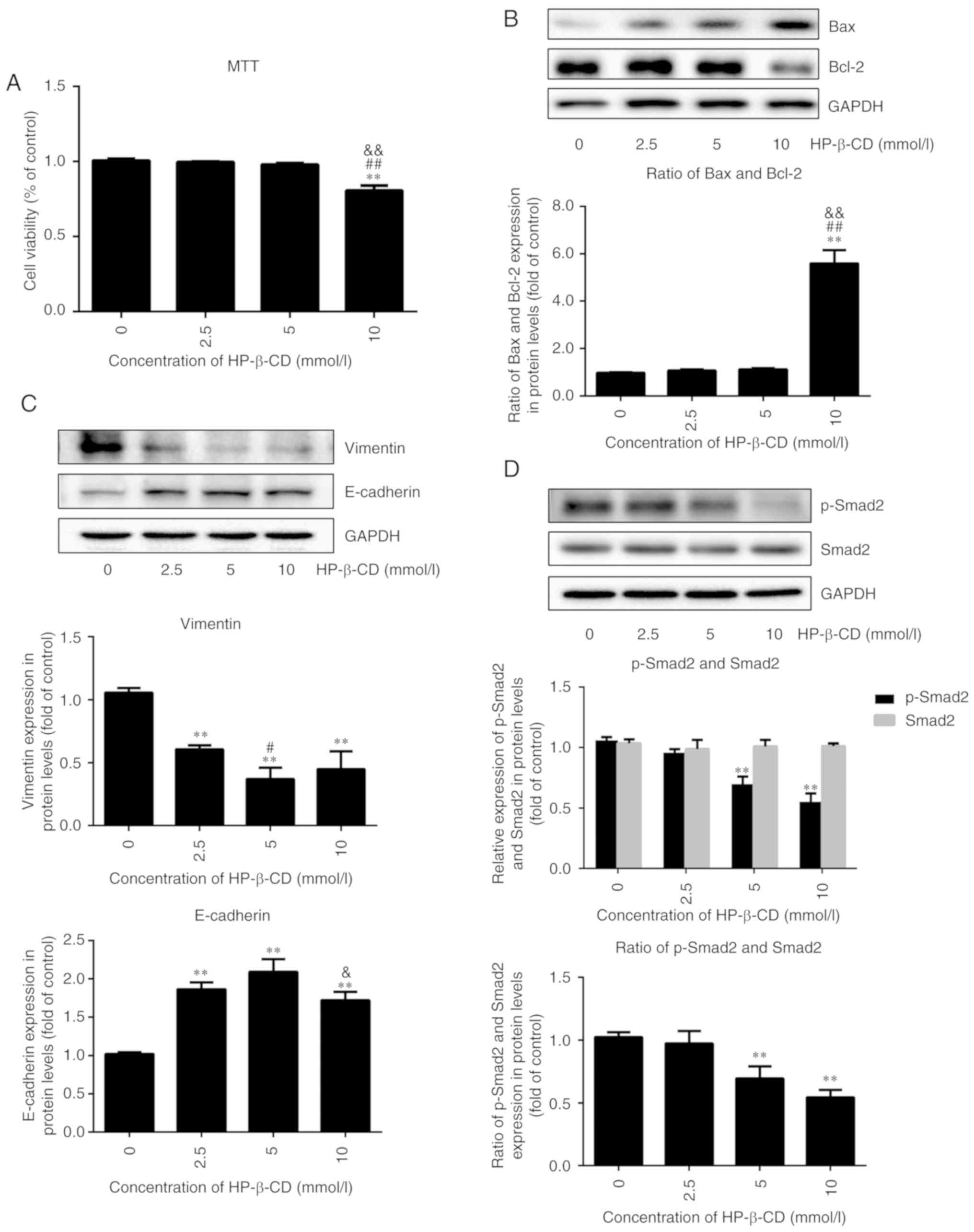
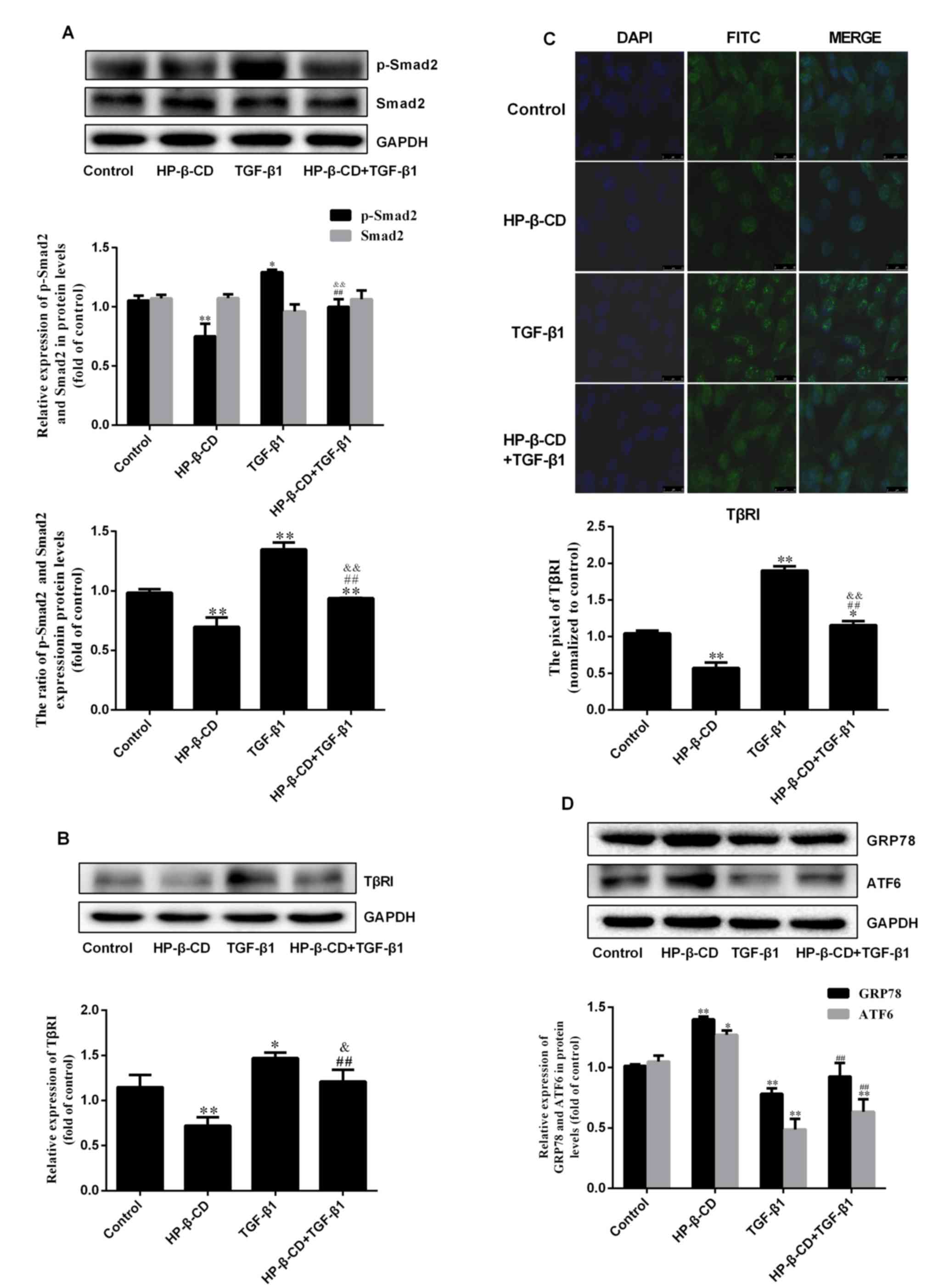
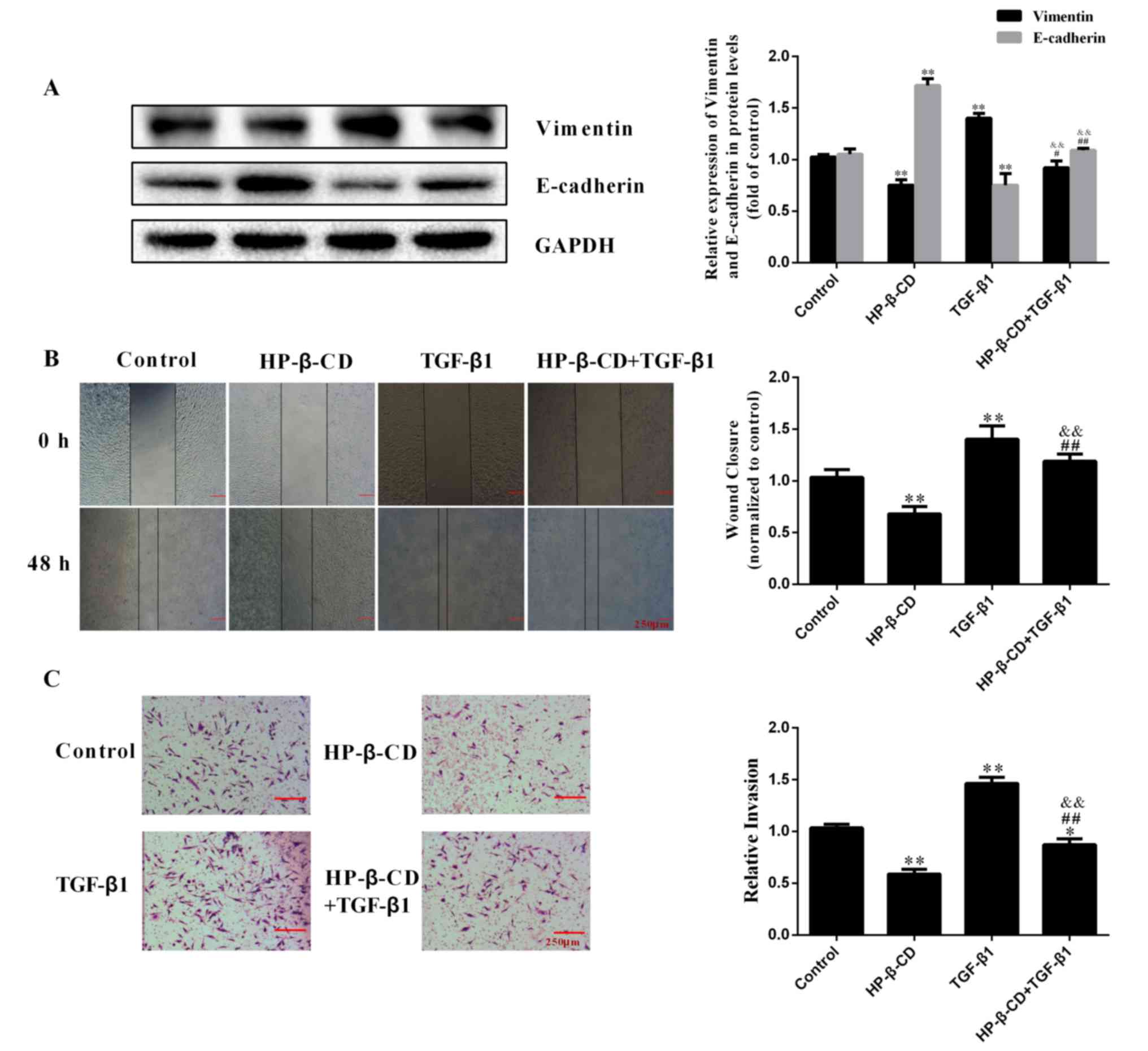
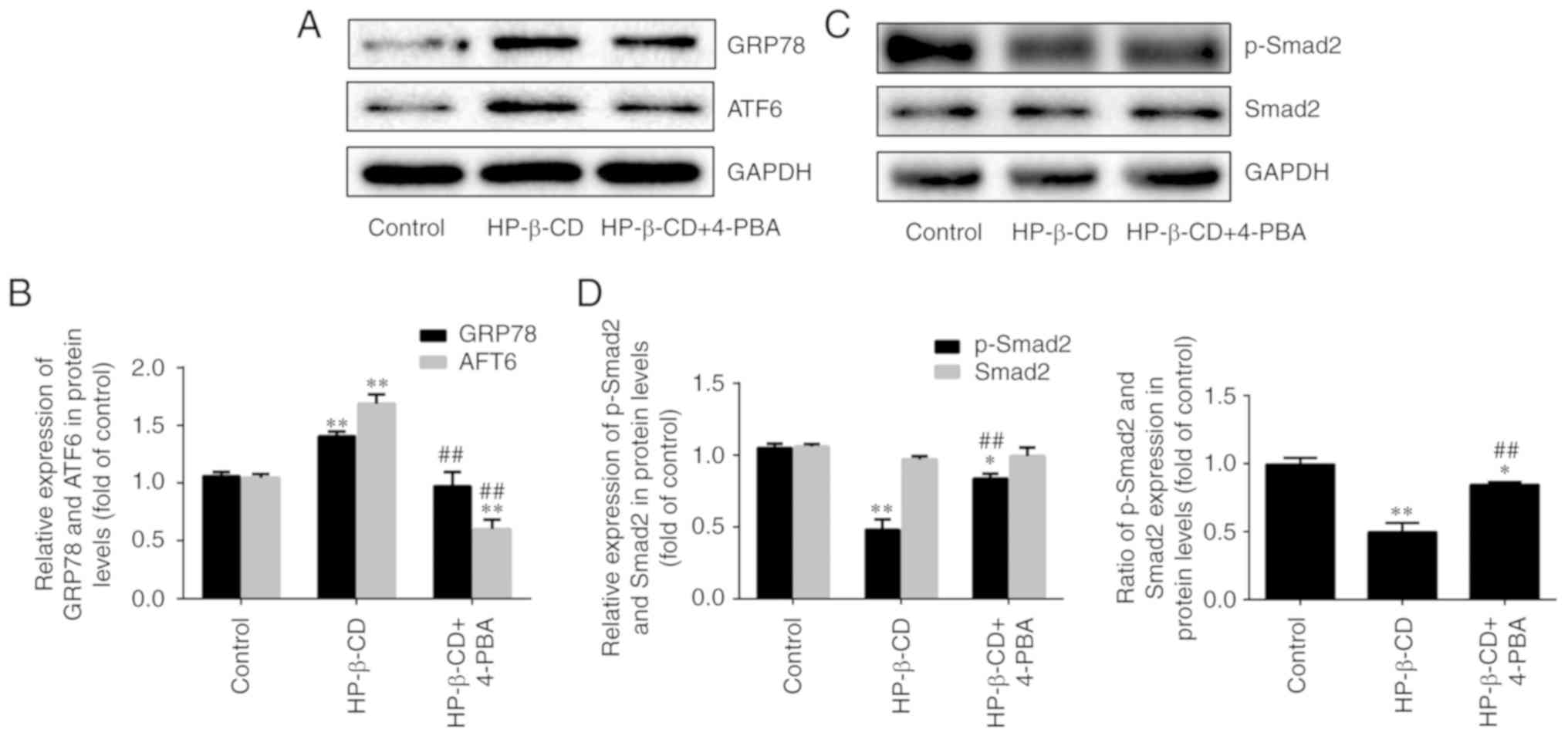
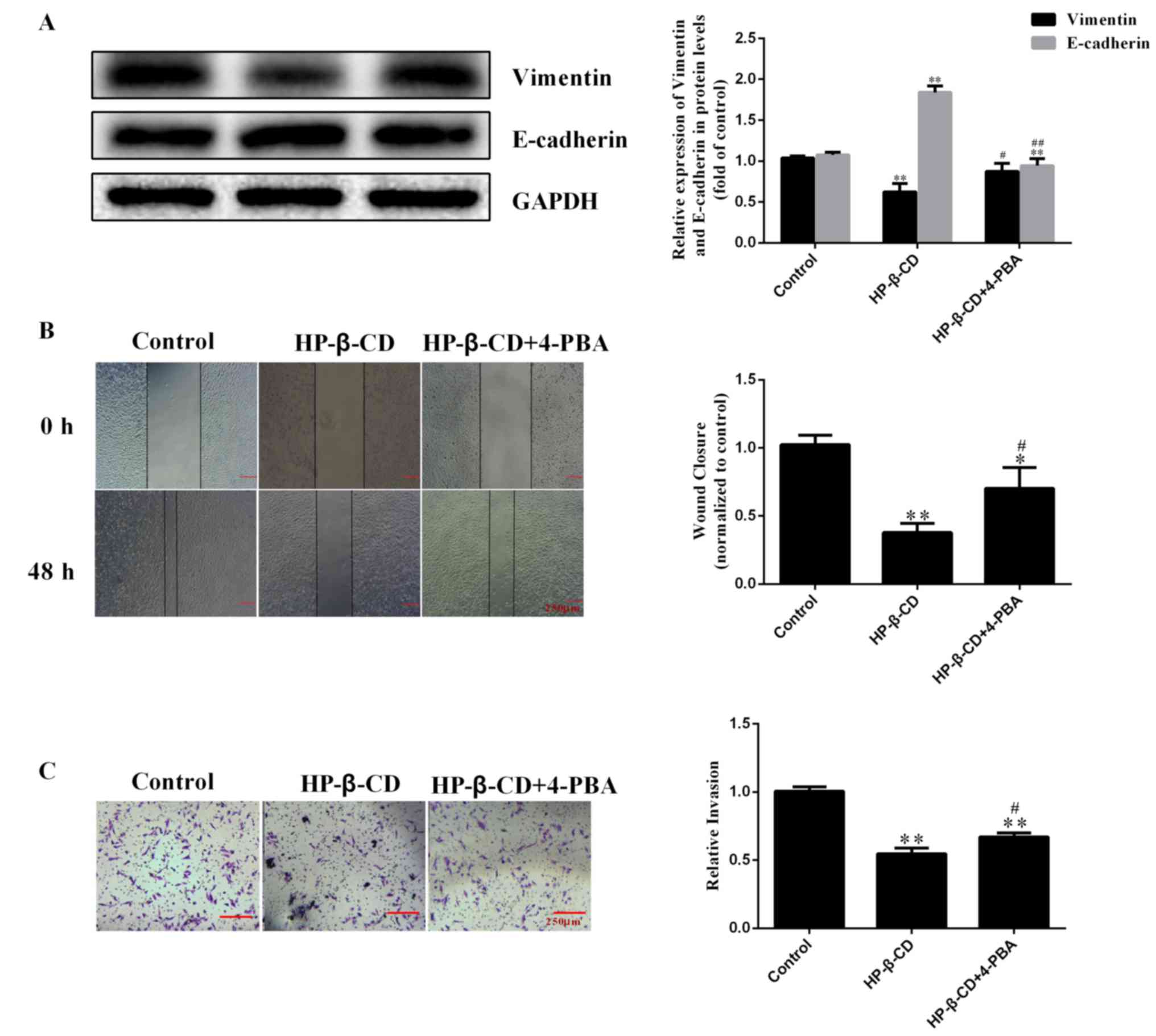
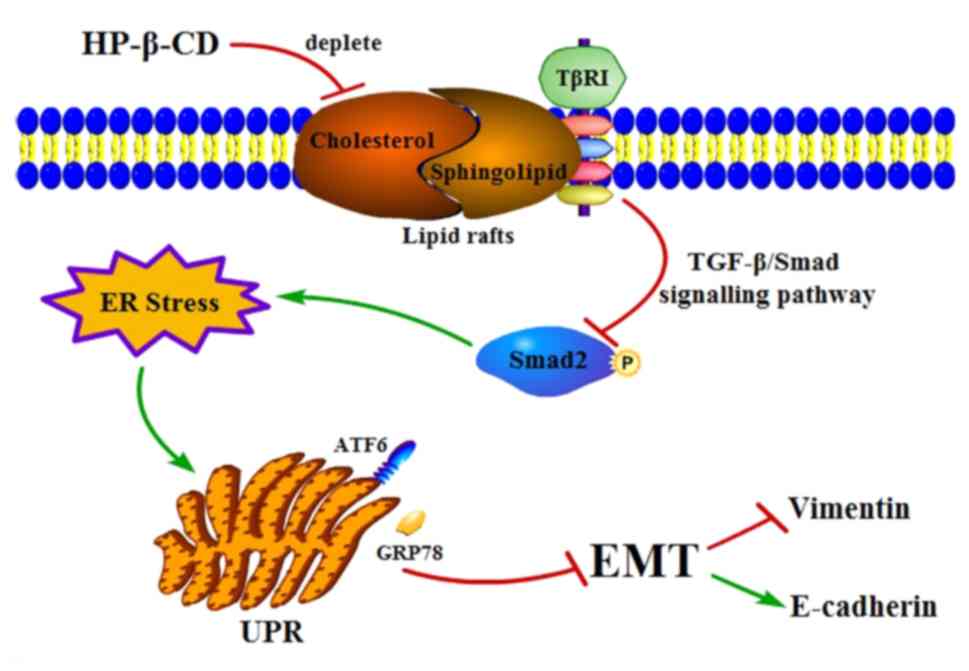
|
1
|
Wittkowski KM, Dadurian C, Seybold MP, Kim
HS, Hoshino A and Lyden D: Complex polymorphisms in endocytosis
genes suggest alpha-cyclodextrin as a treatment for breast cancer.
PLoS One. 13:e01990122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li L and Li W: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in human cancer: Comprehensive reprogramming of
metabolism, epigenetics, and differentiation. Pharmacol Ther.
150:33–46. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ruben B and Gerhard C: The relevance of
EMT in breast cancer metastasis: Correlation or causality? FEBS
Lett. 589:1577–1587. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Das V, Bhattacharya S, Chikkaputtaiah C,
Hazra S and Pal M: The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition
(EMT): A study from a structure, dynamics, and functional
perspective. J Cell Physiol. Feb 5–2019.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Heldin CH, Landström M and Moustakas A:
Mechanism of TGF-beta signaling to growth arrest, apoptosis, and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 21:166–176.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sánchez-Tilló E, Liu Y, de Barrios O,
Siles L, Fanlo L, Cuatrecasas M, Darling DS, Dean DC, Castells A
and Postigo A: EMT-activating transcription factors in cancer:
Beyond EMT and tumor invasiveness. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:3429–3456.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Beloribi-Djefaflia S, Vasseur S and
Guillaumond F: Lipid metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells.
Oncogenesis. 5:e1892016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kraft ML: Plasma membrane organization and
function: Moving past lipid rafts. Mol Biol Cell. 24:2765–2768.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li YC, Park MJ, Ye SK, Kim CW and Kim YN:
Elevated levels of cholesterol-rich lipid rafts in cancer cells are
correlated with apoptosis sensitivity induced by
cholesterol-depleting agents. Am J Pathol. 168:1107–1118. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Razani B, Zhang XL, Bitzer M, von
Gersdorff G, Böttinger EP and Lisanti MP: Caveolin-1 regulates
transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta/SMAD signaling through an
interaction with the TGF-beta type I receptor. J Biol Chem.
276:6727–6738. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Le Roy C and Wrana JL: Clathrin- and
non-clathrin-mediated endocytic regulation of cell signalling. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:112–126. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu S, Hou H, Zhang P, Wu Y, He Q, Li H
and Yan N: Sphingomyelin synthase 1 regulates the
epithelialtomesenchymal transition mediated by the TGF-β/Smad
pathway in MDA-MB-231 cells. Mol Med Rep. 19:1159–1167.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Maxfield FR and Tabas I: Role of
cholesterol and lipid organization in disease. Nature. 438:612–621.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kline MA, O'Connor Butler ES, Hinzey A,
Sliman S, Kotha SR, Marsh CB, Uppu RM and Parinandi NL: A simple
method for effective and safe removal of membrane cholesterol from
lipid rafts in vascular endothelial cells: Implications in
oxidant-mediated lipid signaling. Methods Mol Biol. 610:201–2011.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Engin F and Hotamisligil GS: Restoring
endoplasmic reticulum function by chemical chaperones: An emerging
therapeutic approach for metabolic diseases. Diabetes Obes Metab.
12:108–115. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ron D and Walter P: Signal integration in
the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 8:519–529. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang S and Kaufman R: The impact of the
unfolded protein response on human disease. J Cell Biol.
197:857–867. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamashita M, Ogasawara M, Kawasaki Y,
Niisato M, Saito H, Kasai S, Maesawa C, Maemondo M and Yamauchi K:
Deficiency of protein-L-isoaspartate (D-aspartate)
O-methyl-transferase expression under endoplasmic reticulum stress
promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition in lung adenocarcinoma.
Oncotarget. 9:13287–13300. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen CA, Chang JM, Chang EE, Chen HC and
Yang YL: Crosstalk between transforming growth factor-beta1 and
endoplasmic reticulum stress regulates alpha-smooth muscle cell
actin expression in podocytes. Life Sci. 209:9–14. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang Y, Du J, Mi Y, Li T, Gong Y, Ouyang
H and Hou Y: Long non-coding RNAs contribute to the inhibition of
proliferation and EMT by pterostilbene in human breast cancer. Fron
Oncol. 8:6292018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Badana A, Chintala M, Varikuti G, Pudi N,
Kumari S, Kappala RV and Malla RR: Lipid raft integrity is required
for survival of triple negative breast cancer cells. J Breast
Cancer. 19:372–384. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee HM, Kang JH, Shin JM, Lee SA and Park
HO: Chemical chaperone of endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibits
epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by TGF-β1 in airway
epithelium via the c-src pathway. Mediators Inflamm. 2017:1–9.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Deans JP, Li H and Polyak MJ:
CD20-mediated apoptosis: Signalling through lipid rafts.
Immunology. 107:176–182. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gómez-Llobregat J, Buceta J and Reigada R:
Interplay of cytoskeletal activity and lipid phase stability in
dynamic protein recruitment and clustering. Sci Rep. 3:26082013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang R, Bi J, Ampah KK, Ba X, Liu W and
Zeng X: Lipid rafts control human melanoma cell migration by
regulating focal adhesion disassembly. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1833:3195–3205. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Head BP, Patel HH and Insel PA:
Interaction of membrane/lipid rafts with the cytoskeleton: Impact
on signaling and function: Membrane/lipid rafts, mediators of
cytoskeletal arrangement and cell signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1838:532–545. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Alawin OA, Ahmed RA, Ibrahim BA, Briski KP
and Sylvester PW: Antiproliferative effects of γ-tocotrienol are
associated with lipid raft disruption in HER2-positive human breast
cancer cells. J Nutr Biochem. 27:266–277. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Badana AK, Chintala M, Gavara MM, Naika S,
Kumari S, Kappala VR, Iska BR and Malla RR: Lipid rafts disruption
induces apoptosis by attenuating expression of LRP6 and survivin in
triple negative breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 97:359–369.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mitchell H, Choudhury A, Pagano RE and
Leof EB: Ligand-dependent and -independent transforming growth
factor-beta receptor recycling regulated by clathrin-mediated
endocytosis and Rab11. Mol Biol Cell. 15:4166–4178. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Le Roy C and Wrana JL: Clathrin- and
non-clathrin-mediated endocytic regulation of cell signalling. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:112–126. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Midgley AC, Rogers M, Hallett MB, Clayton
A, Bowen T, Phillips AO and Steadman R: Transforming growth
factor-β1 (TGF-β1) stimulated fibroblast to myofibroblast
differentiation is mediated by hyaluronan (HA)-facilitated
epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and CD44 co-localization in
lipid rafts. J Biol Chem. 288:14824–14838. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen YG: Endocytic regulation of TGF-beta
signaling. Cell Res. 19:58–70. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Derynck R, Muthusamy BP and Saeteurn KY:
Signaling pathway cooperation in TGF-β-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 31:56–66.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Takebe N, Warren RQ and Ivy SP: Breast
cancer growth and metastasis: Interplay between cancer stem cells,
embryonic signaling pathways and epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Breast Cancer Res. 13:211. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Conner SD and Schmid SL: Regulated portals
of entry into the cell. Nature. 422:37–44. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ewers H and Helenius A: Lipid-mediated
endocytosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 3:a0047212011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Moon SY, Kim HS, Nho KW, Jang YJ and Lee
SK: Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces epithelial-mesenchymal
transition through autophagy via activation of c-Src kinase.
Nephron. Exp Nephrol. 126:127–140. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Dasgupta A, Sawant MA, Kavishwar G,
Lavhale M and Sitasawad S: AECHL-1 targets breast cancer
progression via inhibition of metastasis, prevention of EMT and
suppression of cancer stem cell characteristics. Sci Rep.
6:380452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huang S, Wang D, Zhang S, Huang X, Wang D,
Ljaz M and Shi Y: Tunicamycin potentiates paclitaxel-induced
apoptosis through inhibition of PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways in
breast cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 80:685–696. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
He Z, He X, Liu M, Hua L, Wang T, Liu Q,
Chen L and Yan N: Simvastatin attenuates H2O2-induced endothelial
cell dysfunction by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Molecules. 24(pii): E17822019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu F, Xu K, Liu L, Zhang K, Xia L, Zhang
M, Teng C, Tong H, He Y, Xue Y, et al: Vitamin B12 enhances nerve
repair and improves functional recovery after traumatic brain
injury by inhibiting ER stress-induced neuron injury. Front
Pharmacol. 10:4062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang EH, Yao SQ, Tao L and Xi JY: Sodium
4-phenylbutyrate attenuates high-fat diet-induced impaired
spermatogenesis. Biomed Environ Sci. 12:876–882. 2018.
|
|
44
|
Guo Q, Hu H, Zhou Y, Yan Y, Wei X, Fan X,
Yang D, He H, Oh Y, Chen K, et al: Glucosamine induces increased
musclin gene expression through endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced unfolding protein response signaling pathways in
mouse skeletal muscle cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 125:95–105. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|