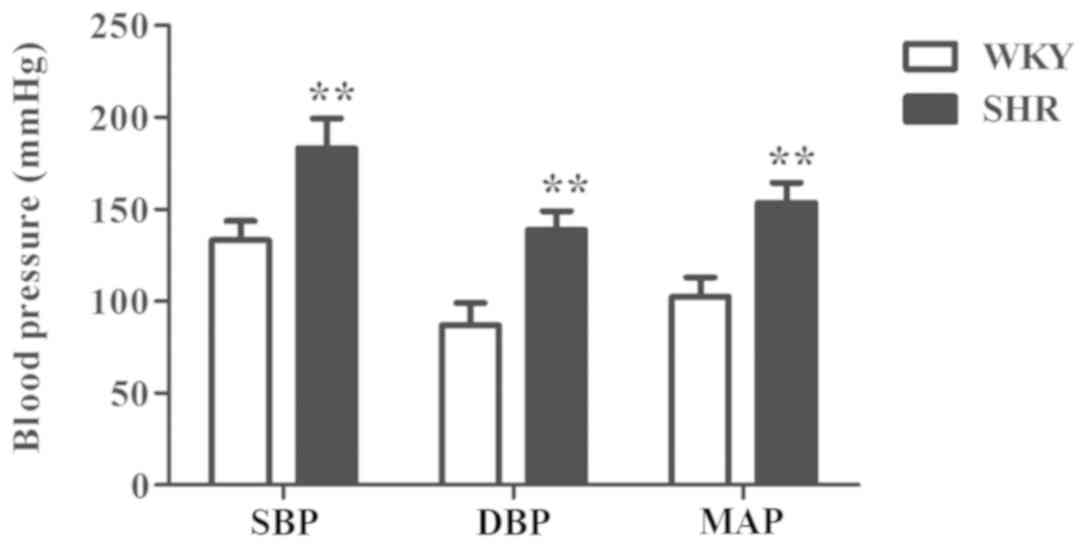
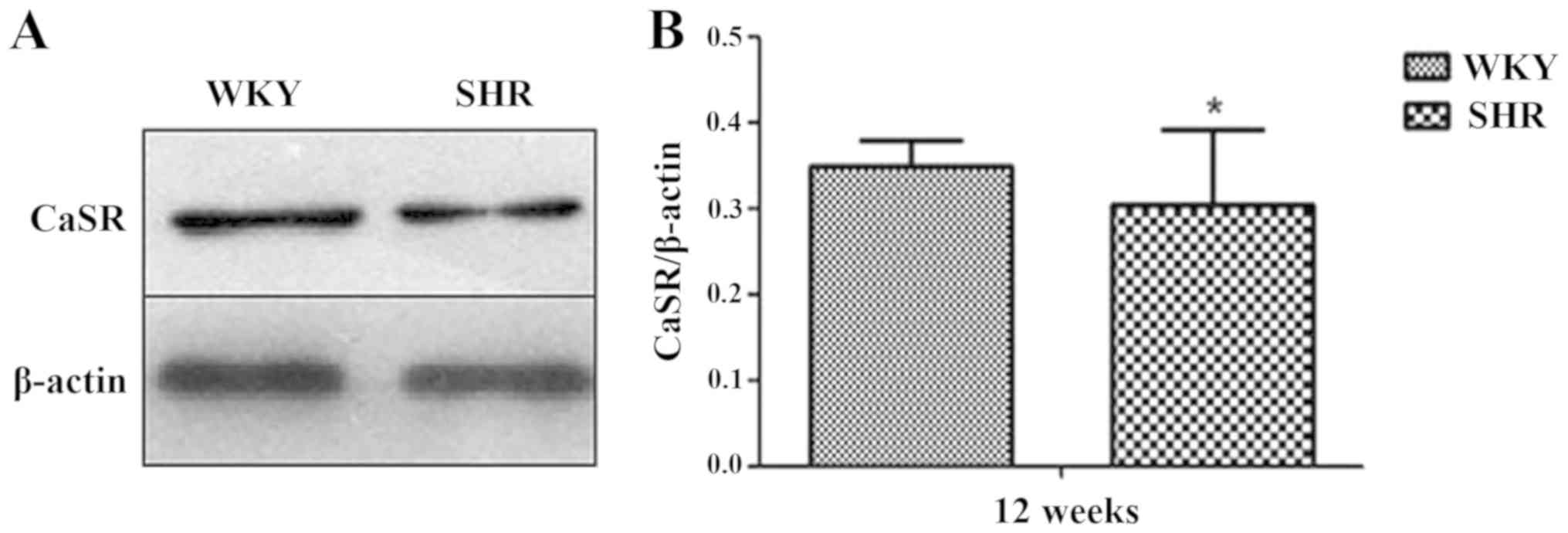
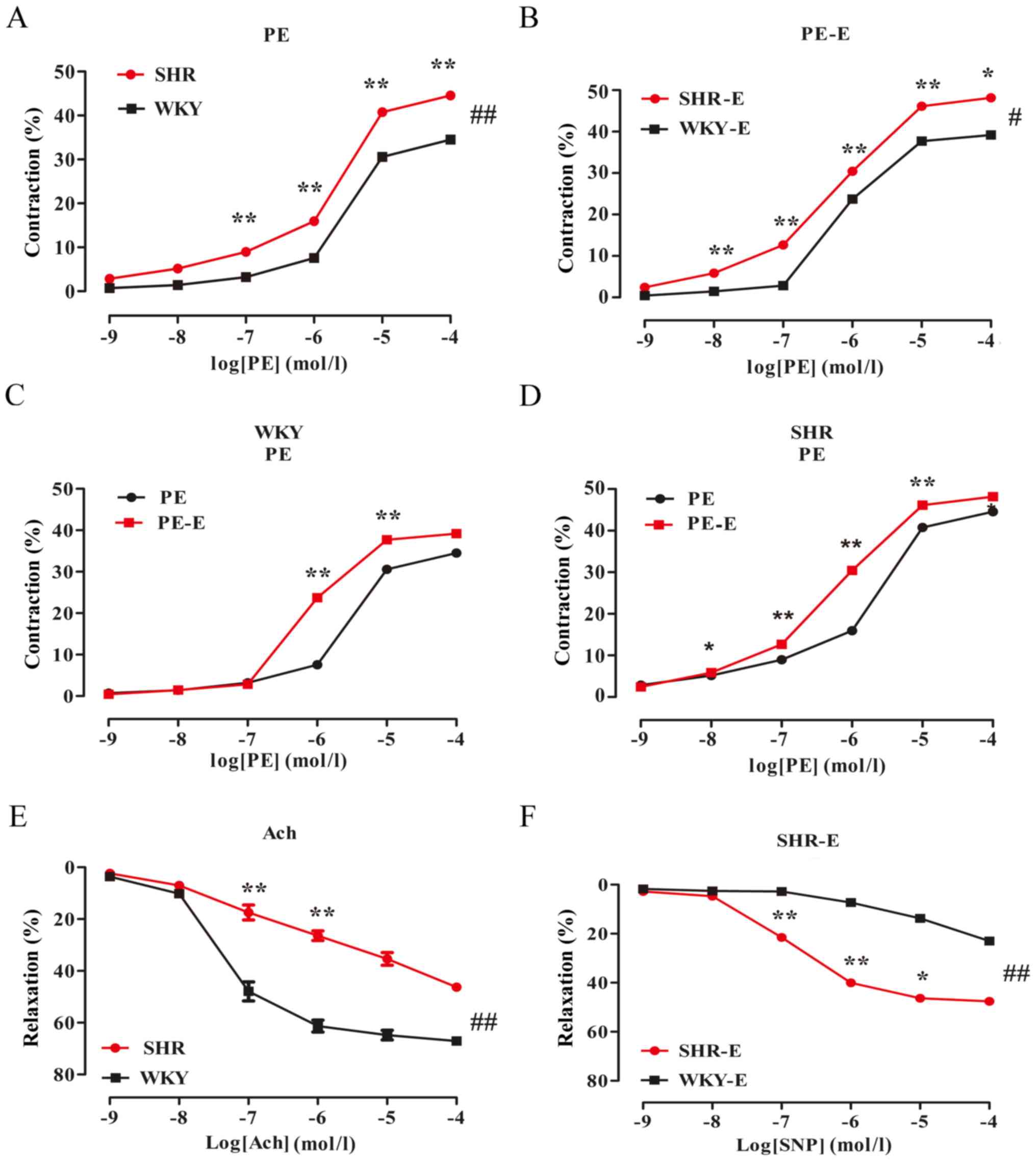
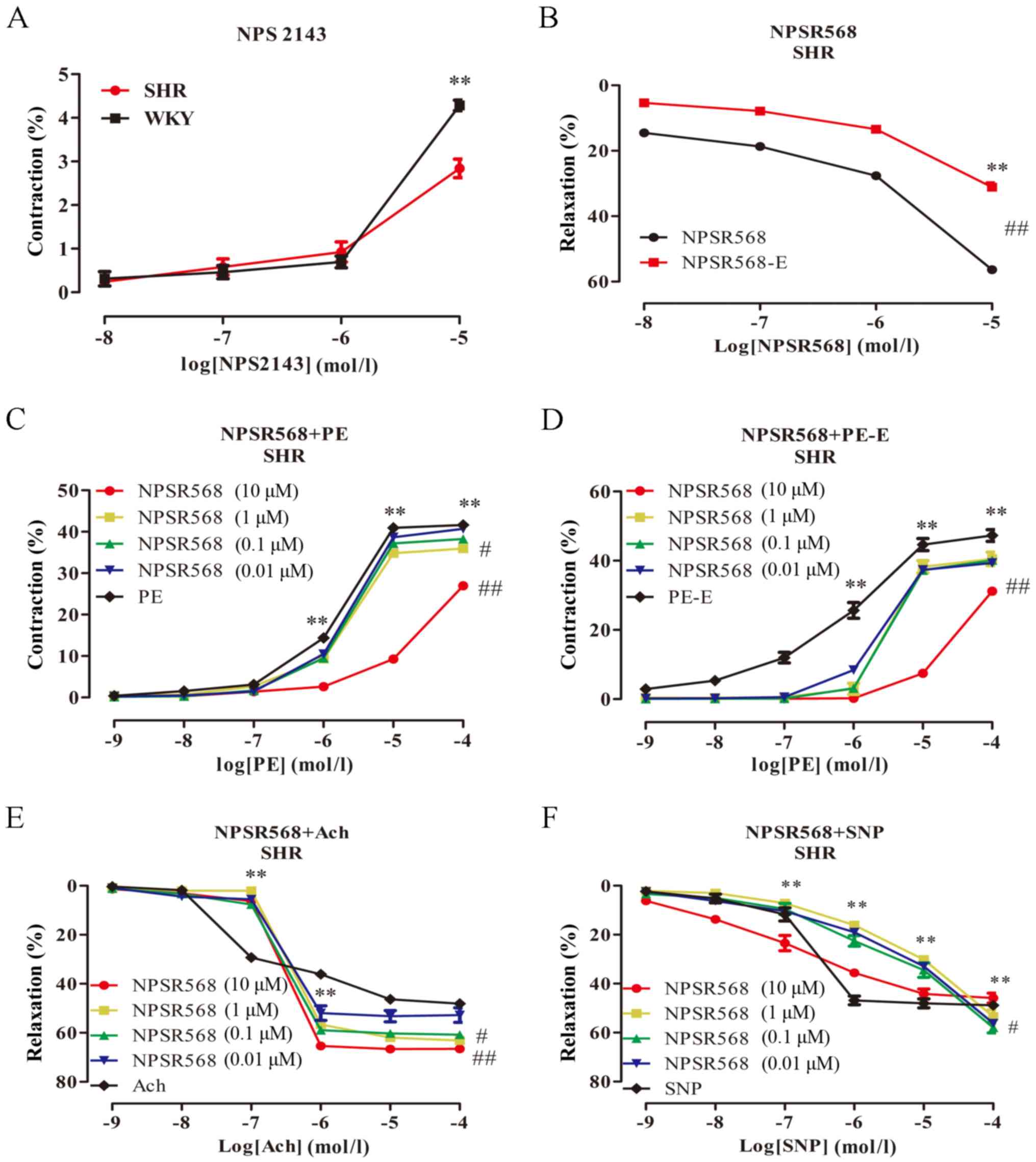
|
1
|
Lim S, Vos T and Bruce N: ‘The burden of
disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor
clusters in 21 regions 1990–2010: A systematic analysis.’. Lancet.
380:2224–2260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Akpunonu BE, Mulrow PJ and Hoffman EA:
Secondary hypertension: Evaluation and treatment. Dis Mon.
42:609–722. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
WRITING GROUP MEMBERS, ; Lloyd-Jones D,
Adams RJ, Brown TM, Carnethon M, Dai S, De Simone G, Ferguson TB,
Ford E, Furie K, et al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2008
Update: A report from the american heart association statistics
committee and stroke statistics subcommittee. Circulation.
121:e46–e215. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sharp SI, Aarsland D, Day S Nnesyn H;
Alzheimer's Society Vascular Dementia Systematic Review Group, ;
Ballard C: Hypertension is a potential risk factor for vascular
dementia: Systematic review. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 26:661–669.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Figueroa XF, Isakson BE and Duling BR:
Vascular gap junctions in hypertension. Hypertension. 48:804–811.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Allender PS, Cutler JA, Follmann D,
Cappuccio FP, Pryer J and Elliott P: Dietary calcium and blood
pressure: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Ann Intern
Med. 124:825–831. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
He K, Liu K, Daviglus ML, Morris SJ, Loria
CM, Van Horn L, Jacobs DR Jr and Savage PJ: Magnesium intake and
incidence of metabolic syndrome among young adults. Circulation.
113:1675–1682. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ayachi S: Increased dietary calcium lowers
blood pressure in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Metabolism.
28:1234–1238. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brown EM, Gamba G, Riccardi D, Lombardi M,
Butters R, Kifor O, Sun A, Hediger MA, Lytton J and Hebert SC:
Cloning and characterization of an extracellular Ca (2+)-sensing
receptor from bovine parathyroid. Nature. 366:575–580. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Weston AH, Geraghty A, Egner I and Edwards
G: The vascular extracellular calcium-sensing receptor: An update.
Acta Physiol (Oxf). 203:127–137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Weston AH, Absi M, Ward DT, Ohanian J,
Dodd RH, Dauban P, Petrel C, Ruat M and Edwards G: Evidence in
favor of a calcium-sensing receptor in arterial endothelial cells.
Circ Res. 97:391–398. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ortiz-Capisano MC, Reddy M, Mendez M,
Garvin JL and Beierwaltes WH: Juxtaglomerular cell CaSR stimulation
decreases renin release via activation of the PLC/IP3
pathway and the ryanodine receptor. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
304:F248–F256. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Brown EM and Macleod RJ: Extracellular
calcium sensing and extracellular calcium signaling. Physiol Rev.
81:239–297. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Churchill PC: Second messengers in renin
secretion. Am J Physiol. 249:175–184. 1985.
|
|
15
|
Atchison DK, Ortiz-Capisano MC and
Beierwaltes WH: Acute activation of the calcium-sensing receptor
inhibits plasma renin activity in vivo. Am J Physiol Regul Integr
Comp Physiol. 299:R1020–R1026. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park CS, Honeyman TW, Chung ES, Lee JS,
Sigmon DH and Fray JC: Involvement of calmodulin in mediating
inhibitory action of intracellular Ca2+ on renin
secretion. Am J Physiol. 251:F1055–F1062. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Smajilovic S, Yano S, Jabbari R and
Tfelthansen J: The calcium-sensing receptor and calcimimetics in
blood pressure modulation. Br J Pharmacol. 164:884–893. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qu Y, Jing H, Wang LM, Tang N, Zhong H,
Liu YM, Li Z, Feng Q and He F: Reduced expression of the
extracellular calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) is associated with
activation of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) to promote
vascular remodeling in the pathogenesis of essential hypertension.
PLoS One. 11:e01574562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Smajilovic S and Tfelt-Hansen J: Novel
role of the calcium-sensing receptor in blood pressure modulation.
Hypertension. 52:994–1000. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cow D: Some reactions of surviving
arteries. J Physiol. 42:125–143. 1911. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang R, Xu C, Zhao W, Zhang J, Cao K, Yang
B and Wu L: Calcium and polyamine regulated calcium-sensing
receptors in cardiac tissues. Eur J Biochem. 270:2680–2688. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Loot AE, Pierson I, Syzonenko T,
Elgheznawy A, Randriamboavonjy V, Zivković A, Stark H and Fleming
I: Ca2+-sensing receptor cleavage by calpain partially
accounts for altered vascular reactivity in mice fed a high-fat
diet. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 61:528–535. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ziegelstein RC, Xiong Y, He C and Hu Q:
Expression of a functional extracellular calcium-sensing receptor
in human aortic endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
342:153–163. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Weston AH, Absi M, Ward DT, Ohanian J,
Dodd RH, Dauban P, Petrel C, Ruat M and Edwards G: Evidence in
favor of a calcium-sensing receptor in arterial endothelial cells:
Studies with calindol and Calhex 231. Circ Res. 97:391–398. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vizard TN, O'Keeffe GW, Gutierrez H, Kos
CH, Riccardi D and Davies AM: Regulation of axonal and dendritic
growth by the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor. Nat Neurosci.
11:285–291. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Finn R: New animal care guide leaves
details to scientists' discretion-the scientist-magazine of the
life sciences. Scientist. 10:1996.
|
|
27
|
Chen YC, Yuan TY, Zhang HF, Wang DS, Niu
ZR, Li L, Fang LH and Du GH: Fasudil evokes vasodilatation of rat
mesenteric vascular bed via Ca(2+) channels and Rho/ROCK pathway.
Eur J Pharmacol. 788:226–233. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Choi S, Ryu KH, Park SH, Jun JY, Shin BC,
Chung JH and Yeum CH: Direct vascular actions of quercetin in aorta
from renal hypertensive rats. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 35:15–21.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu XM, Fang LH, Li YJ and Du GH:
Endothelium-dependent and -independent relaxation induced by
pinocembrin in rat aortic rings. Vascul Pharmacol. 46:160–165.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saito M, Tsounapi P, Oikawa R, Shimizu S,
Honda M, Sejima T, Kinoshita Y and Tomita S: Prostatic ischemia
induces ventral prostatic hyperplasia in the SHR; possible
mechanism of development of BPH. Sci Rep. 4:38222014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wonneberger K, Scofield MA and Wangemann
P: Evidence for a calcium-sensing receptor in the vascular smooth
muscle cells of the spiral modiolar artery. J Membr Biol.
175:203–212. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chan YC, Leung FP, Wong WT, Tian XY, Yung
LM, Lau CW, Tsang SY, Yao X, Chen ZY and Huang Y: Therapeutically
relevant concentrations of raloxifene dilate pressurized rat
resistance arteries via calcium-dependent endothelial nitric oxide
synthase activation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 30:992–999.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Caniffi C, Cerniello FM, Gobetto MN,
Sueiro ML, Costa MA and Arranz C: Vascular tone regulation induced
by C-type natriuretic peptide: Differences in endothelium-dependent
and -independent mechanisms involved in normotensive and
spontaneously hypertensive rats. PLoS One. 11:e01678172016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sudhahar V, Shaw S and Imig JD: Mechanisms
involved in oleamide-induced vasorelaxation in rat mesenteric
resistance arteries. European J Pharmacol. 607:1432009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Musha Y, Itoh S, Hanson MA and Kinoshita
K: Does estrogen affect the development of abnormal vascular
function in offspring of rats fed a low-protein diet in pregnancy?
Pediatr Res. 59:784–789. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu X, El-mahdy MA, Boslett J, Varadharaj
S, Hemann C, Abdelghany TM, Ismail RS, Little SC, Zhou D, Thuy LT,
et al: Cytoglobin regulates blood pressure and vascular tone
through nitric oxide metabolism in the vascular wall. Nat Communi.
8:148072017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Schepelmann M, Yarova PL, Lopez-Fernandez
I, Davies TS, Brennan SC, Edwards PJ, Aggarwal A, Graça J, Rietdorf
K, Matchkov V, et al: The vascular Ca2+-sensing receptor
regulates blood vessel tone and blood pressure. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 310:C193–C204. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Domenicali M, Ros J, Fernandez-Varo G,
Cejudo-Martín P, Crespo M, Morales-Ruiz M, Briones AM, Campistol
JM, Arroyo V, Vila E, et al: Increased anandamide induced
relaxation in mesenteric arteries of cirrhotic rats: Role of
cannabinoid and vanilloid receptors. Gut. 54:522–527. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lubomirov L, Gagov H, Petkova-Kirova P,
Duridanova D, Kalentchuk VU and Schubert R: Urocortin relaxes rat
tail arteries by a PKA-mediated reduction of the sensitivity of the
contractile apparatus for calcium. Br J Pharmacol. 134:1564–1570.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Foëx P and Sear J: Hypertension:
Pathophysiology and treatment. Continuing Edu Anaesthesia Critical
Care Pain. 4:71–75. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Segal SS: Regulation of blood flow in the
microcirculation. Microcirculation. 12:332005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rapp JP: Genetic analysis of inherited
hypertension in the rat. Physiol Rev. 80:135–172. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Piech A, Dessy C, Havaux X, Feron O and
Balligand JL: Differential regulation of nitric oxide synthases and
their allosteric regulators in heart and vessels of hypertensive
rats. Cardiovasc Res. 57:456–467. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sonoyama K, Greenstein A, Price A,
Khavandi K and Heagerty T: Vascular remodeling: implications for
small artery function and target organ damage. Ther Adv Cardiovasc
Dis. 1:129–137. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Molostvov G, James S, Fletcher S, Bennett
J, Lehnert H, Bland R and Zehnder D: Extracellular calcium-sensing
receptor is functionally expressed in human artery. Am J Physiol
Renal Physiol. 293:F946–F955. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang Y and Bukoski RD: Distribution of the
perivascular nerve Ca2+ receptor in rat arteries. Br J
Pharmacol. 125:1397–1404. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Northcott CA and Watts SW: Low
[Mg2+]e enhances arterial spontaneous tone via
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in DOCA-salt hypertension.
Hypertension. 43:125–129. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ohanian J, Gatfield KM, Ward DT and
Ohanian V: Evidence for a functional calcium-sensing receptor that
modulates myogenic tone in rat subcutaneous small arteries. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 288:H1756–H1762. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Greenberg HZE, Jahan KS, Jian S, Ho WSV
and Albert AP: The calcilytics Calhex-231 and NPS 2143 and the
calcimimetic Calindol reduce vascular reactivity via inhibition of
voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Eur J Pharmacol.
791:659–668. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Nakagawa K, Parekh N, Koleganova N, Ritz
E, Schaefer F and Schmitt CP: Acute cardiovascular effects of the
calcimimetic R-568 and its enantiomer S-568 in rats. Pediatr
Nephrol. 24:1385–1389. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sutherland SK and Benishin CG: Regulation
of parathyroid hypertensive factor secretion by Ca2+ in
spontaneously hypertensive rat parathyroid cells. Am J Hypertens.
17:266–272. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jensen AA and Bräuner-Osborne H:
Allosteric modulation of the calcium-sensing receptor. Curr
Neuropharmacol. 5:180–186. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Saidak Z, Brazier M, Kamel S and
Mentaverri R: Agonists and allosteric modulators of the
calcium-sensing receptor and their therapeutic applications. Mol
Pharmacol. 76:1131–1144. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Thakore P and Ho WS: Vascular actions of
calcimimetics: role of Ca2+-sensing receptors versus
Ca2+ influx through L-type Ca2+ channels. Br
J Pharmacol. 162:749–762. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Qiu HY, Henrion D and Levy BI: Endogenous
angiotensin II enhances phenylephrine-induced tone in hypertensive
rats. Hypertension. 24:317–321. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme
inhibition compared with conventional therapy on cardiovascular
morbidity and mortality in hypertension, . the Captopril Prevention
Project (CAPP) randomized trial. The Captopril Prevention Project
(CAPP) Study Group. Current Hyperten Rep. 1:466–467. 1999.
|
|
57
|
Maeso R, Navarro-Cid J, Muñoz-García R,
Rodrigo E, Ruilope LM, Lahera V and Cachofeiro V: Losartan reduces
phenylephrine constrictor response in aortic rings from
spontaneously hypertensive rats role of nitric oxide and
angiotensin II type 2 receptors. Hypertension. 28:967–972. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Houillier P: Calcium-sensing in the
kidney. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 22:566–571. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|