|
1
|
Weidinger S, Beck LA, Bieber T, Kabashima
K and Irvine AD: Atopic dermatitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 4:12018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bieber T: Atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med.
358:1483–1494. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xu F, Yan S, Li F, Cai M, Chai W, Wu M, Fu
C, Zhao Z, Kan H, Kang K and Xu J: Prevalence of childhood atopic
dermatitis: An urban and rural community-based study in shanghai,
China. PLoS One. 7:e361742012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guo Y, Li P, Tang J, Han X, Zou X, Xu G,
Xu Z, Wei F, Liu Q, Wang M, et al: Prevalence of atopic dermatitis
in Chinese children aged 1–7 ys. Sci Rep. 6:297512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang AX and Xu Landén N: New insights into
T cells and their signature cytokines in atopic dermatitis. IUBMB
Life. 67:601–610. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li S, Liu L, Zhuang X, Yu Y, Liu X, Cui X,
Ji L, Pan Z, Cao X, Mo B, et al: MicroRNAs inhibit the translation
of target mRNAs on the endoplasmic reticulum in arabidopsis. Cell.
153:562–574. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wahid F, Shehzad A, Khan T and Kim YY:
MicroRNAs: Synthesis, mechanism, function, and recent clinical
trials. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1803:1231–1243. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lau PW and MacRae IJ: The molecular
machines that mediate microRNA maturation. J Cell Mol Med.
13:54–60. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sonkoly E and Pivarcsi A: Advances in
microRNAs: Implications for immunity and inflammatory diseases. J
Cell Mol Med. 13:24–38. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yoshizawa JM and Wong DT: Salivary
microRNAs and oral cancer detection. Methods Mol Biol. 936:313–324.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Wernicke D, Alder H,
Costinean S, Volinia S and Croce CM: Mutator activity induced by
microRNA-155 (miR-155) links inflammation and cancer. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 108:4908–4913. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
West C and McDermott MF: Effects of
microRNA-146a on the proliferation and apoptosis of human
osteochondrocytes by targeting TRAF6 through the NF-κB signalling
pathway. Biosci Rep. 37(pii): BSR201701802017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Park H, Huang X, Lu C, Cairo MS and Zhou
X: MicroRNA-146a and microRNA-146b regulate human dendritic cell
apoptosis and cytokine production by targeting TRAF6 and IRAK1
proteins. J Biol Chem. 290:2831–2841. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lindner JM, Kayo H, Hedlund S, Fukuda Y,
Fukao T and Nielsen PJ: Cutting Edge: The transcription factor Bob1
counteracts B cell activation and regulates miR-146a in B cells. J
Immunol. 192:4483–4486. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang S, Zhang X, Ju Y, Zhao B, Yan X, Hu
J, Shi L, Yang L, Ma Z, Chen L, et al: MicroRNA-146a feedback
suppresses T cell immune function by targeting Stat1 in patients
with chronic Hepatitis B. J Immunol. 191:293–301. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Williams AE, Perry MM, Moschos SA,
Larner-Svensson HM and Lindsay MA: Role of miRNA-146a in the
regulation of the innate immune response and cancer. Biochem Soc
Trans. 36:1211–1215. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rebane A, Runnel T, Aab A, Maslovskaja J,
Rückert B, Zimmermann M, Plaas M, Kärner J, Treis A, Pihlap M, et
al: MicroRNA-146a alleviates chronic skin inflammation in atopic
dermatitis through suppression of innate immune responses in
keratinocytes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 134:836–847.e11. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
M HJ and Georg R: Diagnostic features of
atopic dermatitis. Acta Dermatovener. 60:44–47. 1980.
|
|
19
|
Eichenfield LF, Lucky AW, Boguniewicz M,
Langley RG, Cherill R, Marshall K, Bush C and Graeber M: Safety and
efficacy of pimecrolimus (ASM 981) cream 1% in the treatment of
mild and moderate atopic dermatitis in children and adolescents. J
Am Acad Dermatol. 46:495–504. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Heo JC, Nam DY, Seo MS and Lee SH:
Alleviation of atopic dermatitis-related symptoms by Perilla
frutescens Britton. Int J Mol Med. 28:733–737. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Heo JC, Son HU, Kim SL and Lee SH: A
derivative of L-allo threonine alleviates
2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis indications.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 76:2021–2025. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nam DY, Lee JM, Heo JC and Lee SH:
Mitigation of 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene-induced atopic
dermatitis-related symptoms by Terminalia chebula Retzius. Int J
Mol Med. 28:1013–1018. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
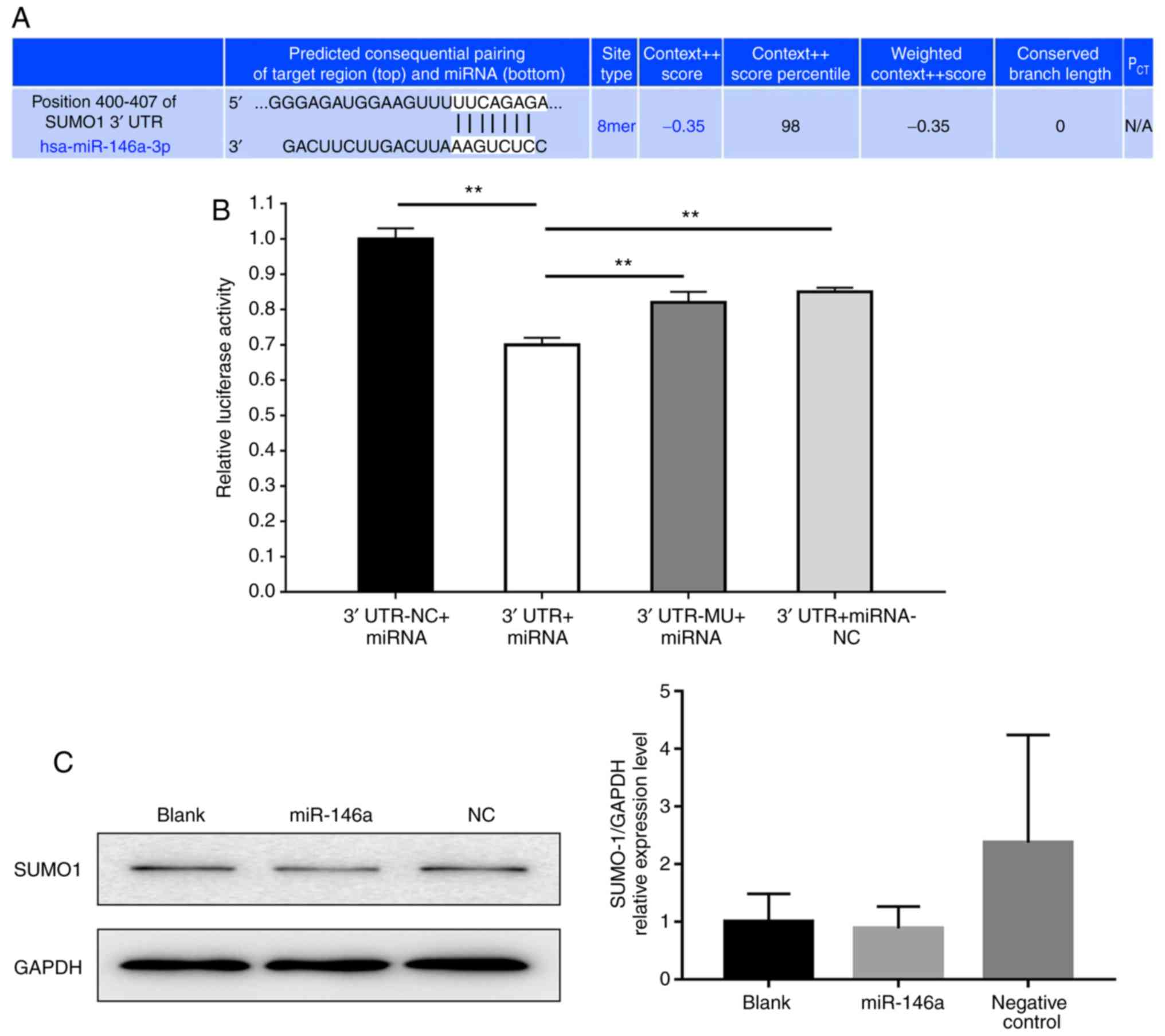
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 42015.doi: 10.7554/eLife.05005.
|
|
25
|
Oh JG, Watanabe S, Lee A, Gorski PA, Lee
P, Jeong D, Liang L, Liang Y, Baccarini A, Sahoo S, et al: miR-146a
suppresses SUMO1 expression and induces cardiac dysfunction in
maladaptive hypertrophy. Circ Res. 123:673–685. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Deleanu D and Nedelea I: Biological
therapies for atopic dermatitis: An update. Exp Ther Med.
17:1061–1067. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Thomsen SF: Atopic dermatitis: Natural
history, diagnosis, and treatment. ISRN Allergy. 2014:3542502014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rożalski M, Rudnicka L and Samochocki Z:
MiRNA in atopic dermatitis. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 33:157–162.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Specjalski K and Jassem E: MicroRNAs:
Potential biomarkers and targets of therapy in allergic diseases?
Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 67:213–223. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bin L and Leung DY: Genetic and epigenetic
studies of atopic dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol.
12:522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sonkoly E, Wei T, Janson PC, Sääf A,
Lundeberg L, Tengvall-Linder M, Norstedt G, Alenius H, Homey B,
Scheynius A, et al: MicroRNAs: Novel regulators involved in the
pathogenesis of psoriasis? PLoS One. 2:e6102007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bhardwaj N: MicroRNAs in atopic
dermatitis: A review. J Transl Genet Genom. 1:15–22. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Sonkoly E, Janson P, Majuri ML, Savinko T,
Fyhrquist N, Eidsmo L, Xu N, Meisgen F, Wei T, Bradley M, et al:
MiR-155 is overexpressed in patients with atopic dermatitis and
modulates T-cell proliferative responses by targeting cytotoxic T
lymphocyte-associated antigen 4. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
126:581–589.e1-e20. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Auriemma M, Vianale G, Amerio P and Reale
M: Cytokines and T cells in atopic dermatitis. Eur Cytokine Netw.
24:37–44. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lipozencić J, Pastar Z, Kulisić SM and
Pavić I: Immunologic aspects of atopic dermatitis. Acta
Dermatovenerol Croat. 17:226–234. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Agrawal R, Wisniewski JA and Woodfolk JA:
The role of regulatory T cells in atopic dermatitis. Curr Probl
Dermatol. 41:112–124. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Miraglia del Giudice M, Decimo F, Leonardi
S, Maioello N, Amelio R, Capasso A, Capristo C and Capristo AF:
Immune dysregulation in atopic dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Proc.
27:451–455. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Grewe M, Bruijnzeel-Koomen CA, Schöpf E,
Maioello N, Amelio R, Capasso A, Capristo C and Capristo AF: A role
for Th1 and Th2 cells in the immunopathogenesis of atopic
dermatitis. Immunol Today. 19:359–361. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li L, Chen XP and Li YJ: MicroRNA-146a and
human disease. Scand J Immunol. 71:227–231. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ammari M, Jorgensen C and Apparailly F:
Impact of microRNAs on the understanding and treatment of
rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 25:225–233. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dai Y, Huang YS, Tang M, Lv TY, Hu CX, Tan
YH, Xu ZM and Yin YB: Microarray analysis of microRNA expression in
peripheral blood cells of systemic lupus erythematosus patients.
Lupus. 16:939–946. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jiménez-Morales S, Gamboa-Becerra R, Baca
V, Del Río-Navarro BE, López-Ley DY, Velázquez-Cruz R,
Saldaña-Alvarez Y, Salas-Martínez G and Orozco L: MiR-146a
polymorphism is associated with asthma but not with systemic lupus
erythematosus and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis in Mexican
patients. Tissue Antigens. 80:317–321. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lu LF, Boldin MP, Chaudhry A, Lin LL,
Taganov KD, Hanada T, Yoshimura A, Baltimore D and Rudensky AY:
Function of miR-146a in controlling Treg cell-mediated regulation
of Th1 responses. Cell. 142:914–929. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tang Y, Luo X, Cui H, Ni X, Yuan M, Guo Y,
Huang X, Zhou H, de Vries N, Tak PP, et al: MicroRNA-146A
contributes to abnormal activation of the type I interferon pathway
in human lupus by targeting the key signaling proteins. Arthritis
Rheum. 60:1065–1075. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kamali K, Korjan ES, Eftekhar E,
Malekzadeh K and Soufi FG: The role of miR-146a on NF-κB expression
level in human umbilical vein endothelial cells under hyperglycemic
condition. Bratisl Lek Listy. 117:376–380. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xie Q, Wei W, Ruan J, Ding Y, Zhuang A, Bi
X, Sun H, Gu P, Wang Z and Fan X: Effects of miR-146a on the
osteogenesis of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and bone
regeneration. Sci Rep. 7:428402017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lyons JJ and Milner JD: Primary atopic
disorders. J Exp Med. 215:1009–1022. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|