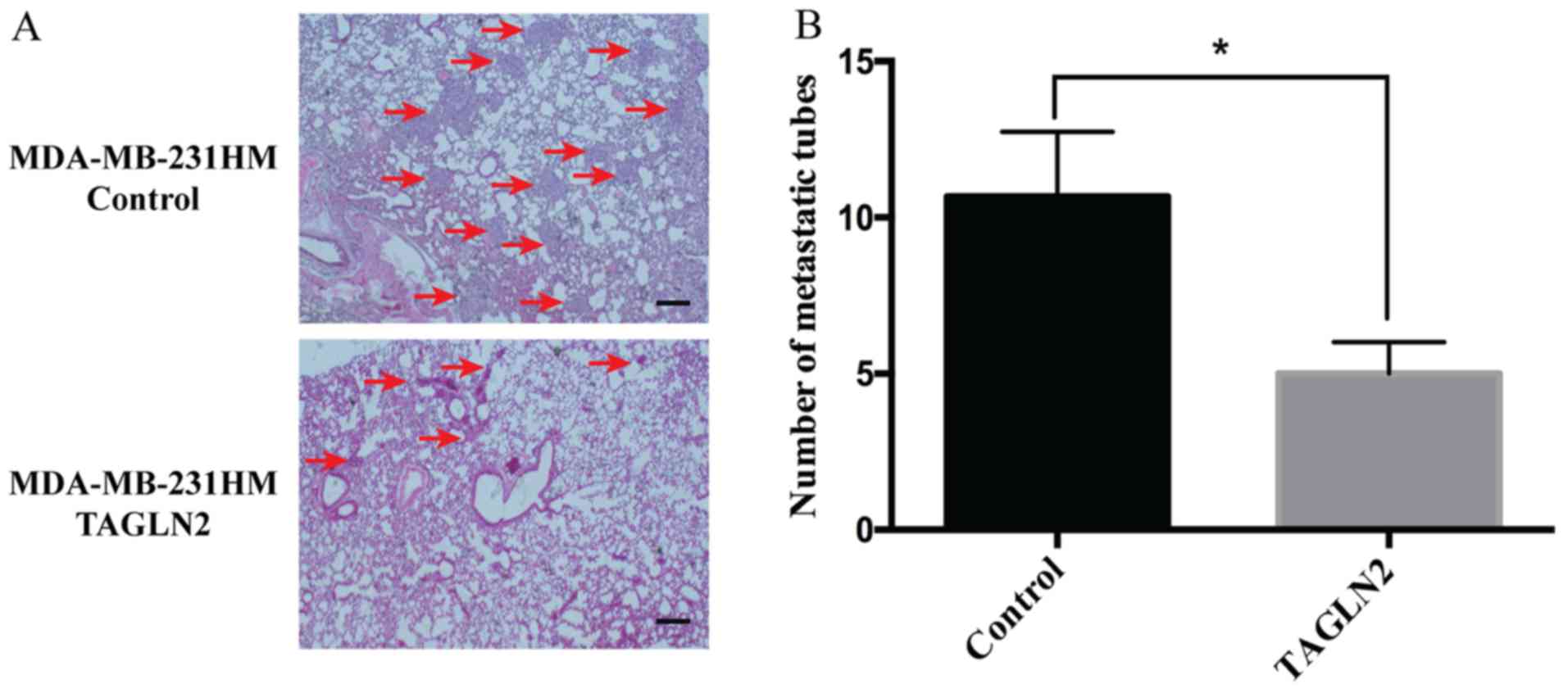
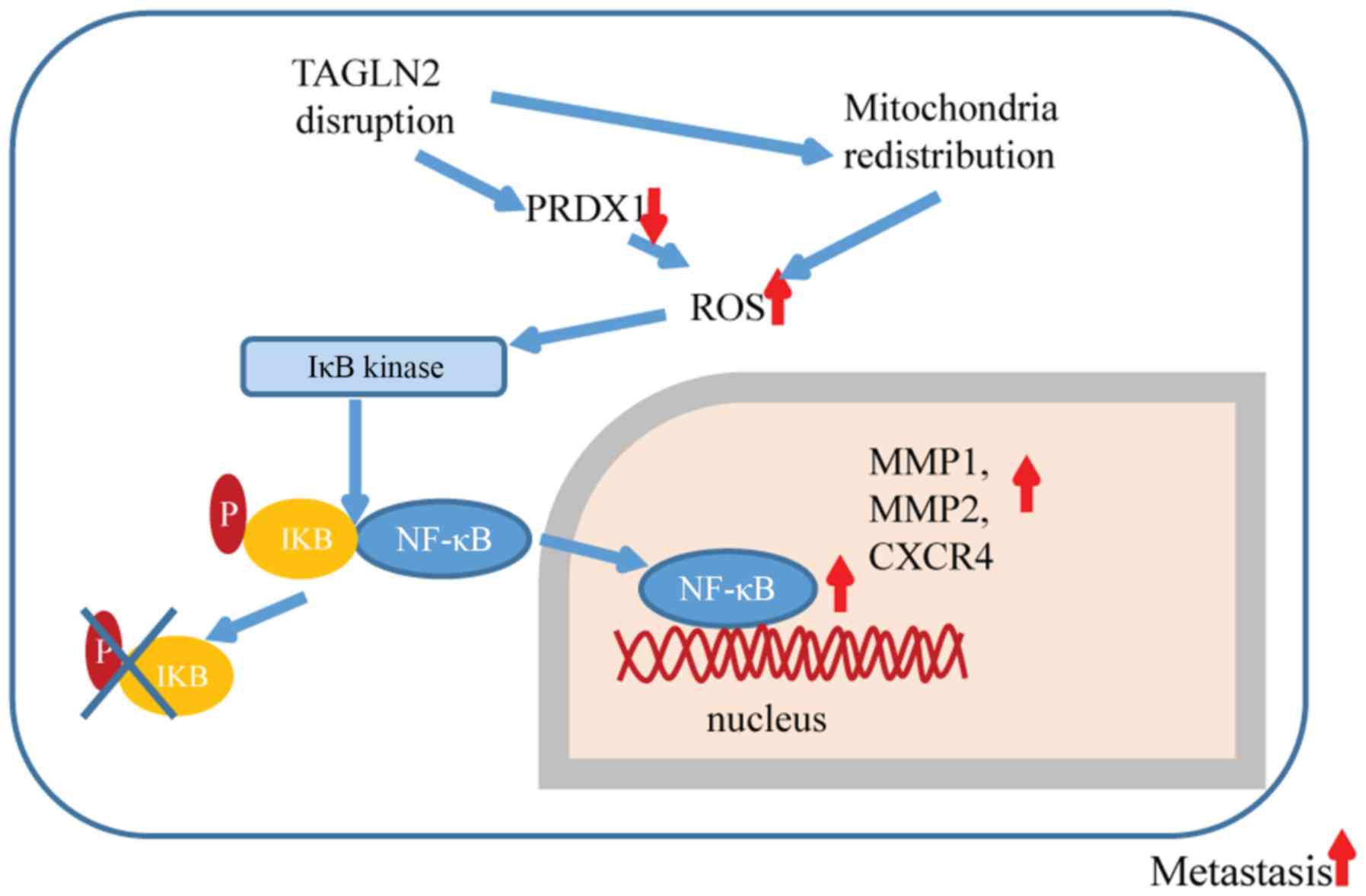
|
1
|
Berry DA, Cronin KA, Plevritis SK, Fryback
DG, Clarke L, Zelen M, Mandelblatt JS, Yakovlev AY, Habbema JD and
Feuer EJ; Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network
(CISNET) Collaborators, : Effect of screening and adjuvant therapy
on mortality from breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 353:1784–1792. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA: A perspective
on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 331:1559–1564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Eccles SA and Welch DR: Metastasis: Recent
discoveries and novel treatment strategies. Lancet. 369:1742–1757.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lambert AW, Pattabiraman DR and Weinberg
RA: Emerging biological principles of metastasis. Cell.
168:670–691. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Geiger T, Madden SF, Gallagher WM, Cox J
and Mann M: Proteomic portrait of human breast cancer progression
identifies novel prognostic markers. Cancer Res. 72:2428–2439.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xu SG, Yan PJ and Shao ZM: Differential
proteomic analysis of a highly metastatic variant of human breast
cancer cells using two-dimensional differential gel
electrophoresis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:1545–1556. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bertucci F, Birnbaum D and Goncalves A:
Proteomics of breast cancer: Principles and potential clinical
applications. Mol Cell Proteomics. 5:1772–1786. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Murugaesu N, Iravani M, van Weverwijk A,
Ivetic A, Johnson DA, Antonopoulos A, Fearns A, Jamal-Hanjani M,
Sims D, Fenwick K, et al: An in vivo functional screen identifies
ST6GalNAc2 sialyltransferase as a breast cancer metastasis
suppressor. Cancer Discov. 4:304–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ooms LM, Binge LC, Davies EM, Rahman P,
Conway JR, Gurung R, Ferguson DT, Papa A, Fedele CG, Vieusseux JL,
et al: The inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase PIPP regulates
AKT1-dependent breast cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Cell.
28:155–169. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Okita Y, Kimura M, Xie R, Chen C, Shen LT,
Kojima Y, Suzuki H, Muratani M, Saitoh M, Semba K, et al: The
transcription factor MAFK induces EMT and malignant progression of
triple-negative breast cancer cells through its target GPNMB. Sci
Signal. 10(pii): eaak93972017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stanier P, Abu-Hayyeh S, Murdoch JN,
Eddleston J and Copp AJ: Paralogous sm22alpha (Tagln) genes map to
mouse chromosomes 1 and 9: Further evidence for a paralogous
relationship. Genomics. 51:144–147. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li M, Li S, Lou Z, Liao X, Zhao X, Meng Z,
Bartlam M and Rao Z: Crystal structure of human transgelin. J
Struct Biol. 162:229–236. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shapland C, Hsuan JJ, Totty NF and Lawson
D: Purification and properties of transgelin: A transformation and
shape change sensitive actin-gelling protein. J Cell Biol.
121:1065–1073. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Elsner M, Rauser S, Maier S, Schöne C,
Balluff B, Meding S, Jung G, Nipp M, Sarioglu H, Maccarrone G, et
al: MALDI imaging mass spectrometry reveals COX7A2, TAGLN2 and
S100-A10 as novel prognostic markers in Barrett's adenocarcinoma. J
Proteomics. 75:4693–4704. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Leung WK, Ching AK, Chan AW, Poon TC, Mian
H, Wong AS, To KF and Wong N: A novel interplay between oncogenic
PFTK1 protein kinase and tumor suppressor TAGLN2 in the control of
liver cancer cell motility. Oncogene. 30:4464–4475. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yoshida A, Okamoto N, Tozawa-Ono A,
Koizumi H, Kiguchi K, Ishizuka B, Kumai T and Suzuki N: Proteomic
analysis of differential protein expression by brain metastases of
gynecological malignancies. Human Cell. 26:56–66. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shields JM, Rogers-Graham K and Der CJ:
Loss of transgelin in breast and colon tumors and in RIE-1 cells by
Ras deregulation of gene expression through Raf-independent
pathways. J Biol Chem. 277:9790–9799. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luanpitpong S, Talbott SJ, Rojanasakul Y,
Nimmannit U, Pongrakhananon V, Wang L and Chanvorachote P:
Regulation of lung cancer cell migration and invasion by reactive
oxygen species and caveolin-1. J Biol Chem. 285:38832–38840. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zheng Y, Miyamoto DT, Wittner BS, Sullivan
JP, Aceto N, Jordan NV, Yu M, Karabacak NM, Comaills V, Morris R,
et al: Expression of β-globin by cancer cells promotes cell
survival during blood-borne dissemination. Nat Commun. 8:143442017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou G, Peng F, Zhong Y, Chen Y, Tang M
and Li D: Rhein suppresses matrix metalloproteinase production by
regulating the Rac1/ROS/MAPK/AP-1 pathway in human ovarian
carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 50:933–941. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen B, Liu J, Ho TT, Ding X and Mo YY:
ERK-mediated NF-κB activation through ASIC1 in response to
acidosis. Oncogenesis. 5:e2792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cao L, Chen X, Xiao X, Ma Q and Li W:
Resveratrol inhibits hyperglycemia-driven ROS-induced invasion and
migration of pancreatic cancer cells via suppression of the ERK and
p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Int J Oncol. 49:735–743. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Księżakowska-Łakoma K, Żyła M and
Wilczyński JR: Mitochondrial dysfunction in cancer. Prz
Menopauzalny. 13:136–144. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Morgan MJ and Liu ZG: Crosstalk of
reactive oxygen species and NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 21:103–115.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vasquez-Dunddel D, Pan F, Zeng Q,
Gorbounov M, Albesiano E, Fu J, Blosser RL, Tam AJ, Bruno T, Zhang
H, et al: STAT3 regulates arginase-I in myeloid-derived suppressor
cells from cancer patients. J Clin Invest. 123:1580–1589. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang CS, Kim JJ, Lee SJ, Hwang JH, Lee CH,
Lee MS and Jo EK: TLR3-triggered reactive oxygen species contribute
to inflammatory responses by activating signal transducer and
activator of transcription-1. J Immunol. 190:6368–6377. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yoon S, Woo SU, Kang JH, Kim K, Kwon MH,
Park S, Shin HJ, Gwak HS and Chwae YJ: STAT3 transcriptional factor
activated by reactive oxygen species induces IL6 in
starvation-induced autophagy of cancer cells. Autophagy.
6:1125–1138. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Q, Raje V, Yakovlev VA, Yacoub A,
Szczepanek K, Meier J, Derecka M, Chen Q, Hu Y, Sisler J, et al:
Mitochondrial-localized Stat3 promotes breast cancer growth via
phosphorylation of serine 727. J Biol Chem. 288:31280–31288. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Egler RA, Fernandes E, Rothermund K,
Sereika S, de Souza-Pinto N, Jaruga P, Dizdaroglu M and Prochownik
EV: Regulation of reactive oxygen species, DNA damage and c-Myc
function by peroxiredoxin 1. Oncogene. 24:8038–8050. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lv WP, Li MX and Wang L: Peroxiredoxin 1
inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress in lung tissue
by regulating P38/JNK signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
21:1876–1883. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ding C, Fan X and Wu G: Peroxiredoxin 1-an
antioxidant enzyme in cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 21:193–202. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang J, Lin D, Peng H, Huang Y, Huang J
and Gu J: Cancer-derived immunoglobulin G promotes tumor cell
growth and proliferation through inducing production of reactive
oxygen species. Cell Death Dis. 4:e9452013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cao J, Schulte J, Knight A, Leslie NR,
Zagozdzon A, Bronson R, Manevich Y, Beeson C and Neumann CA: Prdx1
inhibits tumorigenesis via regulating PTEN/AKT activity. EMBO J.
28:1505–1517. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Singletary SE and Connolly JL: Breast
cancer staging: Working with the sixth edition of the AJCC Cancer
Staging Manual. CA Cancer J Clin. 56:37–47; quiz 50-1. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lundgren DH, Han DK and Eng JK: Protein
identification using TurboSEQUEST. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics
Chapter. 13:Unit 13.3. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Meng T, Liu L, Hao R, Chen S and Dong Y:
Transgelin-2: A potential oncogenic factor. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177026502017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Collins Y, Chouchani ET, James AM, Menger
KE, Cochemé HM and Murphy MP: Mitochondrial redox signalling at a
glance. J Cell Sci. 125:801–806. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Eruslanov E and Kusmartsev S:
Identification of ROS using oxidized DCFDA and flow-cytometry.
Methods Mol Biol. 594:57–72. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang F, Yang JL, Yu KK, Xu M, Xu YZ, Chen
L, Lu YM, Fang HS, Wang XY, Hu ZQ, et al: Activation of the NF-κB
pathway as a mechanism of alcohol enhanced progression and
metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer.
14:102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lu H, Ouyang W and Huang C: Inflammation,
a key event in cancer development. Mol Cancer Res. 4:221–233. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Assinder SJ, Stanton JA and Prasad PD:
Transgelin: An actin-binding protein and tumour suppressor. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 41:482–486. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang Z, Chang YJ, Miyamoto H, Ni J, Niu Y,
Chen Z, Chen YL, Yao JL, di Sant'Agnese PA and Chang C: Transgelin
functions as a suppressor via inhibition of ARA54-enhanced androgen
receptor transactivation and prostate cancer cell growth. Mol
Endocrinol. 21:343–358. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nair RR, Solway J and Boyd DD: Expression
cloning identifies transgelin (SM22) as a Novel repressor of 92-kDa
type IV collagenase (MMP-9) expression. J Biol Chem.
281:26424–26436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Han MZ, Xu R, Xu YY, Zhang X, Ni SL, Huang
B, Chen AJ, Wei YZ, Wang S, Li WJ, et al: TAGLN2 is a candidate
prognostic biomarker promoting tumorigenesis in human gliomas. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:1552017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yakabe K, Murakami A, Kajimura T,
Nishimoto Y, Sueoka K, Sato S, Nawata S and Sugino N: Functional
significance of transgelin-2 in uterine cervical squamous cell
carcinoma. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 42:566–572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Du YY, Zhao LM, Chen L, Sang MX, Li J, Ma
M and Liu JF: The tumor-suppressive function of miR-1 by targeting
LASP1 and TAGLN2 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 31:384–393. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zheng X, Chen S, Yang Q, Cai J, Zhang W,
You H, Xing J and Dong Y: Salvianolic acid A reverses the
paclitaxel resistance and inhibits the migration and invasion
abilities of human breast cancer cells by inactivating transgelin
2. Cancer Biol Ther. 16:1407–1414. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ahmed W and Lingner J: PRDX1 and MTH1
cooperate to prevent ROS-mediated inhibition of telomerase. Genes
Dev. 32:658–669. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Boldogh IR and Pon LA: Interactions of
mitochondria with the actin cytoskeleton. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1763:450–462. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Rappaport L, Oliviero P and Samuel JL:
Cytoskeleton and mitochondrial morphology and function. Mol Cell
Biochem. 184:101–105. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Moore AS, Wong YC, Simpson CL and Holzbaur
EL: Dynamic actin cycling through mitochondrial subpopulations
locally regulates the fission-fusion balance within mitochondrial
networks. Nat Commun. 7:128862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Breitenbach M, Laun P and Gimona M: The
actin cytoskeleton, RAS-cAMP signaling and mitochondrial ROS in
yeast apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 15:637–639. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bhat SS, Parray AA, Mushtaq U, Fazili KM
and Khanday FA: Actin depolymerization mediated loss of SNTA1
phosphorylation and Rac1 activity has implications on ROS
production, cell migration and apoptosis. Apoptosis. 21:737–748.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Roy P, Sarkar UA and Basak S: The NF-κB
activating pathways in multiple myeloma. Biomedicines. 6:E592018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Klein CA: Cancer. The metastasis cascade.
Science. 321:1785–1787. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Shahriari K, Shen F, Worrede-Mahdi A, Liu
Q, Gong Y, Garcia FU and Fatatis A: Cooperation among heterogeneous
prostate cancer cells in the bone metastatic niche. Oncogene.
36:2846–2856. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Shibue T, Brooks MW and Weinberg RA: An
integrin-linked machinery of cytoskeletal regulation that enables
experimental tumor initiation and metastatic colonization. Cancer
Cell. 24:481–498. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhang J, Chen J, Wo D, Yan H, Liu P, Ma E,
Li L, Zheng L, Chen D, Yu Z, et al: LRP6 ectodomain prevents
SDF-1/CXCR4-induced breast cancer metastasis to lung. Clin Cancer
Res. 25:4832–4845. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|