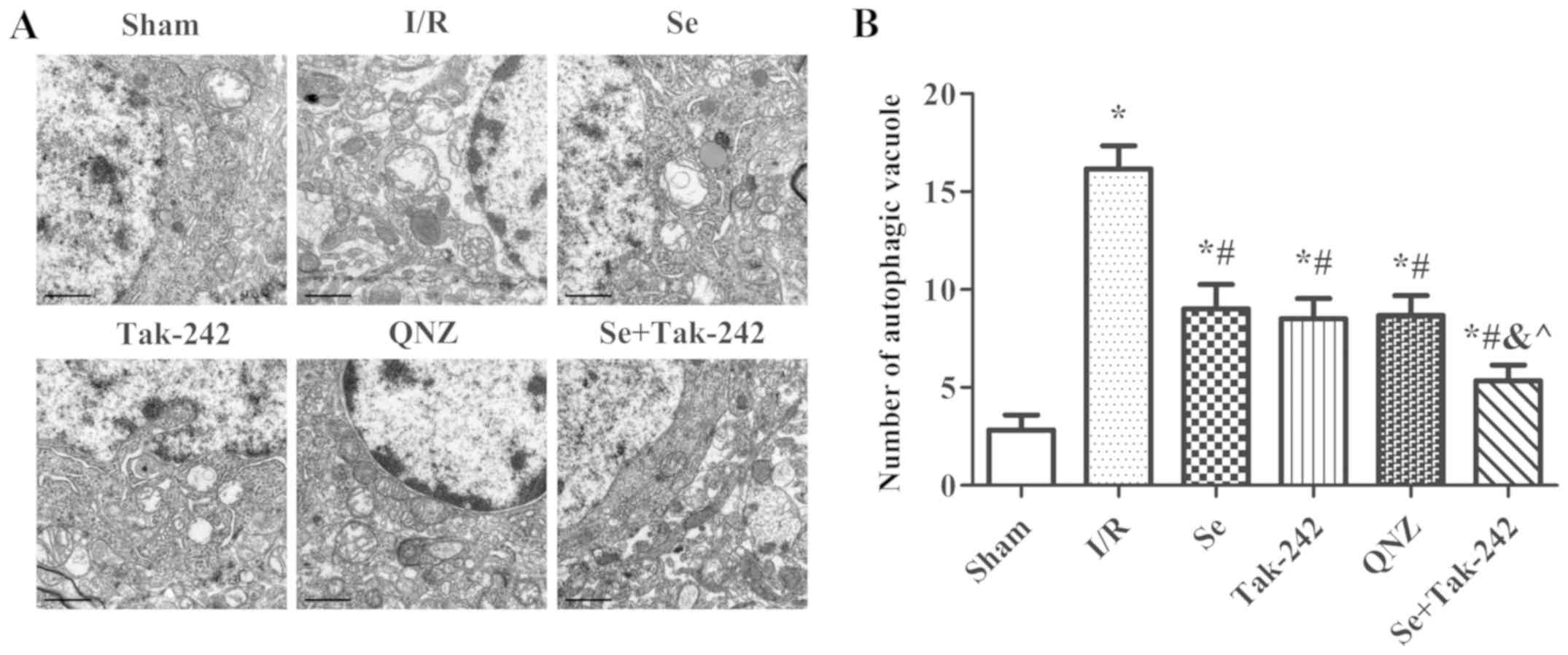
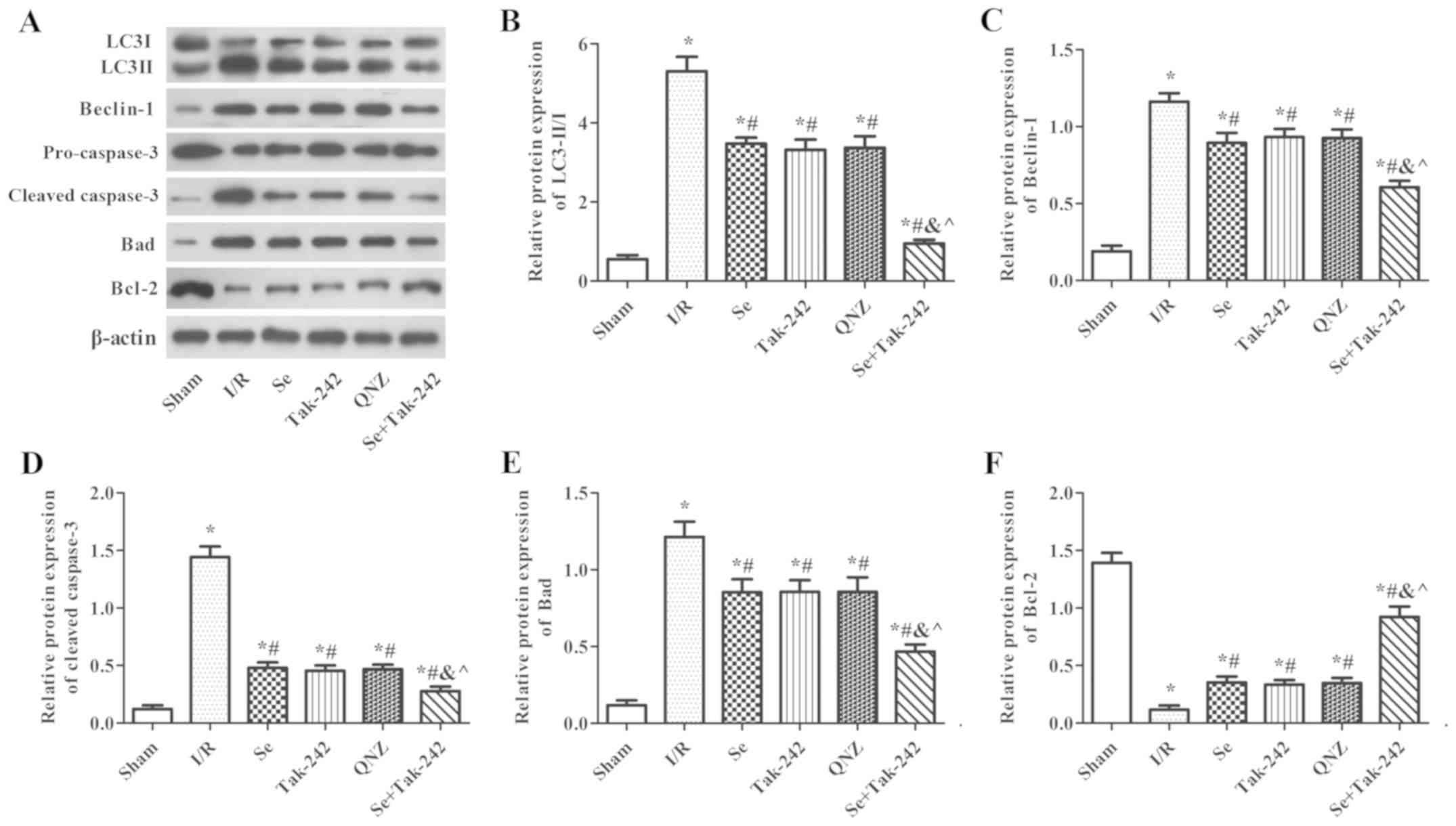
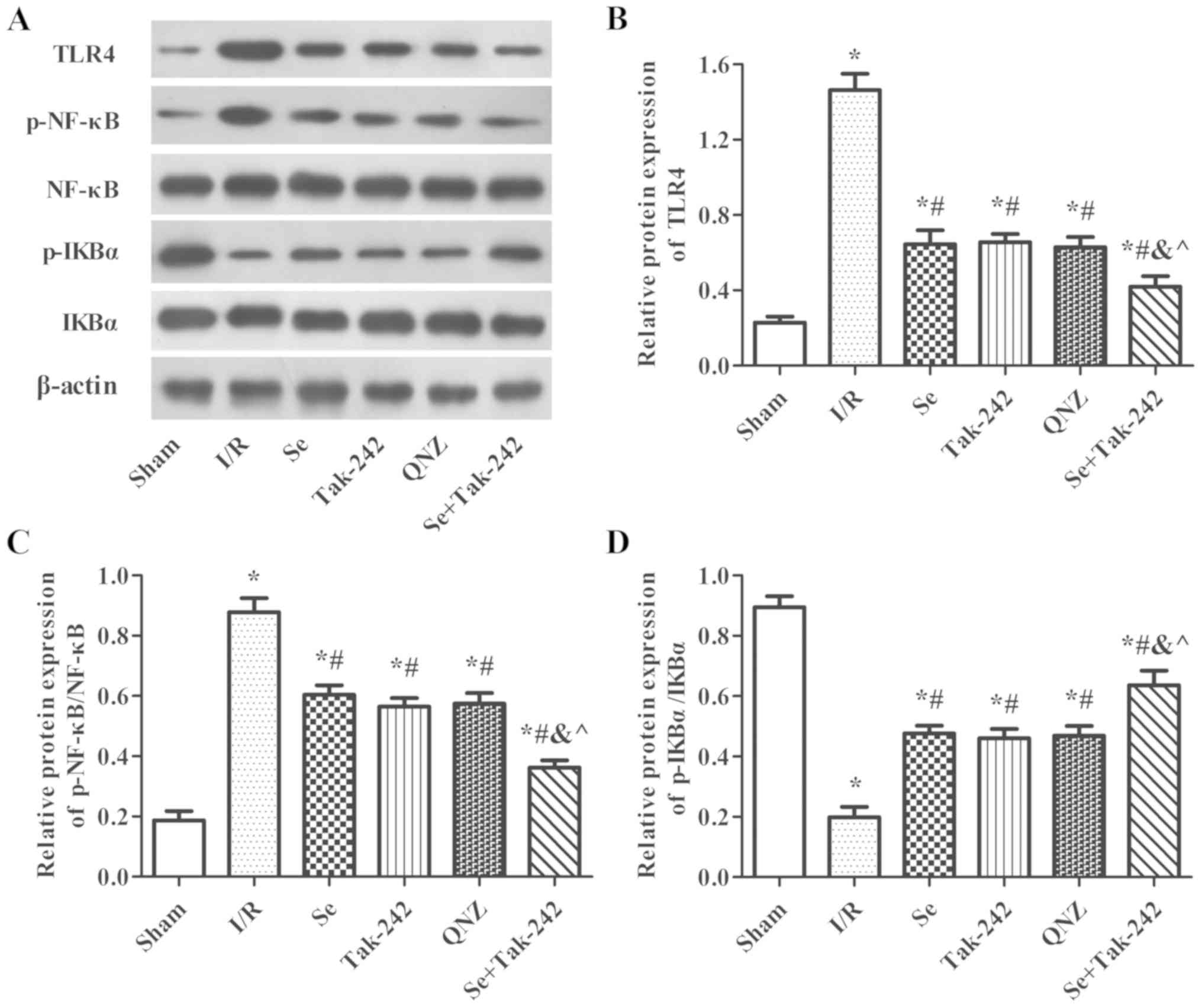
|
1
|
Flynn RW, MacWalter RS and Doney AS: The
cost of cerebral ischaemia. Neuropharmacology. 55:250–256. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Boyko M, Ohayon S, Goldsmith T, Douvdevani
A, Gruenbaum BF, Melamed I, Knyazer B, Shapira Y, Teichberg VI,
Elir A, et al: Cell-free DNA-a marker to predict ischemic brain
damage in a rat stroke experimental model. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol.
23:222–228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fernández A, Ordóñez R, Reiter RJ,
González-Gallego J and Mauriz JL: Melatonin and endoplasmic
reticulum stress: Relation to autophagy and apoptosis. J Pineal
Res. 59:292–307. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang B, Su CJ, Liu TT, Zhou Y, Feng Y,
Huang Y, Liu X, Wang ZH, Chen LH, Luo WF and Liu T: The
neuroprotection of low-dose morphine in cellular and animal models
of parkinson's disease through ameliorating endoplasmic reticulum
(ER) stress and activating autophagy. Front Mol Neurosci.
11:1202018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bildirici I, Longtine MS, Chen B and
Nelson DM: Survival by self-destruction: A role for autophagy in
the placenta? Placenta. 33:591–598. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cugola FR, Fernandes IR, Russo FB, Freitas
BC, Dias JL, Guimarães KP, Benazzato C, Almeida N, Pignatari GC,
Romero S, et al: The Brazilian Zika virus strain causes birth
defects in experimental models. Nature. 534:267–271. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Clark RS, Kochanek PM, Watkins SC, Chen M,
Dixon CE, Seidberg NA, Melick J, Loeffert JE, Nathaniel PD, Jin KL
and Graham SH: Caspase-3 mediated neuronal death after traumatic
brain injury in rats. J Neurochem. 74:740–753. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Graham SH, Chen J and Clark RS: Bcl-2
family gene products in cerebral ischemia and traumatic brain
injury. J Neurotrauma. 17:831–841. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Clark RS, Bayir H, Chu CT, Alber SM,
Kochanek PM and Watkins SC: Autophagy is increased in mice after
traumatic brain injury and is detectable in human brain after
trauma and critical illness. Autophagy. 4:88–90. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Steensma DP, Shampo MA and Kyle RA: Bruce
Beutler: Innate immunity and Toll-like receptors. Mayo Clin Proc.
89:e1012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jack CS, Arbour N, Manusow J, Montgrain V,
Blain M, McCrea E, Shapiro A and Antel JP: TLR signaling tailors
innate immune responses in human microglia and astrocytes. J
Immunol. 175:4320–4330. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dang YM, Huang G, Chen YR, Dang ZF, Chen
C, Liu FL, Guo YF and Xie XD: Sulforaphane inhibits the
proliferation of the BIU87 bladder cancer cell line via IGFBP-3
elevation. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:1517–1520. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ozbek E, Cekmen M, Ilbey YO, Simsek A,
Polat EC and Somay A: Atorvastatin prevents gentamicin-induced
renal damage in rats through the inhibition of p38-MAPK and
NF-kappaB pathways. Ren Fail. 31:382–392. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Song D, Jiang X, Liu Y, Sun Y, Cao S and
Zhang Z: Asiaticoside Attenuates Cell Growth Inhibition and
Apoptosis Induced by by Aβ1-42 via Inhibiting the
TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway in human brain microvascular
endothelial cells. Front Pharmacol. 9:282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang H, Shi H, Yu Q, Chen J, Zhang F and
Gao Y: Sevoflurane preconditioning confers neuroprotection via
anti-apoptosis effects. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 121:55–61. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim HC, Kim E, Bae JI, Lee KH, Jeon YT,
Hwang JW, Lim YJ, Min SW and Park HP: Sevoflurane postconditioning
reduces apoptosis by activating the JAK-STAT pathway after
transient global cerebral ischemia in rats. J Neurosurg
Anesthesiol. 29:37–45. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
He H, Liu W, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Weng P, Li Y
and Fu H: Sevoflurane post-conditioning attenuates traumatic brain
injury-induced neuronal apoptosis by promoting autophagy via the
PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 12:629–638. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shi CX, Ding YB, Jin FYJ, Li T, Ma JH,
Qiao LY, Pan WZ and Li KZ: Effects of sevoflurane post-conditioning
in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via TLR4/NF-κB pathway in
rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:1770–1775. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
National Research Council (US) Institute
for Laboratory Animal Research: Guide for the Care and Use of
Laboratory Animals. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US);
1996
|
|
20
|
Wang YQ, Wang L, Zhang MY, Wang T, Bao HJ,
Liu WL, Dai DK, Zhang L, Chang P, Dong WW, et al: Necrostatin-1
suppresses autophagy and apoptosis in mice traumatic brain injury
model. Neurochem Res. 37:1849–1858. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lai Y, Hickey RW, Chen Y, Bayir H,
Sullivan ML, Chu CT, Kochanek PM, Dixon CE, Jenkins LW, Graham SH,
et al: Autophagy is increased after traumatic brain injury in mice
and is partially inhibited by the antioxidant
gamma.glutamylcysteinyl ethyl ester. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
28:540–550. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yoshii SR and Mizushima N: Monitoring and
measuring autophagy. Int J Mol Sci. 18:2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Levine B:
Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 140:313–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Meschini S, Condello M, Lista P and
Arancia G: Autophagy: Molecular mechanisms and their implications
for anticancer therapies. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 11:357–379.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cao Y and Klionsky DJ: Physiological
functions of Atg6/Beclin 1: A unique autophagy-related protein.
Cell Res. 17:839–849. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P and
Janeway CA Jr: A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein
signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature. 388:394–397. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hyakkoku K, Hamanaka J, Tsuruma K,
Shimazawa M, Tanaka H, Uematsu S, Akira S, Inagaki N, Nagai H and
Hara H: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), but not TLR3 or TLR9,
knock-out mice have neuroprotective effects against focal cerebral
ischemia. Neuroscience. 171:258–267. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ridder DA and Schwaninger M: NF-kappaB
signaling in cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience. 158:995–1006. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Seo EJ, Fischer N and Efferth T:
Phytochemicals as inhibitors of NF-κB for treatment of Alzheimer's
disease. Pharmacol Res. 129:262–273. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|