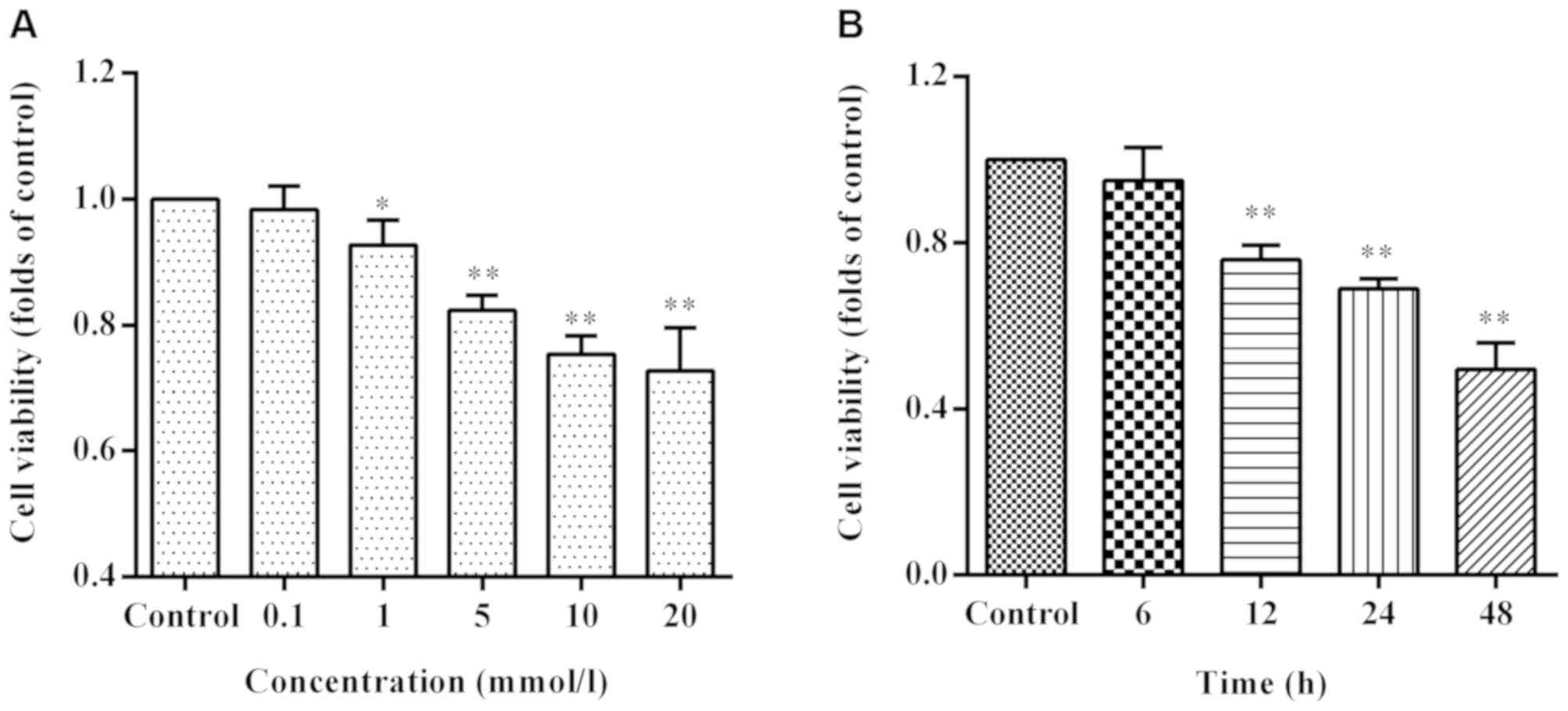
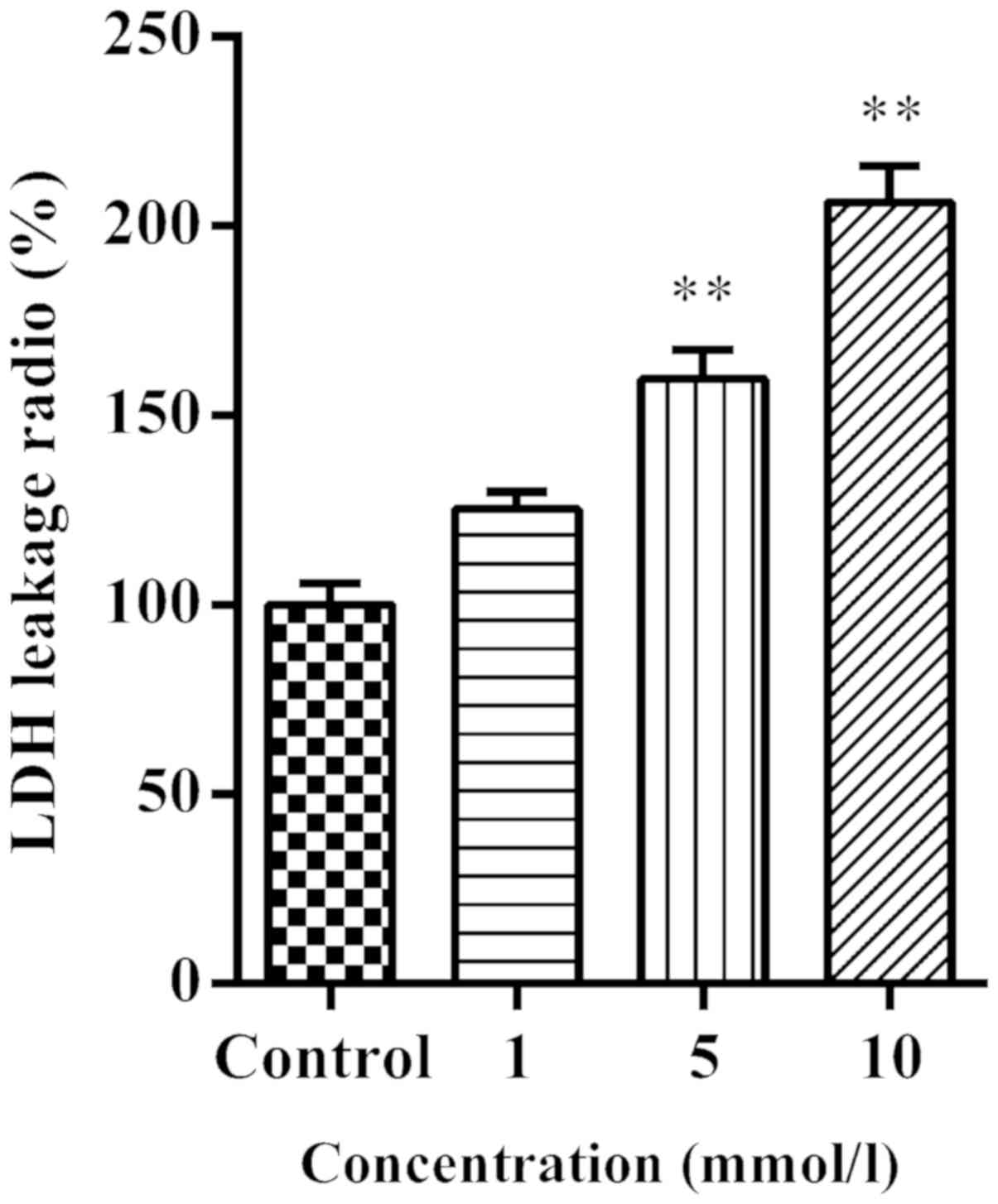
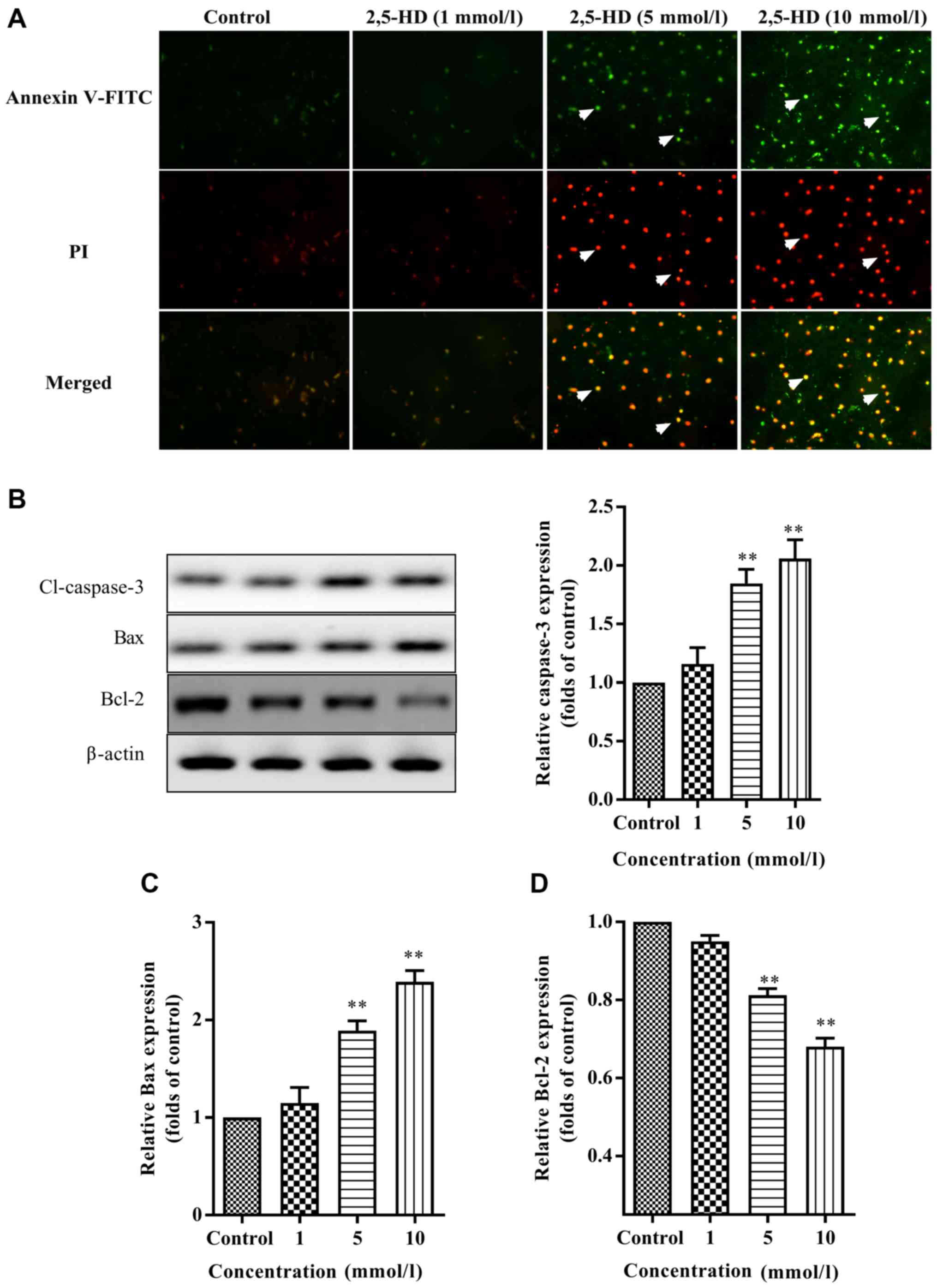
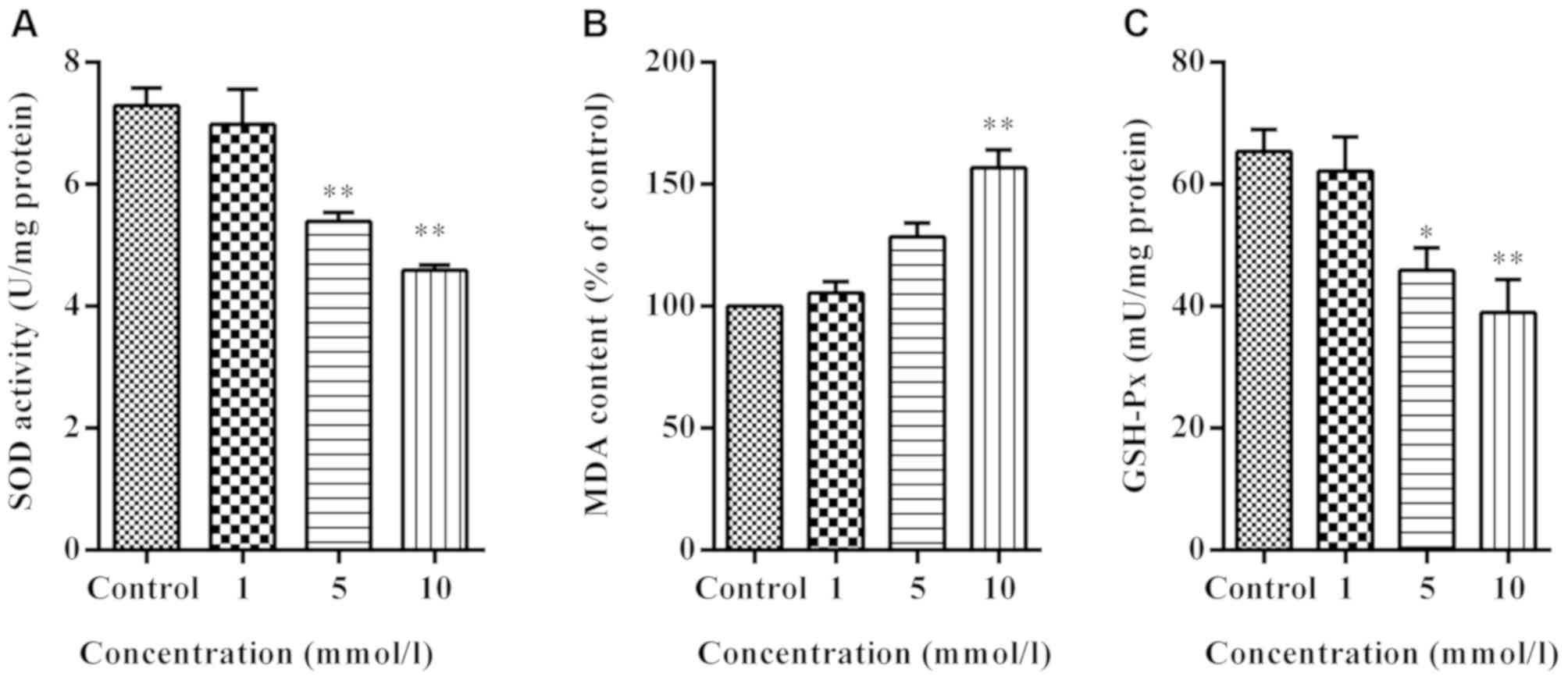
|
1
|
Zhang TL, Han XY, Zhao XL, Zhao L, Zhang
CL, Yu LH, Yu SF and Xie KQ: 2,5-Hexanedione induced reduction in
protein content and mRNA expression of neurofilament in rat
cerebral cortex. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 20:92–98. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sabyrov K, Jiang J, Yaghi OM and Somorjai
GA: Hydroisomerization of n-hexane using acidified metal-organic
framework and platinum nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc.
139:12382–12385. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Puri V, Gupta AD, Chaudhry N and Saran RK:
Reversible cerebral and brain stem dysfunction in n: Hexane
neuropathy. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 18:464–467. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guimaraes-Costa R, Schoindre Y, Metlaine
A, Lefaucheur JP, Camdessanché JP, Maisonobe T and Léger JM:
N-hexane exposure: A cause of small fiber neuropathy. J Peripher
Nerv Syst. 23:143–146. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Boekelheide K, Fleming SL, Allio T,
Embree-Ku ME, Hall SJ, Johnson KJ, Kwon EJ, Patel SR, Rasoulpour
RJ, Schoenfeld HA and Thompson S: 2,5-hexanedioneinduced testicular
injury. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 43:125–147. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xing-Fu P, Ya-Ling Q, Wei Z, Hong-Fang T,
Zheng R, Bang-Hua W, Han-Lin H, Yu-Xin Z and Hui-Fang Y:
Determination of total urinary 2,5-hexanedione in the Chinese
general population. Environ Res. 150:645–650. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu S, Chen F, Wang L and Sun W, Liu Q,
Chen H, Su D, Jiang Y, Piao F, Sun X and Sun W: 2,5-hexanedione
induced apoptosis of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by
reactive oxygen species. J Occup Health. 58:170–178. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brenner C and Kroemer G: Apoptosis.
Mitochondria-the death signal integrators. Science. 289:1150–1151.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
McArthur K, Whitehead LW, Heddleston JM,
Li L, Padman BS, Oorschot V, Geoghegan ND, Chappaz S, Davidson S,
San Chin H, et al: BAK/BAX macropores facilitate mitochondrial
herniation and mtDNA efflux during apoptosis. Science. 359(pii):
eaao60472018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Scorrano L, Oakes SA, Opferman JT, Cheng
EH, Sorcinelli MD, Pozzan T and Korsmeyer SJ: BAX and BAK
regulation of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+: A control point for
apoptosis. Science. 300:135–139. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang C, Hou L, Yang J, Che Y, Sun F, Li H
and Wang Q: 2,5-Hexanedione induces dopaminergic neurodegeneration
through integrin αMβ2/NADPH oxidase axis-mediated microglial
activation. Cell Death Dis. 9:602018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sharma Y, Srivastava N and Bala K:
Neuroprotective ability of TMV coat protein on rat PC-12 cells and
it's in silico study with LRRK2 receptor. Neurol Res. 40:1028–1039.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu W, Lv Z, Zhang L, Gao Z, Chen X, Yang X
and Zhong M: Astragaloside IV reduces the hypoxiainduced injury in
PC-12 cells by inhibiting expression of miR-124. Biomed
Pharmacother. 106:419–425. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang X, Zhu G, Yang S, Wang X, Cheng H,
Wang F, Li X and Li Q: Paeonol prevents excitotoxicity in rat
pheochromocytoma PC12 cells via downregulation of ERK activation
and inhibition of apoptosis. Planta Med. 77:1695–1701. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang CP, Zhang ZH, Zhang LH and Rui HC:
Neuroprotective Role of MicroRNA-22 in a 6-hydroxydopamine-induced
cell model of parkinson's disease via regulation of its target gene
TRPM7. J Mol Neurosci. 60:445–452. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jesko H, Wilkaniec A, Cieslik M, Hilgier
W, Gąssowska M, Lukiw WJ and Adamczyk A: Altered arginine
metabolism in cells transfected with human wildtype beta amyloid
precursor protein (βAPP). Curr Alzheimer Res. 13:1030–1039. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang NK, Lin YL, Cheng JJ and Lai WL:
Gastrodia elata prevents rat pheochromocytoma cells from
serum-deprived apoptosis: The role of the MAPK family. Life Sci.
75:1649–1657. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Seki K, Cueno ME, Kamio N, Saito Y,
Kamimoto A, Kurita-Ochiai T and Ochiai K: Varying butyric acid
amounts induce different stress- and cell death-related signals in
nerve growth factortreated PC12 cells: Implications in neuropathic
pain absence during periodontal disease progression. Apoptosis.
21:699–707. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang CL, Wang KC, Yang YC, Chiou CT, Tan
CH, Lin YL and Huang NK: Gastrodia elata alleviates mutant
huntingtin aggregation through mitochondrial function and
biogenesis mediation. Phytomedicine. 39:75–84. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gozal E, Metz CJ, Dematteis M, Sachleben
LR Jr, Schurr A and Rane MJ: PKA activity exacerbates
hypoxiainduced ROS formation and hypoxic injury in PC-12 cells.
Toxicol Lett. 279:107–114. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kahn LG and Trasande L: Environmental
toxicant exposure and hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: Recent
Findings. Curr Hypertension Rep. 20:872018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chen QS, Wang QW, Zhu JH, Xiao QZ and
Zhang L: Reactive oxygen species: Key regulators in vascular health
and diseases. Brit J Pharmacol. 175:1279–1292. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bondy SC: Anthropogenic pollutants may
increase the incidence of neurodegenerative disease in an aging
population. Toxicology. 341-343:41462016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xu B, Xu ZF, Deng Y, Liu W, Yang HB and
Wei YG: Protective effects of MK-801 on methylmercury-induced
neuronal injury in rat cerebral cortex: Involvement of oxidative
stress and glutamate metabolism dysfunction. Toxicology.
300:1121202012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yankner BA, Dawes LR, Fisher S,
Villa-Komaroff L, Oster-Granite ML and Neve RL: Neurotoxicity of a
fragment of the amyloid precursor associated with Alzheimer's
disease. Science. 245:417–420. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Y, Walker DW and King MA: Peroxide
mediates ethanol-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells. Free Radic
Biol Med. 30:389–392. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li S, Guan H, Qian Z, Sun Y, Gao C, Li G,
Yang Y, Piao F and Hu S: Taurine inhibits 2,5-hexanedione-induced
oxidative stress and mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in PC12
cells. Ind Health. 55:108–118. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Forrester SJ, Kikuchi DS, Hernandes MS, Xu
Q and Griendling KK: Reactive oxygen species in metabolic and
inflammatory signaling. Circ Res. 122:877–902. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Spicer Z and Millhorn DE: Oxygen sensing
in neuroendocrine cells and other cell types: Pheochromocytoma
(PC12) cells as an experimental model. Endocr Pathol. 14:277–291.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gillies PJ, Norton RM and Bus JS: Effect
of 2,5-Hexanedione on lipid biosynthesis in sciatic nerve and brain
of the rat. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 54:210–216. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rossi A, Simonati A, Rizzuto N and Toschi
G: Neurotoxic action of 2,5hexanedione on the autonomic nervous
system: Ultrastructural and functional alterations in the rat
sympathetic superior cervical ganglion. Brain Res. 243:373–377.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cheng X and Ferrell JE Jr: Apoptosis
propagates through the cytoplasm as trigger waves. Science.
361:607–612. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Thompson CB: Apoptosis in the pathogenesis
and treatment of disease. Science. 267:1456–1462. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Spierings D, McStay G, Saleh M, Bender C,
Chipuk J, Maurer U and Green DR: Connected to death: The
(unexpurgated) mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Science.
310:66–67. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mao W and Zhu Z: Parthenolide inhibits
hydrogen peroxideinduced osteoblast apoptosis. Mol Med Rep.
17:8369–8376. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Giorgio M, Migliaccio E, Orsini F,
Paolucci D, Moroni M, Contursi C, Pelliccia G, Luzi L, Minucci S,
Marcaccio M, et al: Electron transfer between cytochrome c and
p66Shc generates reactive oxygen species that trigger mitochondrial
apoptosis. Cell. 122:221–233. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
St-Pierre J, Drori S, Uldry M, Silvaggi
JM, Rhee J, Jäger S, Handschin C, Zheng K, Lin J, Yang W, et al:
Suppression of reactive oxygen species and neurodegeneration by the
PGC-1 transcriptional coactivators. Cell. 127:397–408. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kane DJ, Sarafian TA, Anton R, Hahn H,
Gralla EB, Valentine JS, Ord T and Bredesen DE: Bcl-2 inhibition of
neural death: Decreased generation of reactive oxygen species.
Science. 262:1274–1277. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nesnow S, Grindstaff RD, Lambert G,
Padgett WT, Bruno M, Ge Y, Chen PJ, Wood CE and Murphy L:
Propiconazole increases reactive oxygen species levels in mouse
hepatic cells in culture and in mouse liver by a cytochrome P450
enzyme mediated process. Chem Biol Interact. 194:79–89. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|