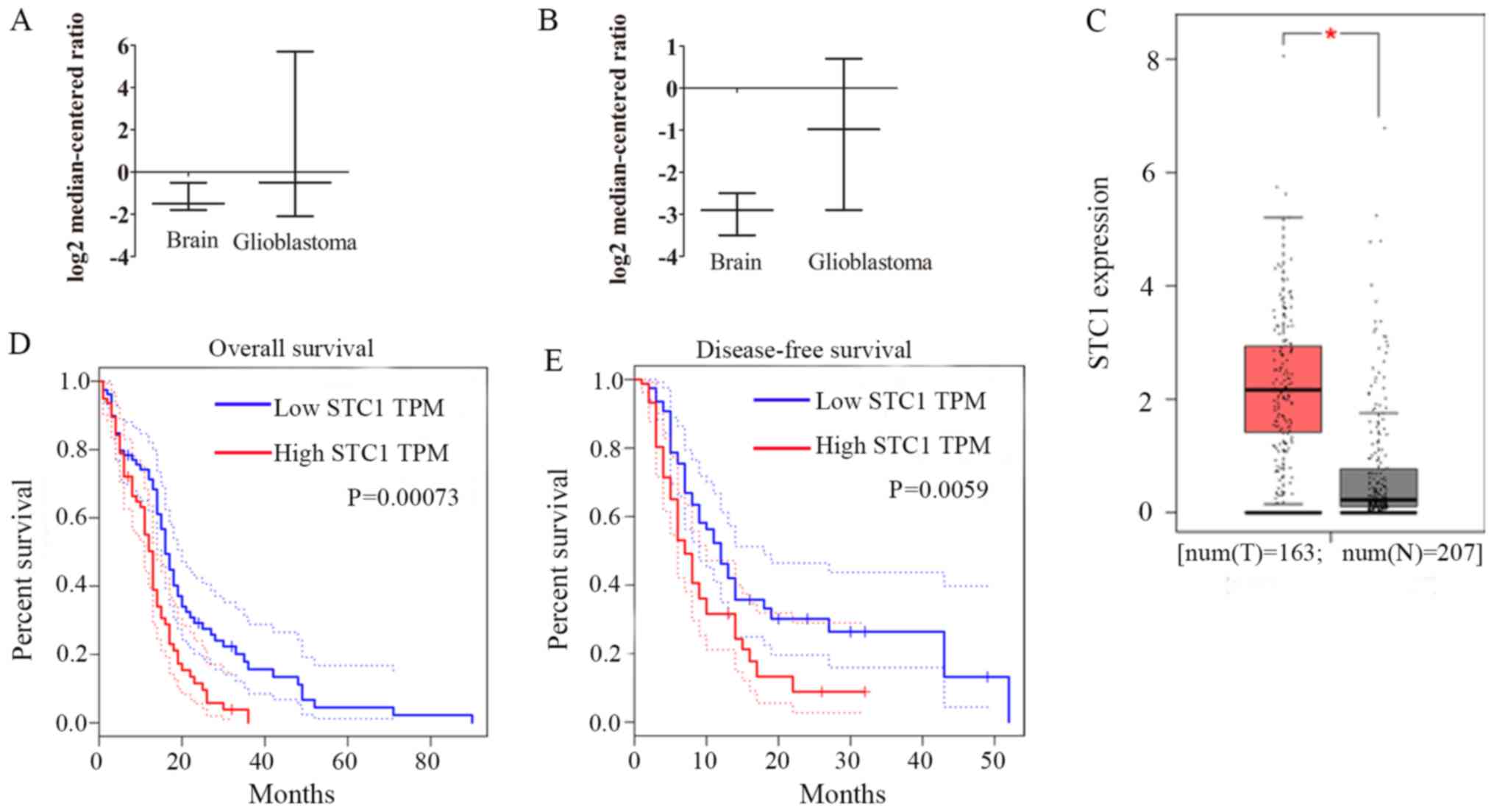
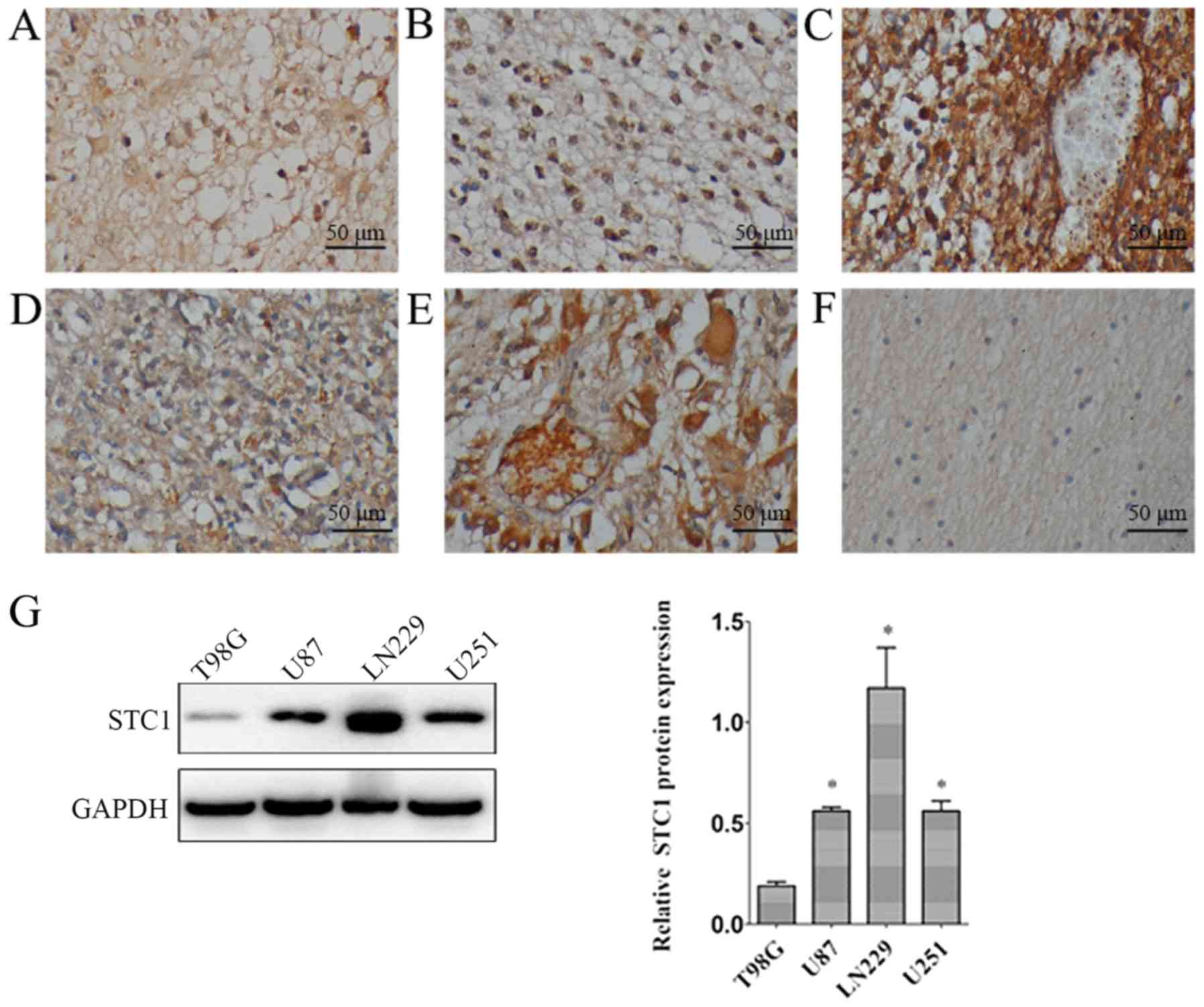
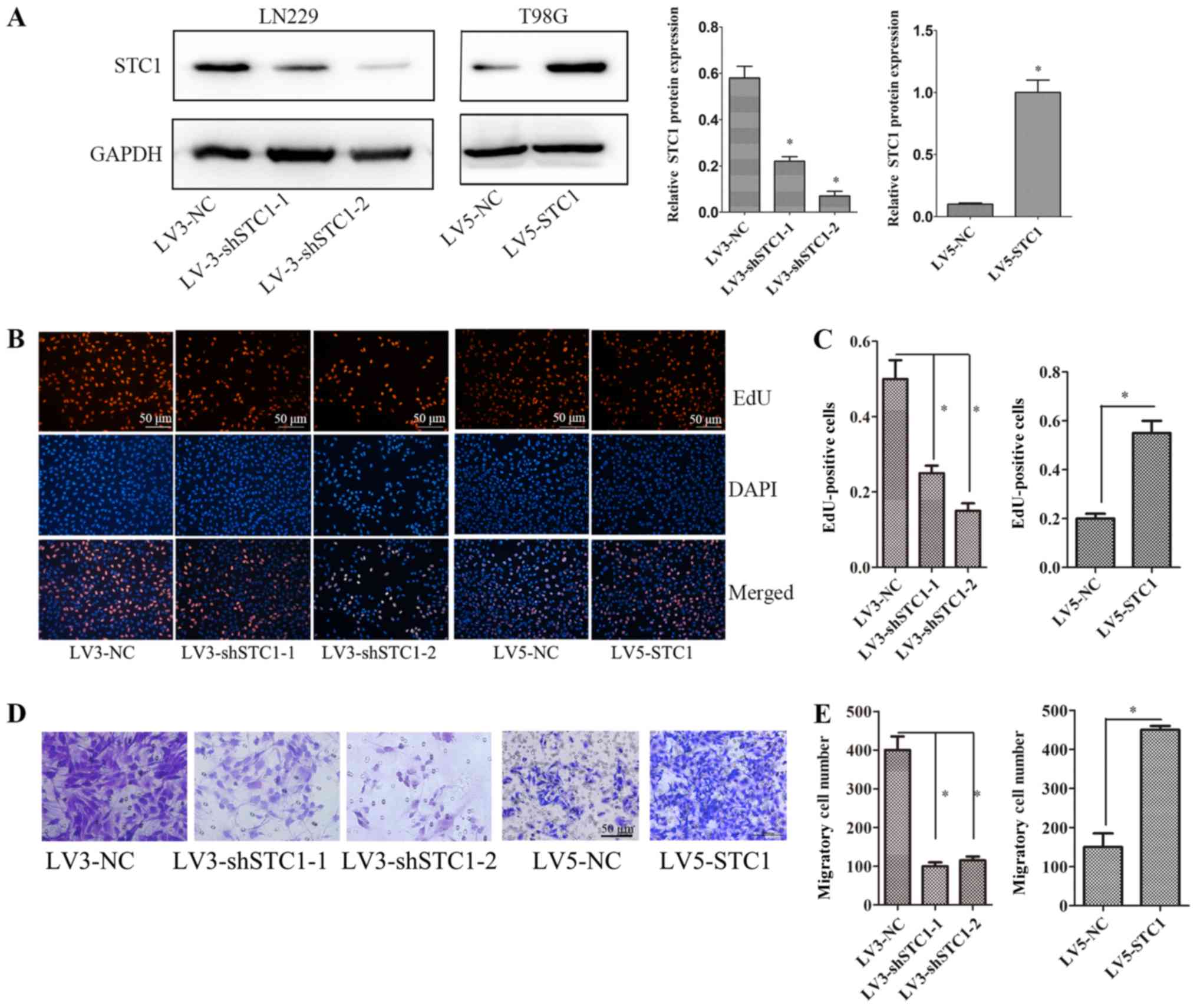
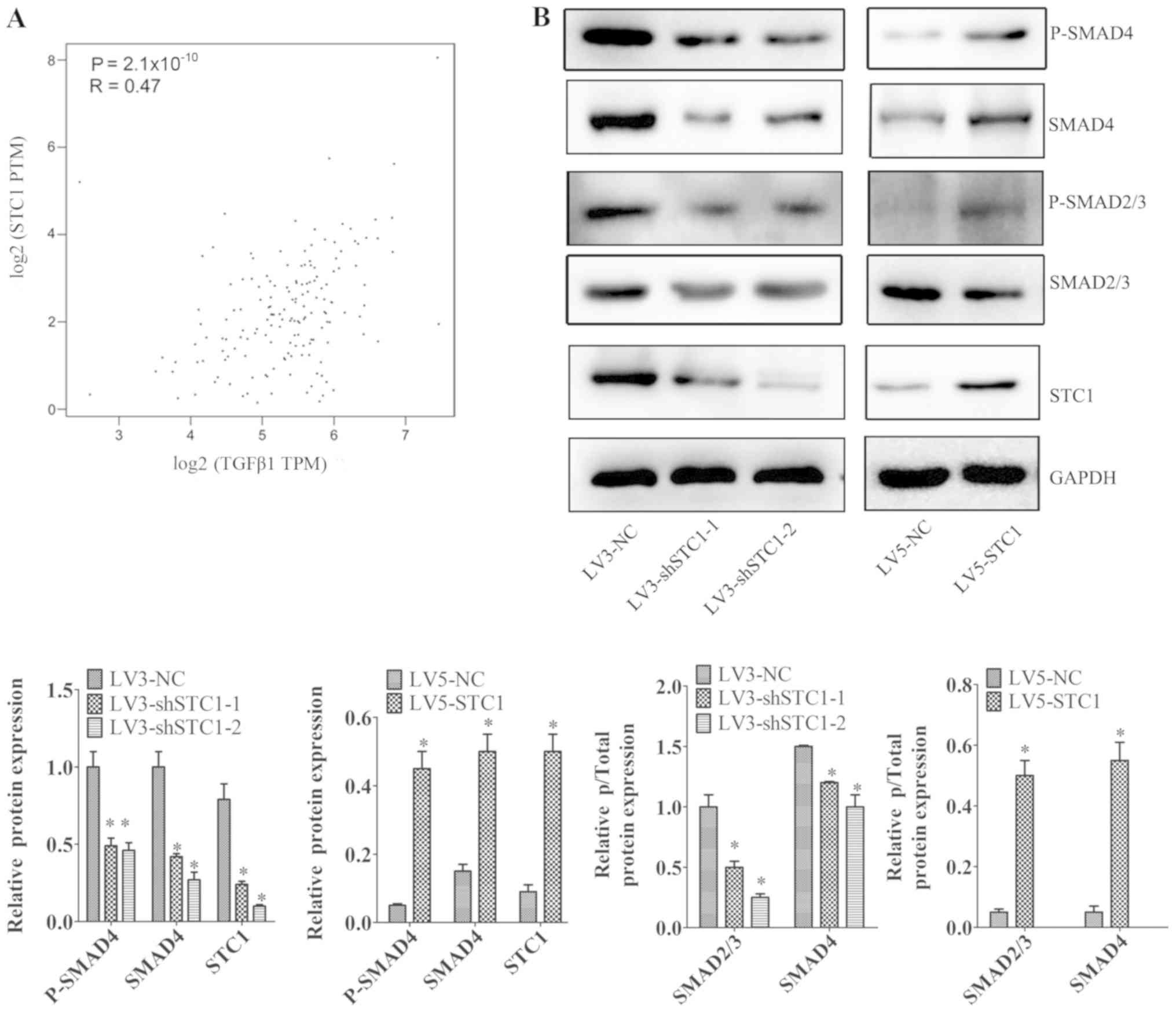
|
1
|
Millauer B, Shawver LK, Plate KH, Risaui W
and Ullrich A: Glioblastoma growth inhibited in vivo by a
dominant-negative Flk-1 mutant. Nature. 367:576–579. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ohgaki H and Kleihues P: Genetic pathways
to primary and secondary glioblastoma. Am J Pathol. 170:1445–1453.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vredenburgh JJ, Desjardins A, Herndon JE
II, Marcello J, Reardon DA, Quinn JA, Rich JN, Sathornsumetee S,
Gururangan S, Sampson J, et al: Bevacizumab plus irinotecan in
recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J Clin Oncol. 25:4722–4729.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang J, Cazzato E, Ladewig E, Frattini V,
Rosenbloom DI, Zairis S, Abate F, Liu Z, Elliott O, Shin YJ, et al:
Clonal evolution of glioblastoma under therapy. Nat Genet.
48:768–776. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brown CE, Alizadeh D, Starr R, Weng L,
Wagner JR, Naranjo A, Ostberg JR, Blanchard MS, Kilpatrick J,
Simpson J, et al: Regression of glioblastoma after chimeric antigen
receptor T-cell therapy. N Engl J Med. 375:2561–2569. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Iwadate Y: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in glioblastoma progression. Oncol Lett. 11:1615–1620.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ozeki S, Baba I, Takaya N and Shoun H: A
novel C1-using denitrifier alcaligenes sp. STC1 and its genes for
copper-containing nitrite reductase and azurin. Biosci Biotechnol
Biochem. 65:1206–1210. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wagner GF, Hampong M, Park CM and Copp DH:
Purification, characterization, and bioassay of teleocalcin, a
glycoprotein from salmon corpuscles of Stannius. Gen Comp
Endocrinol. 63:481–491. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schein V, Cardoso JC, Pinto PI, Anjos L,
Silva N, Power DM and Canário AV: Four stanniocalcin genes in
teleost fish: Structure, phylogenetic analysis, tissue distribution
and expression during hypercalcemic challenge. Gen Comp Endocrinol.
175:344–356. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kawabata M, Umemoto N, Shimada Y,
Nishimura Y, Zhang B, Kuroyanagi J, Miyabe M and Tanaka T:
Downregulation of stanniocalcin 1 is responsible for
sorafenib-induced cardiotoxicity. Toxicol Sci. 143:374–384. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma X, Gu L, Li H, Gao Y, Li X, Shen D,
Gong H, Li S, Niu S, Zhang Y, et al: Hypoxia-induced overexpression
of stanniocalcin-1 is associated with the metastasis of early stage
clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Transl Med. 13:562015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Su J, Guo B, Zhang T, Wang K, Li X and
Liang G: Stanniocalcin-1, a new biomarker of glioma progression, is
associated with prognosis of patients. Tumour Biol. 36:6333–6339.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Du YZ, Gu XH, Cheng SF, Li L, Liu H, Hu LP
and Gao F: The oncogenetic role of stanniocalcin 1 in lung
adenocarcinoma: A promising serum candidate biomarker for tracking
lung adenocarcinoma progression. Tumour Biol. 37:5633–5644. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jepsen MR, Kløverpris S, Bøtkjær JA,
Wissing ML, Andersen CY and Oxvig C: The proteolytic activity of
pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A is potentially regulated by
stanniocalcin-1 and −2 during human ovarian follicle development.
Hum Reprod. 31:866–874. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Law AY and Wong CK: Stanniocalcin-1 and −2
promote angiogenic sprouting in HUVECs via VEGF/VEGFR2 and
angiopoietin signaling pathways. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 374:73–81.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tang SE, Wu CP, Wu SY, Peng CK, Perng WC,
Kang BH, Chu SJ and Huang KL: Stanniocalcin-1 ameliorates
lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary oxidative stress,
inflammation, and apoptosis in mice. Free Radic Biol Med.
71:321–331. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cornmark L, Lønne GK, Jögi A and Larsson
C: Protein kinase Cα suppresses the expression of STC1 in
MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 32:1023–1030. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tamura S, Oshima T, Yoshihara K, Kanazawa
A, Yamada T, Inagaki D, Sato T, Yamamoto N, Shiozawa M, Morinaga S,
et al: Clinical significance of STC1 gene expression in patients
with colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 31:325–329. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yeung BH, Shek FH, Lee NP and Wong CK:
Stanniocalcin-1 reduces tumor size in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e01399772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Leung CC and Wong CK: Effects of STC1
overexpression on tumorigenicity and metabolism of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 9:6852–6861. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pan X, Jiang B, Liu J, Ding J, Li Y, Sun
R, Peng L, Qin C, Fang S and Li G: STC1 promotes cell apoptosis via
NF-κB phospho-P65 Ser536 in cervical cancer cells. Oncotarget.
8:46249–46261. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Han J, Jeon M, Shin I and Kim S: Elevated
STC-1 augments the invasiveness of triple-negative breast cancer
cells through activation of the JNK/c-Jun signaling pathway. Oncol
Rep. 36:1764–1771. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu J, Meng Y, Zhang Z, Yan Q, Jiang X, Lv
Z and Hu L: MARCH5 RNA promotes autophagy, migration, and invasion
of ovarian cancer cells. Autophagy. 13:333–344. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kurio N, Saunders C, Bechtold TE, Salhab
I, Nah HD, Sinha S, Billings PC, Pacifici M and Koyama E: Roles of
Ihh signaling in chondroprogenitor function in postnatal condylar
cartilage. Matrix Biol. 67:15–31. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tao L, Bei Y, Li Y and Xiao J: Neonatal
rat cardiomyocytes isolation, culture, and determination of
microRNAs' effects in proliferation. Methods Mol Biol.
1733:203–213. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Min X, Liu K, Zhu H and Zhang J: Long
noncoding RNA LINC003121 inhibits proliferation and invasion of
thyroid cancer cells by suppression of the
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway. Med Sci
Monit. 24:4592–4601. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang Z, Li K, Liang Q, Zheng G, Zhang S,
Lao X, Liang Y and Liao G: Elevated hydrostatic pressure promotes
ameloblastoma cell invasion through up-regulation of MMP-2 and
MMP-9 expression via Wnt/β-catenin signalling. J Oral Pathol Med.
47:836–846. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pan Y, Yuan F, Li Y, Wang G, Lin Z and
Chen L: Bromodomain PHD-finger transcription factor promotes glioma
progression and indicates poor prognosis. Oncol Rep. 41:246–256.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yeung HY, Lai KP, Chan HY, Mak NK, Wagner
GF and Wong CK: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-mediated activation of
stanniocalcin-1 in human cancer cells. Endocrinology.
146:4951–4960. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peña C, Céspedes MV, Lindh MB, Kiflemariam
S, Mezheyeuski A, Edqvist PH, Hägglöf C, Birgisson H, Bojmar L,
Jirström K, et al: STC1 expression by cancer-associated fibroblasts
drives metastasis of colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 73:1287–1297.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chang AC, Doherty J, Huschtscha LI,
Redvers R, Restall C, Reddel RR and Anderson RL: STC1 expression is
associated with tumor growth and metastasis in breast cancer. Clin
Exp Metastasis. 32:15–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Karthikeyan A, Gupta N, Tang C,
Mallilankaraman K, Silambarasan M, Shi M, Lu L, Ang BT, Ling EA and
Dheen ST: Microglial SMAD4 regulated by microRNA-146a promotes
migration of microglia which support tumor progression in a glioma
environment. Oncotarget. 9:24950–24969. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang Z, Gong Q, Li M, Xu J, Zheng Y, Ge P
and Chi G: MicroRNA-124 inhibits the proliferation of C6 glioma
cells by targeting Smad4. Int J Mol Med. 40:1226–1234. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu H, Xu D, Zhong X, Xu D, Chen G, Ge J
and Li H: LncRNA-mRNA competing endogenous RNA network depicts
transcriptional regulation in ischaemia reperfusion injury. J Cell
Mol Med. 23:2272–2276. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen HH, Zong J and Wang SJ: LncRNA
GAPLINC promotes the growth and metastasis of glioblastoma by
sponging miR-331-3p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:262–270.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen J, Du G, Chang Y, Wang Y, Shi L, Mi J
and Tang G: Downregulated miR-27b promotes keratinocyte
proliferation by targeting PLK2 in oral lichen planus. J Oral
Pathol Med. 48:326–334. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Werner TV, Hart M, Nickels R, Kim YJ,
Menger MD, Bohle RM, Keller A, Ludwig N and Meese E: MiR-34a-3p
alters proliferation and apoptosis of meningioma cells in vitro and
is directly targeting SMAD4, FRAT1 and BCL2. Aging (Albany NY).
9:932–954. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Dong P, Xiong Y, Yue J, Hanley SJB and
Watari H: miR-34a, miR-424 and miR-513 inhibit MMSET expression to
repress endometrial cancer cell invasion and sphere formation.
Oncotarget. 9:23253–23263. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li ZH, Weng X, Xiong QY, Tu JH, Xiao A,
Qiu W, Gong Y, Hu EW, Huang S and Cao YL: miR-34a expression in
human breast cancer is associated with drug resistance. Oncotarget.
8:106270–106282. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang D, Qiu X, Li J, Zheng S, Li L and
Zhao H: TGF-β secreted by tumor-associated macrophages promotes
proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer via miR-34a-VEGF
axis. Cell Cycle. 17:2766–2778. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|