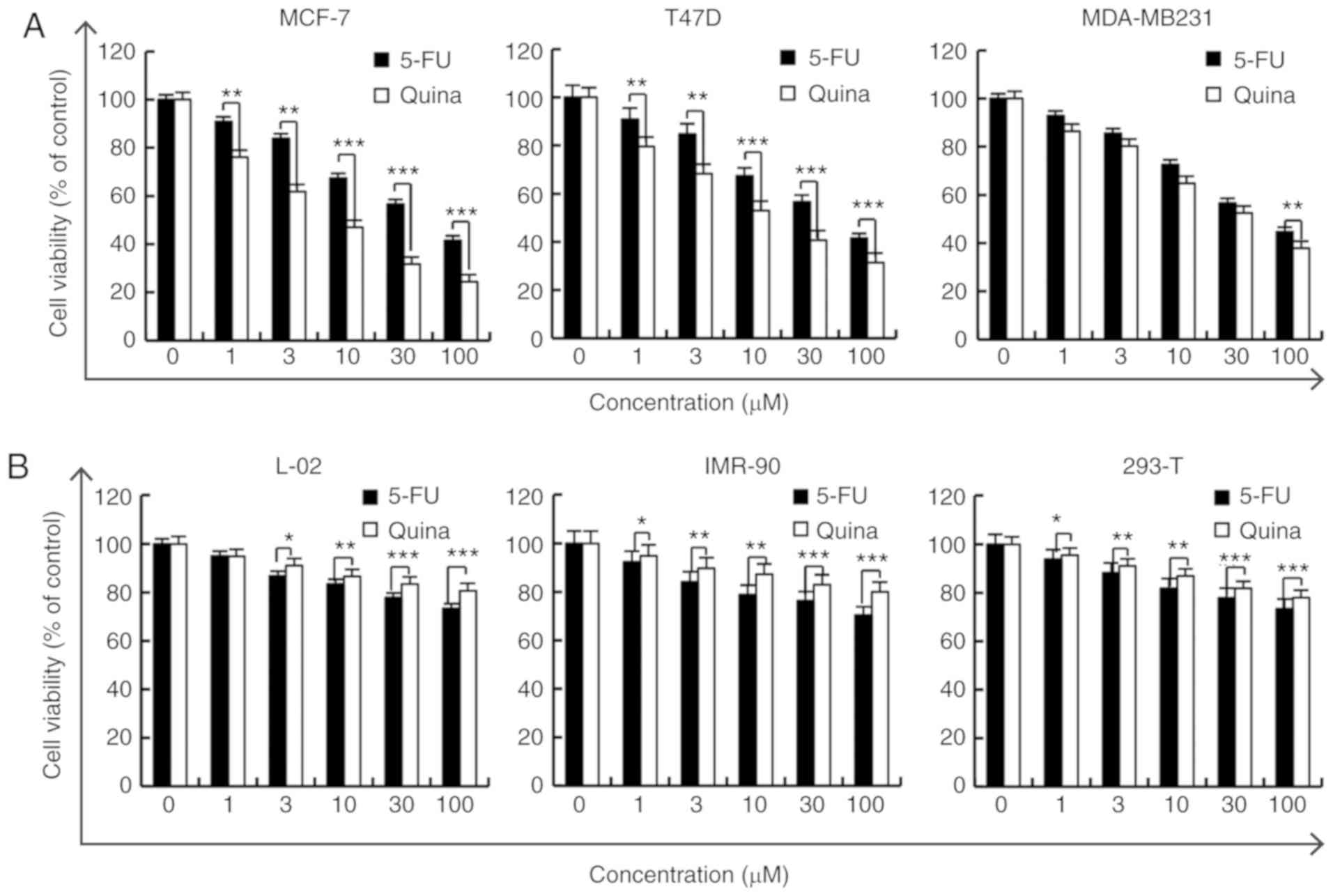
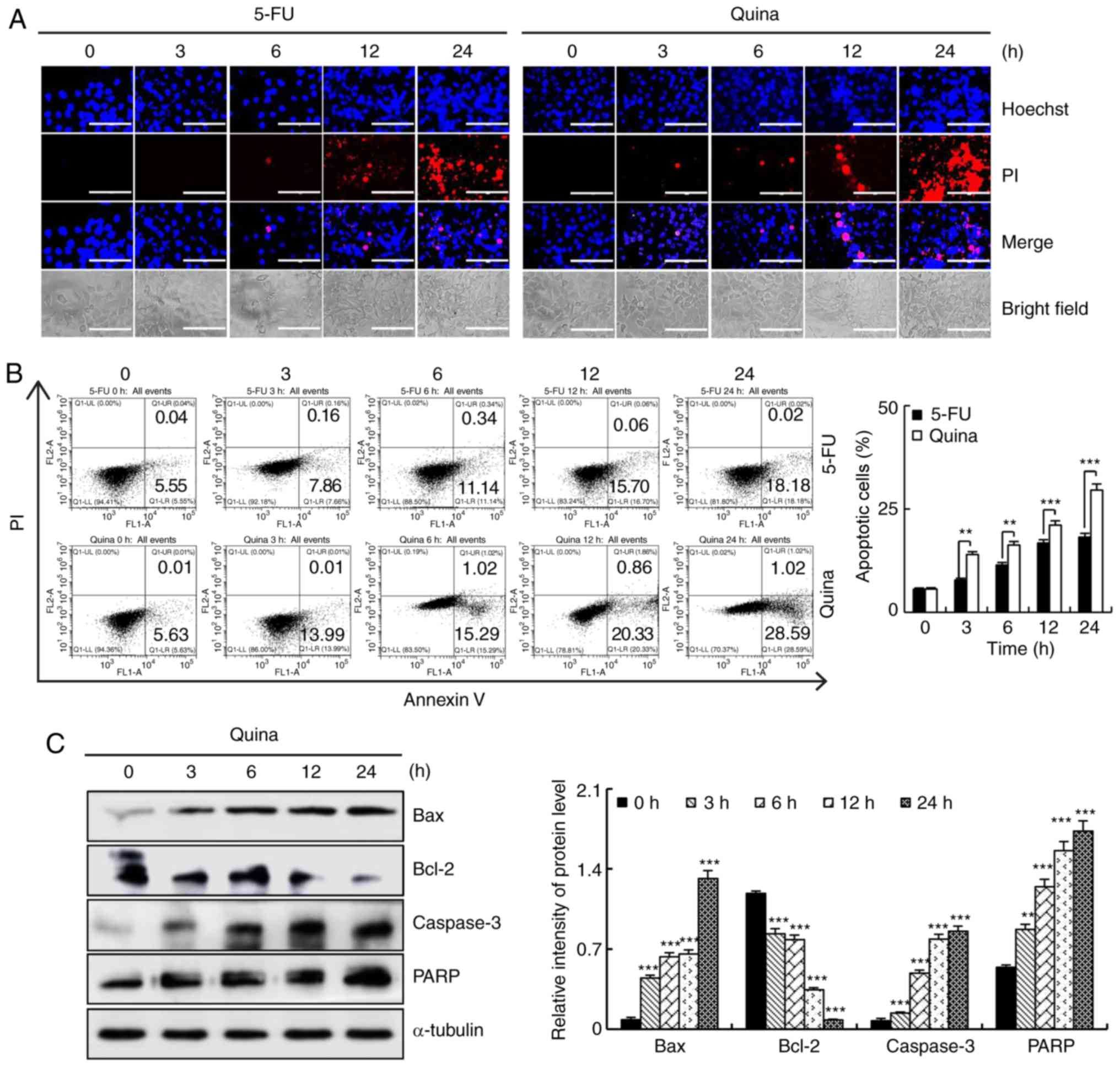
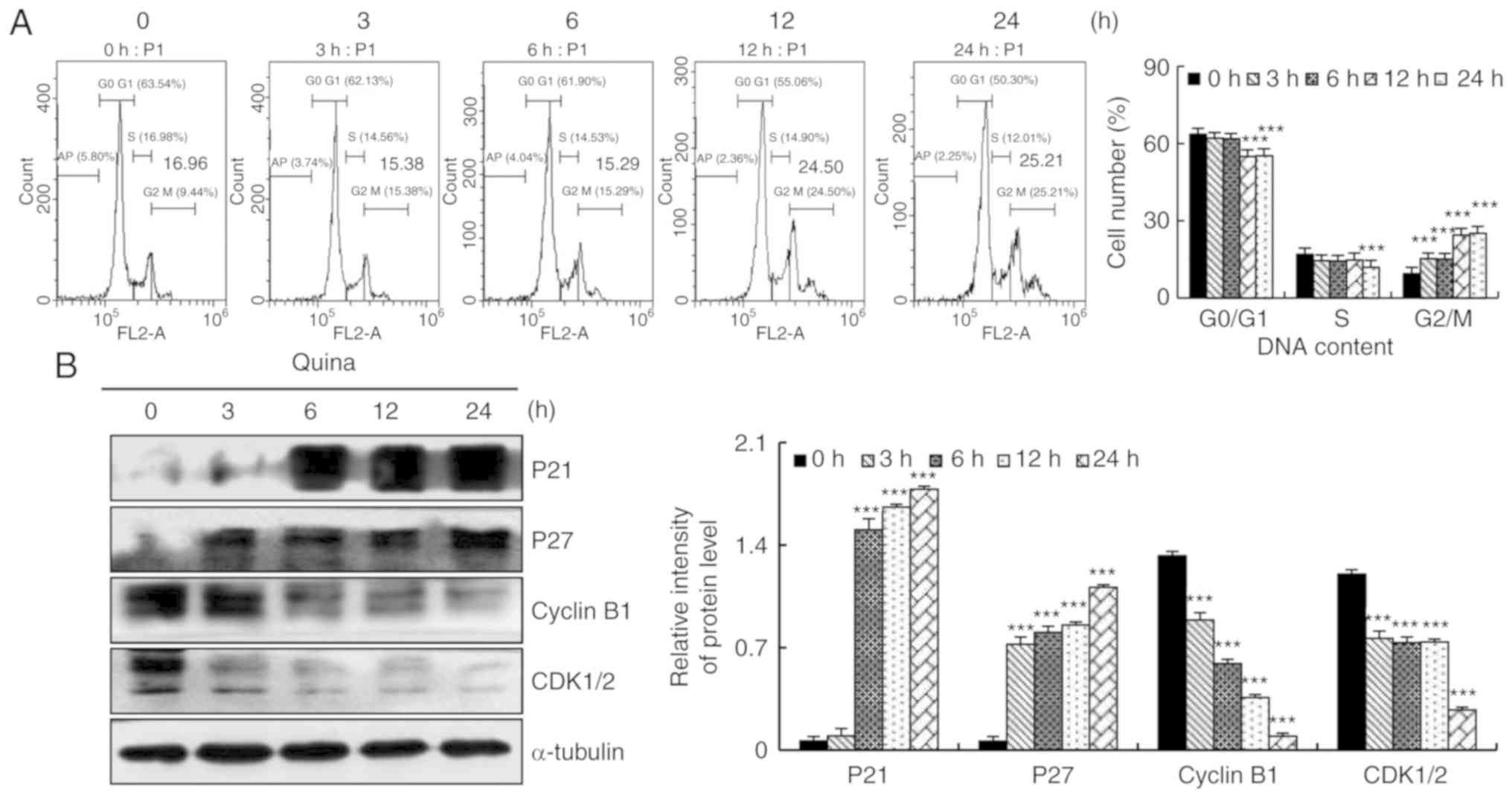
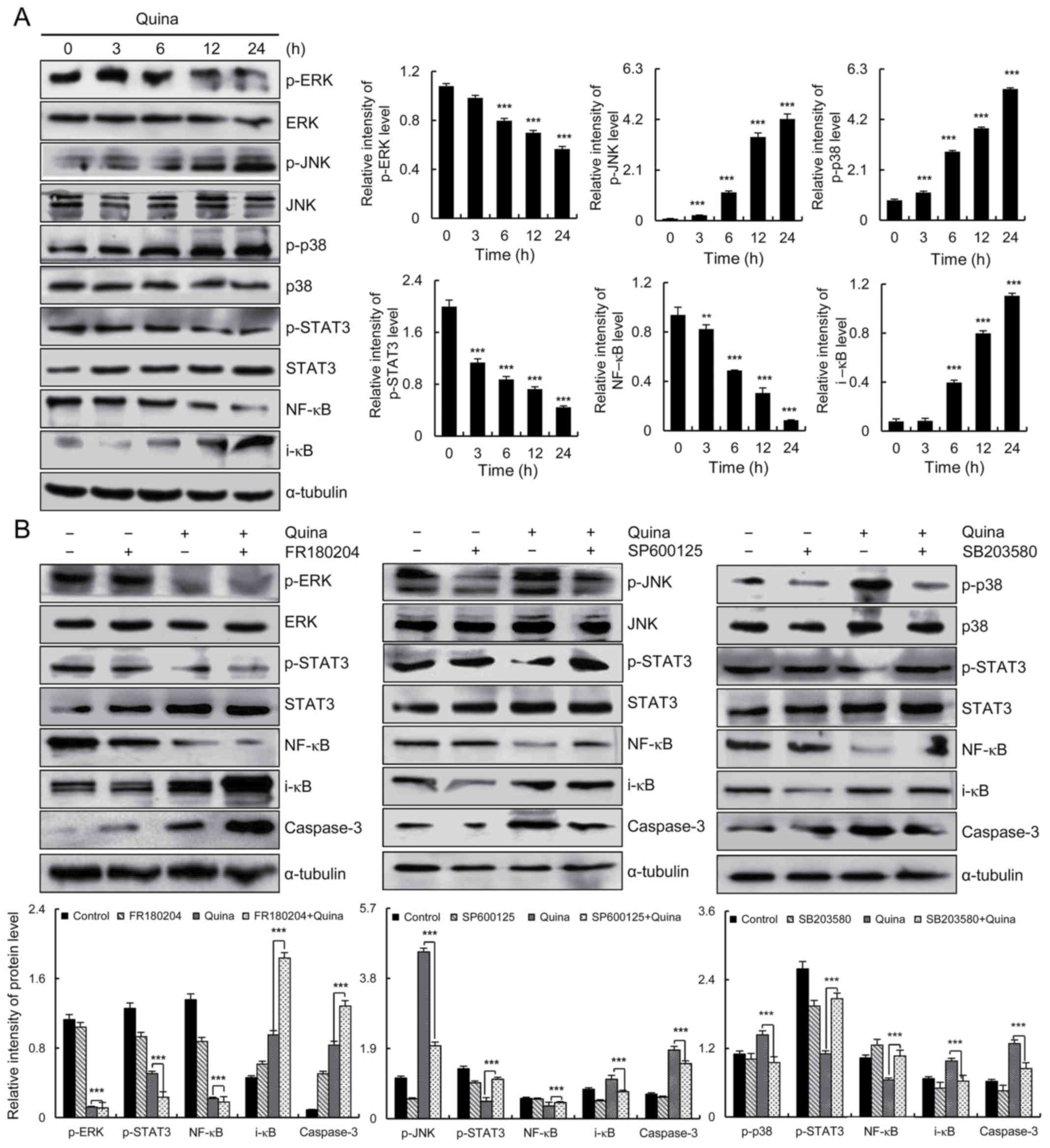
|
1
|
Elzawawy A: Breast cancer systemic
therapy: The need for more economically sustainable scientific
strategies in the world. Breast Care (Base). 3:434–438. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Mccarron P and Parkin DM: The
changing global patterns of female breast cancer incidence and
mortality. Breast Cancer Res. 6:229–239. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Van Agthoven T, Sieuwerts AM, Meijer D,
Meijer-van Gelder ME, van Agthoven TL, Sarwari R, Sleijfer S,
Foekens JA and Dorssers LC: Selective recruitment of breast cancer
anti-estrogen resistance genes and relevance for breast cancer
progression and tamoxifen therapy response. Endocr Relat Cancer.
17:215–230. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Feiten S, Dünnebacke J, Heymanns J,
Köppler H, Thomalla J, Van Roye C, Wey D and Weide R: Breast cancer
morbidity: Questionnaire survey of patients on the long term
effects of disease and adjuvant therapy. Dtsch Arztebl Int.
111:537–544. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Van Cutsem E, Moiseyenko VM, Tjulandin S,
Majlis A, Constenla M, Boni C, Rodrigues A, Fodor M, Chao Y, Voznyi
E, et al: Phase III study of docetaxel and cisplatin plus
fluorouracil compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil as first-line
therapy for advanced gastric cancer: A report of the V325 study
group. J Clin Oncol. 24:4991–4997. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fesik SW: Promoting apoptosis as a
strategy for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:876–885.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu I and Cheung WY: Comparison of 5-FU
versus capecitabine in combination with mitomycin or cisplatin in
the treatment of anal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 35:680. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Haagenson KK and Wu GS: Mitogen activated
protein kinase phosphatases and cancer. Cancer Biol Ther.
9:337–340. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shao Y and Aplin AE: ERK2 phosphorylation
of serine 77 regulates Bmf pro-apoptotic activity. Cell Death Dis.
3:e2532012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Inoue J, Gohda J, Akiyama T and Semba K:
NF-kappaB activation in development and progression of cancer.
Cancer Sci. 98:268–274. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tang X, Soch E, Shishodia S, Diane LJ,
Jack L, Waun KH, Bharat A and Ignacio IW: Immunohistochemical
analysis indicates that nuclear factor-κB (NF-alysis frequently
activated in lung cancer. Cancer Res. 46:1–5. 2005.
|
|
12
|
Grivennikov SI and Karin M: Dangerous
liaisons: STAT3 and NF-kappaB collaboration and crosstalk in
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 21:11–19. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang J, Wang X, Vikash V, Ye Q, Wu D, Liu
Y and Dong W: ROS and ROS-mediated cellular signaling. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2016:43509652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jacquemin G, Margiotta D, Kasahara A,
Bassoy EY, Walch M, Thiery J, Lieberman J and Martinvalet D:
Granzyme B-induced mitochondrial ROS are required for apoptosis.
Cell Death Differ. 22:862–874. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Redzadutordoir M and Averillbates DA:
Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen
species. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:2977–2992. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wen L, Lu X, Wang R, Jin X, Hu L and You
C: Pyrroloquinoline quinone induces chondrosarcoma cell apoptosis
by increasing intracellular reactive oxygen species. Mol Med Rep.
17:7184–7190. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bu HQ, Cai K, Shen F, Bao XD, Xu Y, Yu F,
Pan HQ, Chen CH, Du ZJ and Cui JH: Induction of apoptosis by
capsaicin in hepatocellular cancer cell line SMMC-7721 is mediated
through ROS generation and activation of JNK and p38 MAPK pathways.
Neoplasma. 62:582–591. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vogel J, Bumgarner J, Espinosa N and Young
W: An evaluation of the use of resistivity counters in the touchet
river in washington and the imnaha river in oregon. Am Fish Soc.
33:6953–6960. 2011.
|
|
19
|
Piska K, Koczurkiewicz P, Bucki A,
Wójcik-Pszczoła K, Kołaczkowski M and Pękala E: Metabolic carbonyl
reduction of anthracyclines-role in cardiotoxicity and cancer
resistance. Reducing enzymes as putative targets for novel
cardioprotective and chemosensitizing agents. Invest New Drugs.
35:375–385. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cozza G, Venerando A, Sarno S and Pinna
LA: The selectivity of CK2 inhibitor quinalizarin: A reevaluation.
Biomed Res Int. 2015:1–9. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Meng LQ, Liu C, Luo YH, Piao XJ, Wang Y,
Zhang Y, Wang JR, Wang H, Xu WT, Liu Y, et al: Quinalizarin exerts
an anti-tumour effect on lung cancer A549 cells by modulating the
Akt, MAPK, STAT3 and p53 signaling pathways. Mol Med Rep.
17:2626–2634. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou Y, Li K, Zhang S, Li Q, Li Z, Zhou F,
Dong X, Liu L, Wu G and Meng R: Quinalizarin, a specific CK2
inhibitor, reduces cell viability and suppresses migration and
accelerates apoptosis in different human lung cancer cell lines.
Indian J Cancer. 52 (Suppl 2):e119–e124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Malik EM and Müller CE: Anthraquinones as
pharmacological tools and drugs. Med Res Rev. 36:705–748. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lordan S, O'Neill C and O'Brien NM:
Effects of apigenin, lycopene and astaxanthin on 7
beta-hydroxycholesterol-induced apoptosis and Akt phosphorylation
in U937 cells. Br J Nutr. 100:287–296. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen YY, Chiang SY, Lin JG, Ma YS, Liao
CL, Weng SW, Lai TY and Chung JG: Emodin, aloe-emodin and rhein
inhibit migration and invasion in human tongue cancer SCC-4 cells
through the inhibition of gene expression of matrix
metalloproteinase-9. Int J Oncol. 36:1113–1120. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang YY, Li ZC, Zhu JK, Yang ZY, Wang QJ,
He PG, Hang YZ, Pin JW, Yu GH and Fang Z: Simultaneous
determination of flavonoids and anthraquinones in chrysanthemum by
capillary electrophoresis with amperometry detection. Chin Chem
Lett. 21:1231–1234. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zong JR, Chao ZM, Liu ZL and Wang J:
Review about structure-function relationships of anthraquinone
derivatives from Radix et Rhizoma Rhei. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.
33:2424–2427. 2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Martin KR: Using nutrigenomics to evaluate
apoptosis as a preemptive target in cancer prevention. Curr Cancer
Drug Targets. 7:438–446. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zheng JH, Viacava Follis A, Kriwacki RW
and Moldoveanu T: Discoveries and controversies in BCL-2
proteins-mediated apoptosis. FEBS J. 283:2690–2700. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Alenzi FQ, Lotfy M and Wyse R: Swords of
cell death: Caspase activation and regulation. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 11:271–280. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zu C, Zhang M, Xue H, Cai X, Zhao L, He A,
Qin G, Yang C and Zheng X: Emodin induces apoptosis of human breast
cancer cells by modulating the expression of apoptosis-related
genes. Oncol Lett. 10:2919–2924. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Antonsson A and Persson JL: Induction of
apoptosis by staurosporine involves the inhibition of expression of
the major cell cycle proteins at the G(2)/m checkpoint accompanied
by alterations in Erk and Akt kinase activities. Anticancer Res.
29:2893–2898. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gao SY, Li J, Qu XY, Zhu N and Ji YB:
Downregulation of Cdk1 and cyclinB1 expression contributes to
oridonin-induced cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and growth
inhibition in SGC-7901 gastric cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:6437–6441. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nasheuer HP, Smith R, Bauerschmidt C,
Grosse F and Weisshart K: Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication:
Regulation and mechanisms. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol.
72:41–70. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Santamaria D and Ortega S: Cyclins and
CDKS in development and cancer: Lessons from genetically modified
mice. Front Biosci. 11:1164–1188. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang Z, Leonard SS, Huang C, Castranova V
and Shi X: Role of reactive oxygen species and MAPKs in
vanadate-induced G(2)/M phase arrest. Free Radic Biol Med.
34:1333–1342. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang XH, Liu BR, Qu B, Xing H, Gao SL, Yin
JM, Wang XF and Cheng YQ: Silencing STAT3 may inhibit cell growth
through regulating signaling pathway, telomerase, cell cycle,
apoptosis and angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma: Potential
uses for gene therapy. Neoplasma. 58:158–171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Clotet J, Vendrell J and Escoté X: Control
of the cell cycle progression by the MAPK Hog1. MAP Kinase.
2:e32013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chiu TH, Lai WW, Hsia TC, Yang JS, Lai TY,
Wu PP, Ma CY, Yeh CC, Ho CC, Lu HF, et al: Aloe-emodin induces cell
death through S-phase arrest and caspase-dependent pathways in
human tongue squamous cancer SCC-4 cells. Anticancer Res.
29:4503–4511. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Su Y, Li G, Zhang X, Gu J, Zhang C, Tian Z
and Zhang J: JSI-124 inhibits glioblastoma multiforme cell
proliferation through G(2)/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
augment. Cancer Biol Ther. 7:1243–1249. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Guo Y, Lin D, Zhang M, Zhang X, Li Y, Yang
R, Lu Y, Jin X, Yang M, Wang M, et al: CLDN6-induced apoptosis via
regulating ASK1-p38/JNK signaling in breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Int
J Oncol. 48:2435–2444. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cook SJ, Stuart K, Gilley R and Sale MJ:
Control of cell death and mitochondrial fission by ERK1/2 MAP
Kinase signaling. FEBS J. 284:4177–4195. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tang N, Chang J, Lu HC, Zhuang Z, Cheng
HL, Shi JX and Rao J: Rhein induces apoptosis and autophagy in
human and rat glioma cells and mediates cell differentiation by ERK
inhibition. Microb Pathog. 113:168–175. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Degoricija M, Situm M, Korać J, Miljković
A, Matić K, Paradžik M, Marinović Terzić I, Jerončić A, Tomić S and
Terzić J: High NF-κB and STAT3 activity in human urothelial
carcinoma: A pilot study. World J Urol. 32:1469–1475. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Seo HS, Choi HS, Kim SR, Choi YK, Woo SM,
Shin I, Woo JK, Park SY, Shin YC and Ko SG: Apigenin induces
apoptosis via extrinsic pathway, inducing p53 and inhibiting STAT3
and NFκB signaling in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Mol
Cell Biochem. 366:319–334. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Morier-Teissier E: Effect of a
copper-chelating peptide on the anticancer activity of
anthraquinones. J Pharm Belg. 45:347–354. 1990.(In French).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Morier-Teissier E, Bernier JL, Lohez M,
Catteau JP and Hénichart JP: Free radical production and DNA
cleavage by copper chelating peptide-anthraquinones. Anticancer
Drug Des. 5:291–305. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cozza G, Mazzorana M, Papinutto E, Bain J,
Elliott M, di Maira G, Gianoncelli A, Pagano MA, Sarno S, Ruzzene
M, et al: Quinalizarin as a potent, selective and cell-permeable
inhibitor of protein kinase CK2. Biochem J. 421:387–395. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Prosperini A, Juan-García A, Font G and
Ruiz MJ: Beauvericin-induced cytotoxicity via, ROS production and
mitochondrial damage in Caco-2 cells. Toxicol Lett. 222:204–211.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Conway GE, Casey A, Milosavljevic V, Liu
Y, Howe O, Cullen PJ and Curtin JF: Non-thermal atmospheric plasma
induces ROS-independent cell death in U373MG glioma cells and
augments the cytotoxicity of temozolomide. Br J Cancer.
114:435–443. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang CH, Wu SB, Wu YT and Wei YH:
Oxidative stress response elicited by mitochondrial dysfunction:
Implication in the pathophysiology of aging. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 238:450–460. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Loor G, Kondapalli J, Schriewer JM,
Chandel NS, Vanden Hoek TL and Schumacker PT: Menadione triggers
cell death through ROS-dependent mechanisms involving PARP
activation without requiring apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med.
49:1925–1936. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lo YL and Wang W: Formononetin potentiates
epirubicin-induced apoptosis via ROS production in HeLa cells in
vitro. Chem Biol Interact. 205:188–197. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kim KY, Park KI, Kim SH, Yu SN, Lee D, Kim
YW, Noh KT, Ma JY, Seo YK and Ahn SC: Salinomycin induces reactive
oxygen species and apoptosis in aggressive breast cancer cells as
mediated with regulation of autophagy. Anticancer Res.
37:1747–1758. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
He G and Karin M: NF-κB and STAT3-key
players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res. 21:159–168.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang Y, Luo Q, He X, Wei H, Wang T, Shao J
and Jiang X: Emodin induces apoptosis of colon cancer cells via
induction of autophagy in a ROS-Dependent manner. Oncol Res.
26:889–899. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Su YT, Chang HL, Shyue SK and Hsu SL:
Emodin induces apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cells through
a reactive oxygen species-dependent mitochondrial signaling
pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 70:229–241. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Eruslanov E and Kusmartsev S:
Identification of ROS using oxidized DCFDA and flow-cytometry.
Methods Mol Biol. 594:57–72. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|