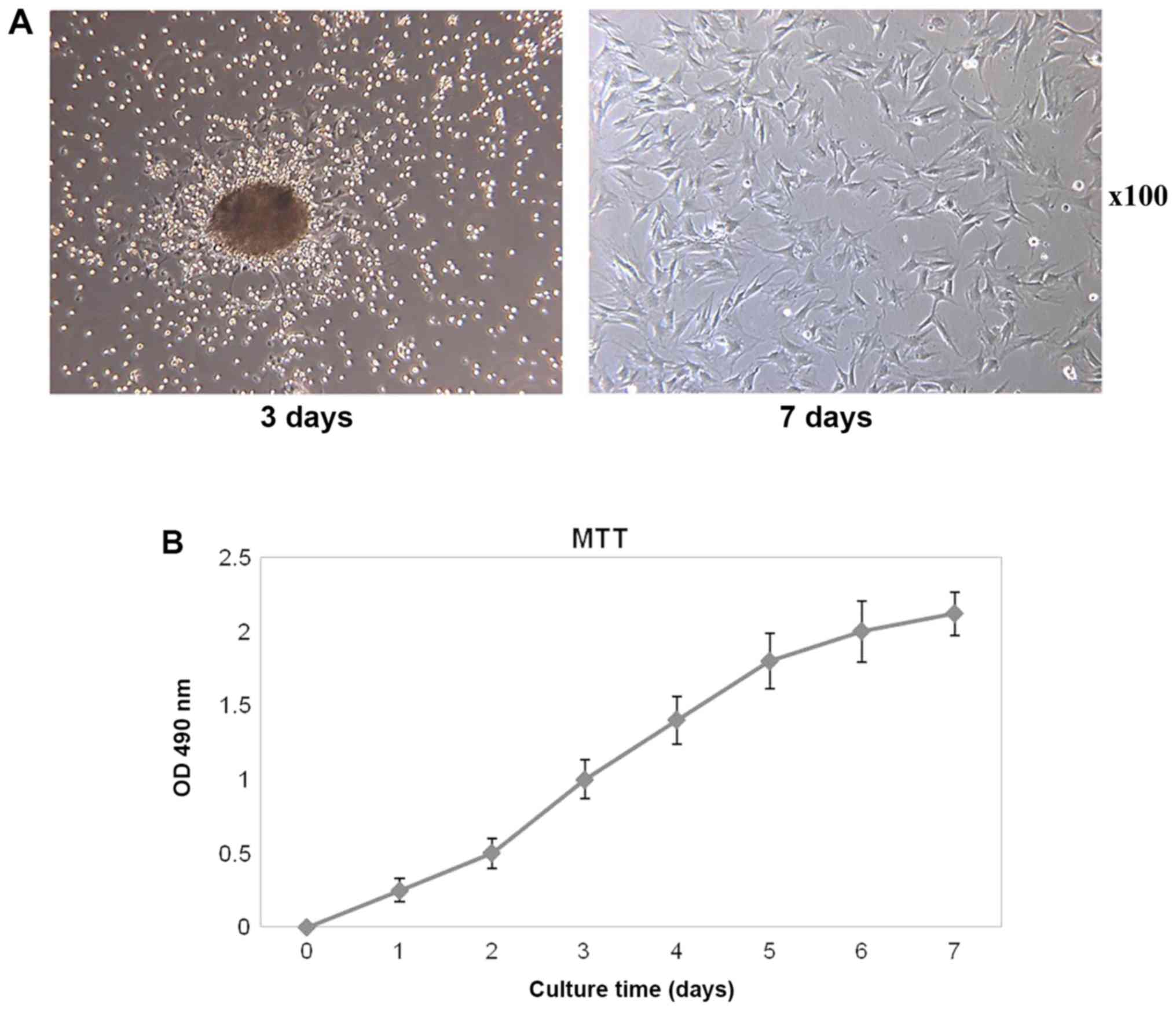
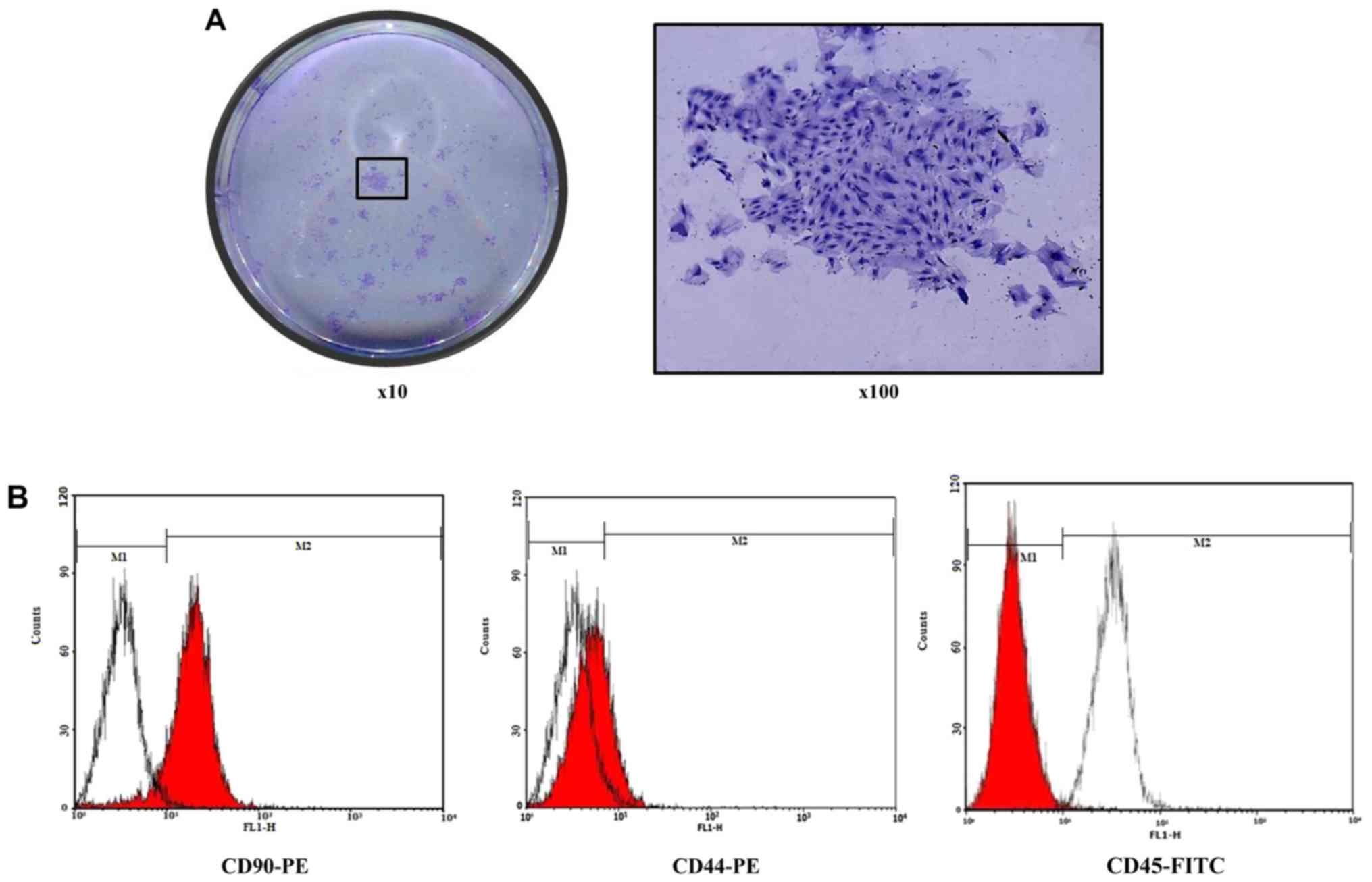
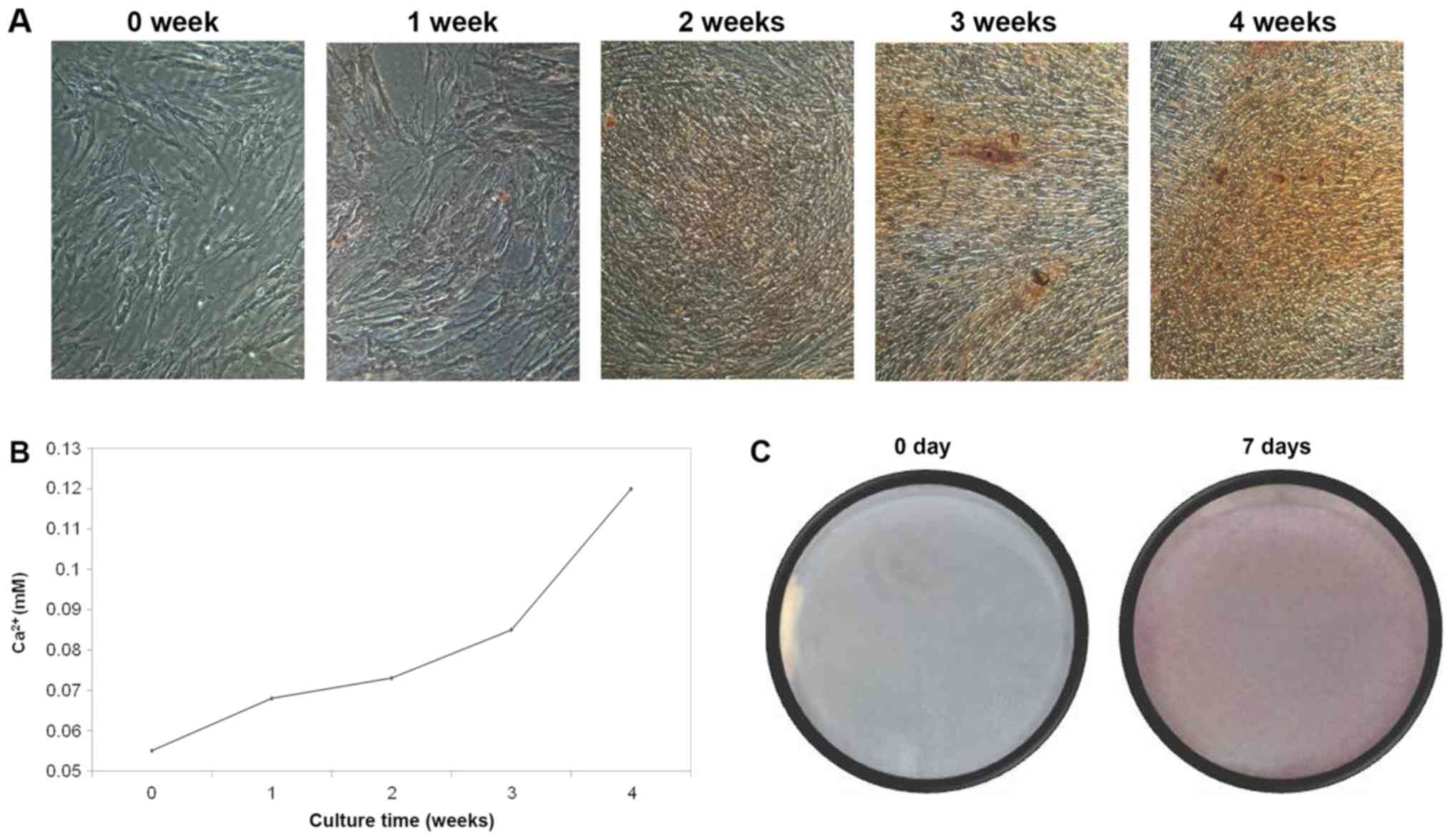
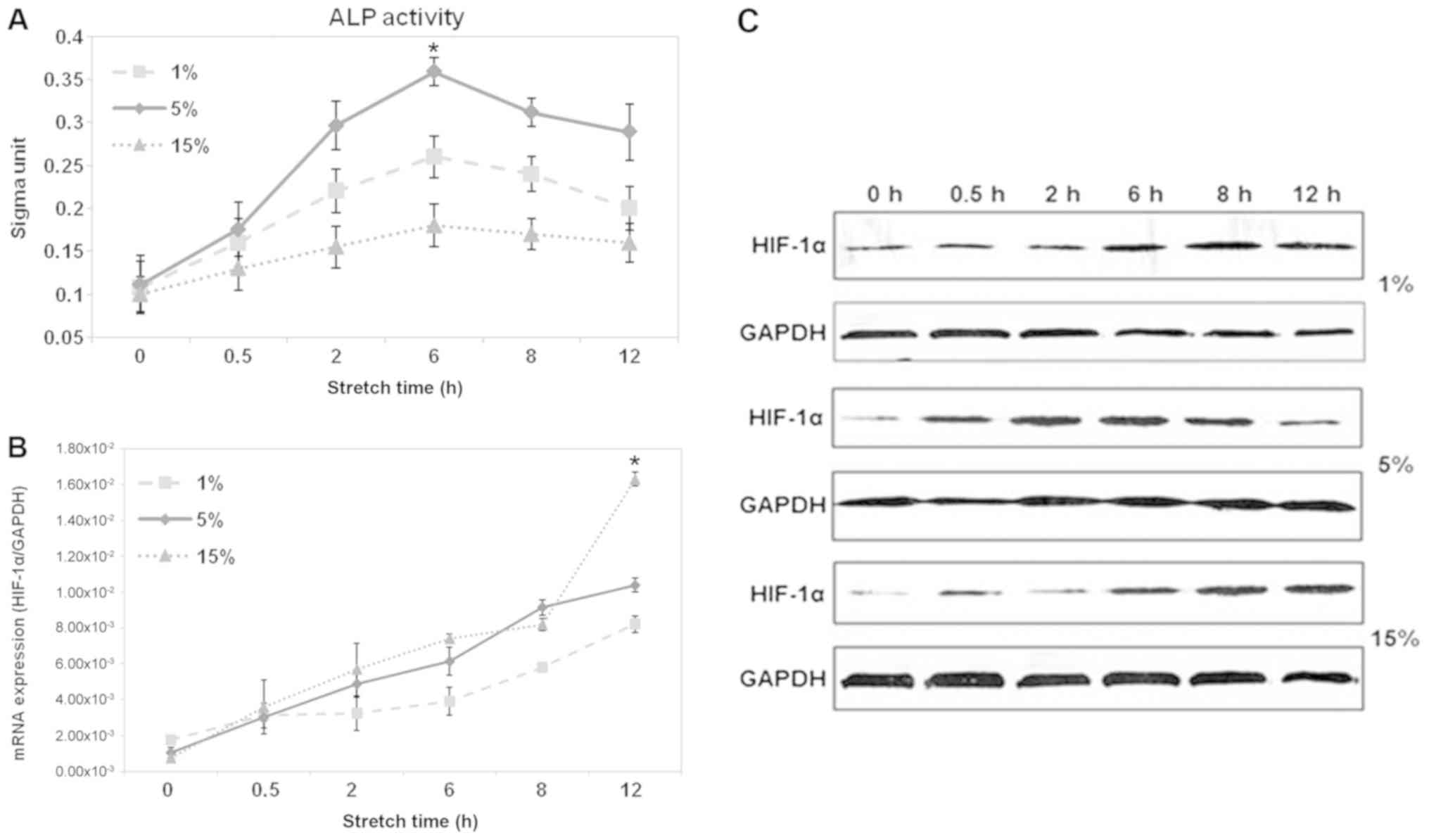
|
1
|
Dibart S, Yee C, Surmenian J, Sebaoun JD,
Baloul S, Goguet-Surmenian E and Kantarci A: Tissue response during
Piezocision-assisted tooth movement: A histological study in rats.
Eur J Orthod. 36:457–464. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Antoun JS, Mei L, Gibbs K and Farella M:
Effect of orthodontic treatment on the periodontal tissues.
Periodontol. 74:140–157. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Vlaikou AM, Kouroupis D, Sgourou A,
Markopoulos GS, Bagli E, Markou M, Papadopoulou Z, Fotsis T, Nakos
G, Lekka ME and Syrrou M: Mechanical stress affects methylation
pattern of GNAS isoforms and osteogenic differentiation of
hAT-MSCs. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1864:1371–1381. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barbieri G, Solano P, Alarcón JA, Vernal
R, Rios-Lugo J, Sanz M and Martín C: Biochemical markers of bone
metabolism in gingival crevicular fluid during early orthodontic
tooth movement. Angle Orthod. 83:63–69. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ohgushi H: Osteogenically differentiated
mesenchymal stem cells and ceramics for bone tissue engineering.
Expert Opin Biol Ther. 14:197–208. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Connelly JT, García AJ and Levenston ME:
Interactions between integrin ligand density and cytoskeletal
integrity regulate BMSC chondrogenesis. J Cell Physiol.
217:145–154. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moreau JE, Chen J, Horan RL, Kaplan DL and
Altman GH: Sequential growth factor application in bone marrow
stromal cell ligament engineering. Tissue Eng. 11:1887–1897. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moreau JE, Bramono DS, Horan RL, Kaplan DL
and Altman GH: Sequential biochemical and mechanical stimulation in
the development of tissue-engineered ligaments. Tissue Eng Part A.
14:1161–1172. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schaffer JL, Rizen M, L'Italien GJ,
Benbrahim A, Megerman J, Gerstenfeld LC and Gray ML: Device for the
application of a dynamic biaxially uniform and Isotropic strain to
a flexible cell culture membrane. J Orthop Res. 12:709–719. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Susilo ME, Bell BJ, Roeder BA,
Voytik-Harbin SL, Kokini K and Nauman EA: Prediction of equibiaxial
loading stress in collagen-based extracellular matrix using a
three-dimensional unit cell model. Acta Biomater. 9:5544–5553.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qi YX, Yao QP, Huang K, Shi Q, Zhang P,
Wang GL, Han Y, Bao H, Wang L, Li HP, et al: Nuclear envelope
proteins modulate proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells
during cyclic stretch application. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:5293–5298. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ursekar CP, Teo SK, Hirata H, Harada I,
Chiam KH and Sawada Y: Design and construction of an equibiaxial
cell stretching system that is improved for biochemical analysis.
PLoS One. 9:e906652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lohberger B, Kaltenegger H, Stuendl N,
Payer M, Rinner B and Leithner A: Effect of cyclic mechanical
stimulation on the expression of osteogenesis genes in human
intraoral mesenchymal stromal and progenitor cells. Biomed Res Int.
2014:1895162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu Y, Huang X, Yu H, Yang J, Li Y, Yuan X
and Guo Q: HIF-1α-TWIST pathway restrains cyclic mechanical
stretch-induced osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells. Connect Tissue Res. 60:544–554. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Niklas A, Proff P, Gosau M and Römer P:
The role of hypoxia in orthodontic tooth movement. Int J Dent.
2013:8418402013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Semenza GL and Wang GL: A nuclear factor
induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human
erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional
activation. Mol Cell Biol. 12:5447–5454. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li Y, Padmanabha D, Gentile LB, Dumur CI,
Beckstead RB and Baker KD: HIF- and non-HIF-regulated hypoxic
responses require the estrogen-related receptor in Drosophila
melanogaster. PLoS Genet. 9:e10032302013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou N, Hu N, Liao JY, Lin LB, Zhao C, Si
WK, Yang Z, Yi SX, Fan TX, Bao W, et al: HIF-1a as a regulator of
BMP2-induced chondrogenic differentiation, osteogenic
differentiation, and endochondral ossification in stem cells. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 36:44–60. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nemeth K, Mayer B, Sworder BJ, Kuznetsov
SA and Mezey E: A practical guide to culturing mouse and human bone
marrow stromal cells. Curr Protoc Immunol. 102:Unit 22F.12.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu HC, Wu TC, Chen MR, Liu SW, Chen JH and
Lin KM: Mechanical stretching induces osteoprotegerin in
differentiating C2C12 precursor cells through noncanonical Wnt
pathways. J Bone Miner Res. 25:1128–1137. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jang Y, Han J, Kim SJ, Kim J, Lee MJ,
Jeong S, Ryu MJ, Seo KS, Choi SY, Shong M, et al: Suppression of
mitochondrial respiration with auraptene inhibits the progression
of renal cell carcinoma: Involvement of HIF-1a degradation.
Oncotarget. 6:38127–38138. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sung WW, Chu YC, Chen PR, Liao MH and Lee
JW: Positive regulation of HIF-1A expression by EBV oncoprotein
LMP1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 382:21–31.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sha Y, Lv Y, Xu Z, Yang L, Hao X and
Afandi R: MGF E peptide pretreatment improves the proliferation and
osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs via MEK-ERK1/2 and PI3K-Akt
pathway under severe hypoxia. Life Sci. 189:52–62. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bruder SP, Jaiswal N and Haynesworth SE:
Growth kinetics, selfrenewal, and the osteogenic potential of
purified human mesenchymal stem cells during extensive
subcultivation and following cryopreservation. J Cell Biochem.
64:278–294. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kusuyama J, Kamisono A, ChangHwan S, Amir
MS, Bandow K, Eiraku N, Ohnishi T and Matsuguchi T: Spleen tyrosine
kinase influences the early stages of multilineage differentiation
of bone marrow stromal cell lines by regulating phospholipase C
gamma activities. J Cell Physiol. 233:2549–2559. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tang Y, Xu Y, Xiao Z, Zhao Y, Li J, Han S,
Chen L, Dai B, Wang L, Chen B and Wang H: The combination of
three-dimensional and rotary cell culture system promotes the
proliferation and maintains the differentiation potential of rat
BMSCs. Sci Rep. 7:1922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xia CS, Zuo AJ, Wang CY and Wang YZ:
Isolation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells using
density gradient centrifugation and adherence screening methods.
Minerva Med. 104:519–525. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Steinert AF, Kunz M, Prager P, Göbel S,
Klein-Hitpass L, Ebert R, Nöth U, Jakob F and Gohlke F:
Characterization of bursa subacromialis-derived mesenchymal stem
cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 6:1142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang F, Xia Z, Li S, Eckert G and Chen J:
Mechanical environment change in root, periodontal ligament, and
alveolar bone in response to two canine retraction treatment
strategies. Orthod Craniofac Res. 18 (Suppl 1):S29–S38. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Stanley A, Heo SJ, Mauck RL, Mourkioti F
and Shore EM: Elevated BMP and mechanical signaling through
YAP1/RhoA poises FOP mesenchymal progenitors for osteogenesis. J
Bone Miner Res. May 20–2019.doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3760 (Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Estes BT, Gimble JM and Guilak F:
Mechanical signals as regulators of stem cell fate. Curr Top Dev
Biol. 60:91–126. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Simmons CA, Matlis S, Thornton AJ, Chen S,
Wang CY and Mooney DJ: Cyclic strain enhances matrix mineralization
by adult human mesenchymal stem cells via the extracellular
signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2) signaling pathway. J Biomech.
36:1087–1096. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jagodzinski M, Drescher M, Zeichen J,
Hankemeier S, Krettek C, Bosch U and van Griensven M: Effects of
cyclic longitudinal mechanical strain and dexamethasone on
osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells. Eur
Cell Mater. 7:35–41. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Boccafoschi F, Sabbatini M, Bosetti M and
Cannas M: Overstressed mechanical stretching activates survival and
apoptotic signals in fibroblasts. Cells Tissues Organs.
192:167–176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Parandakh A, Tafazzoli-Shadpour M and
Khani MM: Stepwise morphological changes and cytoskeletal
reorganization of human mesenchymal stem cells treated by
short-time cyclic uniaxial stretch. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim.
53:547–553. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kajiya H, Katsumata Y, Sasaki M, Tsutsumi
T, Kawaguchi M and Fukushima T: Photothermal stress triggered by
near-infrared-irradiated carbon nanotubes up-regulates osteogenesis
and mineral deposition in tooth-extracted sockets. Int J
Hyperthermia. 31:635–642. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Friedenstein AJ: Precursor cells of
mechanocytes. Int Rev Cytol. 47:327–359. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Han I, Kwon BS, Park HK and Kim KS:
Differentiation potential of mesenchymal stem cells is related to
their intrinsic mechanical properties. Int Neurourol J. 21 (Suppl
1):S24–S31. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huang J, Deng F, Wang L, Xiang XR, Zhou
WW, Hu N and Xu L: Hypoxia induces osteogenesis-related activities
and expression of core binding factor alpha1 in mesenchymal stem
cells. Tohoku J Exp Med. 224:7–12. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Balamurugan K: HIF-1 at the crossroads of
hypoxia, inflammation, and cancer. Int J Cancer. 138:1058–1066.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shah YM: The role of hypoxia in intestinal
inflammation. Mol Cell Pediatr. 3:12016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhu L and Zhao Q: Hypoxia-inducible factor
1a participates in hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition via response gene to complement 32. Exp Ther Med.
14:1825–1831. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
De Luna N, Suárez-Calvet X, Lleixà C,
Diaz-Manera J, Olivé M, Illa I and Gallardo E: Hypoxia triggers
IFN-I production in muscle: Implications in dermatomyositis. Sci
Rep. 7:85952017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Moirangthem RD, Singh S, Adsul A,
Jalnapurkar S, Limaye L and Kale VP: Hypoxic niche-mediated
regeneration of hematopoiesis in the engraftment window is
dominantly affected by oxygen tension in the milieu. Stem Cells
Dev. 24:2423–2436. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jiang Y, Wang Y and Tang G: Cyclic tensile
strain promotes the osteogenic differentiation of a bone marrow
stromal cell and vascular endothelial cell co-culture system. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 607:37–43. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hsu SH, Chen CT and Wei YH: Inhibitory
effects of hypoxia on metabolic switch and osteogenic
differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells.
31:2779–2788. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wei F, Yang S, Xu H, Guo Q, Li Q, Hu L,
Liu D and Wang C: Expression and function of hypoxia inducible
factor-1α and vascular endothelial growth factor in pulp tissue of
teeth under orthodontic movement. Mediators Inflamm.
2015:2157612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang Y, Wan C, Gilbert SR and Clemens TL:
Oxygen sensing and osteogenesis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1117:1–11. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wan C, Shao J, Gilbert SR, Riddle RC, Long
F, Johnson RS, Schipani E and Clemens TL: Role of HIF-1alpha in
skeletal development. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1192:322–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Menon A, Creo P, Piccoli M, Bergante S,
Conforti E, Banfi G, Randelli P and Anastasia L: Chemical
activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor reversibly reduces
tendon stem cell proliferation, inhibits their differentiation, and
maintains cell undifferentiation. Stem Cells Int. 2018:94680852018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lampert FM, Kütscher C, Stark GB and
Finkenzeller G: Overexpression of Hif-1a in mesenchymal stem cells
affects cell-autonomous angiogenic and osteogenic parameters. J
Cell Biochem. 117:760–768. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yang DC, Yang MH, Tsai CC, Huang TF, Chen
YH and Hung SC: Hypoxia inhibits osteogenesis in human mesenchymal
stem cells through direct regulation of RUNX2 by TWIST. PLoS One.
6:e239652011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wagegg M, Gaber T, Lohanatha FL, Hahne M,
Strehl C, Fangradt M, Tran CL, Schönbeck K, Hoff P, Ode A, et al:
Hypoxia promotes osteogenesis but suppresses adipogenesis of human
mesenchymal stromal cells in a hypoxia-inducible factor-1 dependent
manner. PLoS One. 7:e464832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen X, Gu S, Chen BF, Shen WL, Yin Z, Xu
GW, Hu JJ, Zhu T, Li G, Wan C, et al: Nanoparticle delivery of
stable miR-199a-5p agomir improves the osteogenesis of human
mesenchymal stem cells via the HIF1a pathway. Biomaterials.
53:239–250. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|