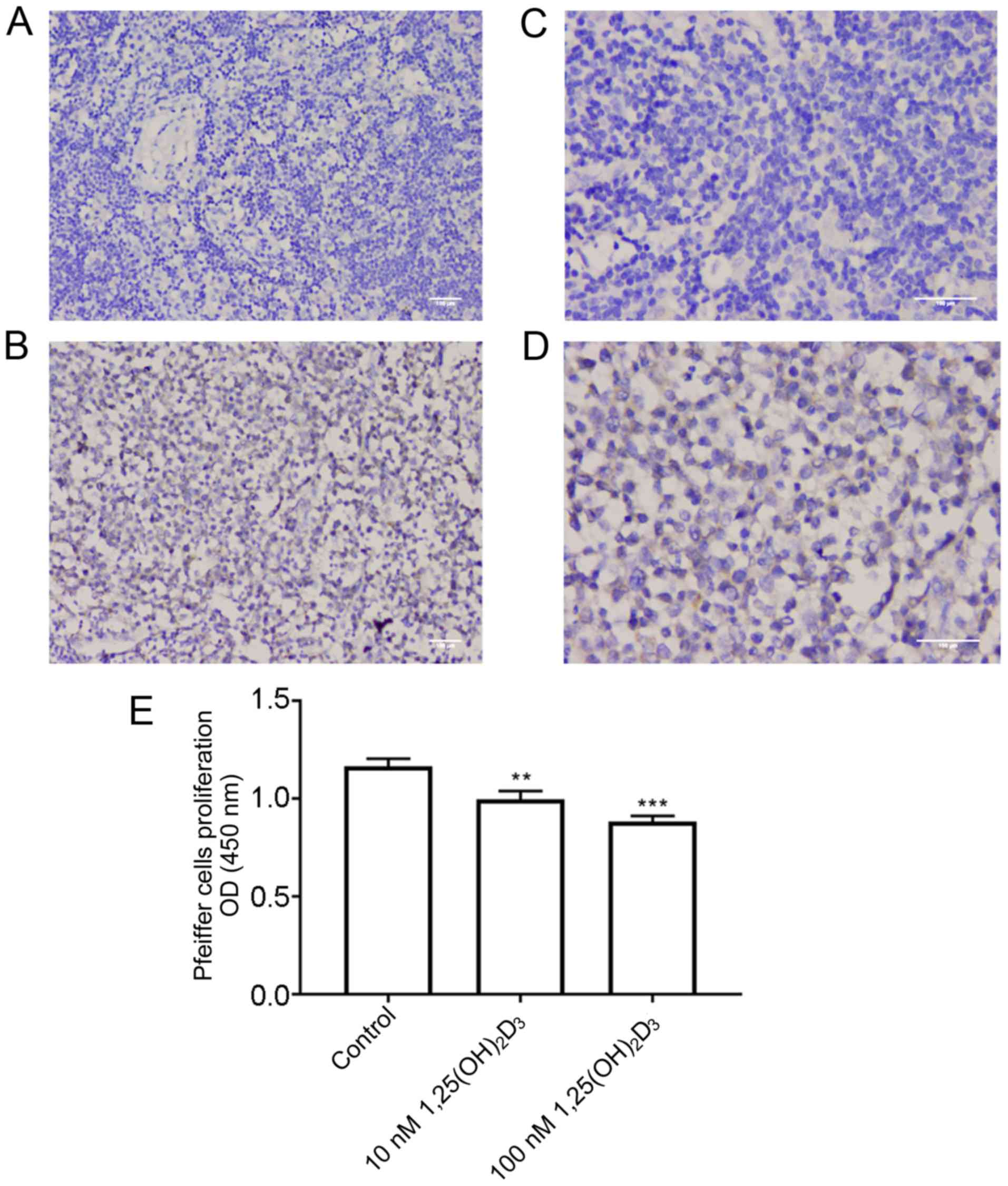
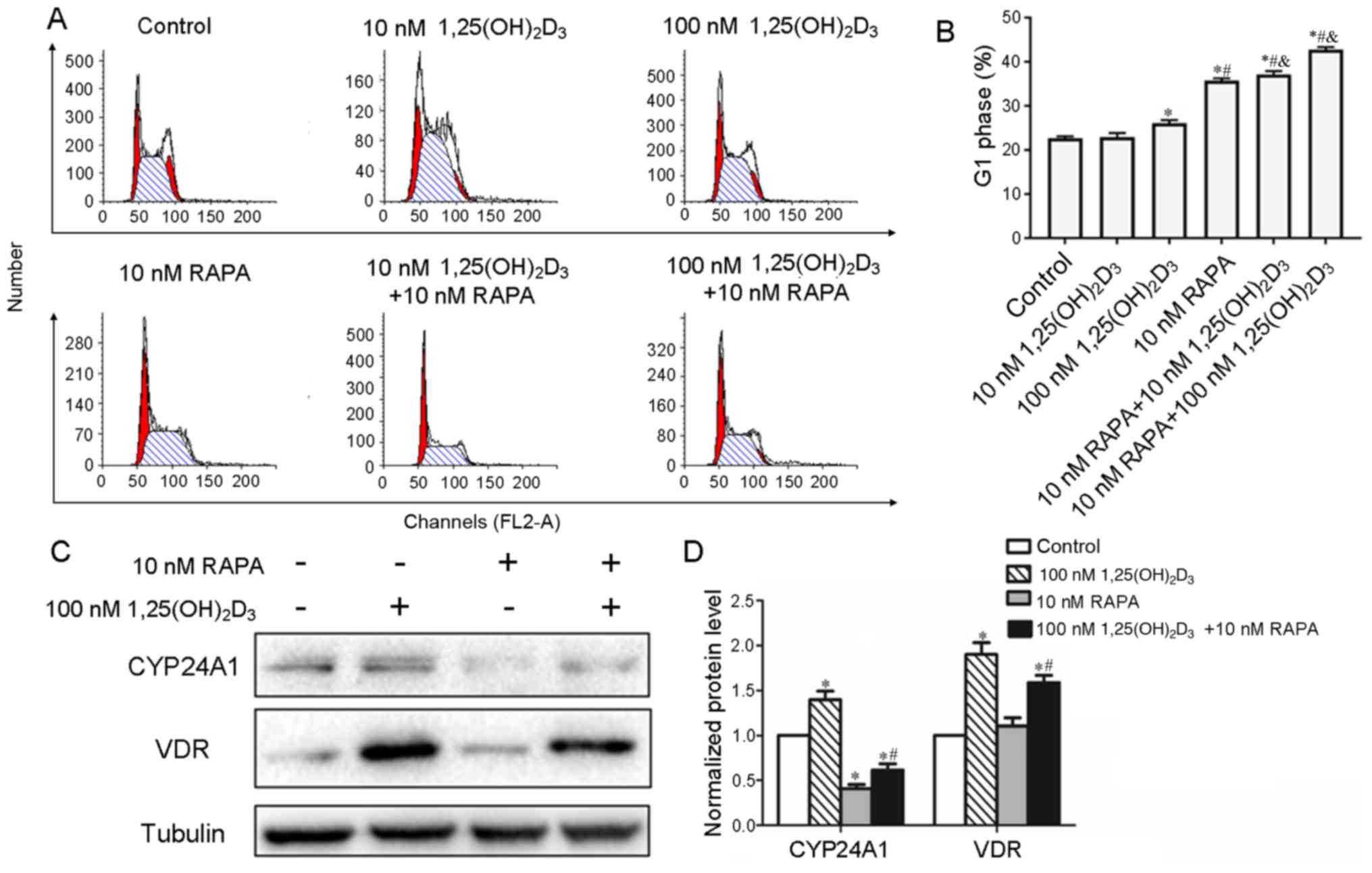
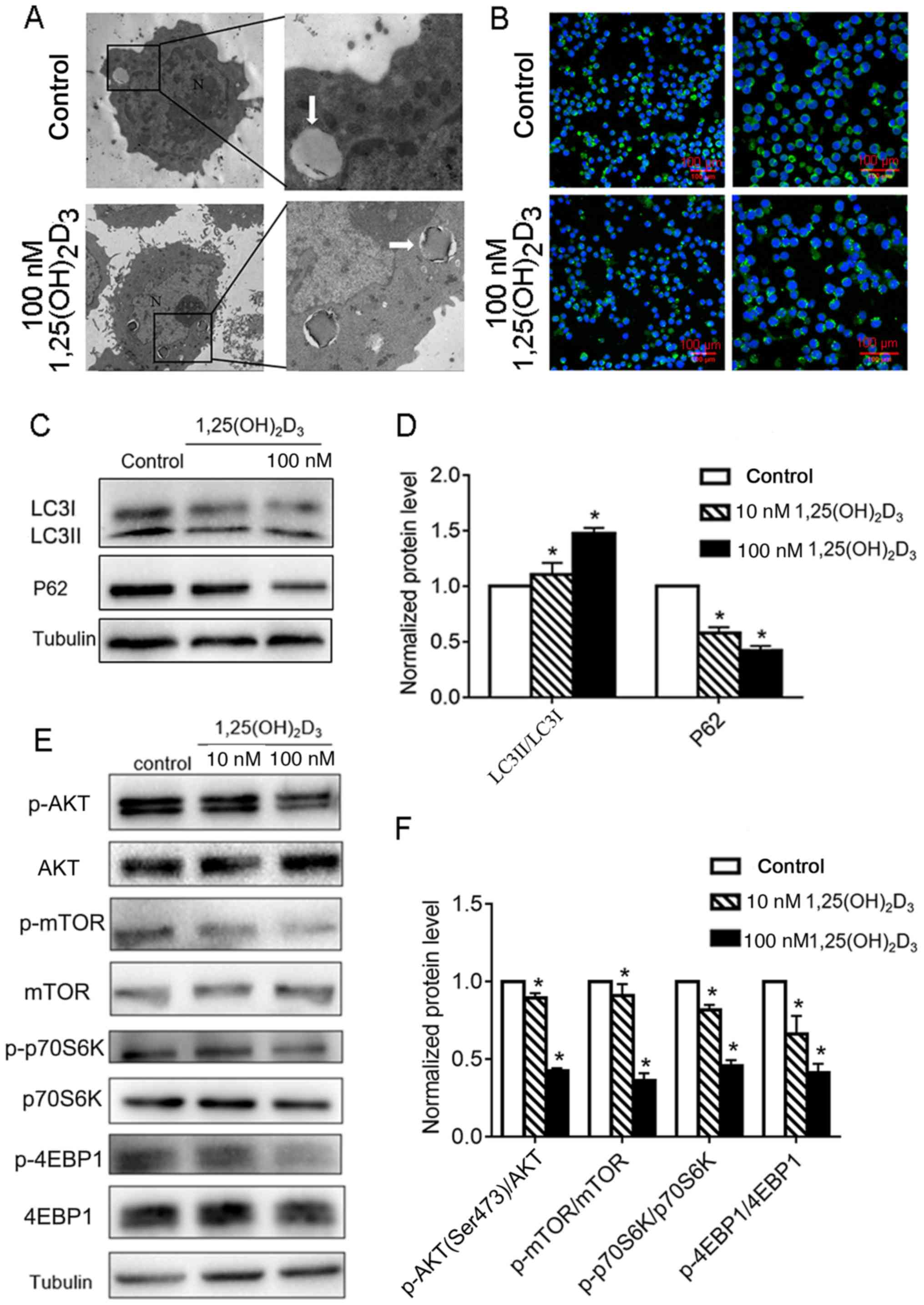
|
1
|
Li S, Young KH and Medeiros LJ: Diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma. Pathology. 50:74–87. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li JM, Wang L, Shen Y, Xia ZG, Chen Y,
Chen QS, Chen Y, Zeng XY, You JH, Qian Y and Shen ZX: Rituximab in
combination with CHOP chemotherapy for the treatment of diffuse
large B cell lymphoma in Chinese patients. Ann Hematol. 86:639–645.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
He F, Wang L, Hu XB, Yin DD, Zhang P, Li
GH, Wang YC, Huang SY, Liang YM and Han H: Notch and BCR signaling
synergistically promote the proliferation of Raji B-lymphoma cells.
Leuk Res. 33:798–802. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Uddin S, Hussain AR, Siraj AK, Manogaran
PS, Al-Jomah NA, Moorji A, Atizado V, Al-Dayel F, Belgaumi A,
El-Solh H, et al: Role of phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/AKT
pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma survival. Blood.
108:4178–4186. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liang J, Zubovitz J, Petrocelli T,
Kotchetkov R, Connor MK, Han K, Lee JH, Ciarallo S, Catzavelos C,
Beniston R, et al: PKB/Akt phosphorylates p27, impairs nuclear
import of p27 and opposes p27-mediated G1 arrest. Nat Med.
8:1153–1160. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Héron-Milhavet L, Franckhauser C, Rana V,
Berthenet C, Fisher D, Hemmings BA, Fernandez A and Lamb NJ: Only
Akt1 is required for proliferation, while Akt2 promotes cell cycle
exit through p21 binding. Mol Cell Biol. 26:8267–8280. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brazil DP, Yang ZZ and Hemmings BA:
Advances in protein kinase B signalling: AKTion on multiple fronts.
Trends Biochem Sci. 29:233–242. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cai SL, Tee AR, Short JD, Bergeron JM, Kim
J, Shen J, Guo R, Johnson CL, Kiguchi K and Walker CL: Activity of
TSC2 is inhibited by AKT-mediated phosphorylation and membrane
partitioning. J Cell Biol. 173:279–289. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cantley LC: The phosphoinositide 3-kinase
pathway. Science. 296:1655–1657. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chang F, Lee JT, Navolanic PM, Steelman
LS, Shelton JG, Blalock WL, Franklin RA and McCubrey JA:
Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression,
apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: A target for cancer
chemotherapy. Leukemia. 17:590–603. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nicoletti F, Fagone P, Meroni P, McCubrey
J and Bendtzen K: mTOR as a multifunctional therapeutic target in
HIV infection. Drug Discov Today. 16:715–721. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu ZZ, Xia ZG, Wang AH, Wang WF, Liu ZY,
Chen LY and Li JM: Activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in
diffuse large B cell lymphoma: Clinical significance and inhibitory
effect of rituximab. Ann Hematol. 92:1351–1358. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC,
Gascoyne RD, Delabie J, Ott G, Müller-Hermelink HK, Campo E,
Braziel RM, Jaffe ES, et al: Confirmation of the molecular
classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by
immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood. 103:275–282.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ott G, Ziepert M, Klapper W, Horn H,
Szczepanowski M, Bernd HW, Thorns C, Feller AC, Lenze D, Hummel M,
et al: Immunoblastic morphology but not the immunohistochemical
GCB/nonGCB classifier predicts outcome in diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma in the RICOVER-60 trial of the DSHNHL. Blood.
116:4916–4925. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mahadevan D, Chiorean EG, Harris WB, Von
Hoff DD, Stejskal-Barnett A, Qi W, Anthony SP, Younger AE, Rensvold
DM, Cordova F, et al: Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic
study of the pan-PI3K/mTORC vascular targeted pro-drug SF1126 in
patients with advanced solid tumours and B-cell malignancies. Eur J
Cancer. 48:3319–3327. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bendell JC, Rodon J, Burris HA, de Jonge
M, Verweij J, Birle D, Demanse D, De Buck SS, Ru QC, Peters M, et
al: Phase I, dose-escalation study of BKM120, an oral pan-Class I
PI3K inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin
Oncol. 30:282–290. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cheng Y, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Ren X,
Huber-Keener KJ, Liu X, Zhou L, Liao J, Keihack H, Yan L, et al:
MK-2206, a novel allosteric inhibitor of Akt, synergizes with
gefitinib against malignant glioma via modulating both autophagy
and apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:154–164. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Donia M, Mangano K, Amoroso A, Mazzarino
MC, Imbesi R, Castrogiovanni P, Coco M, Meroni P and Nicoletti F:
Treatment with rapamycin ameliorates clinical and histological
signs of protracted relapsing experimental allergic
encephalomyelitis in Dark Agouti rats and induces expansion of
peripheral CD4+CD25+Foxp3+
regulatory T cells. J Autoimmun. 33:135–140. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bagherpour B, Salehi M, Jafari R, Bagheri
A, Kiani-Esfahani A, Edalati M, Kardi MT and Shaygannejad V:
Promising effect of rapamycin on multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler
Relat Disord. 26:40–45. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nguyen QD, Merrill PT, Clark WL, Banker
AS, Fardeau C, Franco P, LeHoang P, Ohno S, Rathinam SR, Thurau S,
et al: Intravitreal sirolimus for noninfectious uveitis: A Phase
III sirolimus study assessing double-masKed uveitis TReAtment
(SAKURA). Ophthalmology. 123:2413–2423. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Steelman LS, Martelli AM, Cocco L, Libra
M, Nicoletti F, Abrams SL and McCubrey JA: The therapeutic
potential of mTOR inhibitors in breast cancer. Br J Clin Pharmacol.
82:1189–1212. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Leonardi GC, Falzone L, Salemi R, Zanghì
A, Spandidos DA, Mccubrey JA, Candido S and Libra M: Cutaneous
melanoma: From pathogenesis to therapy (Review). Int J Oncol.
52:1071–1080. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Donia M, McCubrey JA, Bendtzen K and
Nicoletti F: Potential use of rapamycin in HIV infection. Br J Clin
Pharmacol. 70:784–793. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nicoletti F, Lapenta C, Donati S, Spada M,
Ranazzi A, Cacopardo B, Mangano K, Belardelli F, Perno C and Aquaro
S: Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) infection in
human peripheral blood leucocytes-SCID reconstituted mice by
rapamycin. Clin Exp Immunol. 155:28–34. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Caporali S, Alvino E, Lacal PM, Levati L,
Giurato G, Memoli D, Caprini E, Antonini Cappellini GC and D'Atri
S: Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway overcomes the stimulating
effect of dabrafenib on the invasive behavior of melanoma cells
with acquired resistance to the BRAF inhibitor. Int J Oncol.
49:1164–1174. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu Y, Yu X, Ma J, Tong Y and Yao J:
Effects of NVP-BEZ235 on the proliferation, migration, apoptosis
and autophagy in HT-29 human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells. Int J
Oncol. 49:285–293. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chang Z, Shi G, Jin J, Guo H, Guo X, Luo
F, Song Y and Jia X: Dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235-induced
apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines is enhanced by
inhibitors of autophagy. Int J Mol Med. 31:1449–1456. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Paplomata E, Zelnak A and O'Regan R:
Everolimus: Side effect profile and management of toxicities in
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 140:453–462. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lew S and Chamberlain RS: Risk of
metabolic complications in patients with solid tumors treated with
mTOR inhibitors: Meta-analysis. Anticancer Res. 36:1711–1718.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Marcinkowska E, Wallace GR and Brown G:
The use of 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 as an anticancer
agent. Int J Mol Sci. 17:E7292016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Holick MF: Vitamin D and bone health. J
Nutr. 126 (Suppl 4):1159S–1164S. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Abu El Maaty MA and Wölfl S: Vitamin D as
a novel regulator of tumor metabolism: Insights on potential
mechanisms and implications for anti-cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci.
18:E21842017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Barreto SG and Neale RE: Vitamin D and
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 368:1–6. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Castronovo C, Castronovo V, Nikkels A and
Peulen O: Vitamin D anti-cancer activities: Observations, doubts
and certainties. Rev Med Liege. 70:495–500. 2015.(In French).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Duffy MJ, Murray A, Synnott NC, O'Donovan
N and Crown J: Vitamin D analogues: Potential use in cancer
treatment. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 112:190–197. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li MX, Li LF, Zhang L, Xiao ZG, Shen J, Hu
W, Zeng Q and Cho CH: Vitamin D and cancer stem cells in the
gastrointestinal tract. Curr Med Chem. 24:918–927. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang X, Harbeck N, Jeschke U and
Doisneau-Sixou S: Influence of vitamin D signaling on hormone
receptor status and HER2 expression in breast cancer. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 143:1107–1122. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ahn J, Park S, Zuniga B, Bera A, Song CS
and Chatterjee B: Vitamin D in prostate cancer. Vitam Horm.
100:321–355. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lisse TS, Liu T, Irmler M, Beckers J, Chen
H, Adams JS and Hewison M: Gene targeting by the vitamin D response
element binding protein reveals a role for vitamin D in osteoblast
mTOR signaling. FASEB J. 25:937–947. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jang W, Kim HJ, Li H, Jo KD, Lee MK, Song
SH and Yang HO: 1,25-Dyhydroxyvitamin D3 attenuates
rotenone-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells through induction
of autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 451:142–147. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Datta Mitra A, Raychaudhuri SP, Abria CJ,
Mitra A, Wright R, Ray R and Kundu-Raychaudhuri S:
1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin-D3-3-bromoacetate regulates AKT/mTOR
signaling cascades: A therapeutic agent for psoriasis. J Invest
Dermatol. 133:1556–1564. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gröschel C, Tennakoon S and Kállay E:
Cytochrome P450 Vitamin D hydroxylases in inflammation and cancer.
Adv Pharmacol. 74:413–458. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tannour-Louet M, Lewis SK, Louet JF,
Stewart J, Addai JB, Sahin A, Vangapandu HV, Lewis AL, Dittmar K,
Pautler RG, et al: Increased expression of CYP24A1 correlates with
advanced stages of prostate cancer and can cause resistance to
vitamin D3-based therapies. FASEB J. 28:364–372. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sun H, Wang C, Hao M, Sun R, Wang Y, Liu
T, Cong X and Liu Y: CYP24A1 is a potential biomarker for the
progression and prognosis of human colorectal cancer. Hum Pathol.
50:101–108. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sakaki T, Yasuda K, Kittaka A, Yamamoto K
and Chen TC: CYP24A1 as a potential target for cancer therapy.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 14:97–108. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Osanai M and Lee GH: CYP24A1-induced
vitamin D insufficiency promotes breast cancer growth. Oncol Rep.
36:2755–2762. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hu N and Zhang H: CYP24A1 depletion
facilitates the antitumor effect of vitamin D3 on thyroid cancer
cells. Exp Ther Med. 16:2821–2830. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ng AK, Weiss L and LaCasce AS: Chapter 74
- Hodgkin's LymphomaClinical Radiation Oncology. 3rd. Gunderson LL
and Tepper JE: W.B. Saunders; Philadelphia: pp. 1527–1543. 2012,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Kozielewicz P, Grafton G, Kutner A, Curnow
SJ, Gordon J and Barnes NM: Novel vitamin D analogues; cytotoxic
and anti-proliferative activity against a diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma cell line and B-cells from healthy donors. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 164:98–105. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hickish T, Cunningham D, Colston K, Millar
BC, Sandle J, Mackay AG, Soukop M and Sloane J: The effect of
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on lymphoma cell lines and expression of
vitamin D receptor in lymphoma. Br J Cancer. 68:668–672. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H,
Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M,
Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy.
8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chung I, Karpf AR, Muindi JR, Conroy JM,
Nowak NJ, Johnson CS and Trump DL: Epigenetic silencing of CYP24 in
tumor-derived endothelial cells contributes to selective growth
inhibition by calcitriol. J Biol Chem. 282:8704–8714. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Drake MT, Maurer MJ, Link BK, Habermann
TM, Ansell SM, Micallef IN, Kelly JL, Macon WR, Nowakowski GS,
Inwards DJ, et al: Vitamin D insufficiency and prognosis in
non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 28:4191–4198. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ikezoe T, Bandobashi K, Yang Y, Takeuchi
S, Sekiguchi N, Sakai S, Koeffler HP and Taguchi H: HIV-1 protease
inhibitor ritonavir potentiates the effect of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin
D3 to induce growth arrest and differentiation of human myeloid
leukemia cells via down-regulation of CYP24. Leuk Res.
30:1005–1011. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ly LH, Zhao XY, Holloway L and Feldman D:
Liarozole acts synergistically with 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3
to inhibit growth of DU 145 human prostate cancer cells by blocking
24-hydroxylase activity. Endocrinology. 140:2071–2076. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Adorini L and Penna G: Control of
autoimmune diseases by the vitamin D endocrine system. Nat Clin
Pract Rheumatol. 4:404–412. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Agmon-Levin N, Theodor E, Segal RM and
Shoenfeld Y: Vitamin D in systemic and organ-specific autoimmune
diseases. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 45:256–266. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Young KA, Munroe ME, Guthridge JM, Kamen
DL, Niewold TB, Gilkeson GS, Weisman MH, Ishimori ML, Kelly J,
Gaffney PM, et al: Combined role of vitamin D status and CYP24A1 in
the transition to systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis.
76:153–158. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kleinstern G, Averbuch M, Abu Seir R,
Perlman R, Ben Yehuda D and Paltiel O: Presence of autoimmune
disease affects not only risk but also survival in patients with
B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Hematol Oncol. 36:457–462. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Barcellini W, Rizzardi GP, Borghi MO,
Nicoletti F, Fain C, Del Papa N and Meroni PL: In vitro type-1 and
type-2 cytokine production in systemic lupus erythematosus: Lack of
relationship with clinical disease activity. Lupus. 5:139–145.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Narazaki M and Kishimoto T: The two-faced
cytokine IL-6 in host defense and diseases. Int J Mol Sci.
19:E35282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Dlouhy I, Filella X, Rovira J, Magnano L,
Rivas-Delgado A, Baumann T, Martínez-Trillos A, Balagué O, Martínez
A, González-Farre B, et al: High serum levels of soluble
interleukin-2 receptor (sIL2-R), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor
necrosis factor alpha (TNF) are associated with adverse clinical
features and predict poor outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Leuk Res. 59:20–25. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ysmail-Dahlouk L, Nouari W and Aribi M:
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 down-modulates the production
of proinflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide and enhances the
phosphorylation of monocyte-expressed STAT6 at the recent-onset
type 1 diabetes. Immunol Lett. 179:122–130. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yang M, Xu J, Yu J, Yang B, Gan H, Li S
and Li X: Anti-inflammatory effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in
monocytes cultured in serum from patients with type 2 diabetes
mellitus and diabetic nephropathy with uremia via Toll-like
receptor 4 and nuclear factor-κB p65. Mol Med Rep. 12:8215–8222.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lockshin RA and Zakeri Z:
Caspase-independent cell deaths. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 14:727–733.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Matsui Y, Takagi H, Qu X, Abdellatif M,
Sakoda H, Asano T, Levine B and Sadoshima J: Distinct roles of
autophagy in the heart during ischemia and reperfusion: Roles of
AMP-activated protein kinase and Beclin 1 in mediating autophagy.
Circ Res. 100:914–922. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Takagi H, Matsui Y, Hirotani S, Sakoda H,
Asano T and Sadoshima J: AMPK mediates autophagy during myocardial
ischemia in vivo. Autophagy. 3:405–407. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Maiuri MC, Tasdemir E, Criollo A, Morselli
E, Vicencio JM, Carnuccio R and Kroemer G: Control of autophagy by
oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. Cell Death Differ. 16:87–93.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Wullschleger S, Loewith R and Hall MN: TOR
signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell. 124:471–484. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Lisse TS and Hewison M: Vitamin D: A new
player in the world of mTOR signaling. Cell Cycle. 10:1888–1889.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Peponi E, Drakos E, Reyes G, Leventaki V,
Rassidakis GZ and Medeiros LJ: Activation of mammalian target of
rapamycin signaling promotes cell cycle progression and protects
cells from apoptosis in mantle cell lymphoma. Am J Pathol.
169:2171–2180. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Rudelius M, Pittaluga S, Nishizuka S, Pham
TH, Fend F, Jaffe ES, Quintanilla-Martinez L and Raffeld M:
Constitutive activation of Akt contributes to the pathogenesis and
survival of mantle cell lymphoma. Blood. 108:1668–1676. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Hasselblom S, Hansson U, Olsson M, Torén
L, Bergström A, Nilsson-Ehle H and Andersson PO: High
immunohistochemical expression of p-AKT predicts inferior survival
in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with
immunochemotherapy. Br J Haematol. 149:560–568. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Maksimovic-Ivanic D, Fagone P, McCubrey J,
Bendtzen K, Mijatovic S and Nicoletti F: HIV-protease inhibitors
for the treatment of cancer: Repositioning HIV protease inhibitors
while developing more potent NO-hybridized derivatives? Int J
Cancer. 140:1713–1726. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Rothweiler F, Michaelis M, Brauer P, Otte
J, Weber K, Fehse B, Doerr HW, Wiese M, Kreuter J, Al-Abed Y, et
al: Anticancer effects of the nitric oxide-modified saquinavir
derivative saquinavir-NO against multidrug-resistant cancer cells.
Neoplasia. 12:1023–1030. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Maksimovic-Ivanic D, Mojic M, Bulatovic M,
Radojkovic M, Kuzmanovic M, Ristic S, Stosic-Grujicic S, Miljkovic
D, Cavalli E, Libra M, et al: The NO-modified HIV protease
inhibitor as a valuable drug for hematological malignancies: Role
of p70S6K. Leuk Res. 39:1088–1095. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Pearce LR, Alton GR, Richter DT, Kath JC,
Lingardo L, Chapman J, Hwang C and Alessi DR: Characterization of
PF-4708671, a novel and highly specific inhibitor of p70 ribosomal
S6 kinase (S6K1). Biochem J. 431:245–255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Guo LS, Li HX, Li CY, Zhang SY, Chen J,
Wang QL, Gao JM, Liang JQ, Gao MT and Wu YJ: Synergistic antitumor
activity of vitamin D3 combined with metformin in human breast
carcinoma MDA-MB-231 cells involves m-TOR related signaling
pathways. Pharmazie. 70:117–122. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Yang J, Ikezoe T, Nishioka C, Ni L,
Koeffler HP and Yokoyama A: Inhibition of mTORC1 by RAD001
(everolimus) potentiates the effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3)
to induce growth arrest and differentiation of AML cells in vitro
and in vivo. Exp Hematol. 38:666–676. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|