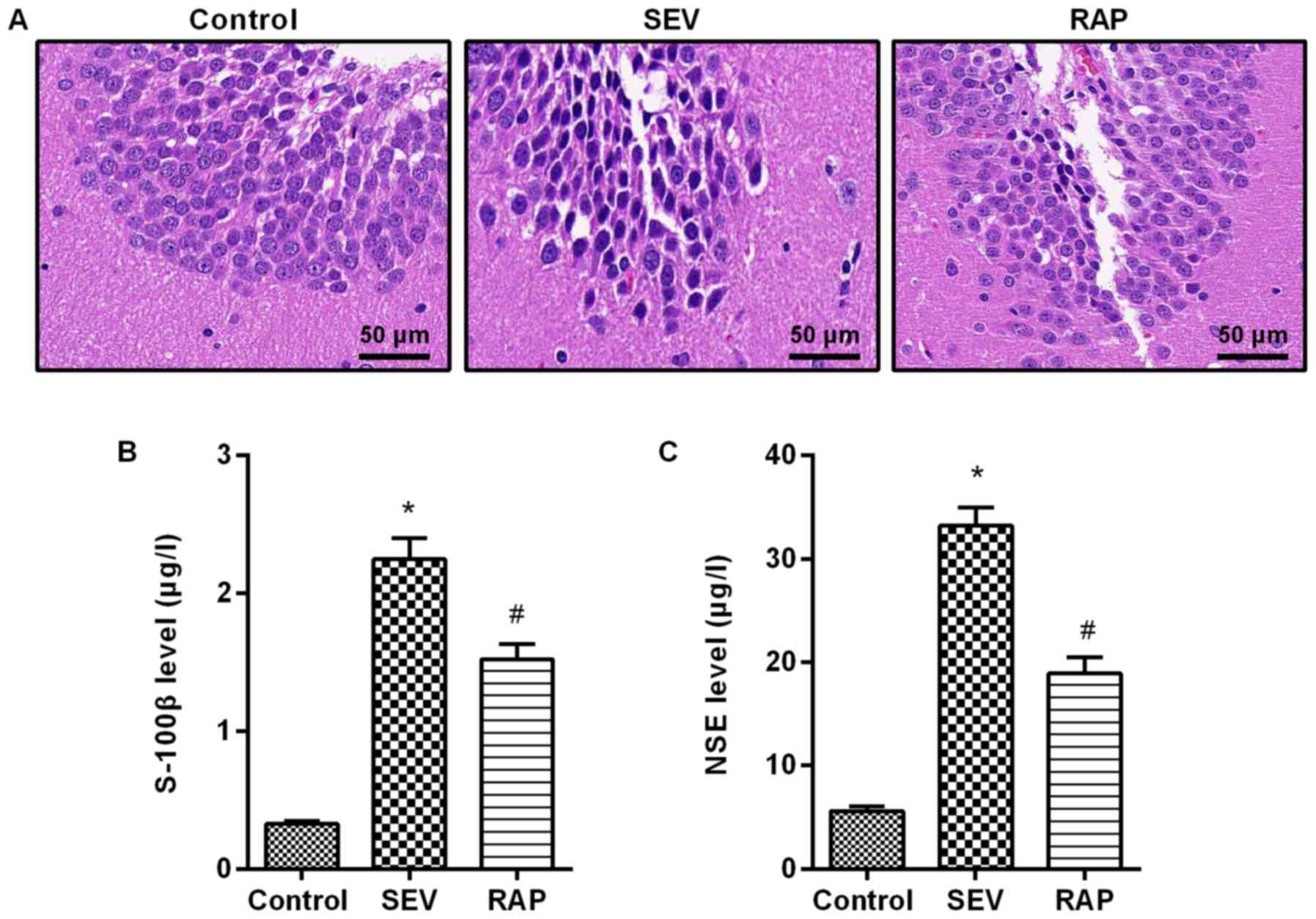
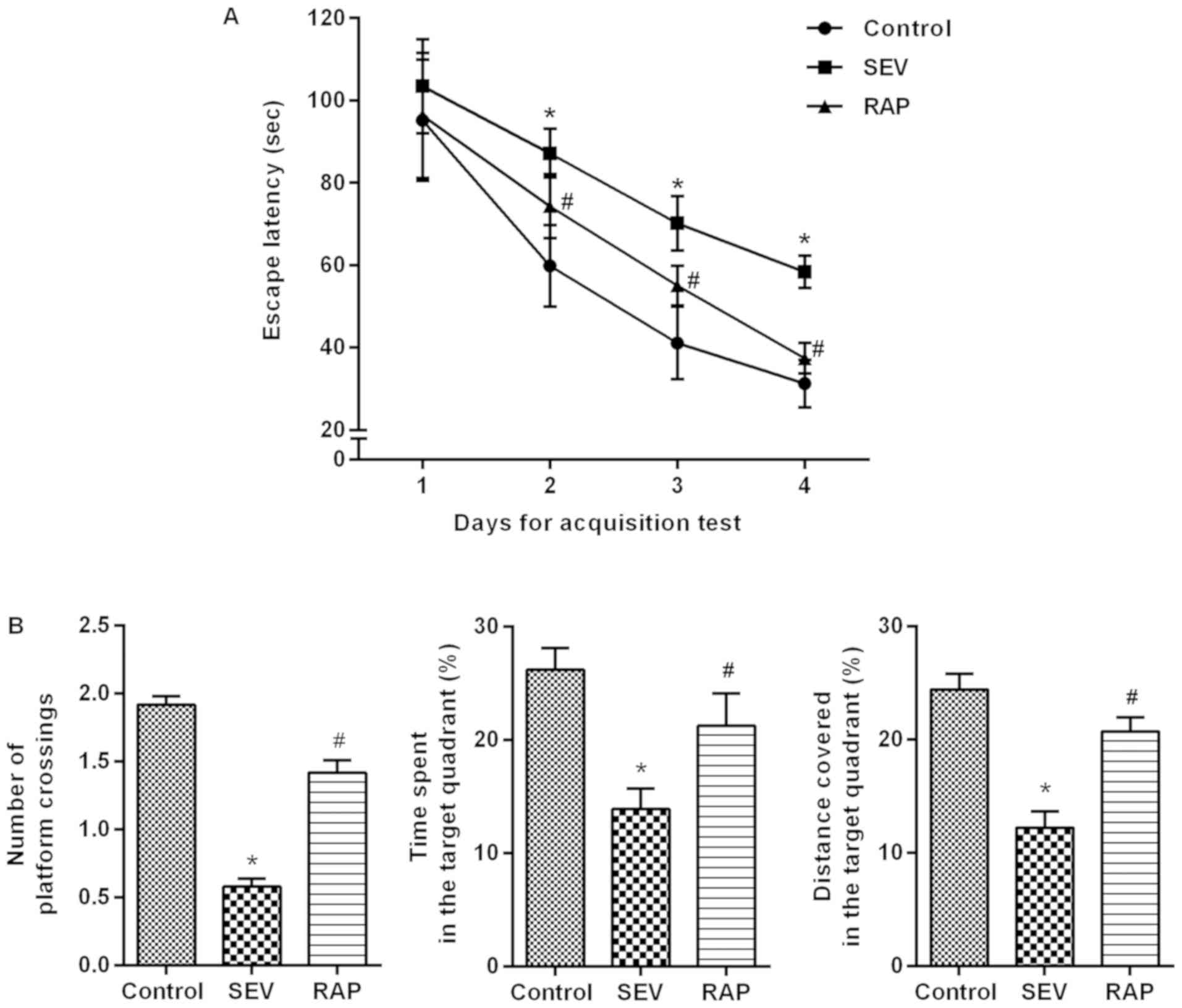
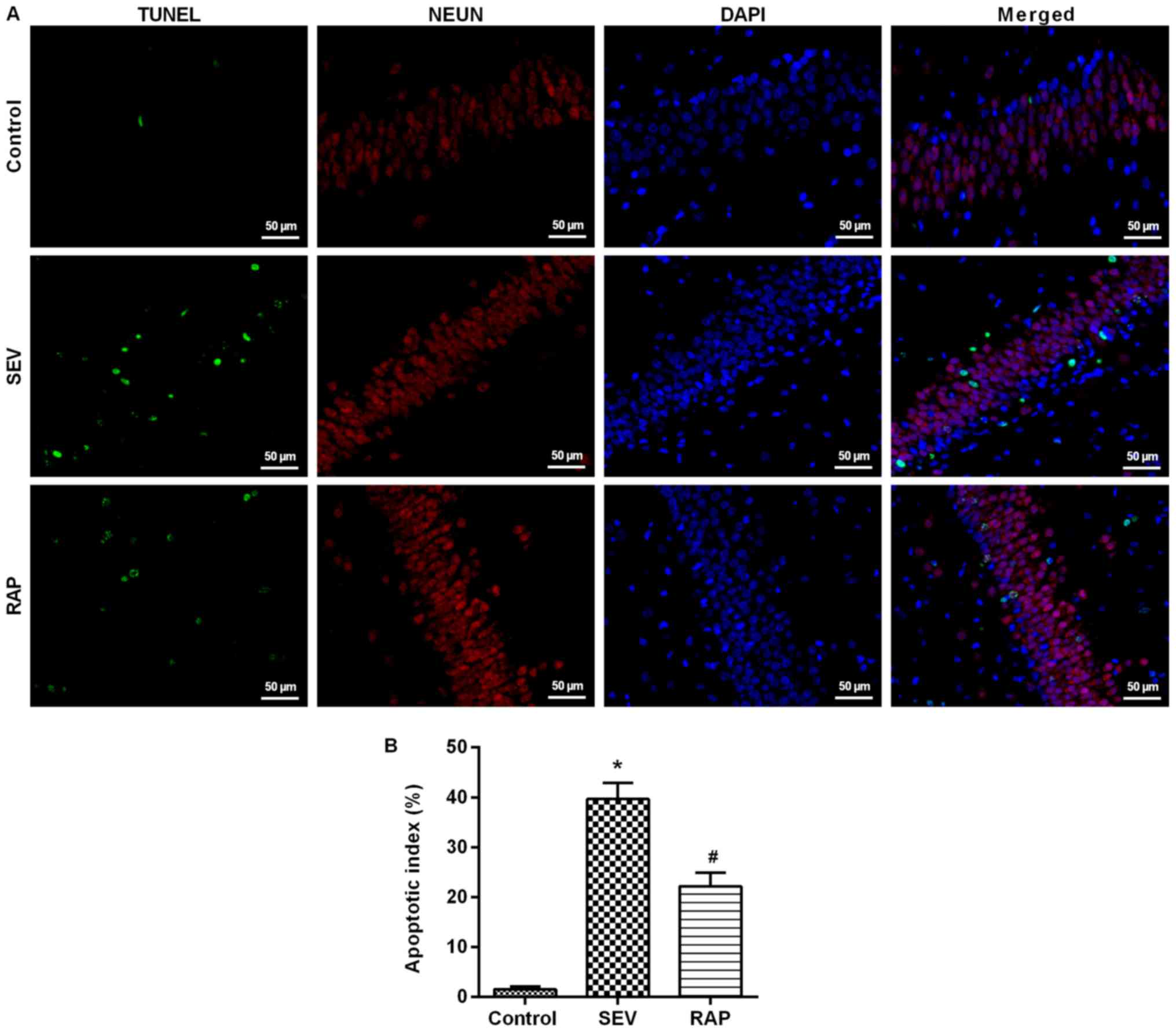
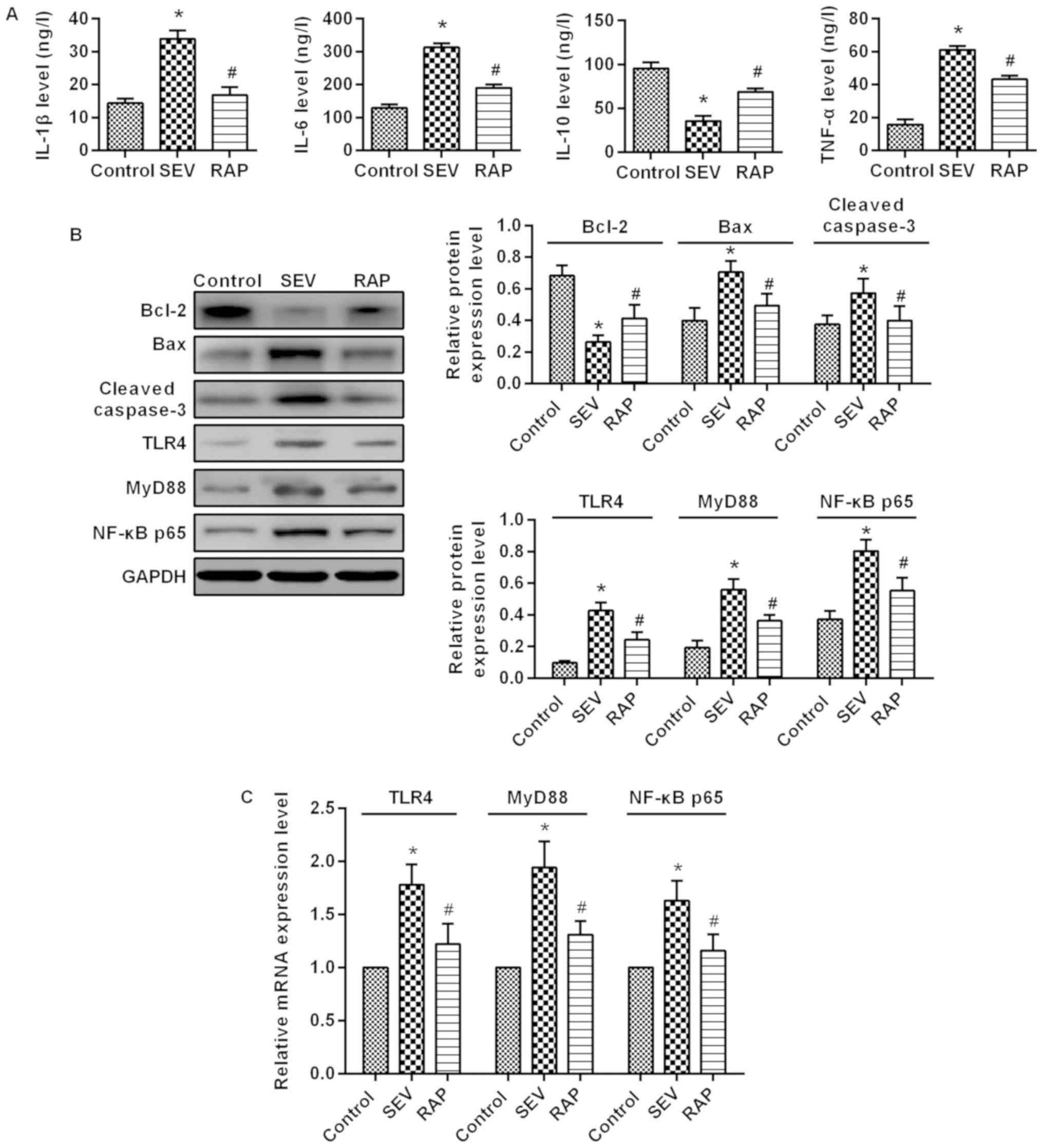
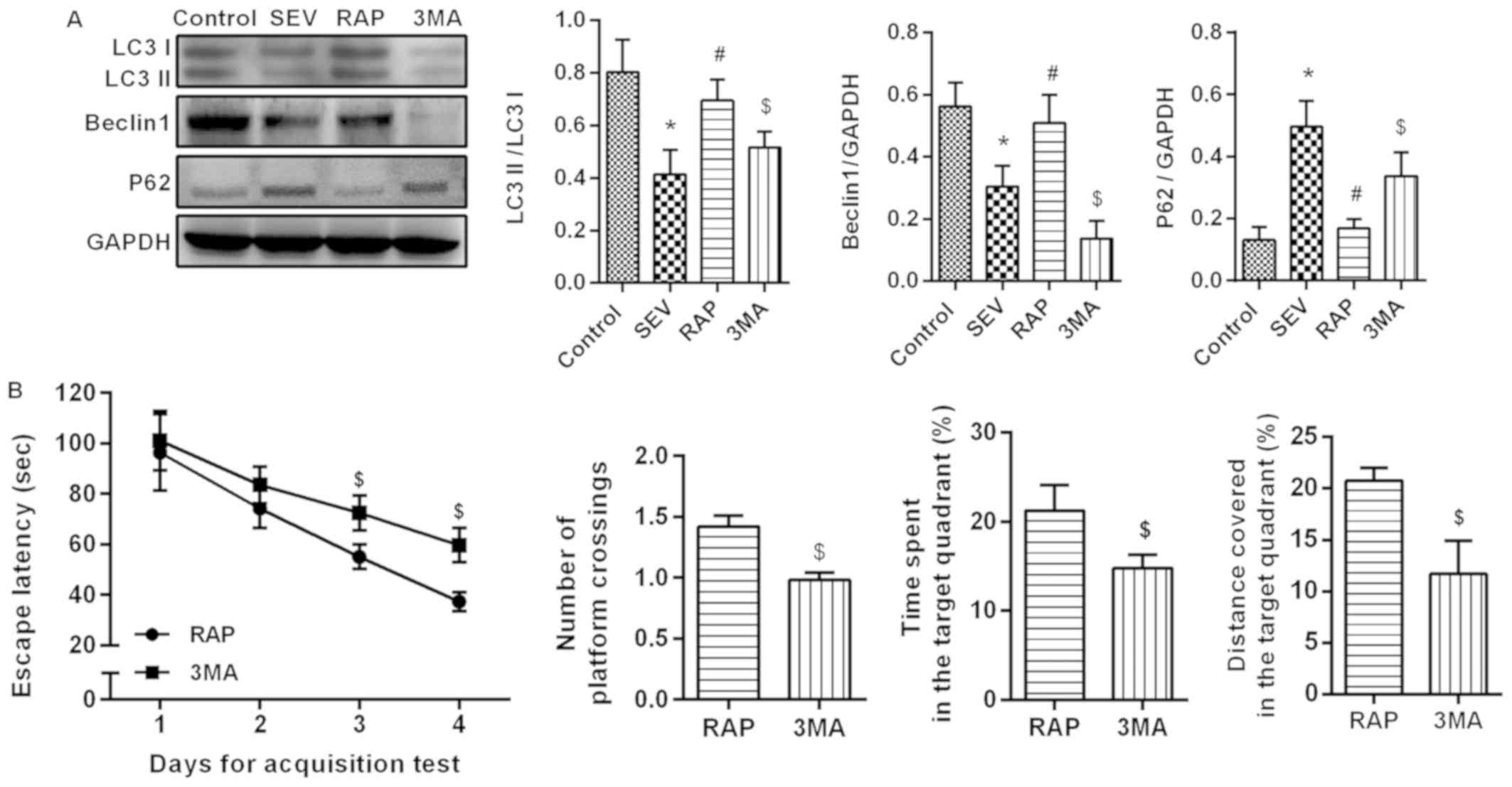
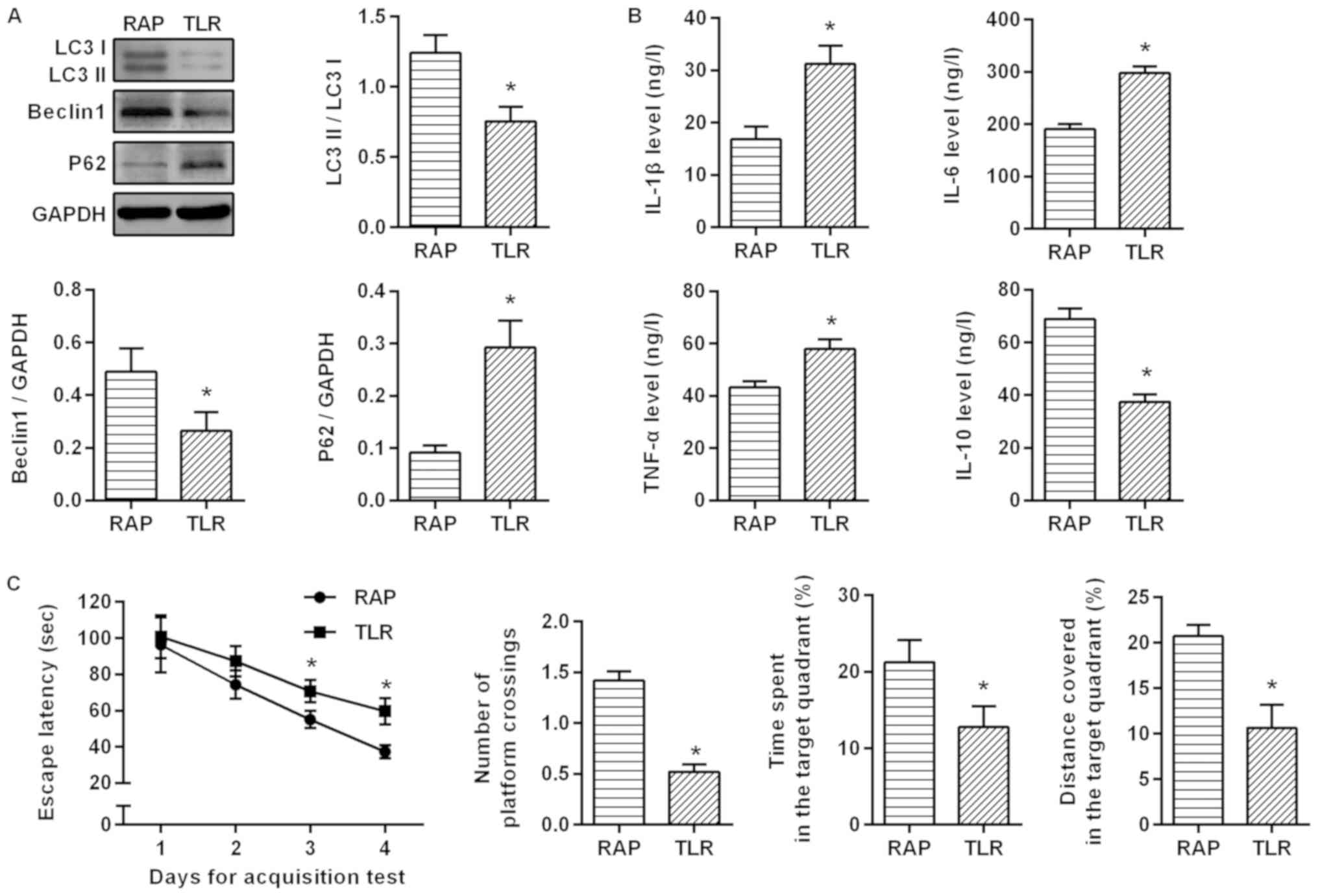
|
1
|
Benhamou D and Brouquet A: Postoperative
cerebral dysfunction in the elderly: Diagnosis and prophylaxis. J
Visc Surg. 153:S27–S32. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brioni JD, Varughese S, Ahmed R and Bein
B: A clinical review of inhalation anesthesia with sevoflurane:
From early research to emerging topics. J Anesth. 31:764–778. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang L, Huang K and Ning H: Autophagy
induction by hispidulin provides protection against
sevoflurane-induced neuronal apoptosis in aged rats. Biomed
Pharmacother. 98:460–468. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yoo YJ, Kim H, Park SR and Yoon YJ: An
overview of rapamycin: from discovery to future perspectives. J Ind
Microbiol Biotechnol. 44:537–553. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maiese K: The mechanistic target of
rapamycin (mTOR) and the silent mating-type information regulation
2 homolog 1 (SIRT1): Oversight for neurodegenerative disorders.
Biochem Soc Trans. 46:351–360. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang X, Zhou Y, Xu M and Chen G:
Autophagy Is Involved in the Sevoflurane Anesthesia-Induced
Cognitive Dysfunction of Aged Rats. PLoS One. 11:e01535052016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cai Z, Zhao B, Li K, Zhang L, Li C, Quazi
SH and Tan Y: Mammalian target of rapamycin: A valid therapeutic
target through the autophagy pathway for Alzheimer's disease? J
Neurosci Res. 90:1105–1118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nah J, Yuan J and Jung YK: Autophagy in
neurodegenerative diseases: From mechanism to therapeutic approach.
Mol Cells. 38:381–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gewirtz DA: The four faces of autophagy:
implications for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 74:647–651. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Espert L, Beaumelle B and Vergne I:
Autophagy in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and HIV infections. Front
Cell Infect Microbiol. 5:492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ntsapi C, Lumkwana D, Swart C, du Toit A
and Loos B: New insights into autophagy dysfunction related to
amyloid beta toxicity and neuropathology in alzheimer's disease.
Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 336:321–361. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Segura-Aguilar J and Huenchuguala S:
Aminochrome Induces Irreversible Mitochondrial Dysfunction by
Inducing Autophagy Dysfunction in Parkinson's Disease. Front
Neurosci. 12:1062018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Z, Liu D, Wang F, Liu S, Zhao S, Ling
EA and Hao A: Saturated fatty acids activate microglia via
Toll-like receptor 4/NF-κB signalling. Br J Nutr. 107:229–241.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chi OZ, Mellender SJ, Barsoum S, Liu X,
Damito S and Weiss HR: Effects of rapamycin pretreatment on
blood-brain barrier disruption in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion.
Neurosci Lett. 620:132–136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Feng Y, Gao J, Cui Y, Li M, Li R, Cui C
and Cui J: Neuroprotective effects of resatorvid against traumatic
brain injury in rat: Involvement of neuronal autophagy and TLR4
signaling pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 37:155–168. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zatroch KK, Knight CG, Reimer JN and Pang
DS: Refinement of intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital
for euthanasia in laboratory rats (Rattus norvegicus). BMC Vet Res.
13:602017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rundshagen I: Postoperative cognitive
dysfunction. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 111:119–125. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Berger M, Nadler JW, Browndyke J, Terrando
N, Ponnusamy V, Cohen HJ, Whitson HE and Mathew JP: Postoperative
cognitive dysfunction: Minding the gaps in our knowledge of a
common postoperative complication in the elderly. Anesthesiol Clin.
33:517–550. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tang Y, Wang X, Zhang S, Duan S, Qing W,
Chen G, Ye F, Le Y and Ouyang W: Pre-existing weakness is critical
for the occurrence of postoperative cognitive dysfunction in mice
of the same age. PLoS One. 12:e01824712017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Z, Liu F, Ma H, White PF, Yumul R,
Jiang Y, Wang N and Cao X: Age exacerbates surgery-induced
cognitive impairment and neuroinflammation in sprague-dawley rats:
The role of IL-4. Brain Res. 1665:65–73. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Coburn M, Fahlenkamp A, Zoremba N and
Schaelte G: Postoperative cognitive dysfunction: Incidence and
prophylaxis. Anaesthesist. 59:177–184; quiz 185. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Silbert B, Evered L, Scott DA, McMahon S,
Choong P, Ames D, Maruff P and Jamrozik K: Preexisting cognitive
impairment is associated with postoperative cognitive dysfunction
after hip joint replacement surgery. Anesthesiology. 122:1224–1234.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li L: The molecular mechanism of
glucagon-like peptide-1 Therapy in Alzheimer's disease, based on a
mechanistic target of rapamycin pathway. CNS Drugs. 31:535–549.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang J, Jiang J, Zuo Y and Gu Z:
Rapamycin protects the mitochondria against oxidative stress and
apoptosis in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Int J Mol Med.
31:825–832. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jove M, Portero-Otin M, Naudi A, Ferrer I
and Pamplona R: Metabolomics of human brain aging and age-related
neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 73:640–657.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Krzesniak M, Zajkowicz A, Matuszczyk I and
Rusin M: Rapamycin prevents strong phosphorylation of p53 on serine
46 and attenuates activation of the p53 pathway in A549 lung cancer
cells exposed to actinomycin D. Mech Ageing Dev. 139:11–21. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang Y, Ma Q, Ma X, Zhang Z, Liu N and
Wang M: Role of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in
autophagy and the neurodegenerative process using a senescence
accelerated mouse-prone 8 model. Exp Ther Med. 14:1051–1057. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Parzych KR and Klionsky DJ: An overview of
autophagy: morphology, mechanism, and regulation. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 20:460–473. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Twayana KS and Ravanan P: Eukaryotic cell
survival mechanisms: Disease relevance and therapeutic
intervention. Life Sci. 205:73–90. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Saha S, Panigrahi DP, Patil S and Bhutia
SK: Autophagy in health and disease: A comprehensive review. Biomed
Pharmacother. 104:485–495. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Luo T, Liu G, Ma H, Lu B, Xu H, Wang Y, Wu
J, Ge P and Liang J: Inhibition of autophagy via activation of
PI3K/Akt pathway contributes to the protection of ginsenoside Rb1
against neuronal death caused by ischemic insults. Int J Mol Sci.
15:15426–15442. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen S, Yuan J, Yao S, Jin Y, Chen G, Tian
W, Xi J, Xu Z, Weng D and Chen J: Lipopolysaccharides may aggravate
apoptosis through accumulation of autophagosomes in alveolar
macrophages of human silicosis. Autophagy. 11:2346–2357. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nair AR, Masson GS, Ebenezer PJ, Del Piero
F and Francis J: Role of TLR4 in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute
kidney injury: protection by blueberry. Free Radic Biol Med.
71:16–25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dong RQ, Wang ZF, Zhao C, Gu HR, Hu ZW,
Xie J and Wu YQ: Toll-like receptor 4 knockout protects against
isoproterenol-induced cardiac fibrosis: The role of autophagy. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 20:84–92. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|