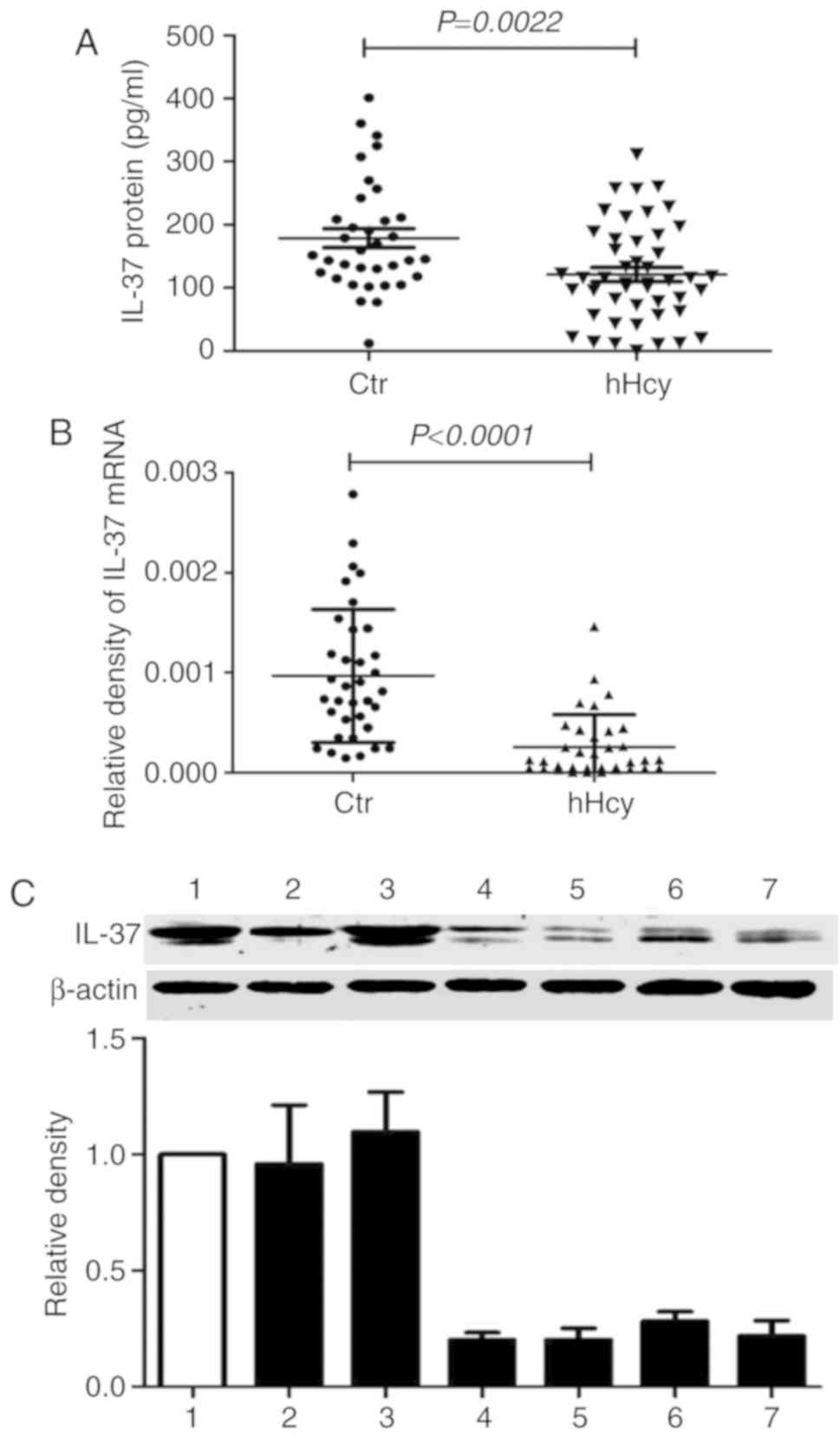
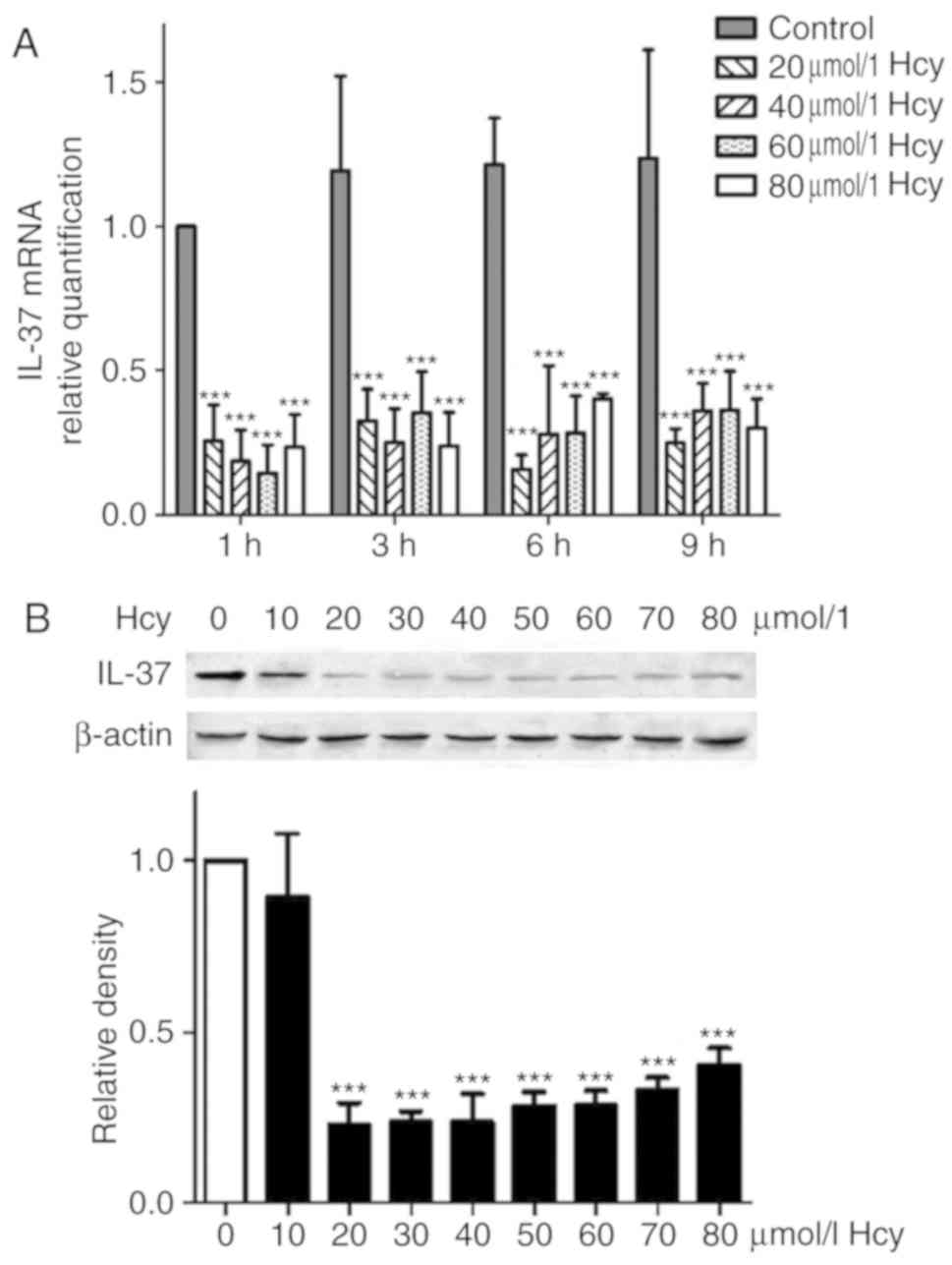
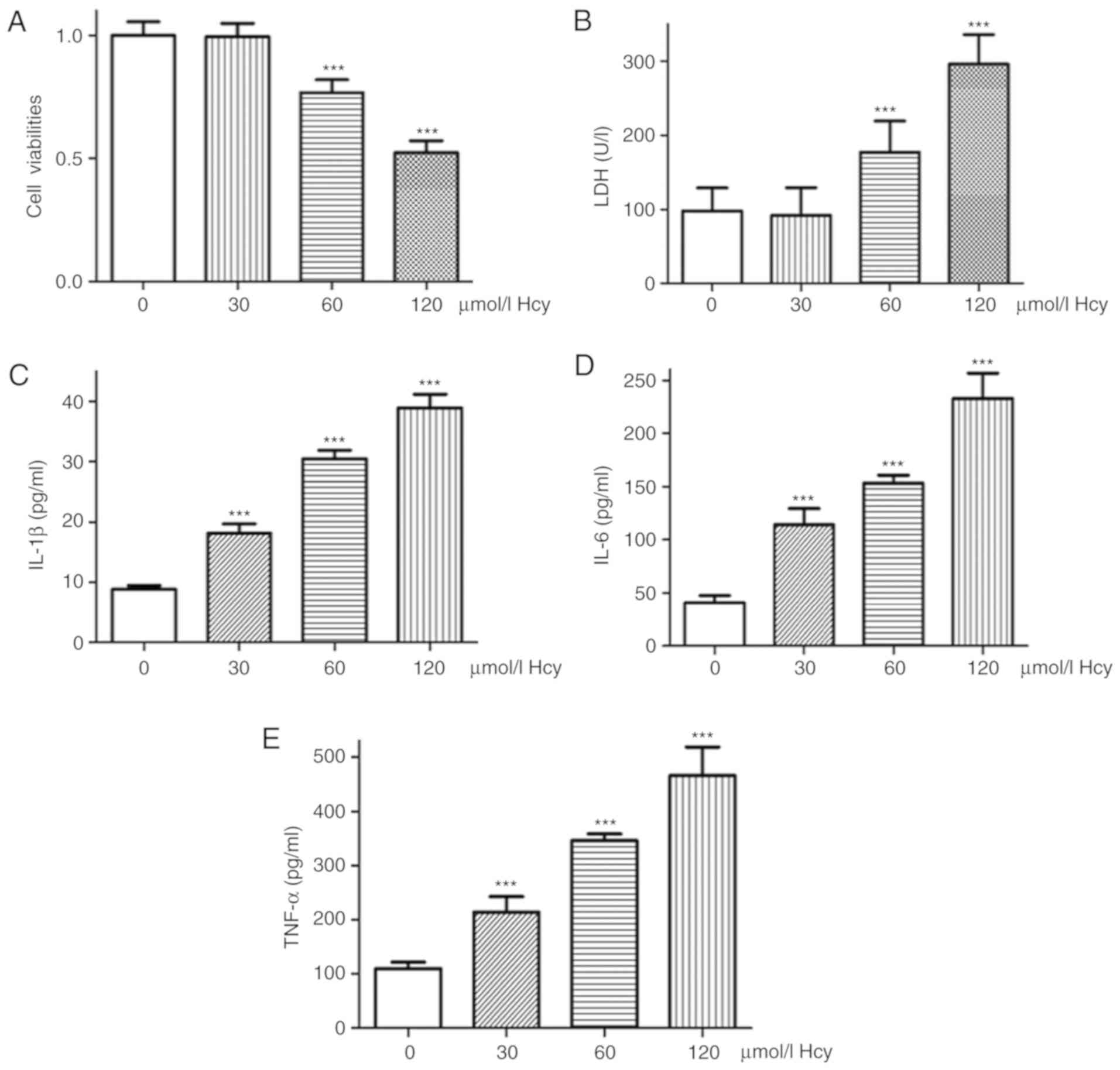
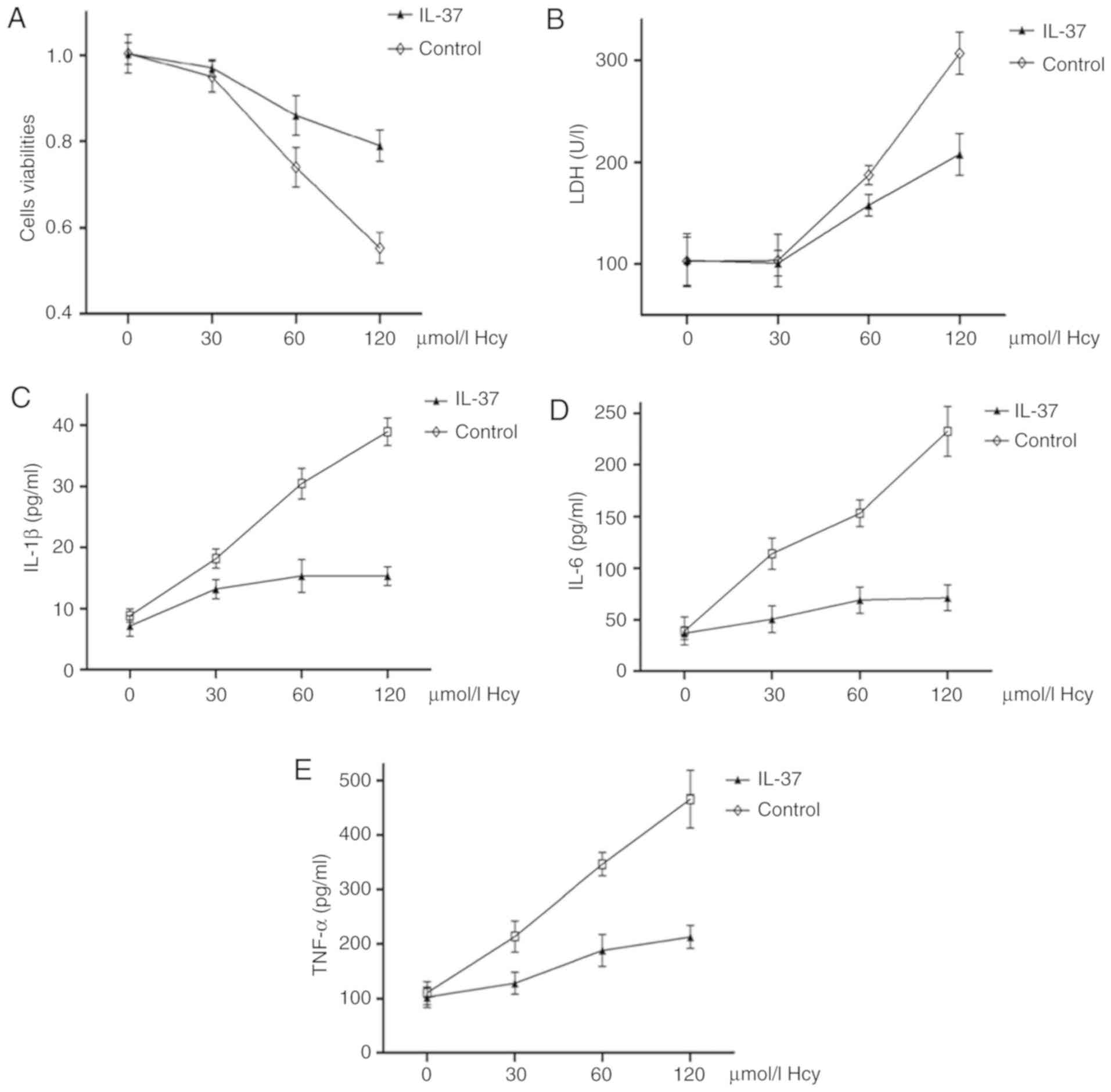
|
1
|
Zhao J, Chen H, Liu N, Chen J, Gu Y, Chen
J and Yang K: Role of hyperhomocysteinemia and hyperuricemia in
pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis.
26:2695–2699. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jakubowski H: Homocysteine modification in
protein structure/function and human disease. Physiol Rev.
99:555–604. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rong D, Liu J, Jia X, Al-Nafisee D, Jia S,
Sun G, Li Y, Lu W, Li H, Zhang H, et al: Hyperhomocysteinaemia is
an independent risk factor for peripheral arterial disease in a
Chinese Han population. Atherosclerosis. 263:205–210. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cao C, Hu J, Dong Y, Zhan R, Li P, Su H,
Peng Q, Wu T, Lei L, Hang X, et al: Gender differences in the risk
factors for endothelial dysfunction in Chinese hypertensive
patients: Homocysteine is an independent risk factor in females.
PLoS One. 10:e01186862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xie D, Yuan Y, Guo J, Yang S, Xu X, Wang
Q, Li Y, Qin X, Tang G, Huo Y, et al: Hyperhomocysteinemia predicts
renal function decline: A prospective study in hypertensive adults.
Sci Rep. 5:162682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Suszyńska-Zajczyk J, Utyro O and
Jakubowski H: Methionine-induced hyperhomocysteinemia and bleomycin
hydrolase deficiency alter the expression of mouse kidney proteins
involved in renal disease. Mol Genet Metab. 112:339–346. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Petras M, Tatarkova Z, Kovalska M, Mokra
D, Dobrota D, Lehotsky J and Drgova A: Hyperhomocysteinemia as a
risk factor for the neuronal system disorders. J Physiol Pharmacol.
65:15–23. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ashjazadeh N, Fathi M and Shariat A:
Evaluation of homocysteine level as a risk factor among patients
with ischemic stroke and its subtypes. Iran J Med Sci. 38:233–239.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kamat PK, Vacek JC, Kalani A and Tyagi N:
Homocysteine induced cerebrovascular dysfunction: A link to
Alzheimer's disease etiology. Open Neurol J. 9:9–14. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nazef K, Khelil M, Chelouti H, Kacimi G,
Bendini M, Tazir M, Belarbi S, El Hadi Cherifi M and Djerdjouri B:
Hyperhomocysteinemia is a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease in an
Algerian population. Arch Med Res. 45:247–250. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Han L, Wu Q, Wang C, Hao Y, Zhao J, Zhang
L, Fan R, Liu Y, Li R, Chen Z, et al: Homocysteine, ischemic stroke
and coronary heart disease in hypertensive patients. Stroke.
46:1777–1786. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Durgaprasad R, Akkulagari V, Kasala L,
Velam V and Sarma P: GW27-e0552 Novel single nucleotide
polymorphisms identified in Exon-10 of Human coagulation factor V
gene in patients with pulmonary embolism. J Am Coll Cardiol.
68:C48. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mazza A, Cicero AF, Ramazzina E, Lenti S,
Schiavon L, Casiglia E and Gussoni G: Nutraceutical approaches to
homocysteine lowering in hypertensive subjects at low
cardiovascular risk: A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J
Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 30:921–927. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang CY, Chen ZW, Zhang T, Liu J, Chen SH,
Liu SY, Han LY, Hui ZH and Chen YM: Elevated plasma homocysteine
level is associated with ischemic stroke in Chinese hypertensive
patients. Eur J Intern Med. 25:538–544. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nold MF, Nold-Petry CA, Zepp JA, Palmer
BE, Bufler P and Dinarello CA: IL-37 is a fundamental inhibitor of
innate immunity. Nat Immunol. 11:1014–1022. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Boraschi D, Lucchesi D, Hainzl S, Leitner
M, Maier E, Mangelberger D, Oostingh GJ, Pfaller T, Pixner C,
Posselt G, et al: IL-37: A new anti-inflammatory cytokine of the
IL-1 family. Eur Cytokine Netw. 22:127–147. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Luo Y, Cai X, Liu S, Wang S, Nold-Petry
CA, Nold MF, Bufler P, Norris D, Dinarello CA and Fujita M:
Suppression of antigen-specific adaptive immunity by IL-37 via
induction of tolerogenic dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:15178–15183. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Y, Wang Y, Liu Y, Wang Y, Zuo X, Li Y
and Lu X: The possible role of the novel cytokines il-35 and il-37
in inflammatory bowel disease. Mediators Inflamm. 2014:1363292014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ye L, Jiang B, Deng J, Du J, Xiong W, Guan
Y, Wen Z, Huang K and Huang Z: IL-37 Alleviates rheumatoid
arthritis by suppressing IL-17 and IL-17-triggering cytokine
production and limiting Th17 cell proliferation. J Immunol.
194:5110–5119. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao PW, Jiang WG, Wang L, Jiang ZY, Shan
YX and Jiang YF: Plasma levels of IL-37 and correlation with TNF-α,
IL-17A, and disease activity during DMARD treatment of rheumatoid
arthritis. PLoS One. 9:e953462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ye L, Ji L, Wen Z, Zhou Y, Hu D, Li Y, Yu
T, Chen B, Zhang J, Ding L, et al: IL-37 inhibits the production of
inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of
patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Its correlation with
disease activity. J Transl Med. 12:692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Conti P, Lessiani G, Kritas SK, Ronconi G,
Caraffa A and Theoharides TC: Mast cells emerge as mediators of
atherosclerosis: Special emphasis on IL-37 inhibition. Tissue Cell.
49:393–400. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ji Q, Zeng Q, Huang H, Shi Y, Lin Y, Lu Z,
Meng K, Wu B, Yu K, Chai M, et al: Elevated plasma IL-37, IL-18,
and IL-18BP concentrations in patients with acute coronary
syndrome. Mediat Inflamm. 2014:1657422014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wu B, Meng K, Ji Q, Cheng M, Yu K, Zhao X,
Tony H, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Chang C, et al: Interleukin-37 ameliorates
myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Clin Exp Immunol.
176:438–451. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ye Z, Wang C, Tang J, Zhou Y, Bai L, Liu
Y, Kijlstra A and Yang P: Decreased interleukin-37 expression in
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease and upregulation following
immunosuppressive treatment. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 35:265–272.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Asanuma Y, Oeser A, Stanley E, Shintani A
and Stein CM: The effect of homocysteine on the production of
inflammatory cytokines. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 75:P492004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zanin RF, Bergamin LS, Morrone FB,
Coutinho-Silva R, de Souza Wyse AT and Battastini AM: Pathological
concentrations of homocysteine increases IL-1β production in
macrophages in a P2X7, NF-ĸB, and erk-dependent manner. Purinergic
Signal. 11:463–470. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Han S, Wu H, Li W and Gao P: Protective
effects of genistein in homocysteine-induced endothelial cell
inflammatory injury. Mol Cell Biochem. 403:43–49. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
McNamee EN, Masterson JC, Jedlicka P,
McManus M, Grenz A, Collins CB, Nold MF, Nold-Petry C, Bufler P,
Dinarello CA and Rivera-Nieves J: Interleukin 37 expression
protects mice from colitis. Proc Natl Acda Sci USA.
108:16711–16716. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|