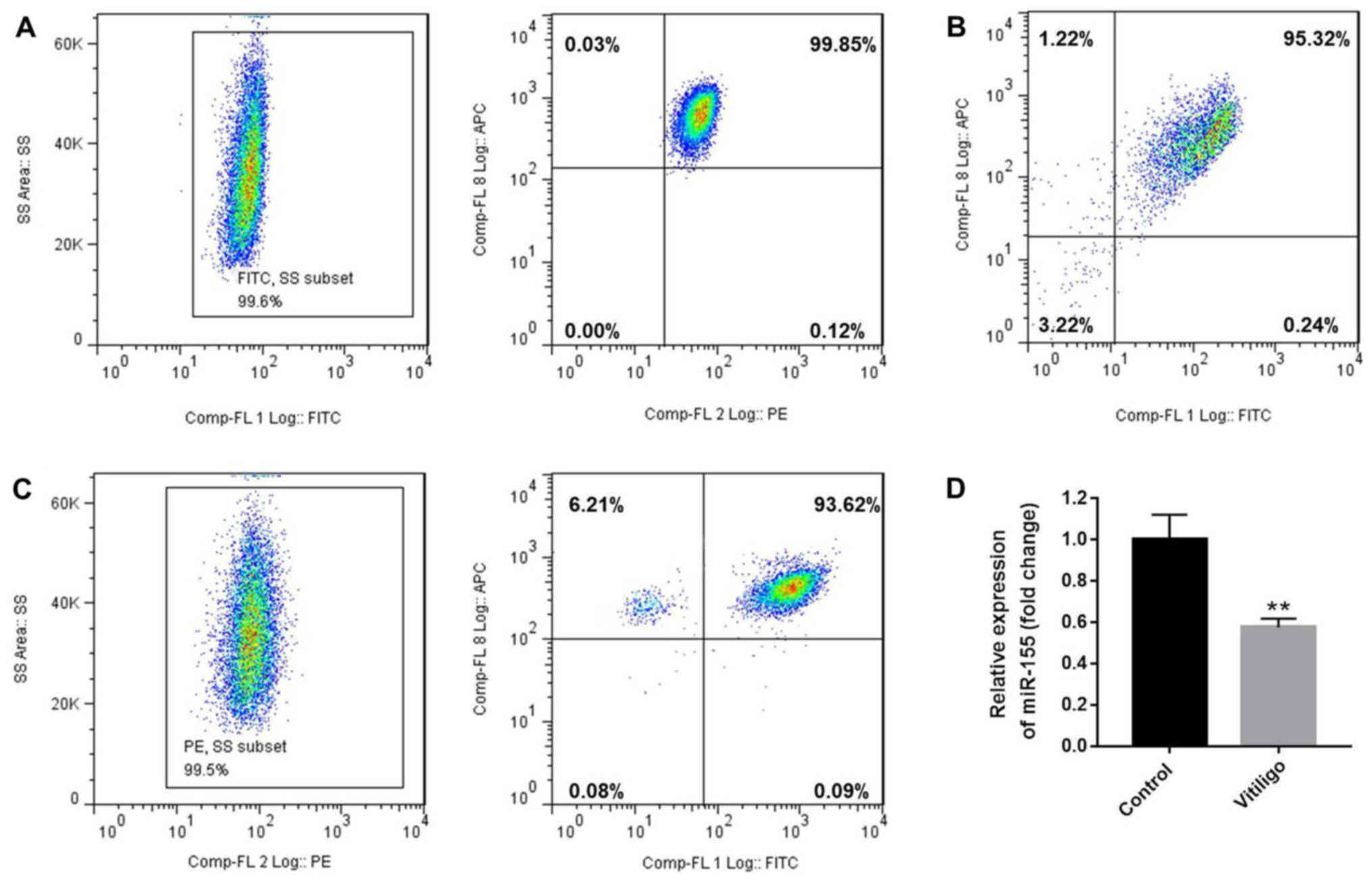
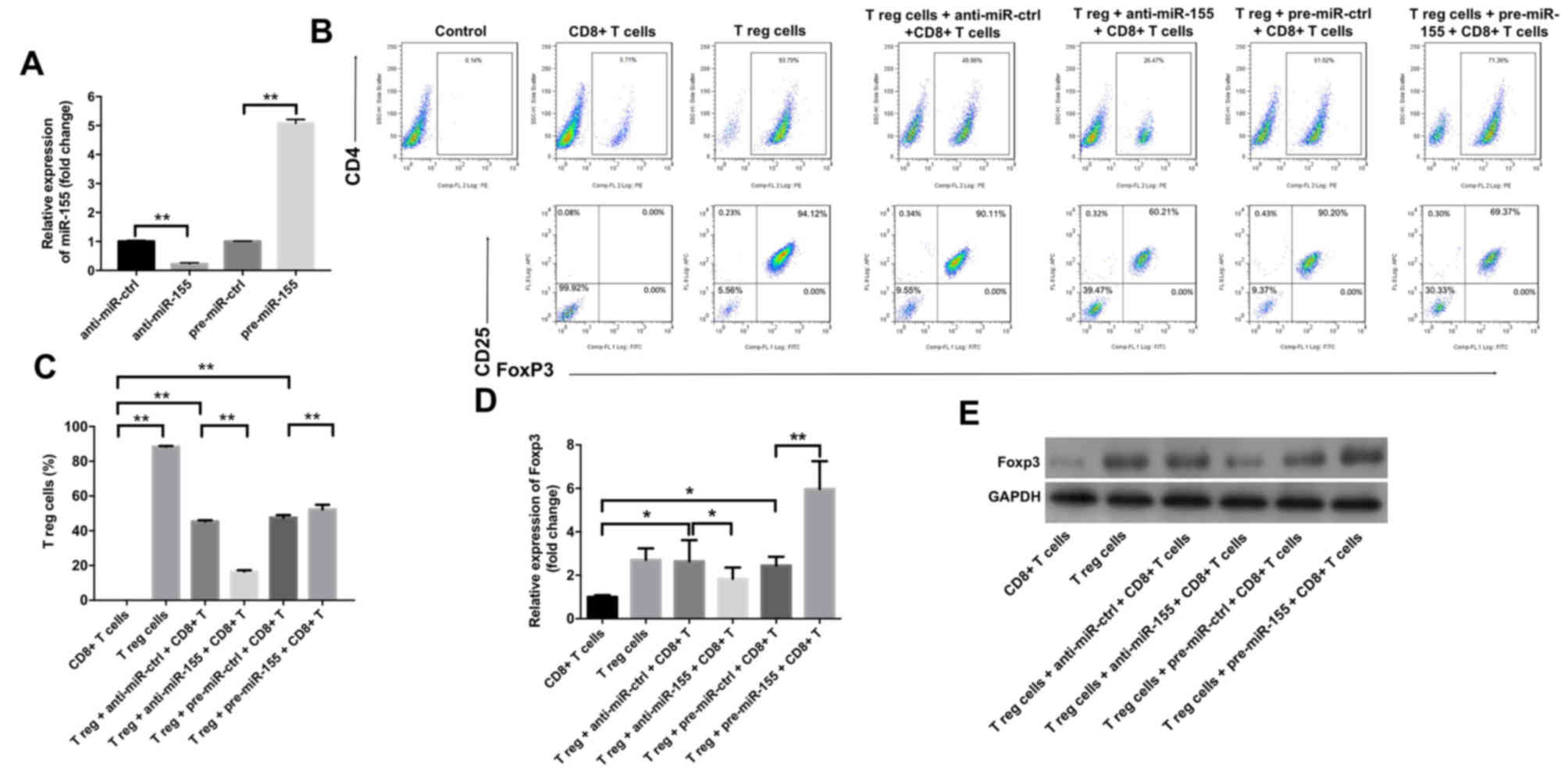
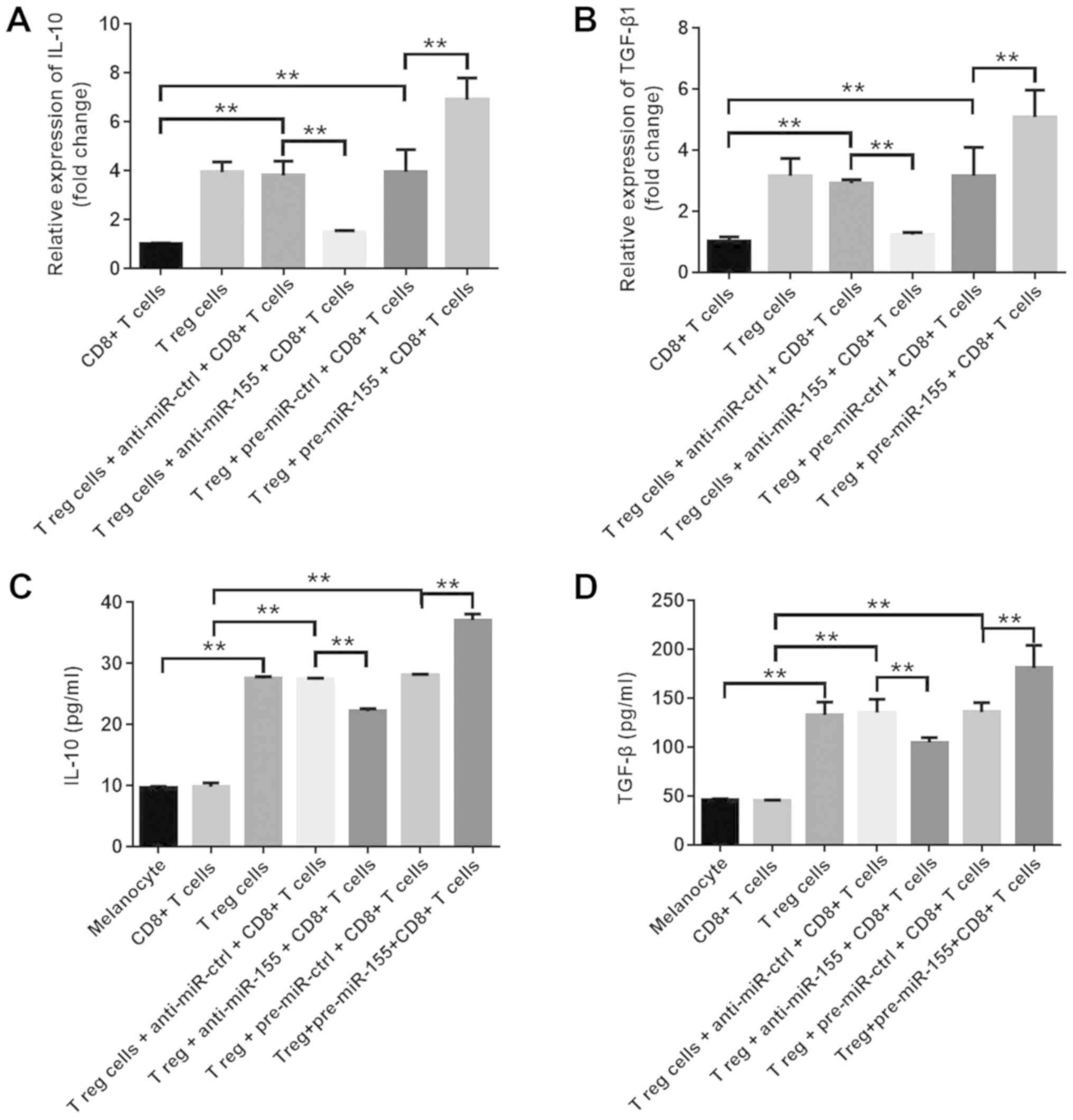
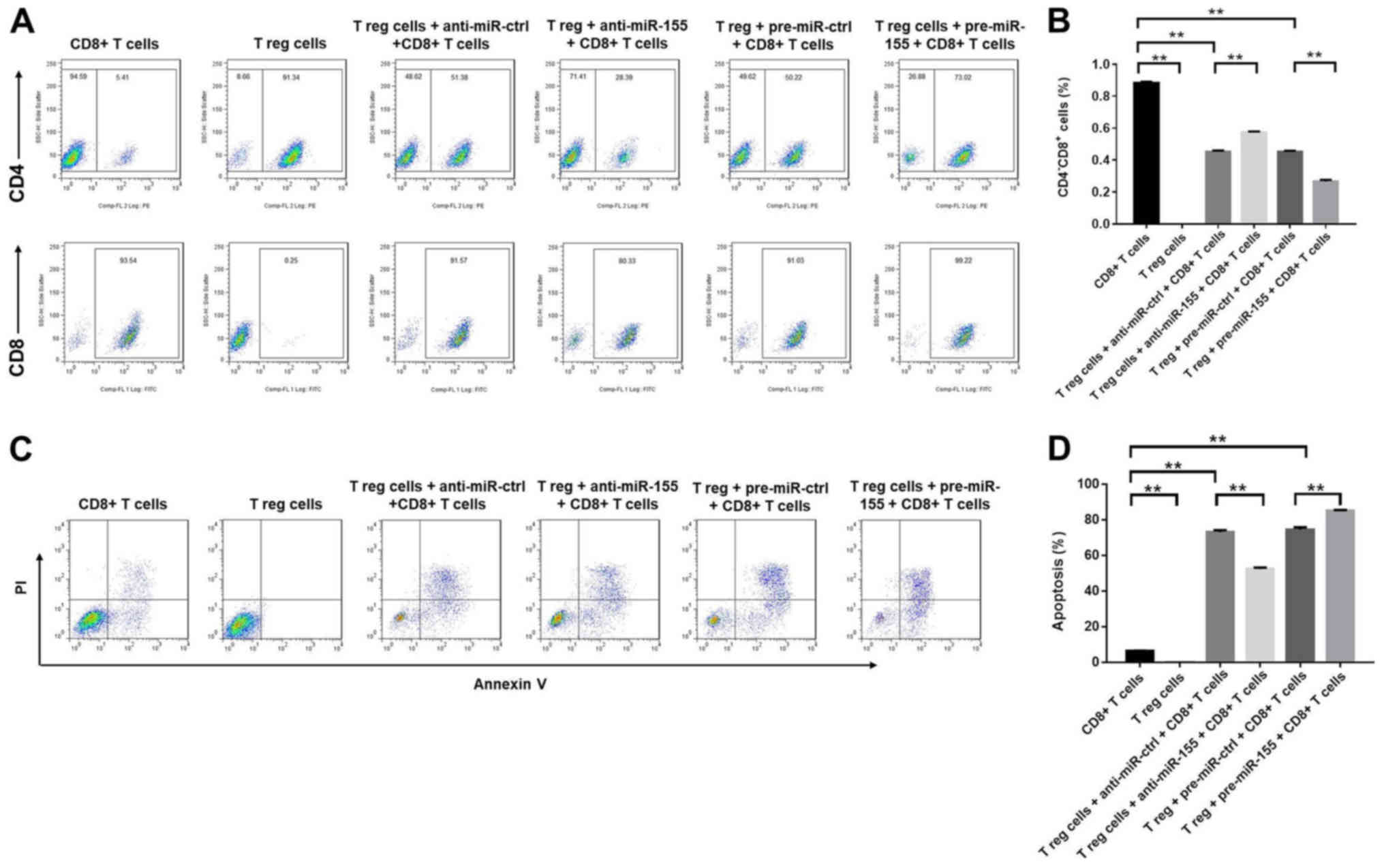
|
1
|
Krüger C and Schallreuter KU: A review of
the worldwide prevalence of vitiligo in children/adolescents and
adults. Int J Dermatol. 51:1206–1212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jin Y, Birlea SA, Fain PR, Ferrara TM, Ben
S, Riccardi SL, Cole JB, Gowan K, Holland PJ, Bennett DC, et al:
Genome-wide association analyses identify 13 new susceptibility
loci for generalized vitiligo. Nat Genet. 44:676–680. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ezzedine K, Eleftheriadou V, Whitton M and
van Geel N: Vitiligo. Lancet. 386:74–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gey A, Diallo A, Seneschal J,
Leaute-Labreze C, Boralevi F, Jouary T, Taieb A and Ezzedine K:
Autoimmune thyroid disease in vitiligo: multivariate analysis
indicates intricate pathomechanisms. Br J Dermatol. 168:756–761.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shi Q, Zhang W, Guo S, Jian Z, Li S, Li K,
Ge R, Dai W, Wang G, Gao T and Li C: Oxidative stress-induced
overexpression of miR-25: The mechanism underlying the degeneration
of melanocytes in vitiligo. Cell Death Differ. 23:496–508. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lu W, Zhao Y, Kong Y, Zhang W, Ma W, Li W
and Wang K: Geniposide prevents H2 O2 -induced oxidative damage in
melanocytes by activating the PI3K-Akt signalling pathway. Clin Exp
Dermatol. 43:667–674. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Patel S, Rauf A, Khan H, Meher BR and
Hassan SSU: A holistic review on the autoimmune disease vitiligo
with emphasis on the causal factors. Biomed Pharmacother.
92:501–508. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Strassner JP and Harris JE: Understanding
mechanisms of autoimmunity through translational research in
vitiligo. Curr Opin Immunol. 43:81–88. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
van den Boorn JG, Konijnenberg D,
Dellemijn TA, van der Veen JP, Bos JD, Melief CJ, Vyth-Dreese FA
and Luiten RM: Autoimmune destruction of skin melanocytes by
perilesional T cells from vitiligo patients. J Invest Dermatol.
129:2220–2232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wankowicz-Kalinska A, van den Wijngaard
RM, Tigges BJ, Westerhof W, Ogg GS, Cerundolo V, Storkus WJ and Das
PK: Immunopolarization of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells to Type-1-like is
associated with melanocyte loss in human vitiligo. Lab Invest.
83:683–695. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kleinewietfeld M and Hafler DA: Regulatory
T cells in autoimmune neuroinflammation. Immunol Rev. 259:231–244.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Askenasy N, Kaminitz A and Yarkoni S:
Mechanisms of tregulatory cell function. Autoimmun Rev. 7:370–375.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lan Q, Zhou X, Fan H, Chen M, Wang J,
Ryffel B, Brand D, Ramalingam R, Kiela PR, Horwitz DA, et al:
Polyclonal CD4+Foxp3+ Treg cells induce TGFβ-dependent tolerogenic
dendritic cells that suppress the murine lupus-like syndrome. J Mol
Cell Biol. 4:409–419. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dwivedi M, Laddha NC, Arora P, Marfatia YS
and Begum R: Decreased regulatory T-cells and CD4(+) /CD8(+) ratio
correlate with disease onset and progression in patients with
generalized vitiligo. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 26:586–591. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ben Ahmed M, Zaraa I, Rekik R,
Elbeldi-Ferchiou A, Kourda N, Belhadj Hmida N, Abdeladhim M, Karoui
O, Ben Osman A, Mokni M and Louzir H: Functional defects of
peripheral regulatory T lymphocytes in patients with progressive
vitiligo. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 25:99–109. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pauley KM, Cha S and Chan EK: MicroRNA in
autoimmunity and autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun. 32:189–194.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Malmhäll C, Alawieh S, Lu Y, Sjöstrand M,
Bossios A, Eldh M and Rådinger M: MicroRNA-155 is essential for
T(H)2-mediated allergen-induced eosinophilic inflammation in the
lung. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 133:1429–1438, 1438.e1421-1427. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dudda JC, Salaun B, Ji Y, Palmer DC,
Monnot GC, Merck E, Boudousquie C, Utzschneider DT, Escobar TM,
Perret R, et al: MicroRNA-155 is required for effector CD8+ T cell
responses to virus infection and cancer. Immunity. 38:742–753.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liston A, Lu LF, O'Carroll D, Tarakhovsky
A and Rudensky AY: Dicer-dependent microRNA pathway safeguards
regulatory T cell function. J Exp Med. 205:1993–2004. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kempinska-Podhorodecka A, Milkiewicz M,
Wasik U, Ligocka J, Zawadzki M, Krawczyk M and Milkiewicz P:
Decreased expression of vitamin D receptor affects an immune
response in primary biliary cholangitis via the VDR-miRNA155-SOCS1
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 18:E2892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Šahmatova L, Tankov S, Prans E, Aab A,
Hermann H, Reemann P, Pihlap M, Karelson M, Abram K, Kisand K, et
al: MicroRNA-155 is dysregulated in the skin of patients with
vitiligo and inhibits melanogenesis-associated genes in melanocytes
and keratinocytes. Acta Derm Venereol. 96:742–747. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yao R, Ma YL, Liang W, Li HH, Ma ZJ, Yu X
and Liao YH: MicroRNA-155 modulates treg and Th17 cells
differentiation and Th17 cell function by targeting SOCS1. PLoS
One. 7:e460822012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Karagiannidis C, Akdis M, Holopainen P,
Woolley NJ, Hense G, Ruckert B, Mantel PY, Menz G, Akdis CA, Blaser
K and Schmidt-Weber CB: Glucocorticoids upregulate FOXP3 expression
and regulatory T cells in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
114:1425–1433. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ganesh BB, Bhattacharya P, Gopisetty A,
Sheng J, Vasu C and Prabhakar BS: IL-1β promotes TGF-β1 and IL-2
dependent Foxp3 expression in regulatory T cells. PLoS One.
6:e219492011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Polanczyk MJ, Walker E, Haley D,
Guerrouahen BS and Akporiaye ET: Blockade of TGF-β signaling to
enhance the antitumor response is accompanied by dysregulation of
the functional activity of CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + and CD4 + CD25 -
Foxp3 + T cells. J Transl Med. 17:2192019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mucida D, Pino-Lagos K, Kim G, Nowak E,
Benson MJ, Kronenberg M, Noelle RJ and Cheroutre H: Retinoic acid
can directly promote TGF-beta-mediated Foxp3(+) Treg cell
conversion of naive T cells. Immunity. 30:471–472. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Klarquist J, Eby JM, Henning SW, Li M,
Wainwright DA, Westerhof W, Luiten RM, Nishimura MI and Le Poole
IC: Functional cloning of a gp100-reactive T-cell receptor from
vitiligo patient skin. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 29:379–384. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nigam PK, Patra PK, Khodiar PK and Gual J:
A study of blood CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T cell levels and CD4+:CD8+
ratio in vitiligo patients. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol.
77:1112011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lili Y, Yi W, Ji Y, Yue S, Weimin S and
Ming L: Global activation of CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes
correlates with an impairment in regulatory T cells in patients
with generalized vitiligo. PLoS One. 7:e375132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Le Poole IC and Mehrotra S: Replenishing
regulatory T cells to halt depigmentation in vitiligo. J Investig
Dermatol Symp Proc. 18:S38–S45. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gracias DT, Stelekati E, Hope JL,
Boesteanu AC, Doering TA, Norton J, Mueller YM, Fraietta JA, Wherry
EJ, Turner M and Katsikis PD: The microRNA miR-155 controls CD8(+)
T cell responses by regulating interferon signaling. Nat Immunol.
14:593–602. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu J, Zhou M, Wan Y and Xu A: CD8+ T cells
from vitiligo perilesional margins induce autologous melanocyte
apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 7:237–241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Glassman SJ: Vitiligo, reactive oxygen
species and T-cells. Clin Sci (Lond). 120:99–120. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang L, Yang S, Lei J, Hu W, Chen R, Lin F
and Xu AE: Role of chemokines and the corresponding receptors in
vitiligo: A pilot study. J Dermatol. 45:31–38. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guan C, Li Q, Song X, Xu W, Li L and Xu A:
Antroquinonol exerts immunosuppressive effect on CD8(+) T Cell
proliferation and activation to resist depigmentation induced by
H2O2. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:93030542017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Arneth BM: Activation of CD4 and CD8 T
cell receptors and regulatory T cells in response to human
proteins. PeerJ. 6:e44622018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|