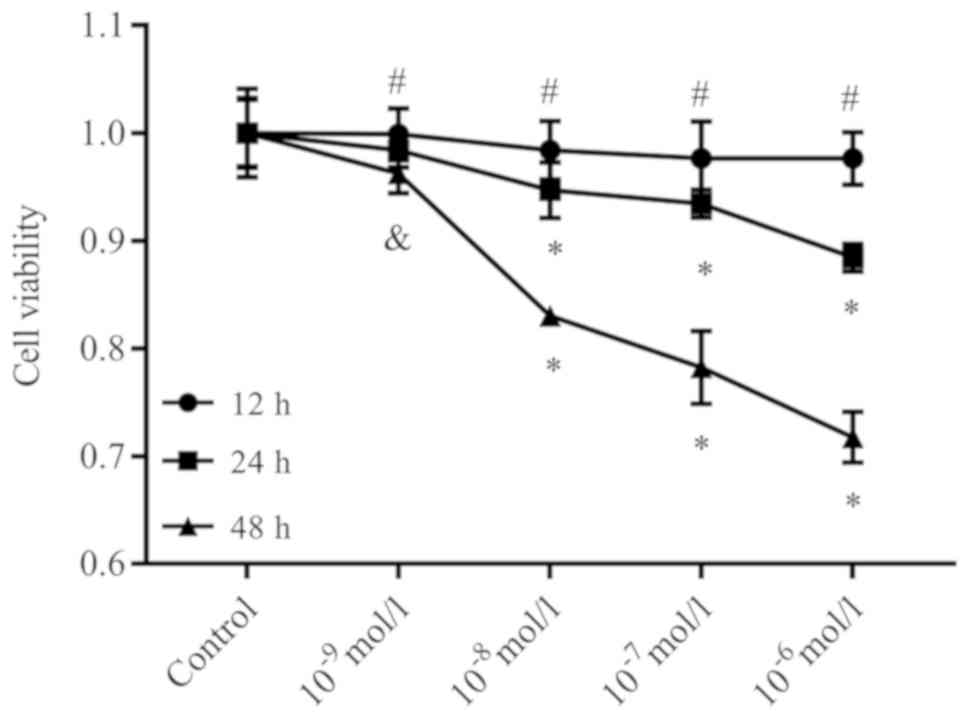
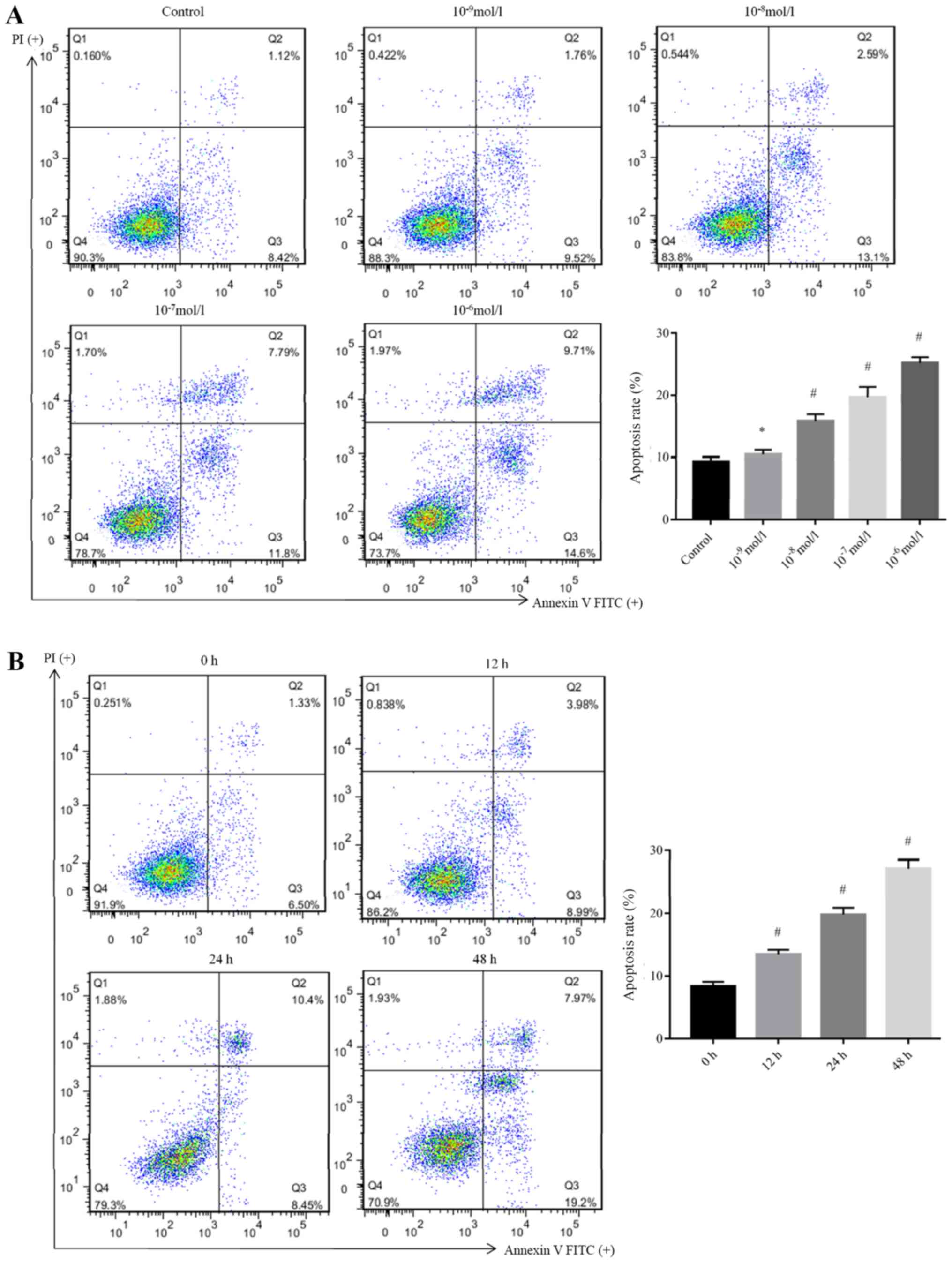
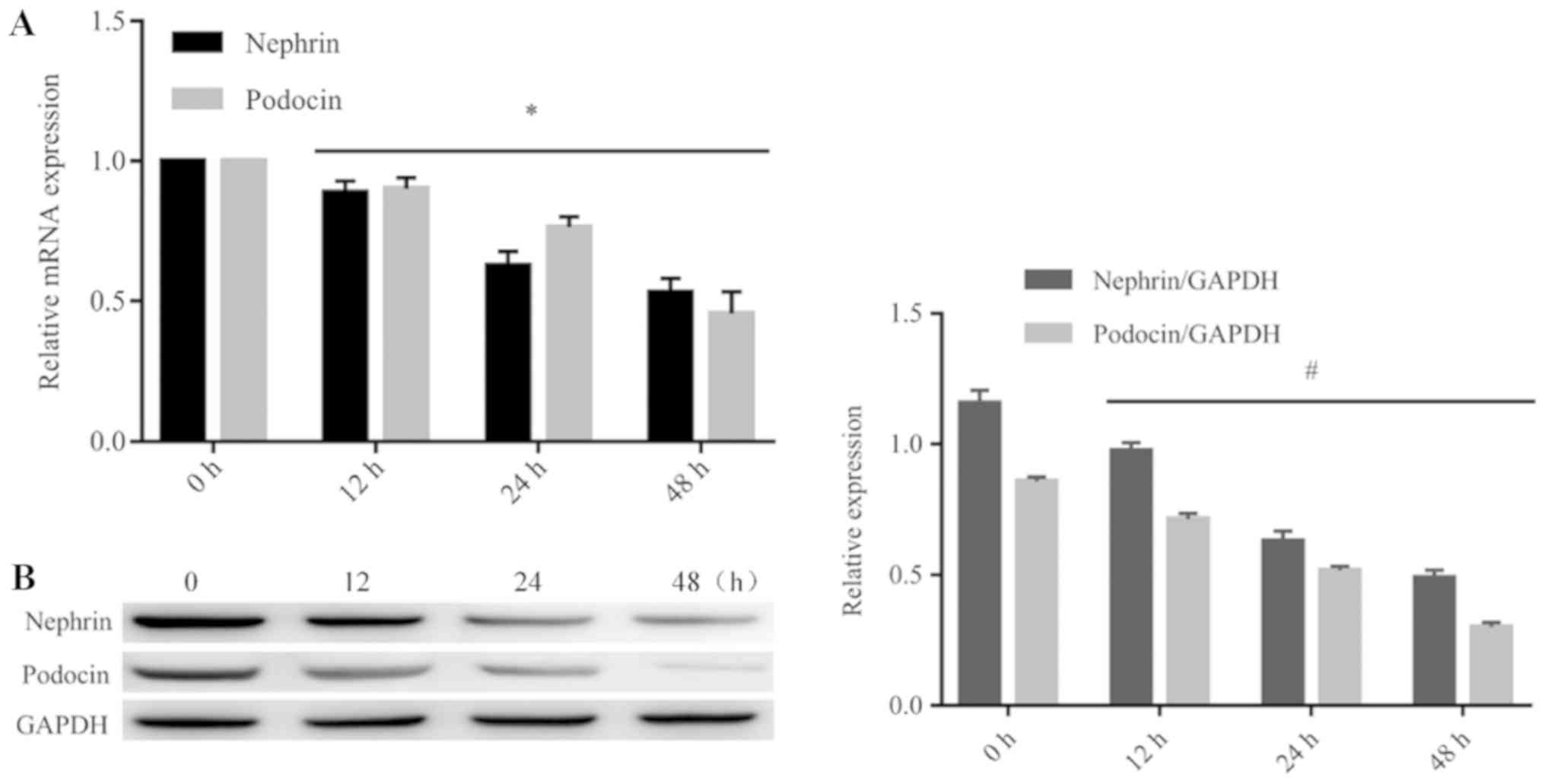
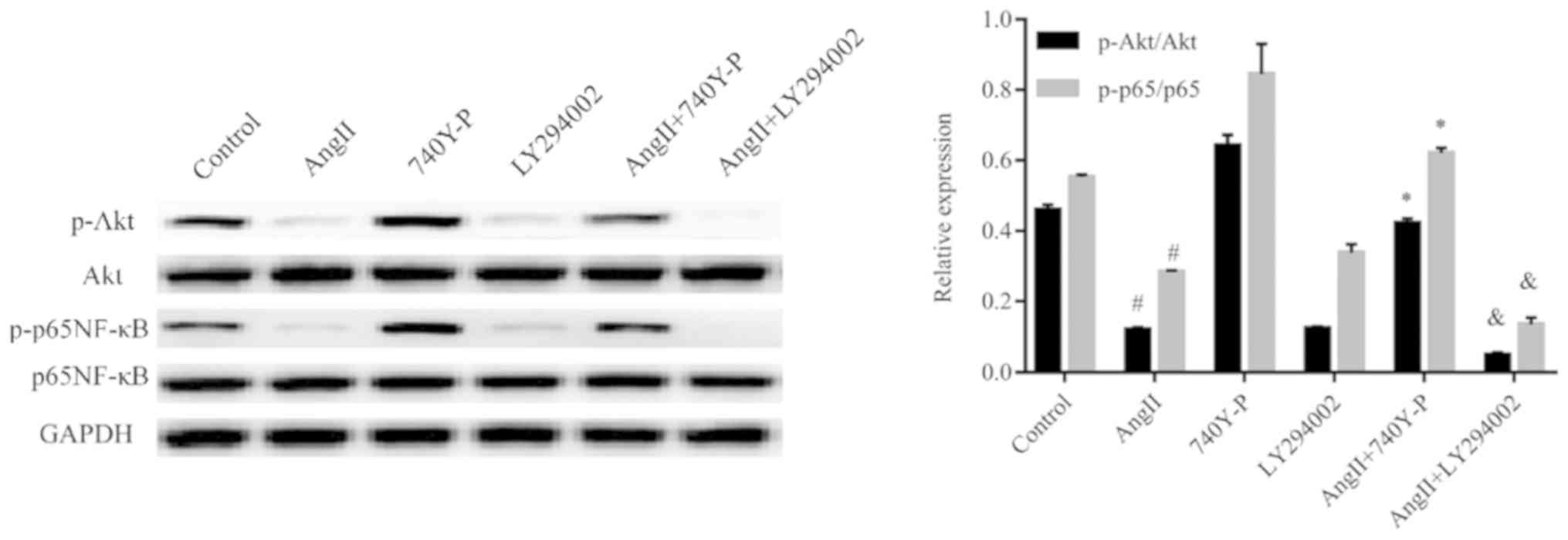
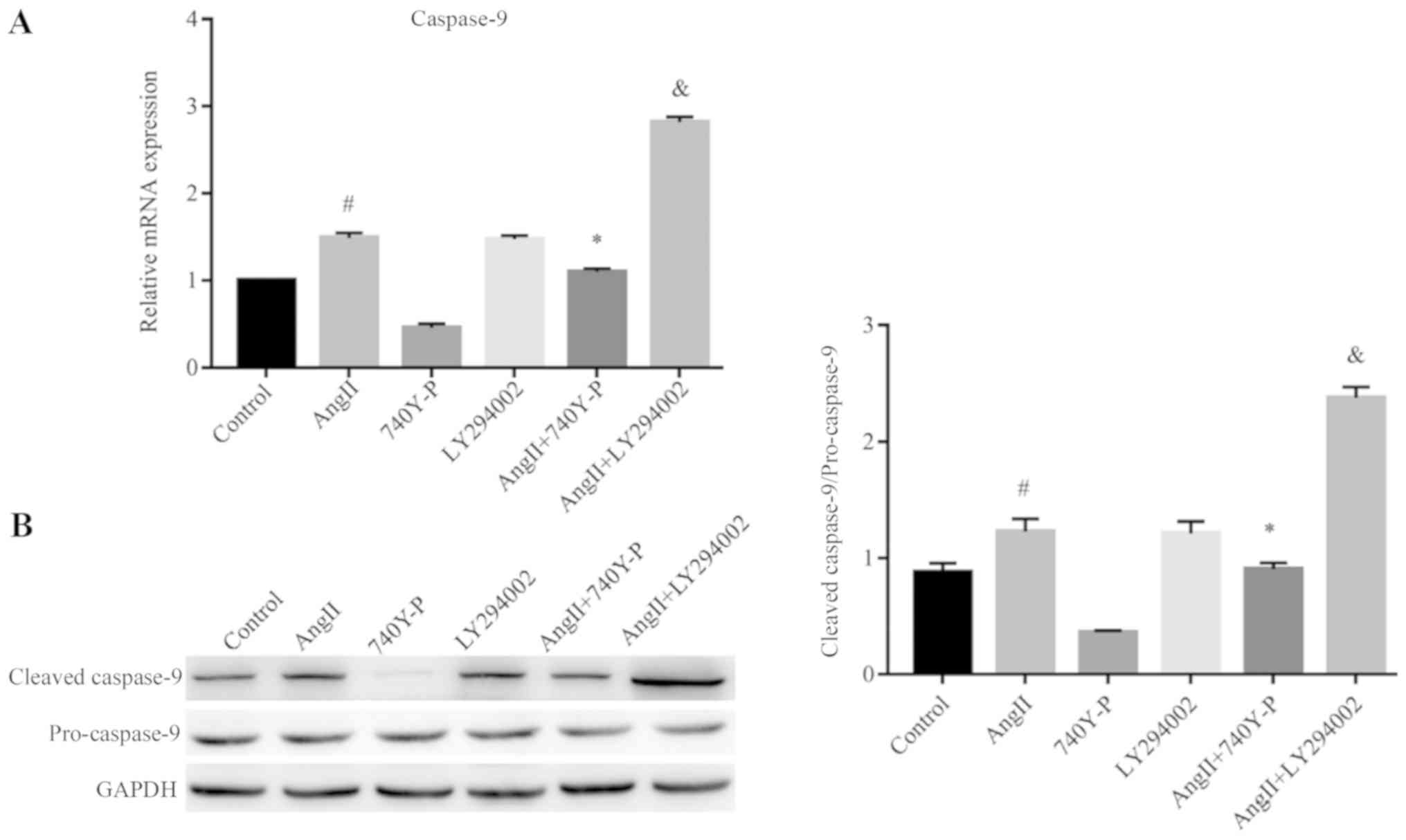
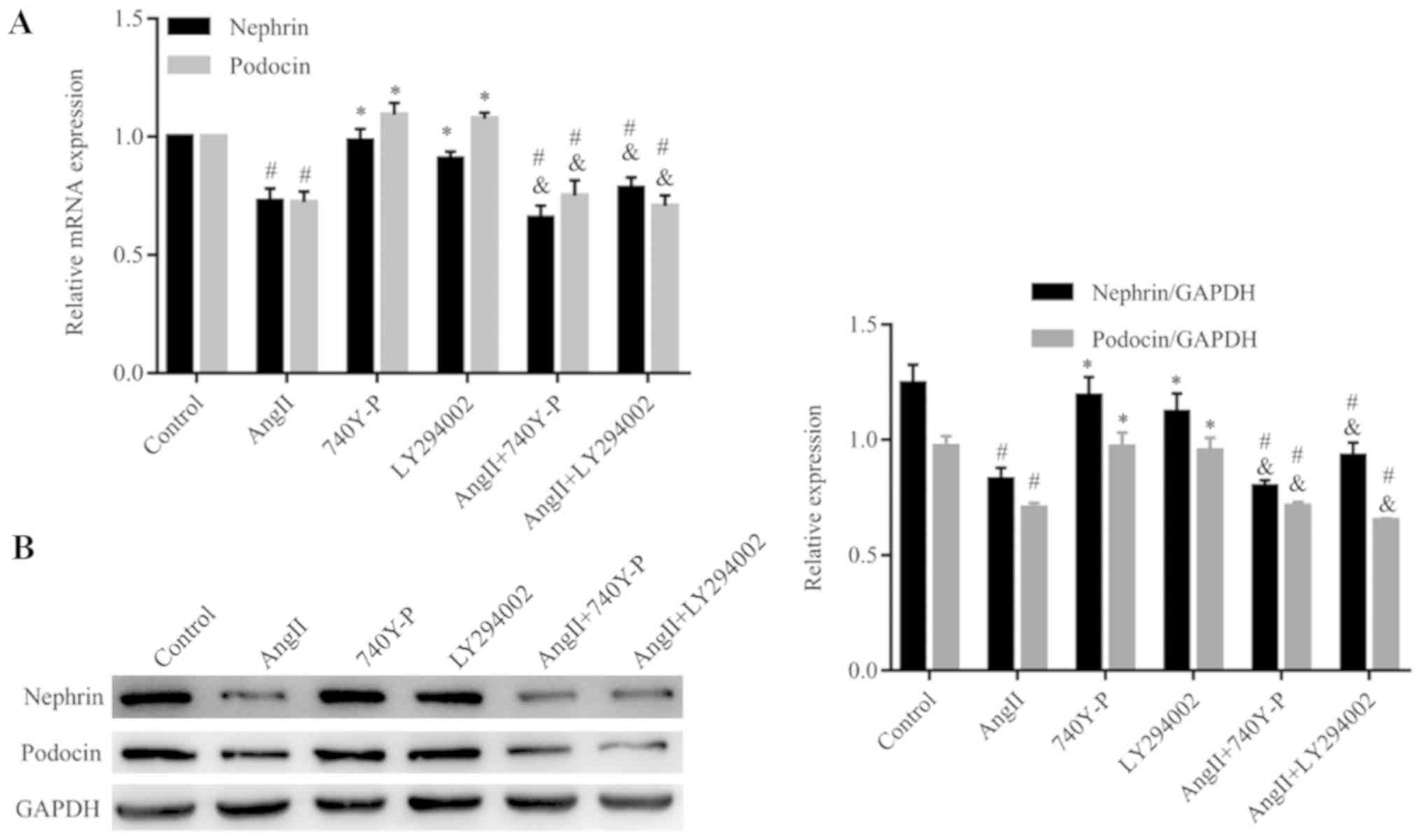
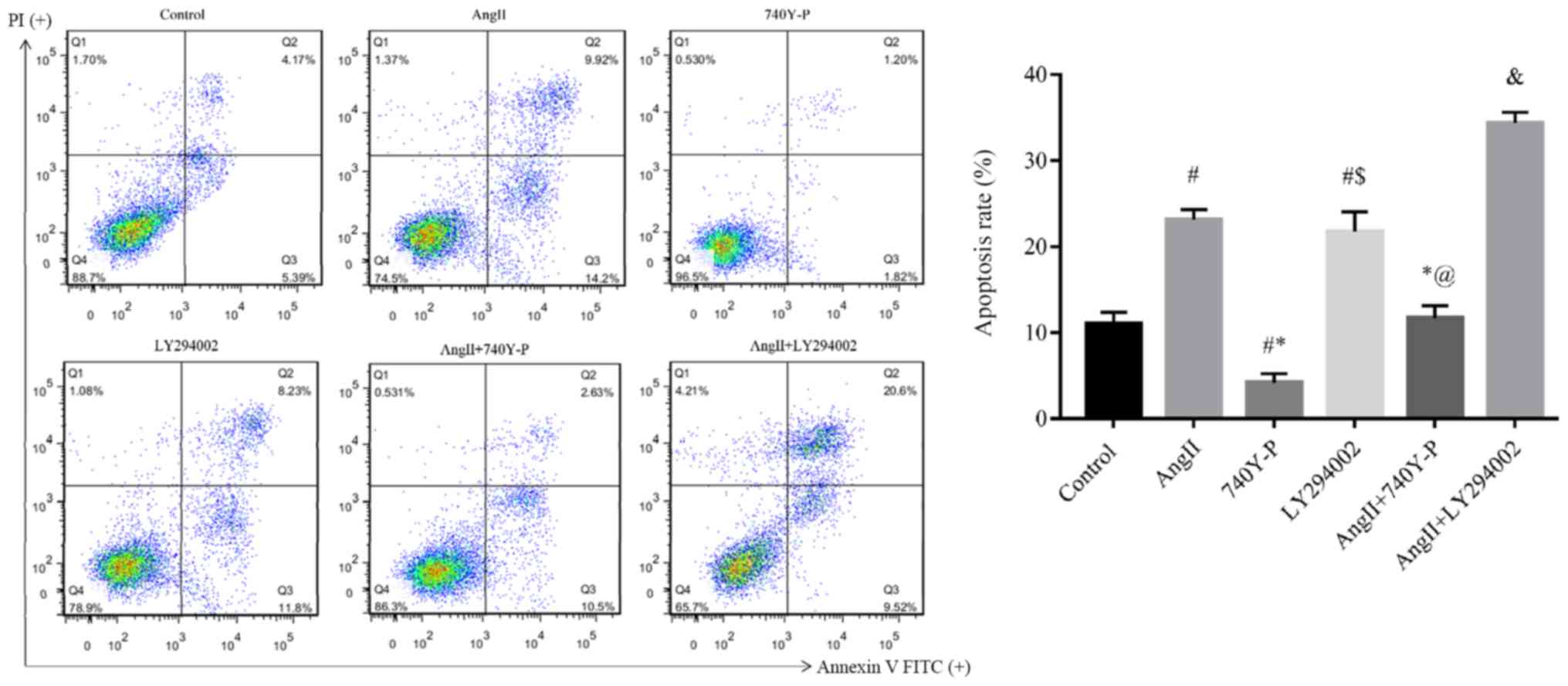
|
1
|
Nath JD and Kashem A: Etiology and
frequency of hospital admissions in maintenance hemodialysis
patients in chronic kidney disease. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl.
30:508–512. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vaidya SR and Aeddula NR: Chronic Renal
FailureStatPearls. StatPearls Publishing LLC.; Treasure Island, FL:
2019
|
|
3
|
Coresh J, Astor BC, Greene T, Eknoyan G
and Levey AS: Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and decreased
kidney function in the adult US population: Third National Health
and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Kidney Dis. 41:1–12. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Webster AC, Nagler EV, Morton RL and
Masson P: Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 389:1238–1252. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Reiser J and Altintas MM: Podocytes.
F1000Res. 5:F10002016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vivarelli M, Massella L, Ruggiero B and
Emma F: Minimal change disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 12:332–345.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lal MA and Patrakka J: Understanding
podocyte biology to develop novel kidney therapeutics. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:4092018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Asanuma K: The role of podocyte injury in
chronic kidney disease. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi.
38:26–36. 2015.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Doublier S, Salvidio G, Lupia E,
Ruotsalainen V, Verzola D, Deferrari G and Camussi G: Nephrin
expression is reduced in human diabetic nephropathy: Evidence for a
distinct role for glycated albumin and angiotensin II. Diabetes.
52:1023–1030. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bertuccio CA: Relevance of VEGF and
nephrin expression in glomerular diseases. J Signal Transduct.
2011:7186092011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Verma R, Venkatareddy M, Kalinowski A, Li
T, Kukla J, Mollin A, Cara-Fuentes G, Patel SR and Garg P: Nephrin
is necessary for podocyte recovery following injury in an adult
mature glomerulus. PLoS One. 13:e01980132018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li X, Chuang PY, D'Agati VD, Dai Y, Yacoub
R, Fu J, Xu J, Taku O, Premsrirut PK, Holzman LB and He JC: Nephrin
preserves podocyte viability and glomerular structure and function
in adult kidneys. J Am Soc Nephrol. 26:2361–2377. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Aya K, Tanaka H and Seino Y: Novel
mutation in the nephrin gene of a Japanese patient with congenital
nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type. Kidney Int. 57:401–404.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kestilä M, Lenkkeri U, Männikkö M,
Lamerdin J, McCready P, Putaala H, Ruotsalainen V, Morita T,
Nissinen M, Herva R, et al: Positionally cloned gene for a novel
glomerular protein-nephrin is mutated in congenital nephrotic
syndrome. Mol Cell. 1:575–582. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mollet G, Ratelade J, Boyer O, Muda AO,
Morisset L, Lavin TA, Kitzis D, Dallman MJ, Bugeon L, Hubner N, et
al: Podocin inactivation in mature kidneys causes focal segmental
glomerulosclerosis and nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol.
20:2181–2189. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tabatabaeifar M, Wlodkowski T, Simic I,
Denc H, Mollet G, Weber S, Moyers JJ, Brühl B, Randles MJ, Lennon
R, et al: An inducible mouse model of podocin-mutation-related
nephrotic syndrome. PLoS One. 12:e01865742017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Roselli S, Heidet L, Sich M, Henger A,
Kretzler M, Gubler MC and Antignac C: Early glomerular filtration
defect and severe renal disease in podocin-deficient mice. Mol Cell
Biol. 24:550–560. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lewko B, Maryn A, Latawiec E, Daca A and
Rybczynska A: Angiotensin II modulates podocyte glucose transport.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:4182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Remuzzi G, Benigni A and Remuzzi A:
Mechanisms of progression and regression of renal lesions of
chronic nephropathies and diabetes. J Clin Invest. 116:288–296.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu S: Role of nephrin in podocyte injury
induced by angiotension II. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 36:1–5.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cardoso VG, Gonçalves GL, Costa-Pessoa JM,
Thieme K, Lins BB, Casare FAM, de Ponte MC, Camara NOS and
Oliveira-Souza M: Angiotensin II-induced podocyte apoptosis is
mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress/PKC-δ/p38 MAPK pathway
activation and trough increased Na+/H+
exchanger isoform 1 activity. BMC Nephrol. 19:1792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang L, Ren Z, Yang Q and Ding G: Csk
regulates angiotensin II-induced podocyte apoptosis. Apoptosis.
21:846–855. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jia J, Ding G, Zhu J, Chen C, Liang W,
Franki N and Singhal PC: Angiotensin II infusion induces nephrin
expression changes and podocyte apoptosis. Am J Nephrol.
28:500–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ding G, Reddy K, Kapasi AA, Franki N,
Gibbons N, Kasinath BS and Singhal PC: Angiotensin II induces
apoptosis in rat glomerular epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 283:F173–F180. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen F, Sun Z, Zhu X and Ma Y: Astilbin
inhibits high glucose-induced autophagy and apoptosis through the
PI3K/Akt pathway in human proximal tubular epithelial cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 106:1175–1181. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang Y, Wang B, Guo F, Li Z and Qin G:
Involvement of the TGFβ1-ILK-Akt signaling pathway in the effects
of hesperidin in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Biomed Pharmacother.
105:766–772. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hong J, Wang X, Zhang N, Fu H and Li W:
D-ribose induces nephropathy through RAGE-dependent NF-κB
inflammation. Arch Pharm Res. 41:838–847. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li X, Wang M, Hong H, Luo C, Liu Z and
Yang R: Sophocarpine attenuates murine lupus nephritis via
inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB activation. Immunol Res.
66:521–527. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lin N, Ji Z and Huang C: Smad7 alleviates
glomerular mesangial cell proliferation via the ROS-NF-κB pathway.
Exp Cell Res. 361:210–216. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hu H, Hu S, Xu S, Gao Y, Zeng F and Shui
H: miR-29b regulates Ang II-induced EMT of rat renal tubular
epithelial cells via targeting PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int J
Mol Med. 42:453–460. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mundel P, Reiser J, Zúñiga Mejía Borja A,
Pavenstädt H, Davidson GR, Kriz W and Zeller R: Rearrangements of
the cytoskeleton and cell contacts induce process formation during
differentiation of conditionally immortalized mouse podocyte cell
lines. Exp Cell Res. 236:248–258. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Derossi D, Williams EJ, Green PJ, Dunican
DJ and Doherty P: Stimulation of mitogenesis by a cell-permeable PI
3-kinase binding peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 251:148–152.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ha TS, Park HY, Seong SB and Ahn HY:
Angiotensin II induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in podocyte,
which would be further augmented by PI3-kinase inhibition. Clin
Hypertens. 21:132015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Martin CE and Jones N: Nephrin signaling
in the podocyte: An updated view of signal regulation at the slit
diaphragm and beyond. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:3022018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Reiser J and Sever S: Podocyte biology and
pathogenesis of kidney disease. Annu Rev Med. 64:357–366. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gong JH, Dong JY, Xie T and Lu SL: The
influence of AGEs environment on proliferation, apoptosis,
homeostasis, and endothelial cell differentiation of human adipose
stem cells. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 16:94–103. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ren Z, Liang W, Chen C, Yang H, Singhal PC
and Ding G: Angiotensin II induces nephrin dephosphorylation and
podocyte injury: Role of caveolin-1. Cell Signal. 24:443–450. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim S and Iwao H: Molecular and cellular
mechanisms of angiotensin II-mediated cardiovascular and renal
diseases. Pharmacol Rev. 52:11–34. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mezzano SA, Ruiz-Ortega M and Egido J:
Angiotensin II and renal fibrosis. Hypertension. 38:635–638. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao M, Bai M, Ding G, Zhang Y, Huang S,
Jia Z and Zhang A: Angiotensin ii stimulates the nlrp3 inflammasome
to induce podocyte injury and mitochondrial dysfunction. Kidney Dis
(Basel). 4:83–94. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang Y, Yang Q, Yang J, Ma Y and Ding G:
Angiotensin II induces cholesterol accumulation and injury in
podocytes. Sci Rep. 7:106722017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang ZZ, Tschopp O, Baudry A, Dummler B,
Hynx D and Hemmings BA: Physiological functions of protein kinase
B/Akt. Biochem Soc Trans. 32:350–354. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lin X, Jiang C, Luo Z and Qu S: Protective
effect of erythropoietin on renal injury induced in rats by four
weeks of exhaustive exercise. BMC Nephrol. 14:1302013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang Y, Chen X, Yuan L, Zhang Y, Wu J,
Guo N, Chen X and Liu J: Down-regulation of IRAK1 attenuates
podocyte apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy through PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 506:529–535. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yu-Shengyou and Li Y: Dexamethasone
inhibits podocyte apoptosis by stabilizing the PI3K/Akt signal
pathway. BioMed Res Int. 2013:3269862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ren Q and You Yu S: CD2-associated protein
participates in podocyte apoptosis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 36:288–291. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang XM, Yao M, Liu SX, Hao J, Liu QJ and
Gao F: Interplay between the Notch and PI3K/Akt pathways in high
glucose-induced podocyte apoptosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
306:F205–F213. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fukuda A, Wickman LT, Venkatareddy MP,
Sato Y, Chowdhury MA, Wang SQ, Shedden KA, Dysko RC, Wiggins JE and
Wiggins RC: Angiotensin II-dependent persistent podocyte loss from
destabilized glomeruli causes progression of end stage kidney
disease. Kidney Int. 81:40–55. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xu P, Wang J, Yang ZW, Lou XL and Chen C:
Regulatory roles of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in rats with
severe acute pancreatitis. PLoS One. 8:e817672013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Seitz CS, Freiberg RA, Hinata K and
Khavari PA: NF-kappaB determines localization and features of cell
death in epidermis. J Clin Invest. 105:253–260. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Markó L, Vigolo E, Hinze C, Park JK, Roël
G, Balogh A, Choi M, Wübken A, Cording J, Blasig IE, et al: Tubular
epithelial NF-κB activity regulates ischemic AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol.
27:2658–2669. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Silva GE, Costa RS, Ravinal RC, Ramalho
LZ, Dos Reis MA, Coimbra TM and Dantas M: NF-κB expression in IgA
nephropathy outcome. Dis Markers. 31:9–15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sun F, Teng J, Yu P, Li W, Chang J and Xu
H: Involvement of TWEAK and the NF-κB signaling pathway in lupus
nephritis. Exp Ther Med. 15:2611–2619. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tang B, Tang F, Wang Z, Qi G, Liang X, Li
B, Yuan S, Liu J, Yu S and He S: Upregulation of
Akt/NF-κB-regulated inflammation and Akt/Bad-related apoptosis
signaling pathway involved in hepatic carcinoma process:
Suppression by carnosic acid nanoparticle. Int J Nanomedicin.
11:6401–6420. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Liu CJ, Lo JF, Kuo CH, Chu CH, Chen LM,
Tsai FJ, Tsai CH, Tzang BS, Kuo WW and Huang CY: Akt mediates
17beta-estradiol and/or estrogen receptor-alpha inhibition of
LPS-induced tumor necresis factor-alpha expression and myocardial
cell apoptosis by suppressing the JNK1/2-NFkappaB pathway. J Cell
Mol Med. 13:3655–3667. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zheng N, Wang D, Ming H, Zhang H and Yu X:
BAFF promotes proliferation of human mesangial cells through
interaction with BAFF-R. BMC Nephrol. 16:722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ory V, Fan Q, Hamdaoui N, Zhang SY,
Desvaux D, Audard V, Candelier M, Noel LH, Lang P, Guellaën G, et
al: c-mip down-regulates NF-κB activity and promotes apoptosis in
podocytes. Am J Pathol. 180:2284–2292. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li S, Liu X, Lei J, Yang J, Tian P and Gao
Y: Crocin protects podocytes against oxidative stress and
inflammation induced by high glucose through inhibition of NF-κB.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 42:1481–1492. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Druskovic M, Suput D and Milisav I:
Overexpression of caspase-9 triggers its activation and apoptosis
in vitro. Croat Med J. 47:832–840. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Song G, Ouyang G and Bao S: The activation
of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med.
9:59–71. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Shiojima I and Walsh K: Role of Akt
signaling in vascular homeostasis and angiogenesis. Circ Res.
90:1243–1250. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Yuan J, Deng Y, Zhang Y, Gan X, Gao S, Hu
H, Hu S, Hu J, Liu H, Li L and Wang J: Bmp4 inhibits goose
granulosa cell apoptosis via PI3K/AKT/Caspase-9 signaling pathway.
Anim Reprod Sci. 200:86–95. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Huber TB, Kottgen M, Schilling B, Walz G
and Benzing T: Interaction with podocin facilitates nephrin
signaling. J Biol Chem. 276:41543–41546. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Perysinaki GS, Moysiadis DK, Bertsias G,
Giannopoulou I, Kyriacou K, Nakopoulou L, Boumpas DT and Daphnis E:
Podocyte main slit diaphragm proteins, nephrin and podocin, are
affected at early stages of lupus nephritis and correlate with
disease histology. Lupus. 20:781–791. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Eichinger A, Ponsel S, Bergmann C,
Günthner R, Hoefele J, Amann K and Lange-Sperandio B: Cyclosporine
A responsive congenital nephrotic syndrome with single heterozygous
variants in NPHS1, NPHS2, and PLCE1. Pediatr Nephrol. 33:1269–1272.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Yu Y, Zhang L, Xu G, Wu Z, Li Q, Gu Y and
Niu J: Angiotensin II type I receptor agonistic autoantibody
induces podocyte injury via activation of the
TRPC6-calcium/calcineurin pathway in pre-eclampsia. Kidney Blood
Press Res. 43:1666–1676. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhao Y, Wu J, Zhang M, Zhou M, Xu F, Zhu
X, Zhou X, Lang Y, Yang F, Yun S, et al: Angiotensin II induces
calcium/calcineurin signaling and podocyte injury by downregulating
microRNA-30 family members. J Mol Med (Berl). 95:887–898. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yang Q, Ma Y, Liu Y, Liang W, Chen X, Ren
Z, Wang H, Singhal PC and Ding G: Angiotensin II down-regulates
nephrin-Akt signaling and induces podocyte injury: Role of c-Abl.
Mol Biol Cell. 27:197–208. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhu J, Sun N, Aoudjit L, Li H, Kawachi H,
Lemay S and Takano T: Nephrin mediates actin reorganization via
phosphoinositide 3-kinase in podocytes. Kidney Int. 73:556–566.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Liu J, Zhang YD, Chen XL, Zhu XL, Chen X,
Wu JH and Guo NF: The protective effect of the EP2 receptor on
TGF-β1 induced podocyte injury via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
PLoS One. 13:e01971582018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|