|
1
|
Abraham TM, Pencina KM, Pencina MJ and Fox
CS: Trends in diabetes incidence: the Framingham heart study.
Diabetes Care. 38:482–487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Geiss LS, Wang J, Cheng YJ, Thompson TJ,
Barker L, Li Y, Albright AL and Gregg EW: Prevalence and incidence
trends for diagnosed diabetes among adults aged 20 to 79 years,
United States, 1980–2012. JAMA. 312:1218–1226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kosiborod M, Gomes MB, Nicolucci A, Pocock
S, Rathmann W, Shestakova MV, Watada H, Shimomura I, Chen H,
Cid-Ruzafa J, et al: Vascular complications in patients with type 2
diabetes: Prevalence and associated factors in 38 countries (the
DISCOVER study program). Cardiovasc Diabetol. 17:1502018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Suzuki LA, Poot M, Gerrity RG and
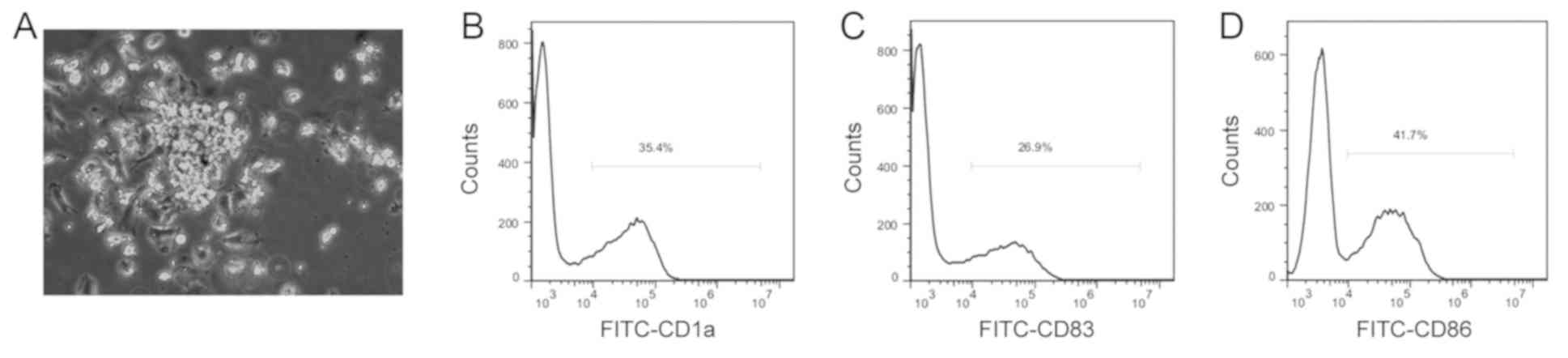
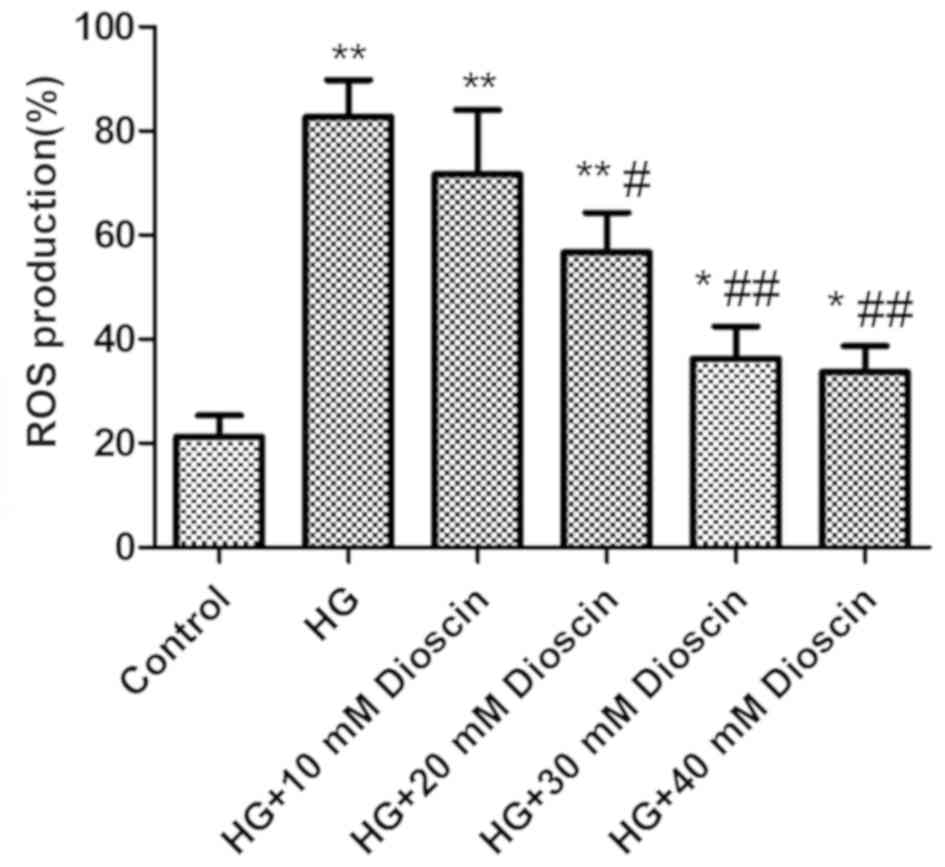
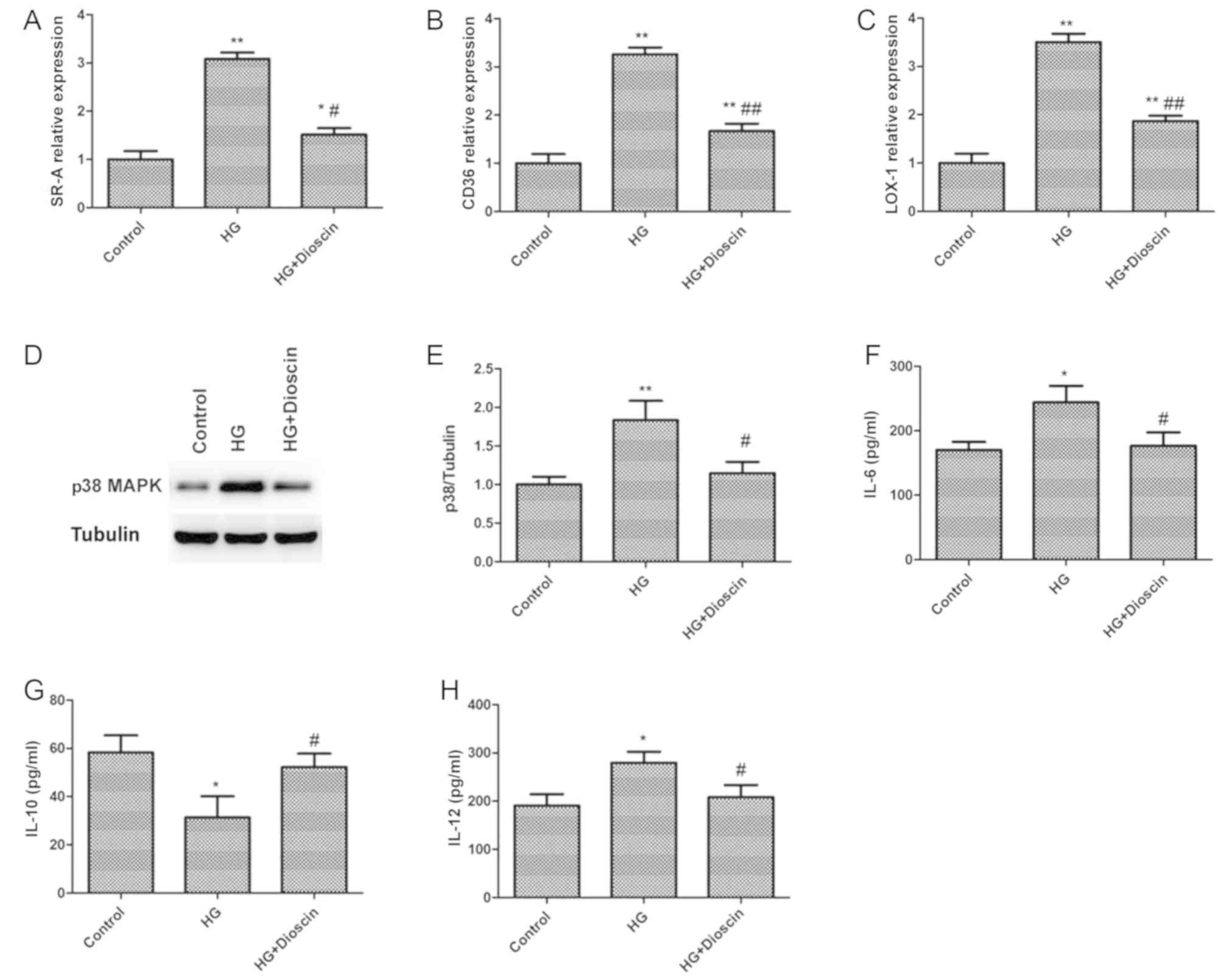
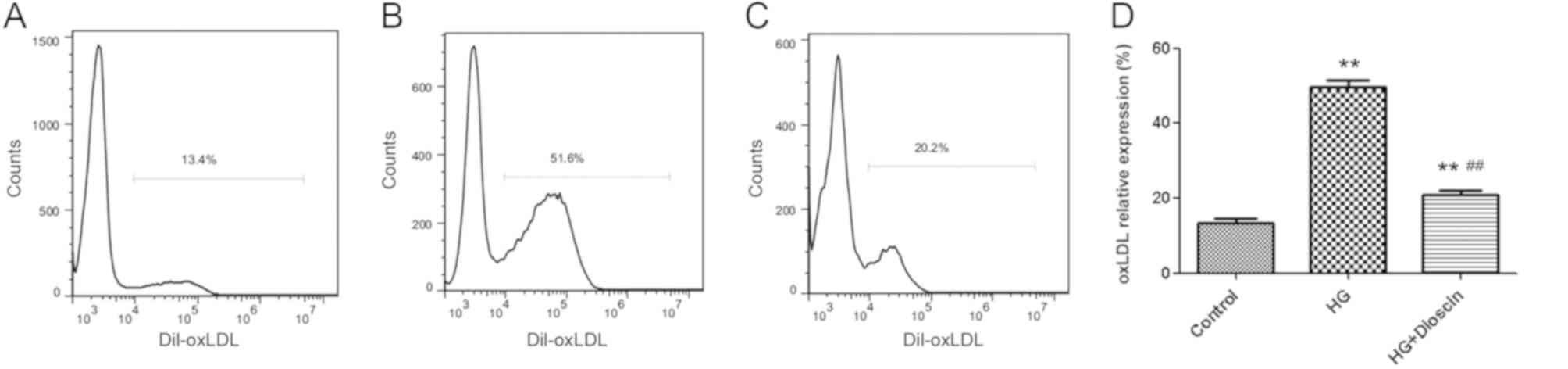
Bornfeldt KE: Diabetes accelerates smooth muscle accumulation in
lesions of atherosclerosis: Lack of direct growth-promoting effects
of high glucose levels. Diabetes. 50:851–860. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gilardini Montani MS, Granato M, Cuomo L,
Valia S, Di Renzo L, D'Orazi G, Faggioni A and Cirone M: High
glucose and hyperglycemic sera from type 2 diabetic patients impair
DC differentiation by inducing ROS and activating Wnt/β-catenin and
p38 MAPK. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1862:805–813. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Consolidated guidelines on the use of
antiretroviral drugs for treating and preventing HIV infection:
Recommendations for a Public Health Approach. 2nd. Geneva: 2016
|
|
7
|
Hansson GK: Inflammation, atherosclerosis,
and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 352:1685–1695. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lu H, Yao K, Huang D, Sun A, Zou Y, Qian J
and Ge J: High glucose induces upregulation of scavenger receptors
and promotes maturation of dendritic cells. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
12:802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ptak W, Klimek M, Bryniarski K, Ptak M and
Majcher P: Macrophage function in alloxan diabetic mice: Expression
of adhesion molecules, generation of monokines and oxygen and NO
radicals. Clin Exp Immunol. 114:13–18. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Beauloye C, Marsin AS, Bertrand L, Krause
U, Hardie DG, Vanoverschelde JL and Hue L: Insulin antagonizes
AMP-activated protein kinase activation by ischemia or anoxia in
rat hearts, without affecting total adenine nucleotides. FEBS Lett.
505:348–352. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu H, Huang D, Yao K, Li C, Chang S, Dai
Y, Sun A, Zou Y, Qian J and Ge J: Insulin enhances dendritic cell
maturation and scavenger receptor-mediated uptake of oxidised
low-density lipoprotein. J Diabetes Complications. 29:465–471.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang D, Lu H, Liu H, Yao K, Sun A, Zou Y
and Ge J: Losartan attenuates human monocyte-derived dendritic cell
immune maturation via downregulation of lectin-like oxidized
low-density lipoprotein receptor-1. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.
60:133–139. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tao X, Yin L, Xu L and Peng J: Dioscin: A
diverse acting natural compound with therapeutic potential in
metabolic diseases, cancer, inflammation and infections. Pharmacol
Res. 137:259–269. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mao Z, Han X, Chen D, Xu Y, Xu L, Yin L,
Sun H, Qi Y, Fang L, Liu K and Peng J: Potent effects of dioscin
against hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating TP53-induced
glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR)-mediated apoptosis,
autophagy, and DNA damage. Br J Pharmacol. 176:919–937. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hu Y, Mao Z, Xu L, Yin L, Tao X, Tang Z,
Qi Y, Sun P and Peng J: Protective effect of dioscin against
intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury via adjusting
miR-351-5p-mediated oxidative stress. Pharmacol Res. 137:56–63.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zheng L, Yin L, Xu L, Qi Y, Li H, Xu Y,
Han X, Liu K and Peng J: Protective effect of dioscin against
thioacetamide-induced acute liver injury via FXR/AMPK signaling
pathway in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother. 97:481–488. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yao H, Tao X, Xu L, Qi Y, Yin L, Han X, Xu
Y, Zheng L and Peng J: Dioscin alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease through adjusting lipid metabolism via SIRT1/AMPK signaling
pathway. Pharmacol Res. 131:51–60. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yao H, Hu C, Yin L, Tao X, Xu L, Qi Y, Han
X, Xu Y, Zhao Y, Wang C and Peng J: Dioscin reduces
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory liver injury via regulating
TLR4/MyD88 signal pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 36:132–141. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yao H, Sun Y, Song S, Qi Y, Tao X, Xu L,
Yin L, Han X, Xu Y, Li H, et al: Protective effects of dioscin
against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through
inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation. Front Pharmacol.
8:1202017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Tao X, Yin L, Xu L, Xu Y, Qi Y,
Han X, Song S, Zhao Y, Lin Y, et al: Protective effects of dioscin
against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via the
microRNA-34a/sirtuin 1 signalling pathway. Br J Pharmacol.
174:2512–2527. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zheng L, Han X, Hu Y, Zhao X, Yin L, Xu L,
Qi Y, Xu Y, Han X, Liu K and Peng J: Dioscin ameliorates intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion injury via adjusting
miR-351-5p/MAPK13-mediated inflammation and apoptosis. Pharmacol
Res. 139:431–439. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tao X, Xu L, Yin L, Han X, Qi Y, Xu Y,
Song S, Zhao Y and Peng J: Dioscin induces prostate cancer cell
apoptosis through activation of estrogen receptor-β. Cell Death
Dis. 8:e29892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Si L, Xu L, Yin L, Qi Y, Han X, Xu Y, Zhao
Y, Liu K and Peng J: Potent effects of dioscin against pancreatic
cancer via miR-149-3P-mediated inhibition of the Akt1 signalling
pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 174:553–568. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao L, Tao X, Qi Y, Xu L, Yin L and Peng
J: Protective effect of dioscin against doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity via adjusting microRNA-140-5p-mediated myocardial
oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 16:189–198. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu S, Xu H, Peng J, Wang C, Jin Y, Liu K,
Sun H and Qin J: Potent anti-inflammatory effect of dioscin
mediated by suppression of TNF-α-induced VCAM-1, ICAM-1and EL
expression via the NF-κB pathway. Biochimie. 110:62–72. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu M, Xu L, Yin L, Qi Y, Xu Y, Han X,
Zhao Y, Sun H, Yao J, Lin Y, et al: Potent effects of dioscin
against obesity in mice. Sci Rep. 5:79732015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tao X, Qi Y, Xu L, Yin L, Han X, Xu Y,
Wang C, Sun H and Peng J: Dioscin reduces ovariectomy-induced bone
loss by enhancing osteoblastogenesis and inhibiting
osteoclastogenesis. Pharmacol Res. 108:90–101. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Coventry BJ, Austyn JM, Chryssidis S,
Hankins D and Harris A: Identification and isolation of CD1a
positive putative tumour infiltrating dendritic cells in human
breast cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 417:571–577. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang LF, Okuma K, Tanaka R, Kodama A,
Kondo K, Ansari AA and Tanaka Y: Generation of mature dendritic
cells with unique phenotype and function by in vitro short-term
culture of human monocytes in the presence of interleukin-4 and
interferon-beta. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 233:721–731. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pan CH and Luo RC: Tumor necrosis
factor-alpha pretreatment for in vitro culture of mature dendritic
cells. Di Yi Jun Yi Da Xue Xue Bao. 23:114–117. 2003.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fernandez Pujol B, Lucibello FC, Zuzarte
M, Lütjens P, Müller R and Havemann K: Dendritic cells derived from
peripheral monocytes express endothelial markers and in the
presence of angiogenic growth factors differentiate into
endothelial-like cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 80:99–110. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kurosaki E and Ogasawara H: Ipragliflozin
and other sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors in the
treatment of type 2 diabetes: Preclinical and clinical data.
Pharmacol Ther. 139:51–59. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu L, Li Y, Dai Y and Peng J: Natural
products for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus:
Pharmacology and mechanisms. Pharmacol Res. 130:451–465. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhu S, Tang S and Su F: Dioscin inhibits
ischemic stroke-induced inflammation through inhibition of the
TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in a rat model. Mol Med Rep.
17:660–666. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li S, Cheng B, Hou L, Huang L, Cui Y, Xu
D, Shen X and Li S: Dioscin inhibits colon cancer cells' growth by
reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and p38
and JNK pathways. Anticancer Drugs. 29:234–242. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qin J, Kang Y, Xu Z, Zang C, Fang B and
Liu X: Dioscin prevents the mitochondrial apoptosis and attenuates
oxidative stress in cardiac H9c2 cells. Drug Res (Stuttg).
64:47–52. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yu H, Zheng L, Xu L, Yin L, Lin Y, Li H,
Liu K and Peng J: Potent effects of the total saponins from
Dioscorea nipponica Makino against streptozotocin-induced type 2
diabetes mellitus in rats. Phytother Res. 29:228–240. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wei Q, Zhu T, Xiao X, Sun L, Zhang Z and
Huang T: Dioscin attenuates myocardial damages in diabetic rats
maybe by regulating NO-sGC-cGMP-PKG pathway. Ann Clin Lab Sci.
49:97–104. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li H, Yu L and Zhao C: Dioscin attenuates
high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance of adipose tissue through
the IRS-1/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 19:1230–1237.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fang Z, Deng Q, Hu H, Wang X, Sun X, Ge X
and Wang P: Characteristics of immunogenic and tolerogenic
dendritic cells within the arterial wall in atherosclerosis and in
vitro. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:4846–4856. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gil-Pulido J and Zernecke A:
Antigen-presenting dendritic cells in atherosclerosis. Eur J
Pharmacol. 816:25–31. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zernecke A: Dendritic cells in
atherosclerosis: Evidence in mice and humans. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 35:763–770. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gu L, Tao X, Xu Y, Han X, Qi Y, Xu L, Yin
L and Peng J: Dioscin alleviates BDL- and DMN-induced hepatic
fibrosis via Sirt1/Nrf2-mediated inhibition of p38 MAPK pathway.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 292:19–29. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Vanden Berghe W, Plaisance S, Boone E, De
Bosscher K, Schmitz ML, Fiers W and Haegeman G: p38 and
extracellular signal-regulated kinase mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathways are required for nuclear factor-kappaB p65
transactivation mediated by tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem.
273:3285–3290. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nishizawa T and Bornfeldt KE: Diabetic
vascular disease and the potential role of macrophage glucose
metabolism. Ann Med. 44:555–563. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Qiao Y, Xu L, Tao X, Yin L, Qi Y, Xu Y,
Han X, Tang Z, Ma X, Liu K and Peng J: Protective effects of
dioscin against fructose-induced renal damage via adjusting
Sirt3-mediated oxidative stress, fibrosis, lipid metabolism and
inflammation. Toxicol Lett. 284:37–45. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang Y, Xu Y, Qi Y, Xu L, Song S, Yin L,
Tao X, Zhen Y, Han X, Ma X, et al: Protective effects of dioscin
against doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity via adjusting
FXR-mediated oxidative stress and inflammation. Toxicology.
378:53–64. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lv L, Zheng L, Dong D, Xu L, Yin L, Xu Y,
Qi Y, Han X and Peng J: Dioscin, a natural steroid saponin, induces
apoptosis and DNA damage through reactive oxygen species: A
potential new drug for treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Food
Chem Toxicol. 59:657–669. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhao X, Xu L, Zheng L, Yin L, Qi Y, Han X,
Xu Y and Peng J: Potent effects of dioscin against gastric cancer
in vitro and in vivo. Phytomedicine. 23:274–282. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Maier W, Altwegg LA, Corti R, Gay S,
Hersberger M, Maly FE, Sütsch G, Roffi M, Neidhart M, Eberli FR, et
al: Inflammatory markers at the site of ruptured plaque in acute
myocardial infarction: Locally increased interleukin-6 and serum
amyloid A but decreased C-reactive protein. Circulation.
111:1355–1361. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang X, Niessner A, Nakajima T, Ma-Krupa
W, Kopecky SL, Frye RL, Goronzy JJ and Weyand CM: Interleukin 12
induces T-cell recruitment into the atherosclerotic plaque. Circ
Res. 98:524–531. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yin Y, Liu W, Ji G and Dai Y: The
essential role of p38 MAPK in mediating the interplay of oxLDL and
IL-10 in regulating endothelial cell apoptosis. Eur J Cell Biol.
92:150–159. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|