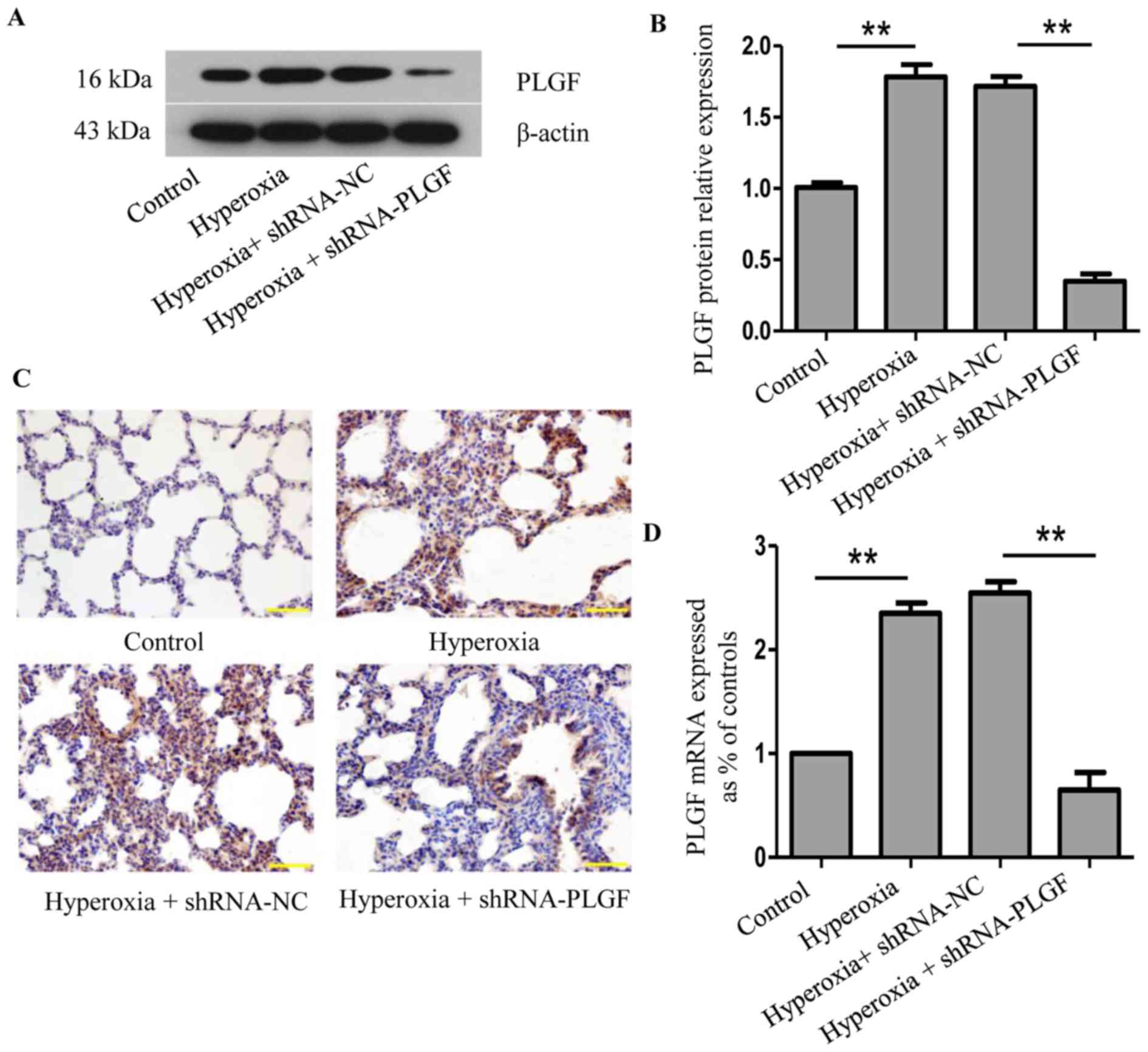
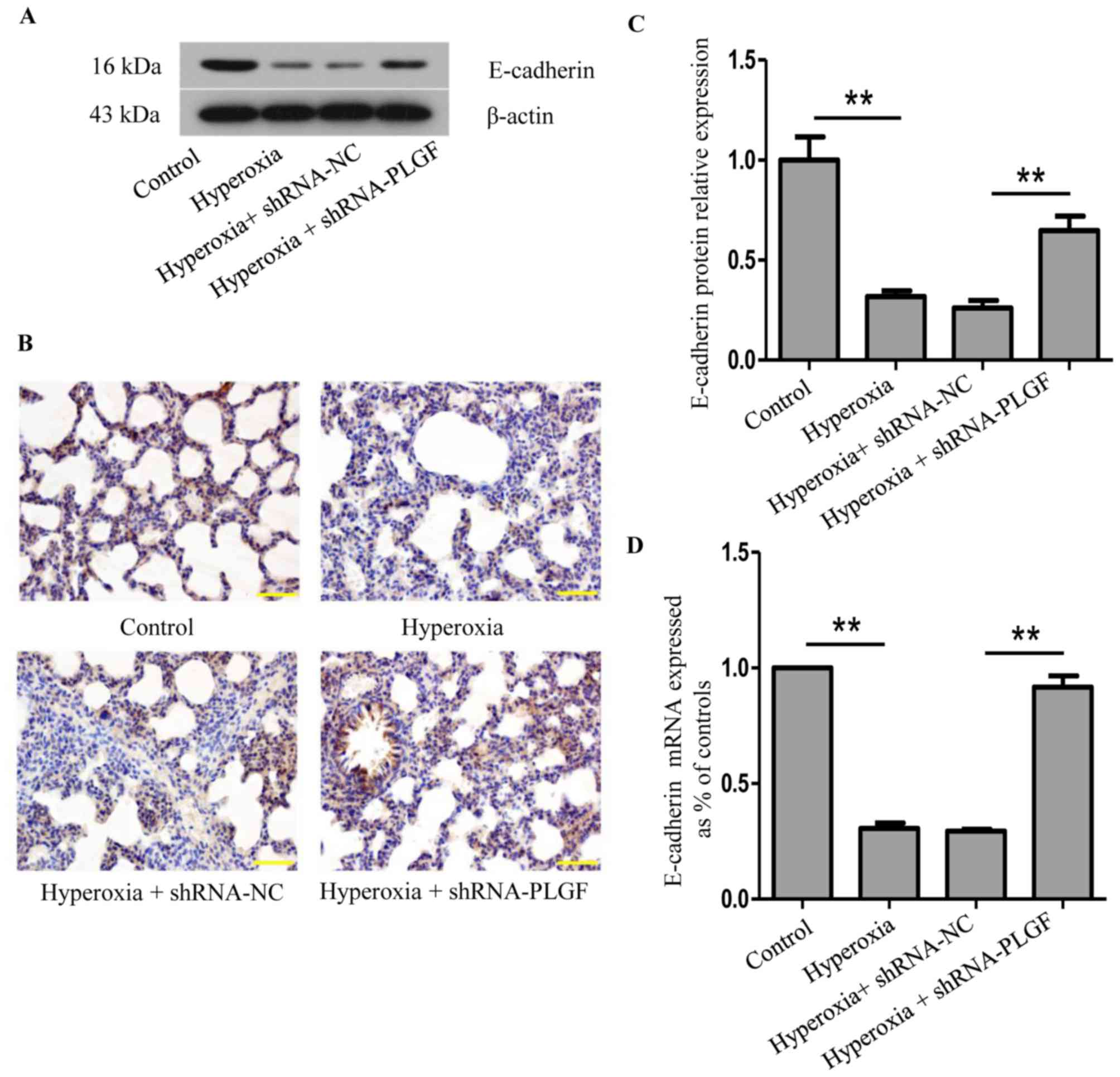
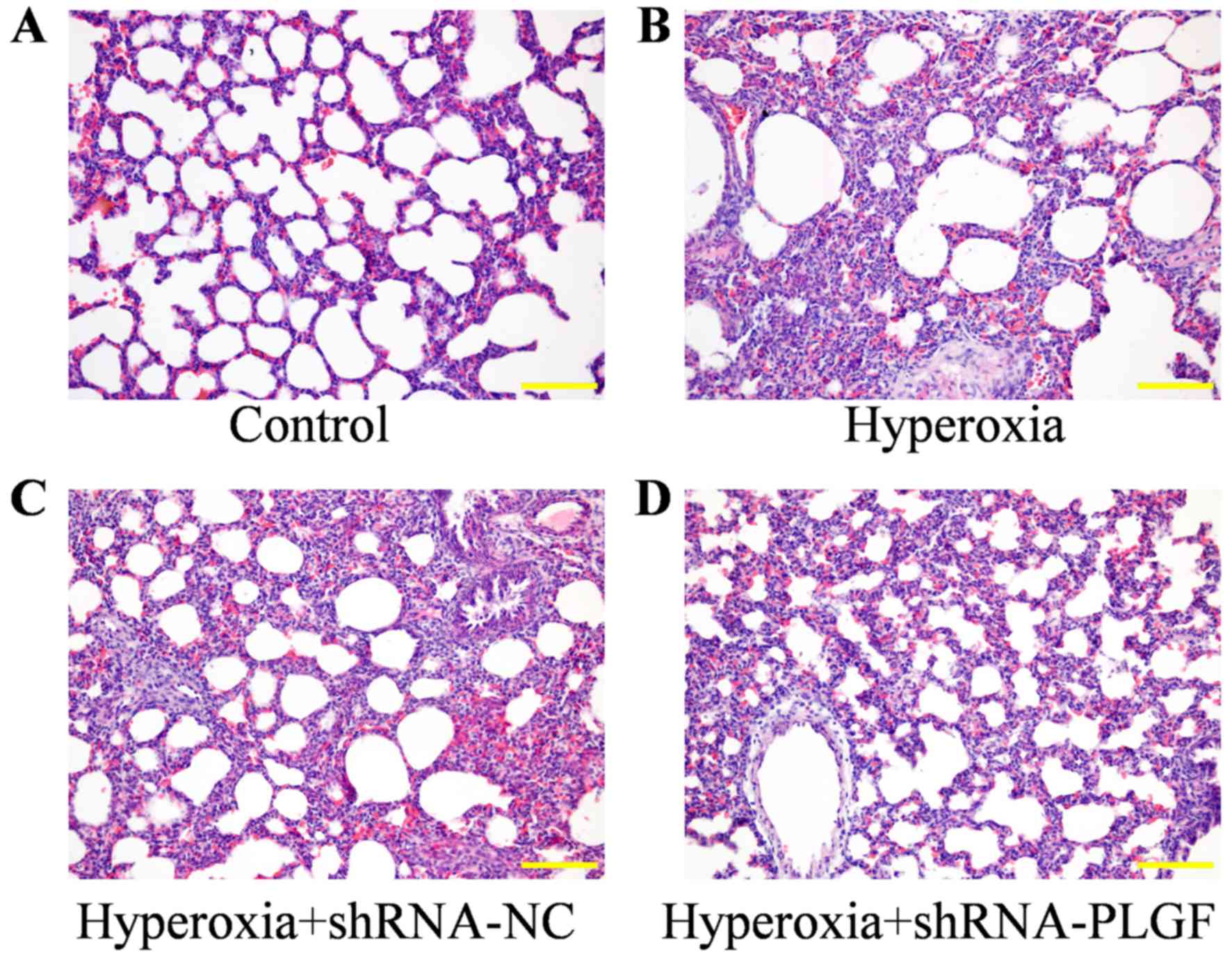
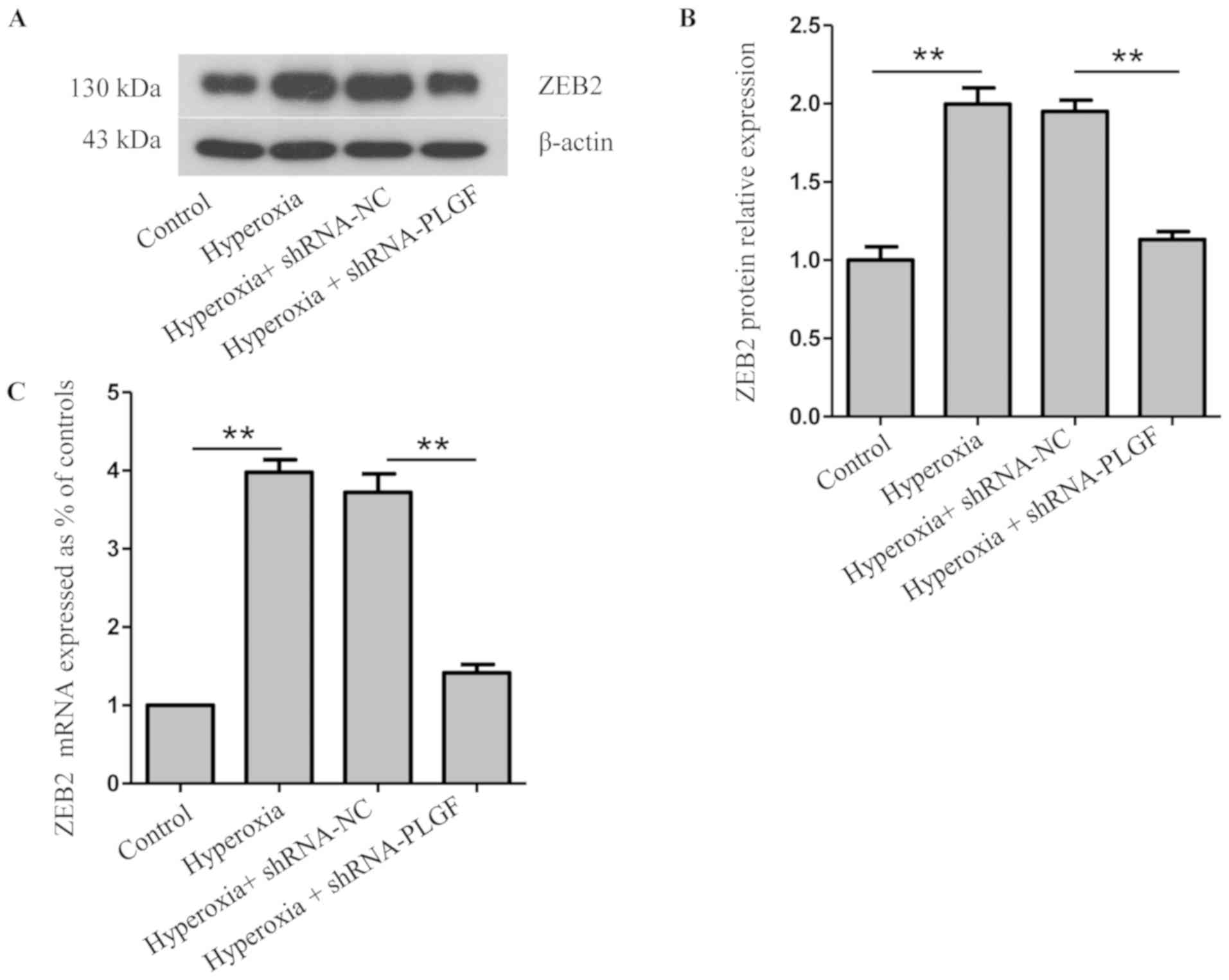
|
1
|
Jobe AH: The new bronchopulmonary
dysplasia. Curr Opin Pediatr. 23:167–172. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Bell EF, Walsh MC,
Carlo WA, Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Sánchez PJ, Van Meurs KP,
Wyckoff M, et al: Trends in care practices, morbidity, and
mortality of extremely preterm neonates, 1993–2012. JAMA.
314:1039–1051. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Greenough A: Long term respiratory
outcomes of very premature birth (<32 weeks). Semin Fetal
Neonatal Med. 17:73–76. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kinsella JP, Greenough A and Abman SH:
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Lancet. 367:1421–1431. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li J, Li Y, He H, Liu C, Li W, Xie L and
Zhang Y: Csk/Src/EGFR signaling regulates migration of
myofibroblasts and alveolarization. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 310:L562–L571. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang H, Fu J, Xue X, Yao L, Qiao L, Hou A,
Jin L and Xing Y: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in
bronchopulmonary dysplasia of newborn rats. Pediatr Pulmonol.
49:1112–1123. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Song JS, Kang CM, Park CK, Yoon HK, Lee
SY, Ahn JH and Moon HS: Inhibitory effect of receptor for advanced
glycation end products (RAGE) on the TGF-β-induced alveolar
epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Exp Mol Med. 43:517–524.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Matsuoka H, Arai T, Mori M, Goya S, Kida
H, Morishita H, Fujiwara H, Tachibana I, Osaki T and Hayashi S: A
p38 MAPK inhibitor, FR-167653, ameliorates murine bleomycin-induced
pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
283:L103–L112. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Feldkoren B, Hutchinson R, Rapoport Y,
Mahajan A and Margulis V: Integrin signaling potentiates
transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1) dependent
down-regulation of E-Cadherin expression-important implications for
epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in renal cell carcinoma.
Exp Cell Res. 355:57–66. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Serrano-Gomez SJ, Maziveyi M and Alahari
SK: Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through
epigenetic and post-translational modifications. Mol Cancer.
15:182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vandewalle C, Van Roy F and Berx G: The
role of the ZEB family of transcription factors in development and
disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 66:773–787. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Andraweera PH, Dekker GA and Roberts CT:
The vascular endothelial growth factor family in adverse pregnancy
outcomes. Hum Reprod Update. 18:436–457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hayes Ryan D, McCarthy FP, O'Donoghue K
and Kenny LC: Placental growth factor: A review of literature and
future applications. Pregnancy Hypertens. 14:260–264. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Iwasaki H, Kawamoto A, Tjwa M, Horii M,
Hayashi S, Oyamada A, Matsumoto T, Suehiro S, Carmeliet P and
Asahara T: PlGF repairs myocardial ischemia through mechanisms of
angiogenesis, cardioprotection and recruitment of myo-angiogenic
competent marrow progenitors. PLoS One. 6:e248722011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tsao PN, Li H, Wei SC, Ko ML, Chou HC,
Hsieh WS and Hsieh FJ: Expression of angiogenic factors and their
receptors in postnatal mouse developing lung. J Formos Med Assoc.
103:137–143. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Korevaar TI, Steegers EA, de Rijke YB,
Visser WE, Jaddoe VW, Visser TJ, Medici M and Peeters RP: Placental
angiogenic factors are associated with maternal thyroid function
and modify hCG-mediated FT4 stimulation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
100:E1328–E1334. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ning Q, Liu C, Hou L, Meng M, Zhang X, Luo
M, Shao S, Zuo X and Zhao X: Vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor-1 activation promotes migration and invasion of breast
cancer cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One.
8:e652172013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang W, Zhu S, Liu Q, Li C and Li L:
Placenta growth factor promotes migration through regulating
epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related protein expression in
cervical cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:8506–8519.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang L, Zhao S, Yuan L, Wu H, Jiang H and
Luo G: Placenta growth factor contributes to cell apoptosis and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in the hyperoxia-induced acute
lung injury. Life Sci. 156:30–37. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhu GJ, Song PP, Zhou H, Shen XH, Wang JG,
Ma XF, Gu YJ, Liu DD, Feng AN, Qian XY and Gao X: Role of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers E-cadherin, N-cadherin,
β-catenin and ZEB2 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol
Lett. 15:3472–3481. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cuadrado A and Nebreda AR: Mechanisms and
functions of p38 MAPK signalling. Biochem J. 429:403–417. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang L, Zhao S, Yuan L, Wu H, Jiang H and
Luo G: Placental growth factor triggers epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition-like changes in rat type II alveolar epithelial cells:
Activation of nuclear factor κB signalling pathway. Basic Clin
Pharmacol Toxicol. 119:498–504. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mourani PM and Abman SH: Pulmonary
hypertension and vascular abnormalities in bronchopulmonary
dysplasia. Clin Perinatol. 42:839–855. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun Y, Liu WZ, Liu T, Feng X, Yang N and
Zhou HF: Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation,
differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept
Signal Transduct Res. 35:600–604. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hu X, Shen H, Wang Y and Zhao M: Liver X
receptor agonist TO901317 attenuates paraquat-induced acute lung
injury through inhibition of NF-κB and JNK/p38 MAPK signal
pathways. Biomed Res Int. 2017:46526952017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang L and Zhao S, Yuan L, Wu H, Jiang H,
Luo G and Zhao S: Knockdown of placental growth factor (PLGF)
mitigates hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury in neonatal rats:
Suppressive effects on NFkappaB signaling pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 38:167–174. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nie M, Wang Y, Lu Y, Yuan Y, Liu Y and Li
X: Protective effects of fucoidan against hyperoxic lung injury via
the ERK signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 17:1813–1818.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bao XC, Fang YQ, You P, Zhang S and Ma J:
Protective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
beta/delta in acute lung injury induced by prolonged hyperbaric
hyperoxia in rats. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 199:9–18. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Porzionato A, Sfriso MM, Mazzatenta A,
Macchi V, De Caro R and Di Giulio C: Effects of hyperoxic exposure
on signal transduction pathways in the lung. Respir Physiol
Neurobiol. 209:106–114. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|