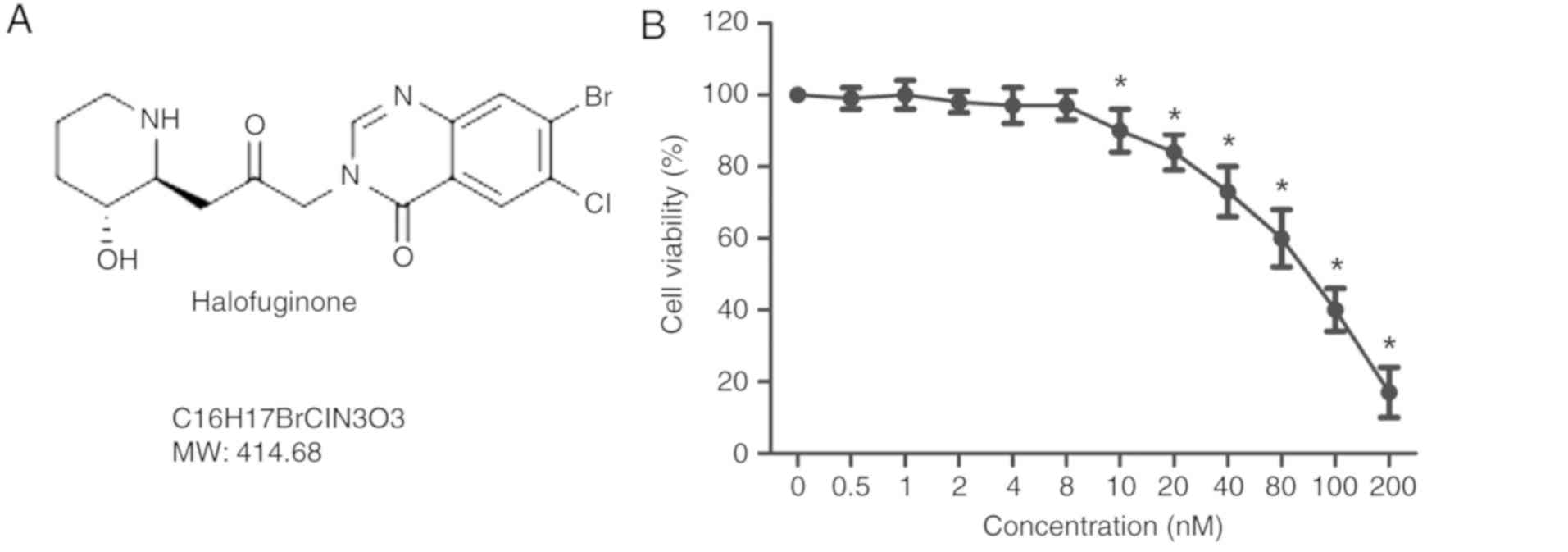
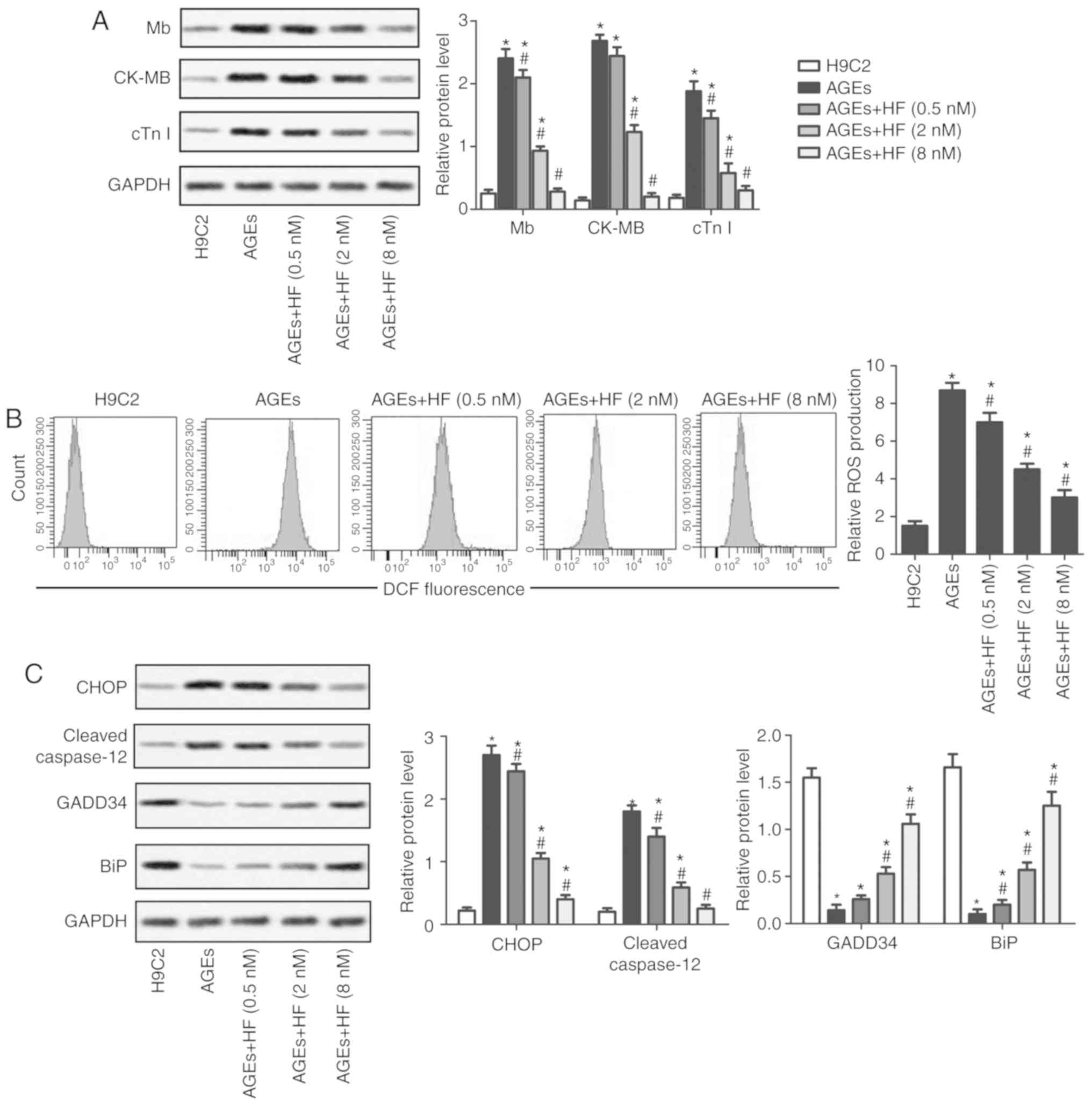
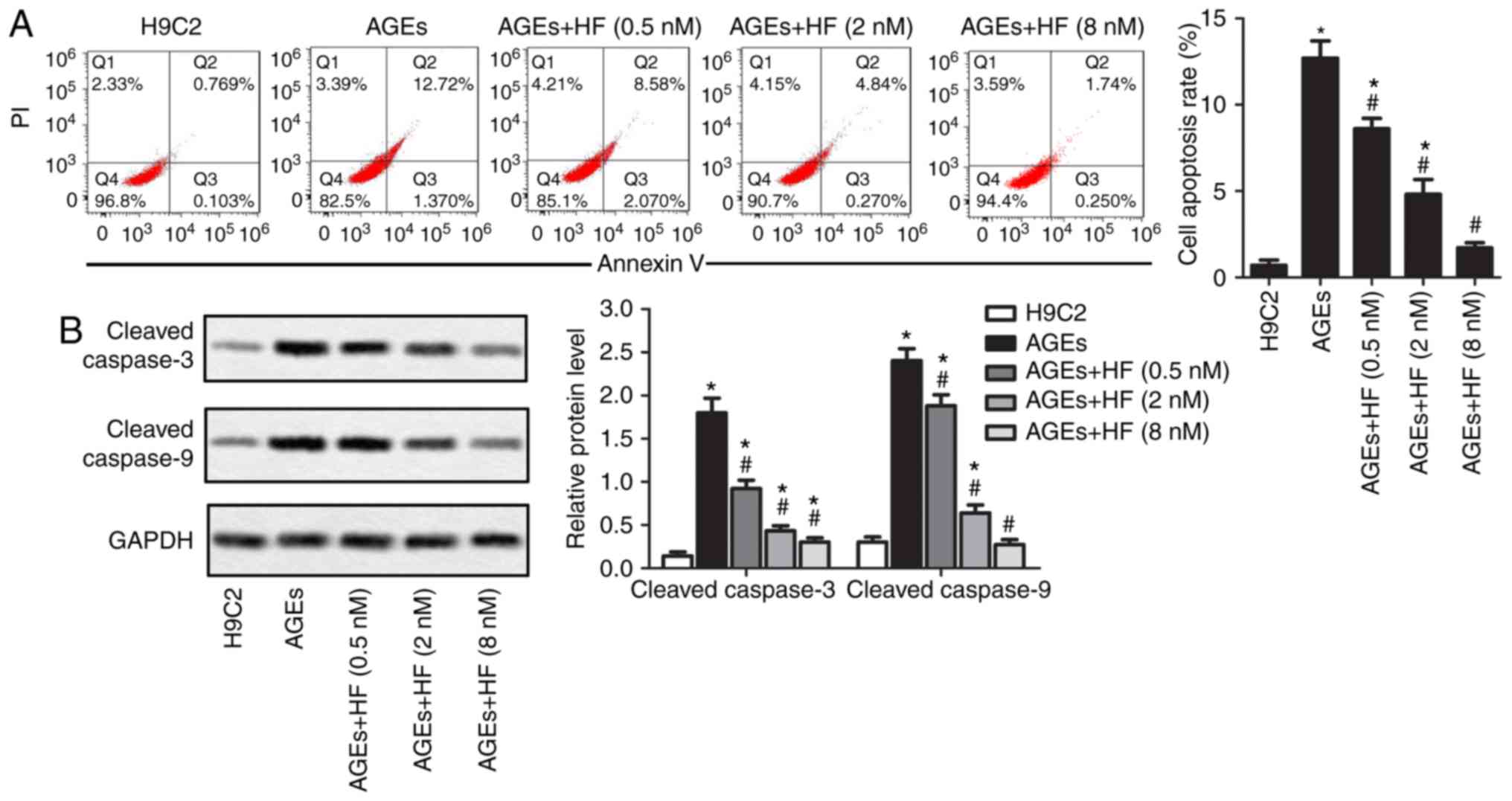
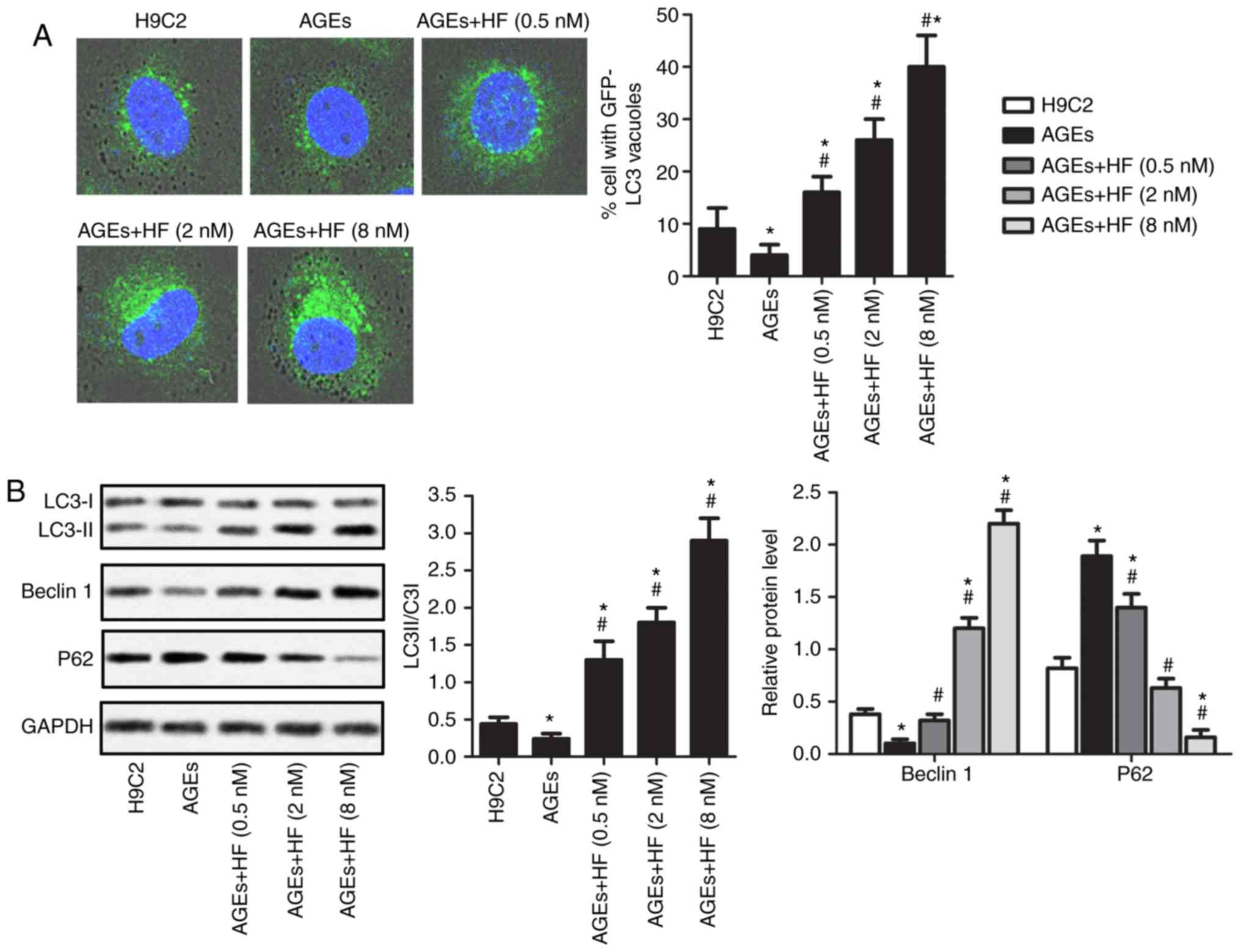
|
1
|
Basta G, Schmidt AM and De Caterina R:
Advanced glycation end products and vascular inflammation:
Implications for accelerated atherosclerosis in diabetes.
Cardiovasc Res. 63:582–592. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Corman B, Duriez M, Poitevin P, Heudes D,
Bruneval P, Tedgui A and Levy BI: Aminoguanidine prevents
age-related arterial stiffening and cardiac hypertrophy. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 95:1301–1306. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rani N, Bharti S, Bhatia J, Nag TC, Ray R
and Arya DS: Chrysin, a PPAR-γ agonist improves myocardial injury
in diabetic rats through inhibiting AGE-RAGE mediated oxidative
stress and inflammation. Chem Biol Interact. 250:59–67. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Swirski FK and Nahrendorf M: Leukocyte
behavior in atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, and heart
failure. Science. 339:161–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zeng S, Wang K, Huang M, Qiu Q, Xiao Y,
Shi M, Zou Y, Yang X, Xu H and Liang L: Halofuginone inhibits
TNF-α-induced the migration and proliferation of fibroblast-like
synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Int
Immunopharmacol. 43:187–194. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calik M, Yavas G, Calik SG, Yavas C, Celik
ZE, Sargon MF and Esme H: Amelioration of radiation-induced lung
injury by halofuginone: An experimental study in Wistar-Albino
rats. Hum Exp Toxicol. 36:638–647. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cerit KK, Karakoyun B, Yüksel M, Ercan F,
Tuğtepe H, Dagli TE and Yeğen BÇ: Halofuginone alleviates
burn-induced hepatic and renal damage in rats. J Burn Care Res.
38:e384–e394. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qin P, Arabacilar P, Bernard RE, Bao W,
Olzinski AR, Guo Y, Lal H, Eisennagel SH, Platchek MC, Xie W, et
al: Activation of the amino acid response pathway blunts the
effects of cardiac stress. J Am Heart Assoc. 6(pii):
e0044532017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao P, Kuai J, Gao J, Sun L, Wang Y and
Yao L: Delta opioid receptor agonist attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced myocardial injury by regulating
autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 492:140–146. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Giricz Z, Mentzer RM Jr and Gottlieb RA:
Autophagy, myocardial protection, and the metabolic syndrome. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 60:125–132. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hashem SI, Perry CN, Bauer M, Han S, Clegg
SD, Ouyang K, Deacon DC, Spinharney M, Panopoulos AD, Izpisua
Belmonte JC, et al: Brief report: Oxidative stress mediates
cardiomyocyte apoptosis in a human model of danon disease and heart
failure. Stem Cells. 33:2343–2350. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim I, Xu W and Reed JC: Cell death and
endoplasmic reticulum stress: Disease relevance and therapeutic
opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:1013–1030. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yao Y, Lu Q, Hu Z, Yu Y, Chen Q and Wang
QK: A non-canonical pathway regulates ER stress signaling and
blocks ER stress-induced apoptosis and heart failure. Nat Commun.
8:1332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Marchi S, Patergnani S and Pinton P: The
endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria connection: One touch, multiple
functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1837:461–469. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen GQ, Gong RH, Yang DJ, Zhang G, Lu AP,
Yan SC, Lin SH and Bian ZX: Halofuginone dually regulates
autophagic flux through nutrient-sensing pathways in colorectal
cancer. Cell Death Dis. 8:e27892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ge J, Jia Q, Liang C, Luo Y, Huang D, Sun
A, Wang K, Zou Y and Chen H: Advanced glycosylation end products
might promote atherosclerosis through inducing the immune
maturation of dendritic cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
25:2157–2163. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu Y, Feng L, Wang S, Zhu Q, Lin J, Lou C,
Xiang P, He B, Zheng Z, Tang D and Zuo G: Phytoestrogen
calycosin-7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside ameliorates advanced glycation
end products-induced HUVEC damage. J Cell Biochem. 112:2953–2965.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hippisley-Cox J and Coupland C: Diabetes
treatments and risk of heart failure, cardiovascular disease, and
all cause mortality: Cohort study in primary care. BMJ.
354:i34772016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Heusch G, Libby P, Gersh B, Yellon D, Böhm
M, Lopaschuk G and Opie L: Cardiovascular remodelling in coronary
artery disease and heart failure. Lancet. 383:1933–1943. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang M, Zhao Z, Shen M, Zhang Y, Duan J,
Guo Y, Zhang D, Hu J, Lin J, Man W, et al: Polydatin protects
cardiomyocytes against myocardial infarction injury by activating
Sirt3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:1962–1972. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Luo Z, Zhong L, Han X, Wang H, Zhong J and
Xuan Z: Astragalus membranaceus prevents daunorubicin-induced
apoptosis of cultured neonatal cardiomyocytes: Role of free radical
effect of Astragalus membranaceus on daunorubicin cardiotoxicity.
Phytother Res. 23:761–767. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Woo AY, Waye MM, Tsui SK, Yeung ST and
Cheng CH: Andrographolide up-regulates cellular-reduced glutathione
level and protects cardiomyocytes against hypoxia/reoxygenation
injury. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 325:226–235. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yavas G, Calik M, Calik G, Yavas C, Ata O
and Esme H: The effect of Halofuginone in the amelioration of
radiation induced-lung fibrosis. Med Hypotheses. 80:357–359. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu ZW, Zhu HT, Chen KL, Dong X, Wei J,
Qiu C and Xue JH: Protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum
kinase (PERK) signaling pathway plays a major role in reactive
oxygen species (ROS)-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced
apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
12:1582013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yan X, Xun M, Dou X, Wu L, Han Y and Zheng
J: Regulation of Na+-K+-ATPase effected high
glucose-induced myocardial cell injury through c-Src dependent
NADPH oxidase/ROS pathway. Exp Cell Res. 357:243–251. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Miyazaki Y, Kaikita K, Endo M, Horio E,
Miura M, Tsujita K, Hokimoto S, Yamamuro M, Iwawaki T, Gotoh T, et
al: C/EBP homologous protein deficiency attenuates myocardial
reperfusion injury by inhibiting myocardial apoptosis and
inflammation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:1124–1132. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Karadeniz Cerit K, Karakoyun B, Yüksel M,
Özkan N, Cetinel Ş, Tolga Dağli E, Yeğen BÇ and Tuğtepe H: The
antifibrotic drug halofuginone reduces ischemia/reperfusion-induced
oxidative renal damage in rats. J Pediatr Urol. 9:174–183. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu D, Zhang M and Yin H: Signaling
pathways involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal
apoptosis. Int J Neurosci. 123:155–162. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bodanovsky A, Guttman N, Barzilai-Tutsch
H, Genin O, Levy O, Pines M and Halevy O: Halofuginone improves
muscle-cell survival in muscular dystrophies. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1843:1339–1347. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nishida K, Yamaguchi O and Otsu K:
Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis in heart disease. Circ
Res. 103:343–351. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pattison JS, Osinska H and Robbins J: Atg7
induces basal autophagy and rescues autophagic deficiency in
CryABR120G cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 109:151–160. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Maron BJ, Roberts WC, Arad M, Haas TS,
Spirito P, Wright GB, Almquist AK, Baffa JM, Saul JP, Ho CY, et al:
Clinical outcome and phenotypic expression in LAMP2 cardiomyopathy.
JAMA. 301:1253–1259. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gottlieb RA and Mentzer RM: Autophagy
during cardiac stress: Joys and frustrations of autophagy. Annu Rev
Physiol. 72:45–59. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|