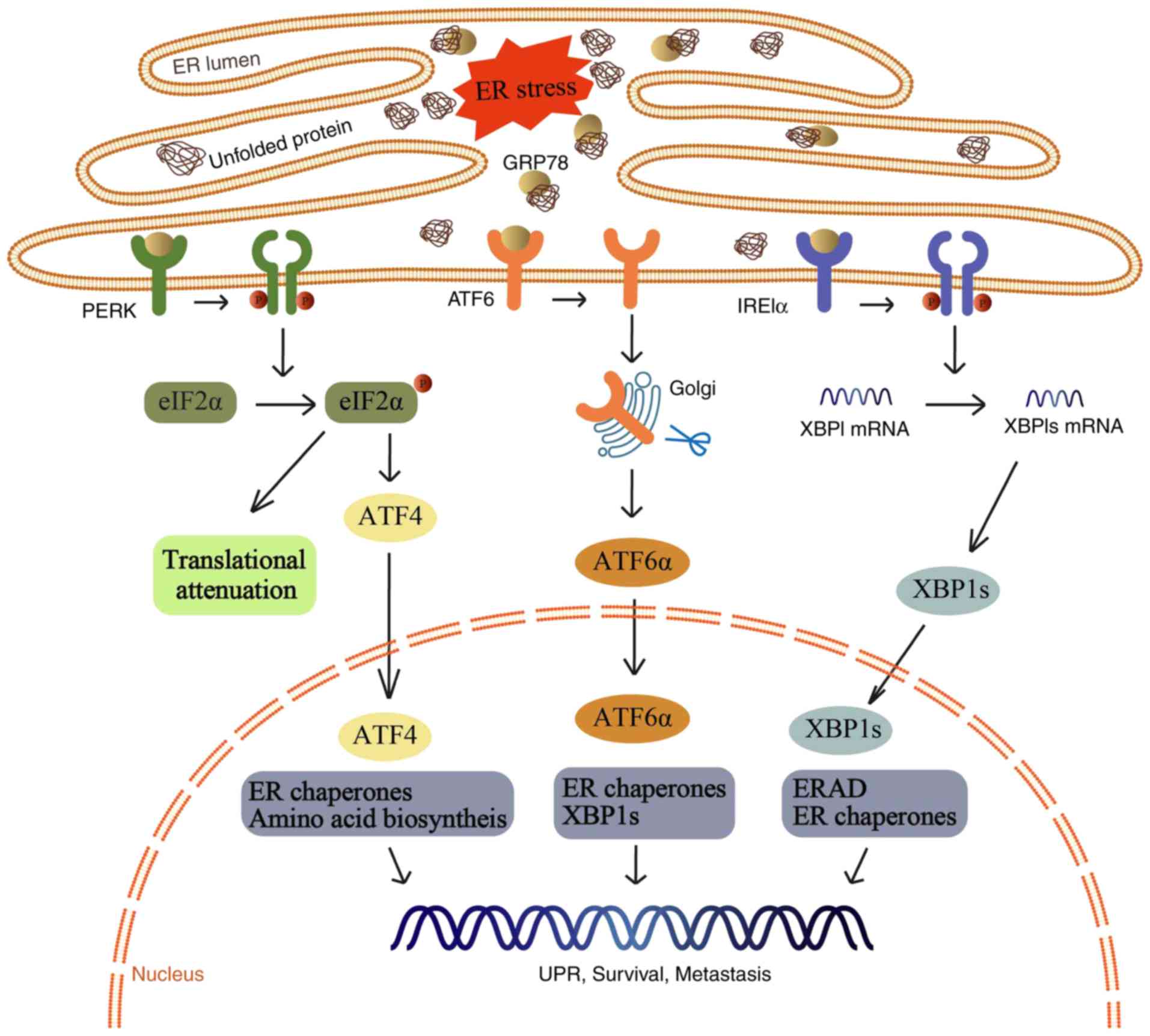
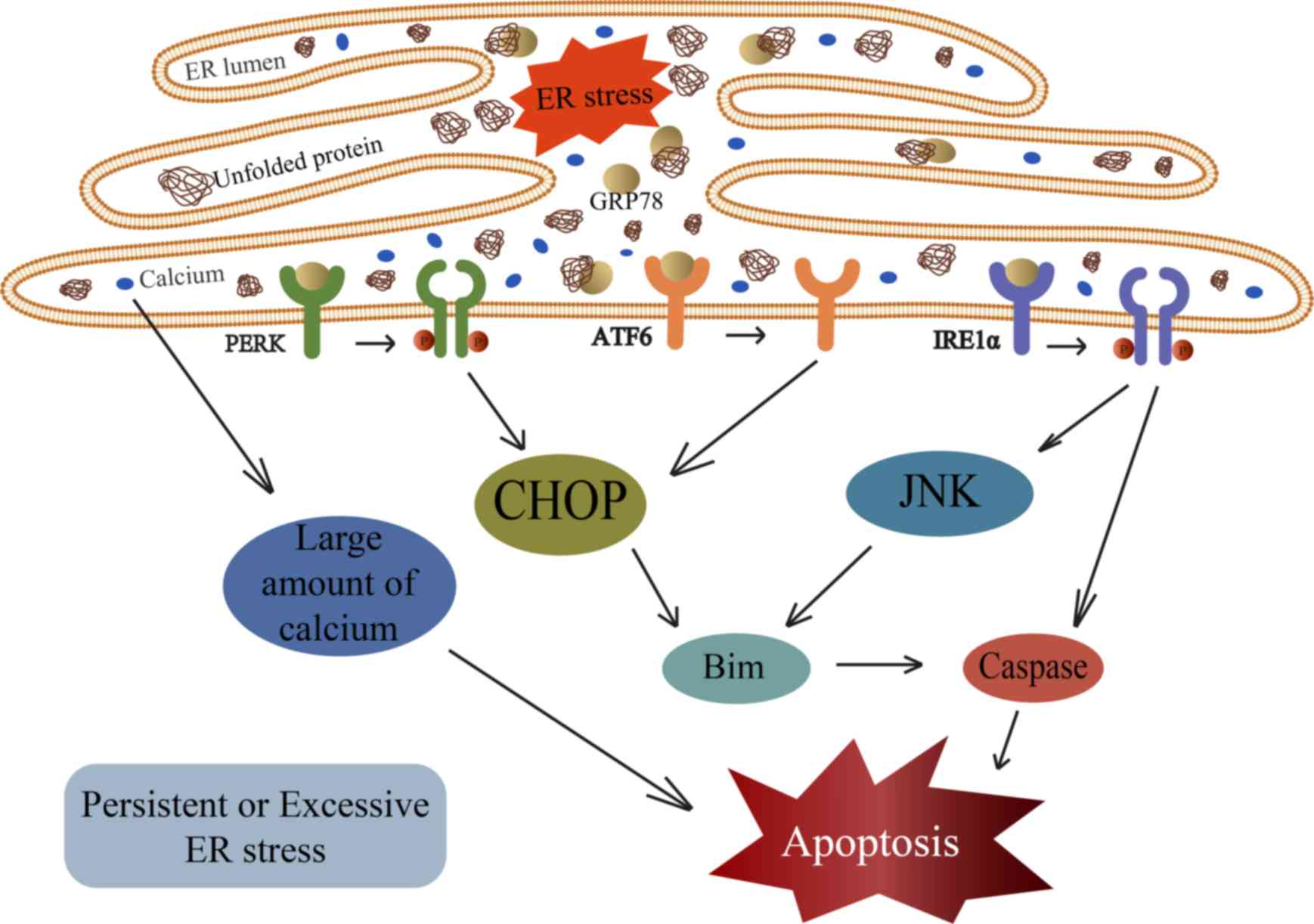
|
1
|
Malhi GS and Mann JJ: DepressionLancet.
London, England: 392. pp. 2299–2312. 2018, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
The burden of depression. Nature.
515:1632014. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ledford H: Medical research: If depression
were cancer. Nature. 515:182–184. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McCaffrey K and Braakman I: Protein
quality control at the endoplasmic reticulum. Essays Biochem.
60:227–235. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hetz C and Papa FR: The unfolded protein
response and cell fate control. Mol Cell. 69:169–181. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hetz C, Chevet E and Oakes SA:
Proteostasis control by the unfolded protein response. Nat Cell
Biol. 17:829–838. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang J, Lee J, Liem D and Ping P: HSPA5
Gene encoding Hsp70 chaperone BiP in the endoplasmic reticulum.
Gene. 618:14–23. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Behnke J, Mann MJ, Scruggs FL, Feige MJ
and Hendershot LM: Members of the Hsp70 family recognize distinct
types of sequences to execute ER quality control. Mol Cell.
63:739–752. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Otero JH, Lizák B and Hendershot LM: Life
and death of a BiP substrate. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 21:472–478.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li J, Ni M, Lee B, Barron E, Hinton DR and
Lee AS: The unfolded protein response regulator GRP78/BiP is
required for endoplasmic reticulum integrity and stress-induced
autophagy in mammalian cells. Cell Death Differ. 15:1460–1471.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nakamura K, Bossy-Wetzel E, Burns K, Fadel
MP, Lozyk M, Goping IS, Opas M, Bleackley RC, Green DR and Michalak
M: Changes in endoplasmic reticulum luminal environment affect cell
sensitivity to apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 150:731–740. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bown C, Wang JF, MacQueen G and Young LT:
Increased temporal cortex ER stress proteins in depressed subjects
who died by suicide. Neuropsychopharmacology. 22:327–332. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nevell L, Zhang K, Aiello AE, Koenen K,
Galea S, Soliven R, Zhang C, Wildman DE and Uddin M: Elevated
systemic expression of ER stress related genes is associated with
stress-related mental disorders in the Detroit Neighborhood Health
Study. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 43:62–70. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Koenig JI, Walker CD, Romeo RD and Lupien
SJ: Effects of stress across the lifespan. Stress. 14:475–480.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dillon DG and Pizzagalli DA: Mechanisms of
memory disruption in depression. Trends Neurosci. 41:137–149. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kadowaki H, Satrimafitrah P, Takami Y and
Nishitoh H: Molecular mechanism of ER stress-induced pre-emptive
quality control involving association of the translocon, Derlin-1,
and HRD1. Sci Rep. 8:73172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Oakes SA and Papa FR: The role of
endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu Rev Pathol.
10:173–194. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shore GC, Papa FR and Oakes SA: Signaling
cell death from the endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 23:143–149. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Scheper W and Hoozemans JJ: The unfolded
protein response in neurodegenerative diseases: A neuropathological
perspective. Acta Neuropathol. 130:315–331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bettigole SE and Glimcher LH: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress in immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 33:107–138. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Korennykh A and Walter P: Structural basis
of the unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
28:251–277. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Casas C: GRP78 at the centre of the stage
in cancer and neuroprotection. Front Neurosci. 11:1772017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Harding HP, Zhang Y, Bertolotti A, Zeng H
and Ron D: Perk is essential for translational regulation and cell
survival during the unfolded protein response. Mol Cell. 5:897–904.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Carrara M, Prischi F, Nowak PR, Kopp MC
and Ali MM: Noncanonical binding of BiP ATPase domain to Ire1 and
Perk is dissociated by unfolded protein CH1 to initiate ER stress
signaling. Elife. 4:2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Han J, Back SH, Hur J, Lin YH,
Gildersleeve R, Shan J, Yuan CL, Krokowski D, Wang S, Hatzoglou M,
et al: ER-stress-induced transcriptional regulation increases
protein synthesis leading to cell death. Nat Cell Biol. 15:481–490.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang J, Liu H, Li L, Liu H, Shi W, Yuan X
and Wu L: Structural insights into IRE1 functions in the unfolded
protein response. Curr Med Chem. 23:4706–4716. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN and Glimcher LH: XBP-1
regulates a subset of endoplasmic reticulum resident chaperone
genes in the unfolded protein response. Mol Cell Biol.
23:7448–7459. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu R, Zhang QH, Lu YJ, Ren K and Yi GH:
Involvement of the IRE1α-XBP1 pathway and XBP1s-dependent
transcriptional reprogramming in metabolic diseases. DNA Cell Biol.
34:6–18. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Papaioannou A, Higa A, Jégou G, Jouan F,
Pineau R, Saas L, Avril T, Pluquet O and Chevet E: Alterations of
EDEM1 functions enhance ATF6 pro-survival signaling. FEBS J.
285:4146–4164. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hillary RF and FitzGerald U: A lifetime of
stress: ATF6 in development and homeostasis. J Biomed Sci.
25:482018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shoulders MD, Ryno LM, Genereux JC,
Moresco JJ, Tu PG, Wu C, Yates JR III, Su AI, Kelly JW and Wiseman
RL: Stress-independent activation of XBP1s and/or ATF6 reveals
three functionally diverse ER proteostasis environments. Cell Rep.
3:1279–1292. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hiramatsu N, Chiang WC, Kurt TD, Sigurdson
CJ and Lin JH: Multiple mechanisms of unfolded protein
response-induced cell death. Am J Pathol. 185:1800–1808. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hill MN, Hellemans KG, Verma P, Gorzalka
BB and Weinberg J: Neurobiology of chronic mild stress: Parallels
to major depression. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 36:2085–2117. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu Y, Yang N, Hao W, Zhao Q, Ying T, Liu
S, Li Q, Liang Y, Wang T, Dong Y, et al: Dynamic proteomic analysis
of protein expression profiles in whole brain of Balb/C mice
subjected to unpredictable chronic mild stress: Implications for
depressive disorders and future therapies. Neurochem Int.
58:904–913. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tan H, Zou W, Jiang J, Tian Y, Xiao Z, Bi
L, Zeng H and Tang X: Disturbance of hippocampal H2S generation
contributes to CUMS-induced depression-like behavior: Involvement
in endoplasmic reticulum stress of hippocampus. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 47:285–291. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang X and Bian JS: Hydrogen sulfide: A
neuromodulator and neuroprotectant in the central nervous system.
ACS Chem Neurosci. 5:876–883. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu SY, Li D, Zeng HY, Kan LY, Zou W,
Zhang P, Gu HF and Tang XQ: Hydrogen sulfide inhibits chronic
unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive-like behavior by
upregulation of Sirt-1: Involvement in suppression of hippocampal
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol.
20:867–876. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chiba S, Numakawa T, Ninomiya M, Richards
MC, Wakabayashi C and Kunugi H: Chronic restraint stress causes
anxiety- and depression-like behaviors, downregulates
glucocorticoid receptor expression, and attenuates glutamate
release induced by brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the
prefrontal cortex. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry.
39:112–119. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jangra A, Dwivedi S, Sriram CS, Gurjar SS,
Kwatra M, Sulakhiya K, Baruah CC and Lahkar M: Honokiol abrogates
chronic restraint stress-induced cognitive impairment and
depressive-like behaviour by blocking endoplasmic reticulum stress
in the hippocampus of mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 770:25–32. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jangra A, Sriram CS, Dwivedi S, Gurjar SS,
Hussain MI, Borah P and Lahkar M: Sodium phenylbutyrate and
edaravone abrogate chronic restraint stress-induced behavioral
deficits: Implication of oxido-nitrosative, endoplasmic reticulum
stress cascade, and neuroinflammation. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
37:65–81. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pavlovsky AA, Boehning D, Li D, Zhang Y,
Fan X and Green TA: Psychological stress, cocaine and natural
reward each induce endoplasmic reticulum stress genes in rat brain.
Neuroscience. 246:160–169. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lawson MA, Parrott JM, McCusker RH,
Dantzer R, Kelley KW and O'Connor JC: Intracerebroventricular
administration of lipopolysaccharide induces
indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase-dependent depression-like behaviors. J
Neuroinflammation. 10:872013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jangra A, Sriram CS and Lahkar M:
Lipopolysaccharide-induced behavioral alterations are alleviated by
sodium phenylbutyrate via attenuation of oxidative stress and
neuroinflammatory cascade. Inflammation. 39:1441–1452. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Huang GB, Zhao T, Muna SS, Bagalkot TR,
Jin HM, Chae HJ and Chung YC: Effects of chronic social defeat
stress on behaviour, endoplasmic reticulum proteins and choline
acetyltransferase in adolescent mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol.
16:1635–1647. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu L, Zhao Z, Lu L, Liu J, Sun J, Wu X
and Dong J: Icariin and icaritin ameliorated hippocampus
neuroinflammation via inhibiting HMGB1-related pro-inflammatory
signals in lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation model in
C57BL/6J mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 68:95–105. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li MX, Li Q, Sun XJ, Luo C, Li Y, Wang YN,
Chen J, Gong CZ, Li YJ, Shi LP, et al: Increased Homer1-mGluR5
mediates chronic stress-induced depressive-like behaviors and
glutamatergic dysregulation via activation of PERK-eIF2α. Prog
Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 95:1096822019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sharma V, Ounallah-Saad H, Chakraborty D,
Hleihil M, Sood R, Barrera I, Edry E, Kolatt Chandran S, Ben Tabou
de Leon S, Kaphzan H and Rosenblum K: Local inhibition of PERK
enhances memory and reverses age-related deterioration of cognitive
and neuronal properties. J Neurosci. 38:648–658. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Timberlake MA II and Dwivedi Y: Altered
expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress associated genes in
hippocampus of learned helpless rats: Relevance to depression
pathophysiology. Front Pharmacol. 6:3192016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Luedtke K, Bouchard SM, Woller SA, Funk
MK, Aceves M and Hook MA: Assessment of depression in a rodent
model of spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma. 31:1107–1121. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Maldonado-Bouchard S, Peters K, Woller SA,
Madahian B, Faghihi U, Patel S, Bake S and Hook MA: Inflammation is
increased with anxiety- and depression-like signs in a rat model of
spinal cord injury. Brain Behav Immun. 51:176–195. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wu J, Zhao Z, Sabirzhanov B, Stoica BA,
Kumar A, Luo T, Skovira J and Faden AI: Spinal cord injury causes
brain inflammation associated with cognitive and affective changes:
Role of cell cycle pathways. J Neurosci. 34:10989–11006. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wu J, Zhao Z, Kumar A, Lipinski MM, Loane
DJ, Stoica BA and Faden AI: Endoplasmic reticulum stress and
disrupted neurogenesis in the brain are associated with cognitive
impairment and depressive-like behavior after spinal cord injury. J
Neurotrauma. 33:1919–1935. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cheng Y, Cawley NX, Yanik T, Murthy SR,
Liu C, Kasikci F, Abebe D and Loh YP: A human carboxypeptidase
E/NF-α1 gene mutation in an Alzheimer's disease patient leads to
dementia and depression in mice. Transl Psychiatry. 6:e9732016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Michel TM, Camara S, Tatschner T, Frangou
S, Sheldrick AJ, Riederer P and Grünblatt E: Increased xanthine
oxidase in the thalamus and putamen in depression. World J Biol
Psychiatry. 11:314–320. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Harrison R: Structure and function of
xanthine oxidoreductase: Where are we now? Free Radic Biol Med.
33:774–797. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ishisaka M, Kakefuda K, Yamauchi M,
Tsuruma K, Shimazawa M, Tsuruta A and Hara H: Luteolin shows an
antidepressant-like effect via suppressing endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:1481–1486. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liu Y, Zhao N, Li C, Chang Q, Liu X, Liao
Y and Pan R: Longistyline C acts antidepressant in vivo and
neuroprotection in vitro against glutamate-induced cytotoxicity by
regulating NMDAR/NR2B-ERK pathway in PC12 cells. PLoS One.
12:e01837022017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Jiang Y, Li Z, Liu Y, Liu X, Chang Q, Liao
Y and Pan R: Neuroprotective effect of water extract of Panax
ginseng on corticosterone-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells and its
underlying molecule mechanisms. J Ethnopharmacol. 159:102–112.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li ZY, Guo Z, Liu YM, Liu XM, Chang Q,
Liao YH and Pan RL: Neuroprotective effects of total saikosaponins
of Bupleurum yinchowense on corticosterone-induced apoptosis in
PC12 cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 148:794–803. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ye T, Meng X, Wang R, Zhang C, He S, Sun G
and Sun X: Gastrodin alleviates cognitive dysfunction and
depressive-like behaviors by inhibiting ER stress and NLRP3
inflammasome activation in db/db Mice. Int J Mol Sci. 19:2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Shikov AN, Pozharitskaya ON and Makarov
VG: Aralia elata var. mandshurica (Rupr. & Maxim.)
J.Wen: An overview of pharmacological studies. Phytomedicine.
23:1409–1421. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Narita N, Hashimoto K, Tomitaka S and
Minabe Y: Interactions of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
with subtypes of sigma receptors in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol.
307:117–119. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hosoi T, Miyahara T, Kayano T, Yokoyama S
and Ozawa K: Fluvoxamine attenuated endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced leptin resistance. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
3:122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hayashi T and Su TP: Sigma-1 receptor
chaperones at the ER-mitochondrion interface regulate Ca(2+)
signaling and cell survival. Cell. 131:596–610. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Omi T, Tanimukai H, Kanayama D, Sakagami
Y, Tagami S, Okochi M, Morihara T, Sato M, Yanagida K, Kitasyoji A,
et al: Fluvoxamine alleviates ER stress via induction of Sigma-1
receptor. Cell Death Dis. 5:e13322014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Terada K, Izumo N, Suzuki B, Karube Y,
Morikawa T, Ishibashi Y, Kameyama T, Chiba K, Sasaki N, Iwata K, et
al: Fluvoxamine moderates reduced voluntary activity following
chronic dexamethasone infusion in mice via recovery of BDNF signal
cascades. Neurochem Int. 69:9–13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Perez-Caballero L, Torres-Sanchez S, Bravo
L, Mico JA and Berrocoso E: Fluoxetine: A case history of its
discovery and preclinical development. Expert Opin Drug Discov.
9:567–578. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ma J, Yang YR, Chen W, Chen MH, Wang H,
Wang XD, Sun LL, Wang FZ and Wang DC: Fluoxetine synergizes with
temozolomide to induce the CHOP-dependent endoplasmic reticulum
stress-related apoptosis pathway in glioma cells. Oncol Rep.
36:676–684. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ma J, Hou LN, Rong ZX, Liang P, Fang C, Li
HF, Qi H and Chen HZ: Antidepressant desipramine leads to C6 glioma
cell autophagy: Implication for the adjuvant therapy of cancer.
Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 13:254–260. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Abelaira HM, Réus GZ, Ignácio ZM, Dos
Santos MA, de Moura AB, Matos D, Demo JP, da Silva JB, Michels M,
Abatti M, et al: Effects of ketamine administration on mTOR and
reticulum stress signaling pathways in the brain after the infusion
of rapamycin into prefrontal cortex. J Psychiatr Res. 87:81–87.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Chen S, Xuan J, Couch L, Iyer A, Wu Y, Li
QZ and Guo L: Sertraline induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in
hepatic cells. Toxicology. 322:78–88. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ren Z, Chen S, Zhang J, Doshi U, Li AP and
Guo L: Endoplasmic reticulum stress induction and ERK1/2 activation
contribute to nefazodone-induced toxicity in hepatic cells. Toxicol
Sci. 154:368–380. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Yang L, Zheng L, Wan Y, Chen Z, Li P and
Wang Y: Metoprolol, N-acetylcysteine, and escitalopram prevents
chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression by inhibition
of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Front Psychiatry. 9:6962018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Li B, Yadav RK, Jeong GS, Kim HR and Chae
HJ: The characteristics of Bax inhibitor-1 and its related
diseases. Curr Mol Med. 14:603–615. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Sui ZY, Chae HJ, Huang GB, Zhao T,
Shrestha Muna S and Chung YC: Effects of chronic mild stress in
female bax inhibitor-1-gene knockout mice. Clin Psychopharmacol
Neurosci. 10:155–162. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hunsberger JG, Machado-Vieira R, Austin
DR, Zarate C, Chuang DM, Chen G, Reed JC and Manji HK: Bax
inhibitor 1, a modulator of calcium homeostasis, confers affective
resilience. Brain Res. 1403:19–27. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Crider A, Nelson T, Davis T, Fagan K,
Vaibhav K, Luo M, Kamalasanan S, Terry AV Jr and Pillai A: Estrogen
receptor β agonist attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced
changes in social behavior and brain connectivity in mice. Mol
Neurobiol. 55:7606–7618. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Swardfager W, Hennebelle M, Yu D, Hammock
BD, Levitt AJ, Hashimoto K and Taha AY:
Metabolic/inflammatory/vascular comorbidity in psychiatric
disorders; soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) as a possible new
target. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 87:56–66. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|