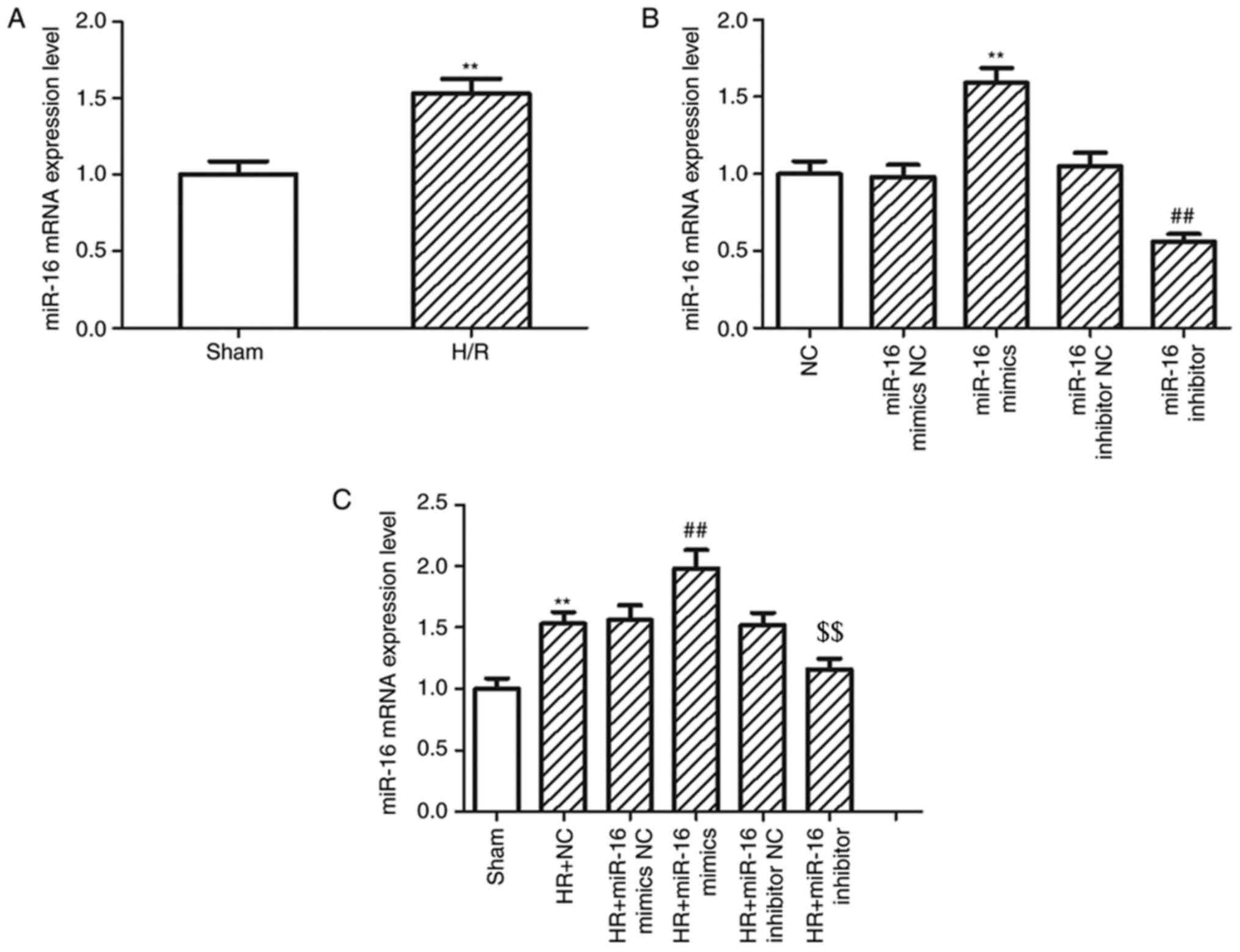
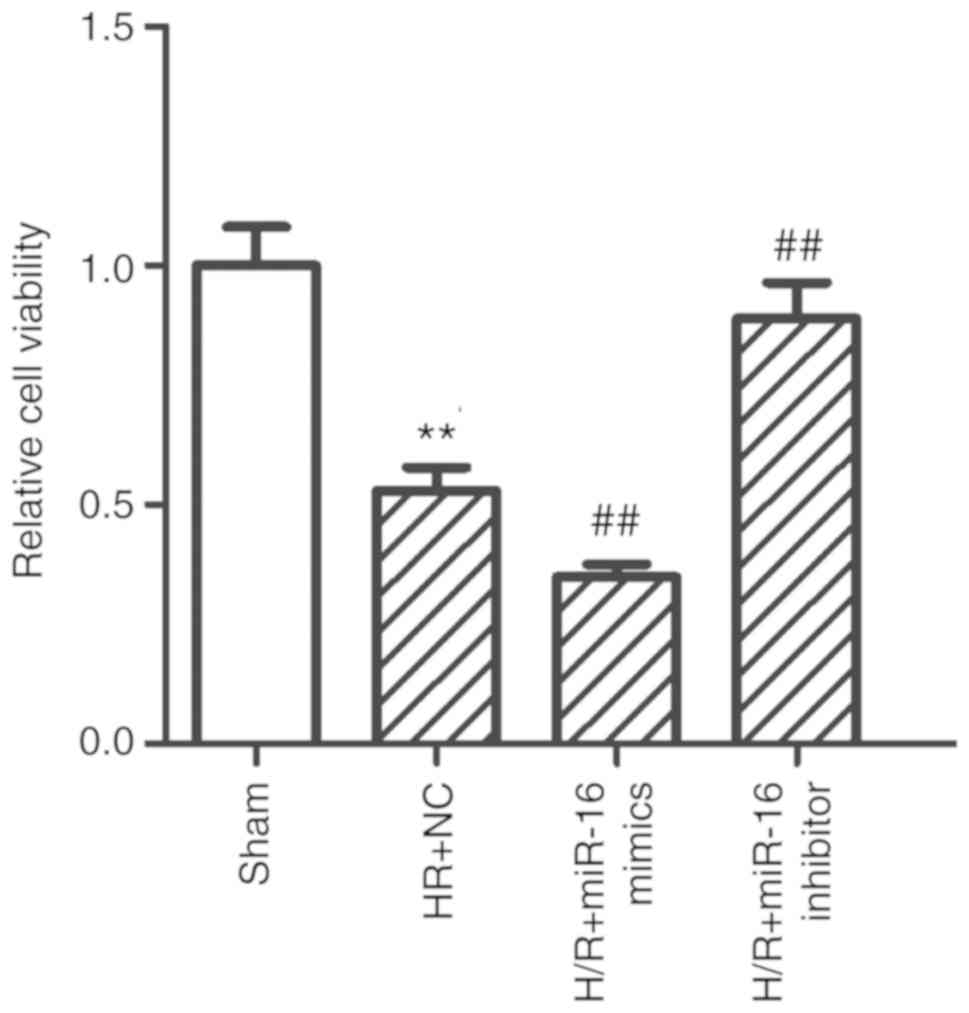
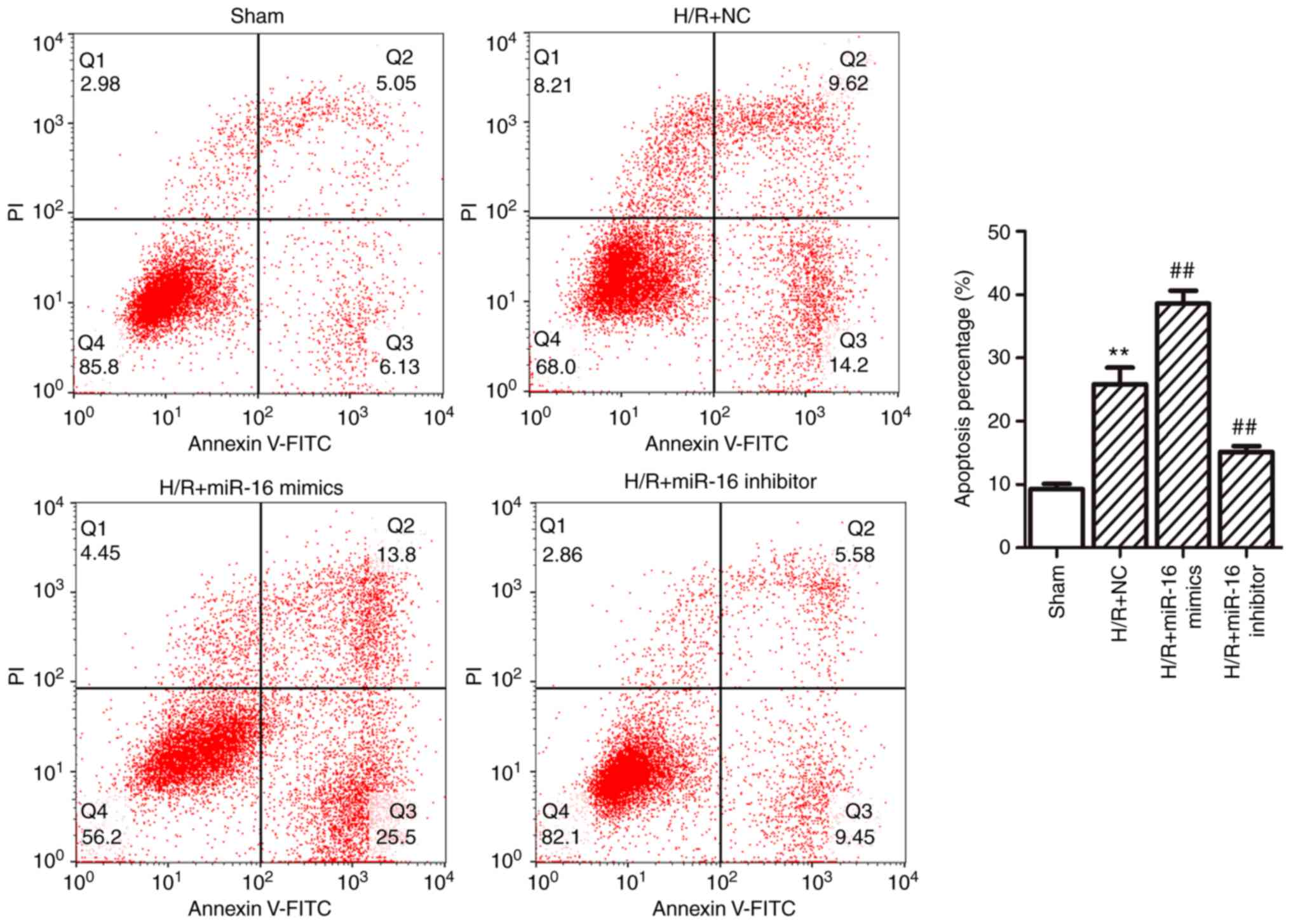
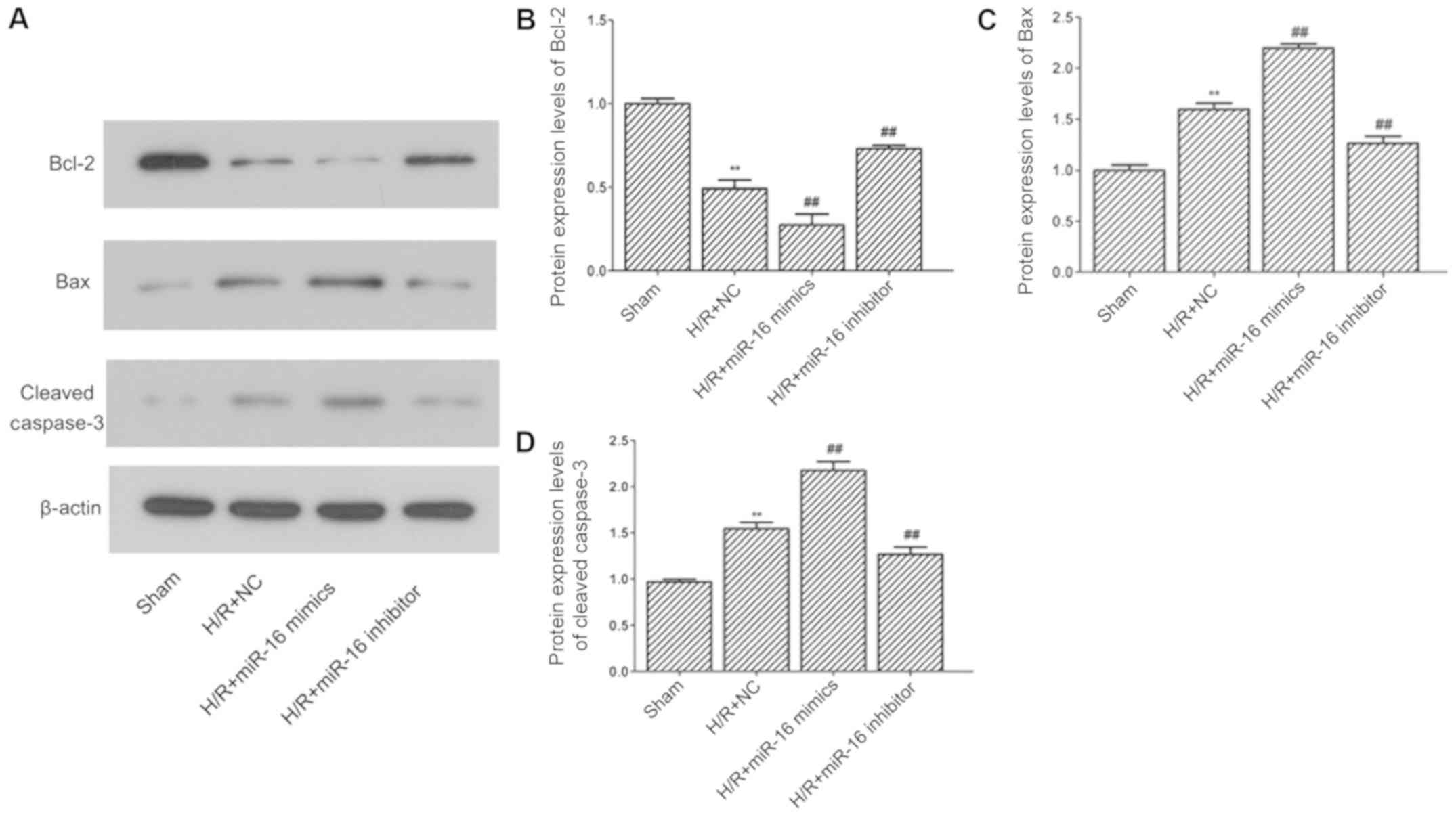
|
1
|
Zhang Y, Fang J and Ma H: Inhibition of
miR-182-5p protects cardiomyocytes from hypoxia-induced apoptosis
by targeting CIAPIN1. Biochem Cell Biol. 96:646–654. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Forouzanfar MH, Moran AE, Flaxman AD, Roth
G, Mensah GA, Ezzati M, Naghavi M and Murray CJ: Assessing the
global burden of ischemic heart disease, part 2: Analytic methods
and estimates of the global epidemiology of ischemic heart disease
in 2010. Glob Heart. 7:331–342. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hillis LD and Lange RA: Myocardial
infarction and the open-artery hypothesis. N. Engl J Med.
355:2475–2477. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Liao YH, Xia N, Zhou SF, Tang TT, Yan XX,
Lv BJ, Nie SF, Wang J, Iwakura Y, Xiao H, et al: Interleukin-17A
contributes to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating
cardiomyocyte apoptosis and neutrophil infiltration. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 59:420–429. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xie J, Hu X, Yi C, Hu G, Zhou X and Jiang
H: MicroRNA-451 protects against cardiomyocyte anoxia/reoxygenation
injury by inhibiting high mobility group box 1 expression. Mol Med
Rep. 13:5335–5341. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zweier JL and Talukder MA: The role of
oxidants and free radicals in reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res.
70:181–190. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ambrosio G and Tritto I: Myocardial
reperfusion injury. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 4:43–45. 2007.
|
|
8
|
Chen Z, Su X, Shen Y, Jin Y, Luo T, Kim
IM, Weintraub NL and Tang Y: miR322 mediates cardioprotection
against ischemia/reperfusion injury via FBXW7/notch pathway. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 133:67–74. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zheng J, Li J, Kou B, Yi Q and Shi T:
MicroRNA-30e protects the heart against ischemia and reperfusion
injury through autophagy and the Notch1/Hes1/Akt signaling pathway.
Int J Mol Med. 41:3221–3230. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu RR, Li J, Gong JY, Kuang F, Liu JY,
Zhang YS, Ma QL, Song CJ, Truax AD, Gao F, et al: MicroRNA-141
regulates the expression level of ICAM-1 on endothelium to decrease
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 309:H1303–H1313. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tian R, Wang J, Yan H, Wu J, Xu Q, Zhan X,
Gui Z, Ding M and He J: Differential expression of miR16 in
glioblastoma and glioblastoma stem cells: Their correlation with
proliferation, differentiation, metastasis and prognosis. Oncogene.
36:5861–5873. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R,
Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, Rassenti L,
et al: Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes
miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 99:15524–15529. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tu Y, Wan L, Fan Y, Wang K, Bu L, Huang T,
Cheng Z and Shen B: Ischemic Postconditioning-mediated miRNA-21
protects against cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury via PTEN/Akt
pathway. PLoS One. 8:e758722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qian L, Van Laake LW, Huang Y, Liu S,
Wendland MF and Srivastava D: miR-24 inhibits apoptosis and
represses Bim in mouse cardiomyocytes. J Exp Med. 208:549–560.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ye Y, Hu Z, Lin Y, Zhang C and Perez-Polo
JR: Downregulation of microRNA-29 by antisense inhibitors and a
PPAR-gamma agonist protects against myocardial
ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 87:535–544. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang X, Zhang C, Wang N, Li Y, Zhang D
and Li Q: MicroRNA-486 alleviates Hypoxia-induced damage in H9c2
cells by targeting NDRG2 to inactivate JNK/C-Jun and NF-κB
signaling pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem. 48:2483–2492. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen HH, Lan YF, Li HF, Cheng CF, Lai PF,
Li WH and Lin H: Urinary miR-16 transactivated by C/EBPβ reduces
kidney function after ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury. Sci Rep.
6:279452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu F, Zhang X, Lei Y, Liu X, Liu Z, Tong T
and Wang W: Loss of repression of HuR translation by miR-16 may be
responsible for the elevation of HuR in human breast carcinoma. J
Cell Biochem. 111:727–734. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu Y, Xia Y, Niu H and Chen Y: miR-16
induced the suppression of cell apoptosis while promote
proliferation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 33:1340–1348. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kang W, Tong JH, Lung RW, Dong Y, Zhao J,
Liang Q, Zhang L, Pan Y, Yang W, Pang JC, et al: Targeting of YAP1
by microRNA-15a and microRNA-16-1 exerts tumor suppressor function
in gastric adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer. 14:522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang CH, Fang XB, Li WF, Shi QY, Wu LP,
Chen XY, Huang ZX, Wu P, Wang ZZ and Liao ZS: Influence of
recombinant lentiviral vector encoding miR-15a/16-1 in biological
features of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE-2Z cells. Zhonghua
Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 48:405–411. 2013.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shibayama H, Takai E, Matsumura I, Kouno
M, Morii E, Kitamura Y, Takeda J and Kanakura Y: Identification of
a cytokine-induced antiapoptotic molecule anamorsin essential for
definitive hematopoiesis. J Exp Med. 199:581–592. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang J, Li Q, Wang C, Xiong Q, Lin Y, Sun
Q, Jin H, Yang F, Ren X and Pang T: Knock-down of CIAPIN1
sensitizes K562 chronic myeloid leukemia cells to Imatinib by
regulation of cell cycle and apoptosis-associated members via NF-κB
and ERK5 signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 99:132–145. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang Z, Su G, Hu W, Bi XX, Zhang L and
Wan G: The study on expression of CIAPIN1 interfering
hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and its mechanisms. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:3054–3060. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qu Y, Wang J, Ray PS, Guo H, Huang J,
Shin-Sim M, Bukoye BA, Liu B, Lee AV, Lin X, et al:
Thioredoxin-like 2 regulates human cancer cell growth and
metastasis via redox homeostasis and NF-κB signaling. J Clin
Invest. 121:212–225. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Santini D, Schiavon G, Vincenzi B, Gaeta
L, Pantano F, Russo A, Ortega C, Porta C, Galluzzo S, Armento G, et
al: Receptor activator of NF-κB (RANK) expression in primary tumors
associates with bone metastasis occurrence in breast cancer
patients. PLoS One. 6:e192342011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiang Y: The effect of overexpressed
CIAPIN1on H9c2 myocytes H/R damageTianjin Medical University;
2016
|
|
29
|
Jin HR, Jin SZ, Cai XF, Li D, Wu X, Nan
JX, Lee JJ and Jin X: Cryptopleurine targets NF-κB pathway, leading
to inhibition of gene products associated with cell survival,
proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis. PLoS One. 7:e403552012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li T, Yu J, Chen R, Wu J, Fei J, Bo Q, Xue
L and Li D: Mycophenolate mofetil attenuates myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury via regulation of the TLR4/NF-κB
signaling pathway. Pharmazie. 69:850–855. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu JY, Shang J, Mu XD and Gao ZY:
Protective effect of down-regulated microRNA-27a mediating high
thoracic epidural block on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
in mice through regulating ABCA1 and NF-κB signaling pathway.
Biomed Pharmacother. 112:1086062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xu Z, Du Q, Yan Y, Wang J, Dou S, Liu C
and Duan J: The protective effect of Luteolin on myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury through TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3
inflammasome pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 91:1042–1052. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tian T, Zhou Y, Feng X, Ye S, Wang H, Wu
W, Tan W, Yu C, Hu J Zheng R, et al: MicroRNA-16 is putatively
involved in the NF-κB pathway regulation in ulcerative colitis
through adenosine A2a receptor (A2aAR) mRNA targeting. Sci Rep.
6:308242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu X, Li S, Li Y, Cheng B, Tan B and Wang
G: Puerarin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by
up-regulation of miR-16 in bladder cancer cell line T24. Oncol Res.
26:1227–1234. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang TQ, Luo XJ, Wu TF, Ding DD, Zhao ZH,
Chen GL, Xie XS, Li B, Wei YX, Guo LC, et al: miR-16 inhibits
glioma cell growth and invasion through the suppression of BCL2 and
NF-κB1/MMP-9 signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 105:265–271. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Baudry A, Mouillet-Richard S, Schneider B,
Launay JM and Kellermann O: miR-16 targets the serotonin
transporter: A new Facet for adaptive responses to antidepressants.
Science. 329:1537–1541. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bhattacharya R, Nicoloso M, Arvizo R, Wang
E, Cortez A, Rossi S, Calin GA and Mukherjee P: miR-15a and miR-16
control Bmi-1 expression in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
69:9090–9095. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|