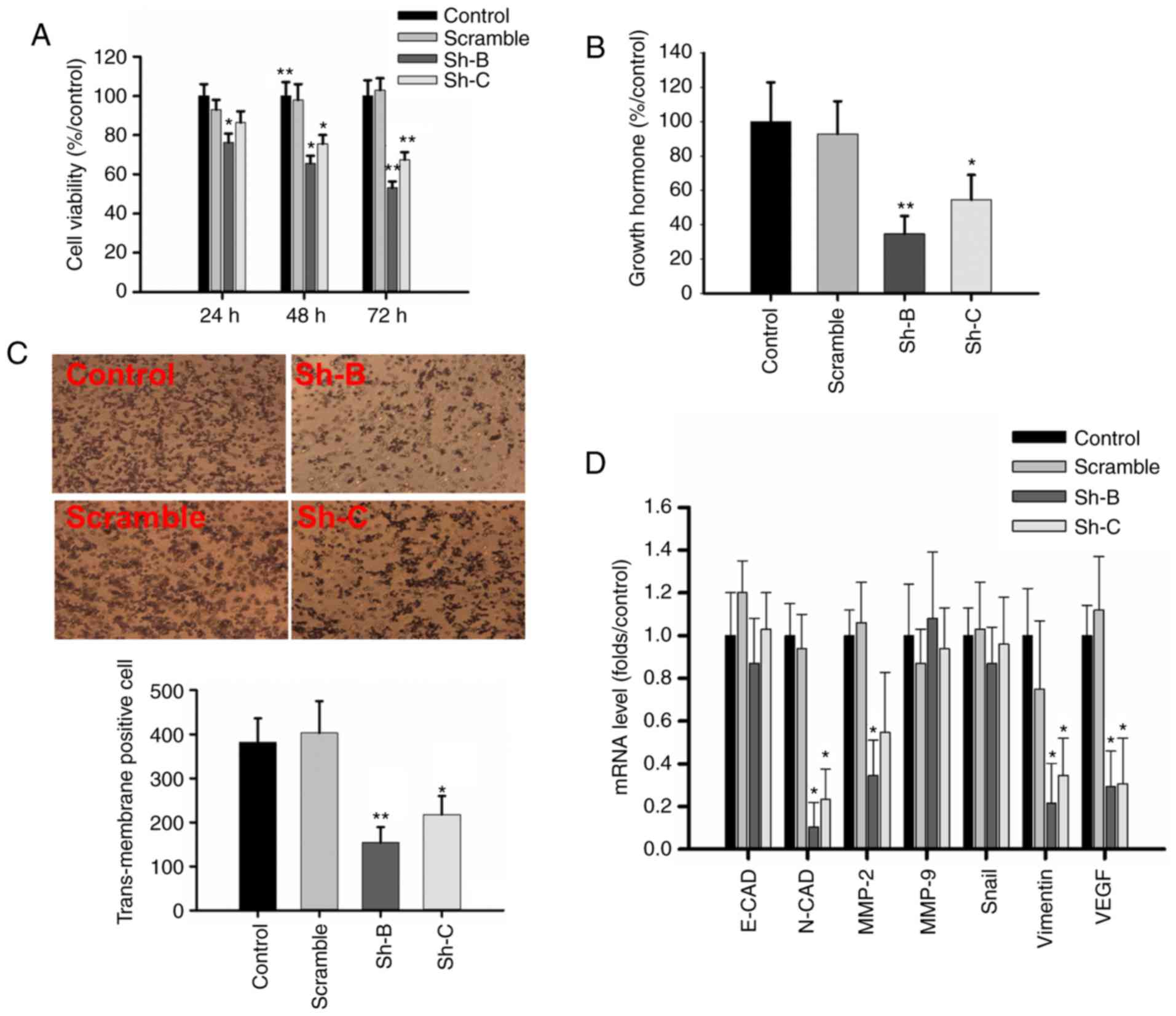
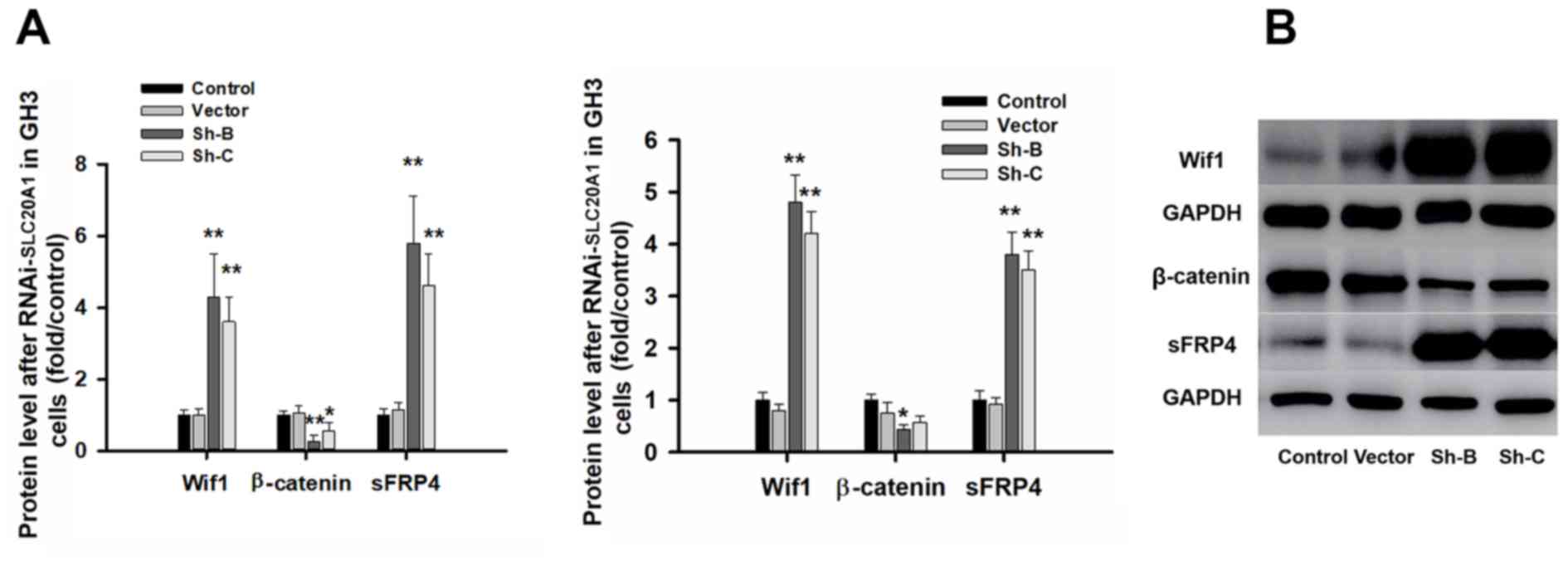
|
1
|
AlDallal S: Acromegaly: A challenging
condition to diagnose. Int J Gen Med. 11:337–343. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Inoshita N and Nishioka H: The 2017 WHO
classification of pituitary adenoma: Overview and comments. Brain
Tumor Pathol. 35:51–56. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abreu A, Tovar AP, Castellanos R,
Valenzuela A, Giraldo CM, Pinedo AC, Guerrero DP, Barrera CA,
Franco HI, Ribeiro-Oliveira A Jr, et al: Challenges in the
diagnosis and management of acromegaly: A focus on comorbidities.
Pituitary. 19:448–457. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kempf J, Schmitz A, Meier A, Delfs N,
Mueller B, Fandino J, Schuetz P and Berkmann S: Adenoma size and
postoperative IGF-1 levels predict surgical outcomes in acromegaly
patients: Results of the Swiss Pituitary Registry (SwissPit). Swiss
Med Wkly. 148:w146532018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Välimäki N, Demir H, Pitkänen E, Kaasinen
E, Karppinen A, Kivipelto L, Schalin-Jäntti C, Aaltonen LA and
Karhu A: Whole-genome sequencing of growth hormone (GH)-secreting
pituitary adenomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 100:3918–3927. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Picard C, Silvy M, Gerard C, Buffat C,
Lavaque E, Figarella-Branger D, Dufour H, Gabert J, Beckers A, Brue
T, et al: Gs alpha overexpression and loss of Gs alpha imprinting
in human somatotroph adenomas: Association with tumor size and
response to pharmacologic treatment. Int J Cancer. 121:1245–1252.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Forster IC, Hernando N, Biber J and Murer
H: Phosphate transporters of the SLC20 and SLC34 families. Mol
Aspects Med. 34:386–395. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ravera S, Virkki LV, Murer H and Forster
IC: Deciphering PiT transport kinetics and substrate specificity
using electrophysiology and flux measurements. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 293:C606–C620. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Byskov K, Jensen N, Kongsfelt IB, Wielsøe
M, Pedersen LE, Haldrup C and Pedersen L: Regulation of cell
proliferation and cell density by the inorganic phosphate
transporter PiT-1. Cell Division. 7:72012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kongsfelt IB, Byskov K, Pedersen LE and
Pedersen L: High levels of the type III inorganic phosphate
transporter PiT-1 (SLC20A1) can confer faster cell adhesion. Exp
Cell Res. 326:57–67. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sato K and Akimoto K: Expression levels of
KMT2C and SLC20A1 identified by information-theoretical analysis
are powerful prognostic biomarkers in ER-positive breast cancer.
Clin Breast Cancer. 17:e135–e142. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Song W, Qian L, Jing G, Jie F, Xiaosong S,
Chunhui L, Yangfang L, Guilin L, Gao H and Yazhuo Z: Aberrant
expression of the sFRP and WIF1 genes in invasive non-functioning
pituitary adenomas. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 474:168–175. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ricardo VL, Robert YO, Gunter K and Juan
R: WHO classification of tumours of endocrine organ. 4th.
International agency for research on cancere; France, Lyon: pp.
19–23. 2018
|
|
15
|
Liu C, Gao H, Cao L, Gui S, Liu Q, Li C,
Li D, Gong L and Zhang Y: The role of FSCN1 in migration and
invasion of pituitary adenomas. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 419:217–224.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pez F, Lopez A, Kim M, Wands JR, Caron de
Fromentel C and Merle P: Wnt signaling and hepatocarcinogenesis:
Molecular targets for the development of innovative anticancer
drugs. J Hepatol. 59:1107–1117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ueland T, Olarescu NC, Jørgensen AP,
Otterdal K, Aukrust P, Godang K, Lekva T and Bollerslev J:
Increased serum and bone matrix levels of the secreted Wnt
antagonist DKK-1 in patients with growth hormone deficiency in
response to growth hormone treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
100:736–743. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hage M, Viengchareun S, Brunet E, Villa C,
Pineau D, Bouligand J, Teglas JP, Adam C, Parker F, Lombès M, et
al: Genomic alterations and complex subclonal architecture in
sporadic GH-secreting pituitary adenomas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
103:1929–1939. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Caimari F and Korbonits M: Novel genetic
causes of pituitary adenomas. Clin Cancer Res. 22:5030–5042. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mete O and Lopes MB: Overview of the 2017
WHO Classification of pituitary tumors. Endocr Pathol. 28:228–243.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park HH, Kim EH, Ku CR, Lee EJ and Kim SH:
Outcomes of aggressive surgical resection in growth
hormone-secreting pituitary adenomas with cavernous sinus invasion.
World Neurosurg. 117:e280–e289. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang J, Liu Q, Gao H, Wan D, Li C, Li Z
and Zhang Y: EGFL7 participates in regulating biological behavior
of growth hormone-secreting pituitary adenomas via Notch2/DLL3
signaling pathway. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283177062032017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Barriuso J, Custodio A, Afonso R, Alonso
V, Astudillo A, Capdevila J, García-Carbonero R, Grande E,
Jimenez-Fonseca P, Marazuela M, et al: Prognostic and predictive
biomarkers for somatostatin analogs, peptide receptor radionuclide
therapy and serotonin pathway targets in neuroendocrine tumours.
Cancer Treat Rev. 70:209–222. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Su Z, Cai L, Lu J, Li C, Gui S, Liu C,
Wang C, Li Q, Zhuge Q and Zhang Y: Global expression profile of
tumor stem-like cells isolated from MMQ rat prolactinoma cell.
Cancer Cell Int. 17:152017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Occhi G, Losa M, Albiger N, Trivellin G,
Regazzo D, Scanarini M, Monteserin-Garcia JL, Fröhlich B, Ferasin
S, Terreni MR, et al: The glucose-dependent insulinotropic
polypeptide receptor is overexpressed amongst GNAS1
mutation-negative somatotropinomas and drives growth hormone
(GH)-promoter activity in GH3 cells. J Neuroendocrin. 23:641–649.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bergeron F, Sirois F and Mbikay M: ACTH
secretion by mouse corticotroph AtT20 cells is negatively modulated
by the intracellular level of 7B2. FEBS Lett. 512:259–262. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Peng H, Fan J, Wu J, Lang J, Wang J, Liu
H, Zhao S and Liao J: Silencing of HEPN1 is responsible for the
aggressive biological behavior of pituitary somatotroph adenomas.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 31:379–388. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Karin M: Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer
development and progression. Nature. 441:431–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Salaün C, Leroy C, Rousseau A, Boitez V,
Beck L and Friedlander G: Identification of a novel
transport-independent function of PiT-1/SLC20A1 in the regulation
of TNF-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 285:34408–34418. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wajant H, Pfizenmaier K and Scheurich P:
Tumor necrosis factor signaling. Cell Death Differ. 10:45–65. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kavitha K, Kowshik J, Kishore TK, Baba AB
and Nagini S: Astaxanthin inhibits NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathways via inactivation of Erk/MAPK and PI3K/Akt to
induce intrinsic apoptosis in a hamster model of oral cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1830:4433–4444. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu C, Wu Y, Yu S, Bai J, Li C, Wu D and
Zhang Y: Increased β-catenin and c-myc expression predict
aggressive growth of non-functioning pituitary adenomas: An
assessment using a tissue microarray-based approach. Mol Med Rep.
5:1793–1799. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Elston MS, Gill AJ, Conaglen JV, Clarkson
A, Shaw JM, Law AJ, Cook RJ, Little NS, Clifton-Bligh RJ, Robinson
BG and McDonald KL: Wnt pathway inhibitors are strongly
down-regulated in pituitary tumors. Endocrinology. 149:1235–1242.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chambers TJ, Giles A, Brabant G and Davis
JR: Wnt signalling in pituitary development and tumorigenesis.
Endocr Relat Cancer. 20:R101–R111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vassallo I, Zinn P, Lai M, Rajakannu P,
Hamou MF and Hegi ME: WIF1 re-expression in glioblastoma inhibits
migration through attenuation of non-canonical WNT signaling by
downregulating the lncRNA MALAT1. Oncogene. 35:12–21. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Y, Sang A, Zhu M, Zhang G, Guan H, Ji
M and Chen H: Tissue factor induces VEGF expression via activation
of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in ARPE-19 cells. Mol Vis.
22:886–897. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shan XS, Liu Q, Li ZY, Li CZ, Gao H and
Zhang YZ: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by SMAD4
activation in invasive growth hormone-secreting adenomas. Open
Chem. 16:571–582. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|