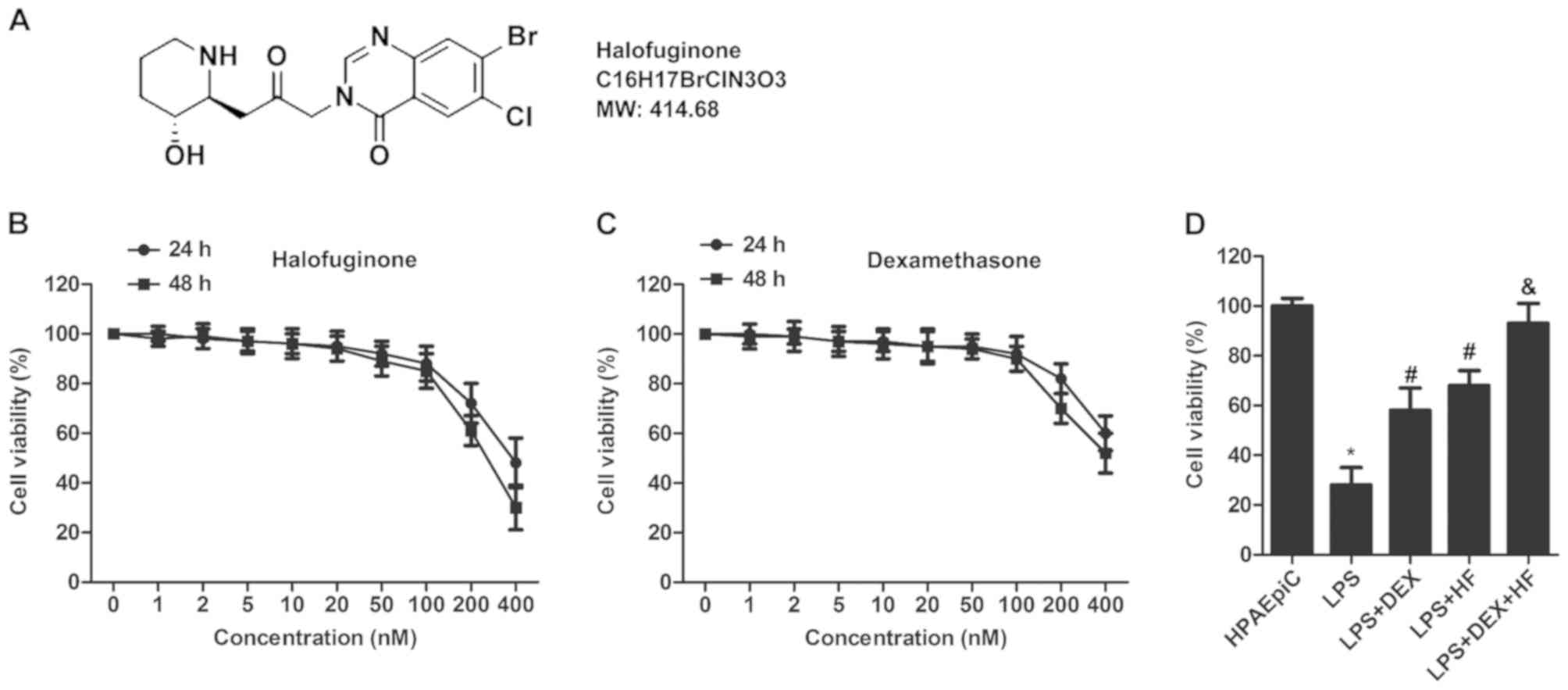
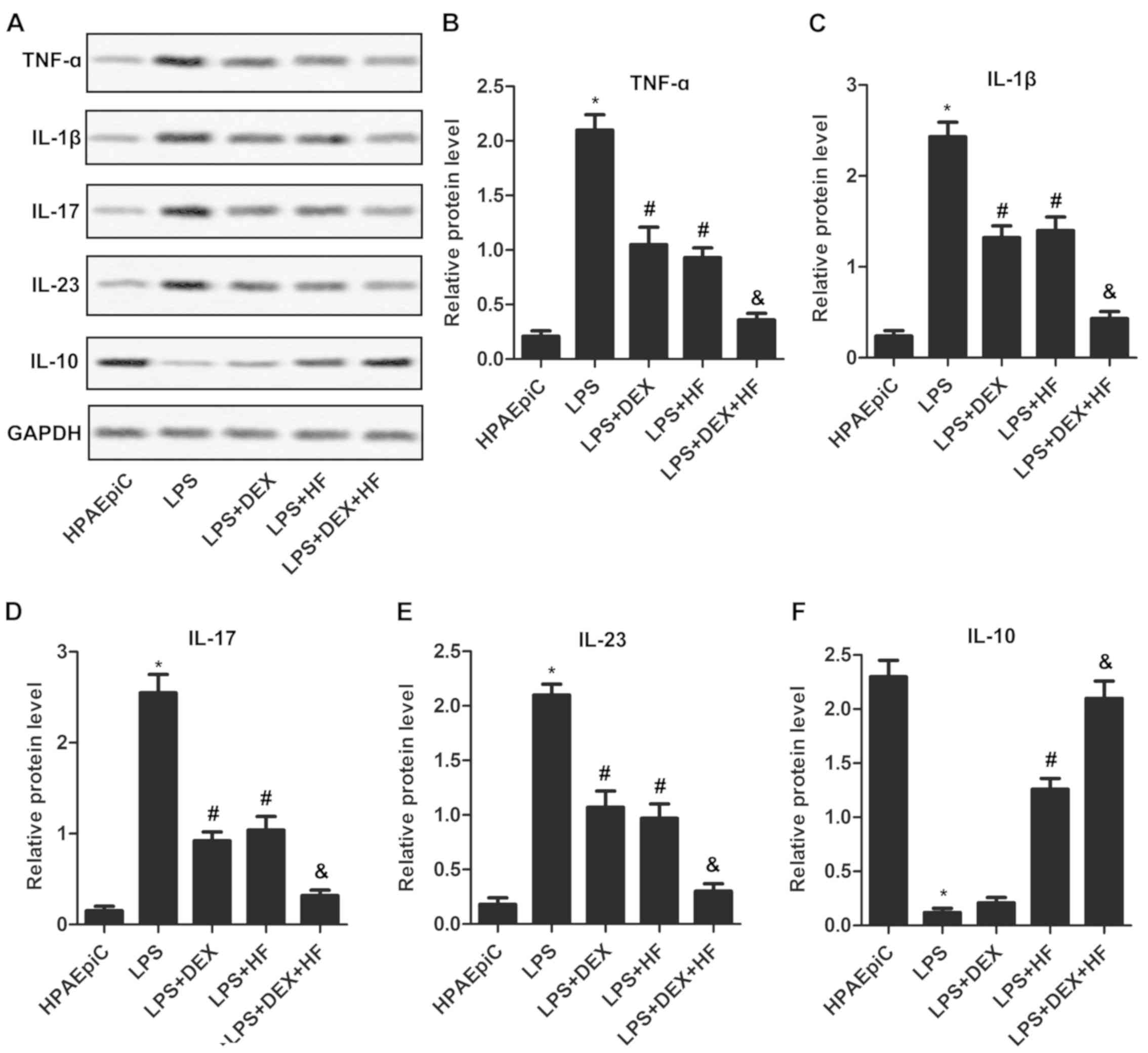
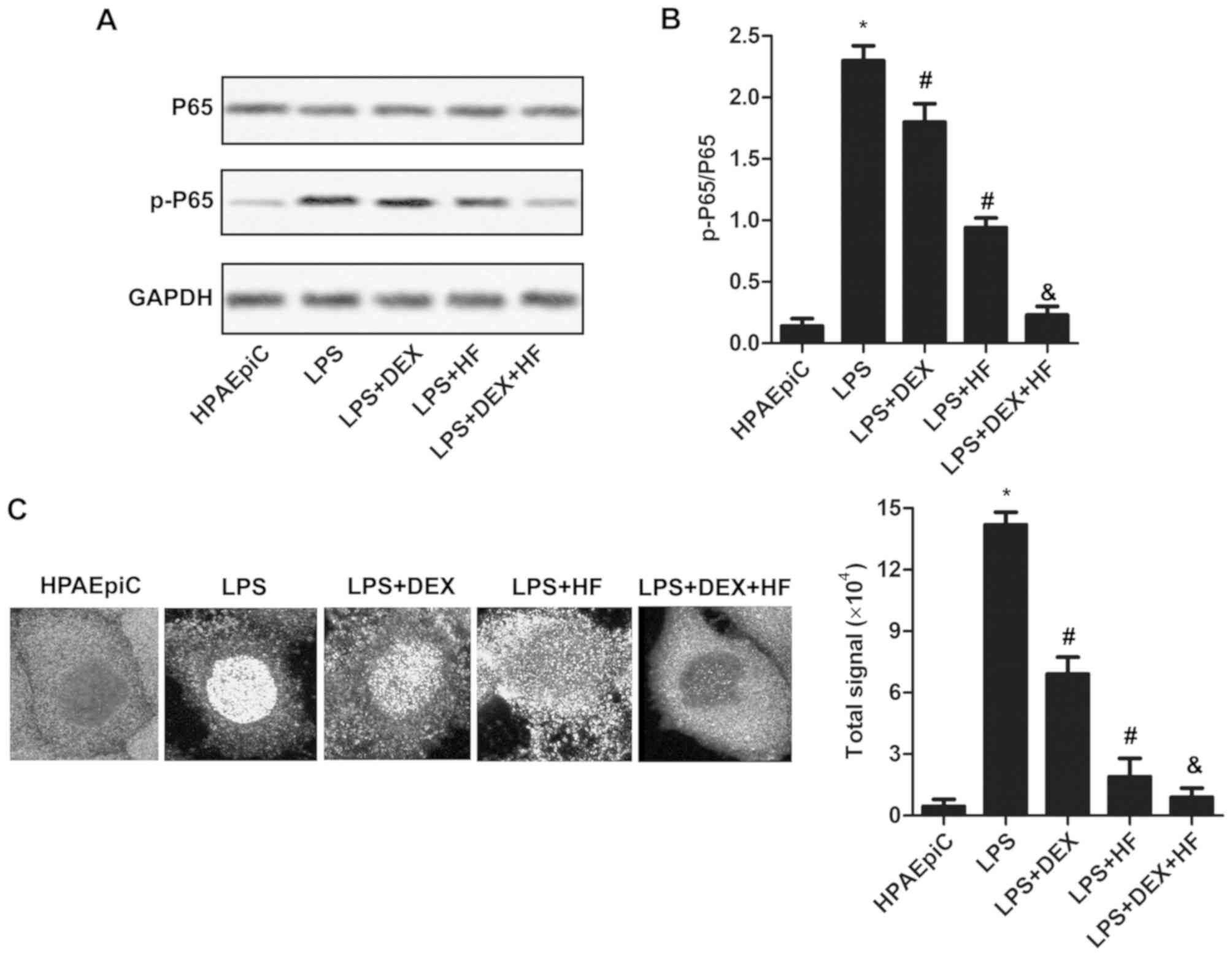
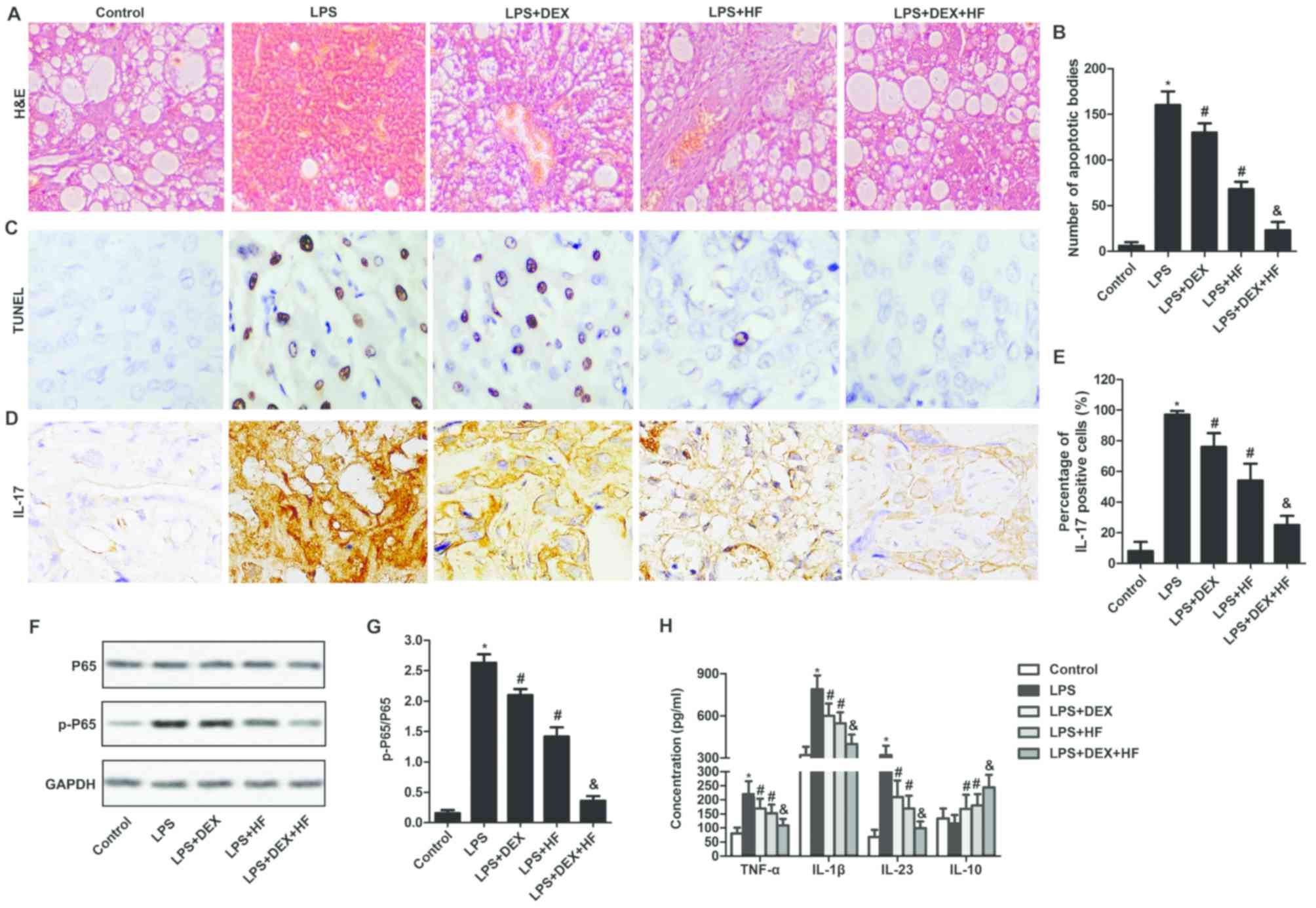
|
1
|
Miyashita T, Ahmed AK, Nakanuma S, Okamoto
K, Sakai S, Kinoshita J, Makino I, Nakamura K, Hayashi H, Oyama K,
et al: A three-phase approach for the early identification of acute
lung injury induced by severe sepsis. In Vivo. 30:341–349.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zimmerman JJ, Akhtar SR, Caldwell E and
Rubenfeld GD: Incidence and outcomes of pediatric acute lung
injury. Pediatrics. 124:87–95. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sawa T: The molecular mechanism of acute
lung injury caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: From bacterial
pathogenesis to host response. J Intensive Care. 2:102014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hu Y, Ren J, Wang L, Zhao X, Zhang M,
Shimizu K and Zhang C: Protective effects of total alkaloids from
Dendrobium crepidatum against LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice
and its chemical components. Phytochemistry. 149:12–23. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Patel VJ, Biswas Roy S, Mehta HJ, Joo M
and Sadikot RT: Alternative and natural therapies for acute lung
injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Biomed Res Int.
2018:24768242018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Johnson ER and Matthay MA: Acute lung
injury: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatment. J Aerosol Med
Pulm Drug Deliv. 23:243–252. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dent P, Yacoub A, Contessa J, Caron R,
Amorino G, Valerie K, Hagan MP, Grant S and Schmidt-Ullrich R:
Stress and radiation-induced activation of multiple intracellular
signaling pathways. Radiat Res. 159:283–300. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pines M, Snyder D, Yarkoni S and Nagler A:
Halofuginone to treat fibrosis in chronic graft-versus-host disease
and scleroderma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 9:417–425. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Park MK, Park JS, Park EM, Lim MA, Kim SM,
Lee DG, Baek SY, Yang EJ, Woo JW, Lee J, et al: Halofuginone
ameliorates autoimmune arthritis in mice by regulating the balance
between Th17 and Treg cells and inhibiting osteoclastogenesis.
Arthritis Rheumatol. 66:1195–1207. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zeng S, Wang K, Huang M, Qiu Q, Xiao Y,
Shi M, Zou Y, Yang X, Xu H and Liang L: Halofuginone inhibits
TNF-α-induced the migration and proliferation of fibroblast-like
synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Int
Immunopharmacol. 43:187–194. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Oishi H, Martinu T, Sato M, Matsuda Y,
Hirayama S, Juvet SC, Guan Z, Saito T, Cypel M, Hwang DM, et al:
Halofuginone treatment reduces interleukin-17A and ameliorates
features of chronic lung allograft dysfunction in a mouse
orthotopic lung transplant model. J Heart Lung Transplant.
35:518–527. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao W, Tong D, Li Q, Huang P and Zhang F:
Dexamethasone promotes regeneration of crushed inferior alveolar
nerve by inhibiting NF-κB activation in adult rats. Arch Oral Biol.
80:101–109. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang A, Wang F, Yin Y, Zhang M and Chen P:
Dexamethasone reduces serum level of IL-17 in Bleomycin-A5-induced
rats model of pulmonary fibrosis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol.
46:783–787. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Roach BL, Kelmendi-Doko A, Balutis EC,
Marra KG, Ateshian GA and Hung CT: Dexamethasone release from
within engineered cartilage as a chondroprotective strategy against
interleukin-1α. Tissue Eng Part A. 22:621–632. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Palma L, Sfara C, Antonelli A and Magnani
M: Dexamethasone restrains ongoing expression of interleukin-23p19
in peripheral blood-derived human macrophages. BMC Pharmacol.
11:82011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Q, Jiang H, Li Y, Chen W, Li H, Peng
K, Zhang Z and Sun X: Targeting NF-κB signaling with polymeric
hybrid micelles that co-deliver siRNA and dexamethasone for
arthritis therapy. Biomaterials. 122:10–22. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shaughnessy AF: Single-dose dexamethasone
an option for acute adult asthma. Am Fam Physician.
95:Online2017.
|
|
18
|
Kosutova P, Mikolka P, Balentova S,
Adamkov M, Kolomaznik M, Calkovska A and Mokra D: Intravenous
dexamethasone attenuated inflammation and influenced apoptosis of
lung cells in an experimental model of acute lung injury. Physiol
Res. 65 (Suppl 5):S663–S672. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu F, Pauluhn J, Trubel H and Wang C:
Single high-dose dexamethasone and sodium salicylate failed to
attenuate phosgene-induced acute lung injury in rats. Toxicology.
315:17–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang S, Chen X, Devshilt I, Yun Q, Huang
C, An L, Dorjbat S and He X: Fennel main constituent,
trans-anethole treatment against LPS-induced acute lung injury by
regulation of Th17/Treg function. Mol Med Rep. 18:1369–1376.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park GY and Christman JW: Nuclear factor
kappa B is a promising therapeutic target in inflammatory lung
disease. Curr Drug Targets. 7:661–668. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ho YC, Lee SS, Yang ML, Huang-Liu R, Lee
CY, Li YC and Kuan YH: Zerumbone reduced the inflammatory response
of acute lung injury in endotoxin-treated mice via Akt-NFκB
pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 271:9–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang T, Hou W and Fu Z: Preventative
effect of OMZ-SPT on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury
and inflammation via nuclear factor-kappa B signaling in mice.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 485:284–289. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li N, Song Y, Zhao W, Han T, Lin S,
Ramirez O and Liang L: Small interfering RNA targeting NF-κB
attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats.
BMC Physiol. 16:72016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li Q, Gu Y, Tu Q, Wang K, Gu X and Ren T:
Blockade of Interleukin-17 restrains the development of acute lung
injury. Scand J Immunol. 83:203–211. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yan B, Chen F, Xu L, Xing J and Wang X:
HMGB1-TLR4-IL23-IL17A axis promotes paraquat-induced acute lung
injury by mediating neutrophil infiltration in mice. Sci Rep.
7:5972017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
D'Alessio FR, Tsushima K, Aggarwal NR,
West EE, Willett MH, Britos MF, Pipeling MR, Brower RG, Tuder RM,
McDyer JF and King LS: CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs resolve experimental
lung injury in mice and are present in humans with acute lung
injury. J Clin Invest. 119:2898–2913. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu TY and Chen SB: Sarcandra
glabra combined with lycopene protect rats from
lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury via reducing
inflammatory response. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:34–41. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wei CY, Sun HL, Yang ML, Yang CP, Chen LY,
Li YC, Lee CY and Kuan YH: Protective effect of wogonin on
endotoxin-induced acute lung injury via reduction of p38 MAPK and
JNK phosphorylation. Environ Toxicol. 32:397–403. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kao ST, Liu CJ and Yeh CC: Protective and
immunomodulatory effect of flos Lonicerae japonicae by augmenting
IL-10 expression in a murine model of acute lung inflammation. J
Ethnopharmacol. 168:108–115. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang X, Zhang L, Duan W, Liu B, Gong P,
Ding Y and Wu X: Anti-inflammatory effects of triptolide by
inhibiting the NF-κB signalling pathway in LPS-induced acute lung
injury in a murine model. Mol Med Rep. 10:447–452. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu J, Xiao HT, Wang HS, Mu HX, Zhao L, Du
J, Yang D, Wang D, Bian ZX and Lin SH: Halofuginone reduces the
inflammatory responses of DSS-induced colitis through metabolic
reprogramming. Mol Biosyst. 12:2296–2303. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sun XH, Fu J and Sun DQ: Halofuginone
alleviates acute viral myocarditis in suckling BALB/c mice by
inhibiting TGF-β1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 473:558–564. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dianzani C, Foglietta F, Ferrara B, Rosa
AC, Muntoni E, Gasco P, Della Pepa C, Canaparo R and Serpe L: Solid
lipid nanoparticles delivering anti-inflammatory drugs to treat
inflammatory bowel disease: Effects in an in vivo model. World J
Gastroenterol. 23:4200–4210. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Leguillette R, Tohver T, Bond SL, Nicol JA
and McDonald KJ: Effect of dexamethasone and fluticasone on airway
hyperresponsiveness in horses with inflammatory airway disease. J
Vet Intern Med. 31:1193–1201. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Soiberman U, Kambhampati SP, Wu T, Mishra
MK, Oh Y, Sharma R, Wang J, Al Towerki AE, Yiu S, Stark WJ and
Kannan RM: Subconjunctival injectable dendrimer-dexamethasone gel
for the treatment of corneal inflammation. Biomaterials. 125:38–53.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kozan A, Kilic N, Alacam H, Guzel A,
Guvenc T and Acikgoz M: The effects of dexamethasone and L-NAME on
acute lung injury in rats with lung contusion. Inflammation.
39:1747–1756. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liang J, Zhang B, Shen RW, Liu JB, Gao MH,
Li Y, Li YY and Zhang W: Preventive effect of halofuginone on
concanavalin A-induced liver fibrosis. PLoS One. 8:e822322013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Carlson TJ, Pellerin A, Djuretic IM,
Trivigno C, Koralov SB, Rao A and Sundrud MS: Halofuginone-induced
amino acid starvation regulates Stat3-dependent Th17 effector
function and reduces established autoimmune inflammation. J
Immunol. 192:2167–2176. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kotthoff P, Heine A, Held SAE and Brossart
P: Dexamethasone induced inhibition of Dectin-1 activation of
antigen presenting cells is mediated via STAT-3 and NF-κB signaling
pathways. Sci Rep. 7:45222017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yeh YC, Yang CP, Lee SS, Horng CT, Chen
HY, Cho TH, Yang ML, Lee CY, Li MC and Kuan YH: Acute lung injury
induced by lipopolysaccharide is inhibited by wogonin in mice via
reduction of Akt phosphorylation and RhoA activation. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 68:257–263. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lu X, Pu Y, Kong W, Tang X, Zhou J, Gou H,
Song X, Zhou H, Gao N and Shen J: Antidesmone, a unique
tetrahydroquinoline alkaloid, prevents acute lung injury via
regulating MAPK and NF-κB activities. Int Immunopharmacol.
45:34–42. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
He J, Zhou J, Yang W, Zhou Q, Liang X,
Pang X, Li J, Pan F and Liang H: Dexamethasone affects cell
growth/apoptosis/chemosensitivity of colon cancer via
glucocorticoid receptor α/NF-κB. Oncotarget. 8:67670–67683.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xu J, Liu D, Yin Q and Guo L: Tetrandrine
suppresses β-glucan-induced macrophage activation via inhibiting
NF-κB, ERK and STAT3 signaling pathways. Mol Med Rep. 13:5177–5184.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang CS, Lin AH, Yang TC, Liu KL, Chen HW
and Lii CK: Shikonin inhibits oxidized LDL-induced monocyte
adhesion by suppressing NFκB activation via up-regulation of
PI3K/Akt/Nrf2-dependent antioxidation in EA.hy926 endothelial
cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 93:352–361. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li K, He Z, Wang X, Pineda M, Chen R, Liu
H, Ma K, Shen H, Wu C, Huang N, et al: Apigenin C-glycosides of
Microcos paniculata protects lipopolysaccharide induced apoptosis
and inflammation in acute lung injury through TLR4 signaling
pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 124:163–175. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Qing R, Huang Z, Tang Y, Xiang Q and Yang
F: Cordycepin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury via Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 60:18–25. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen LJ, Ding YB, Ma PL, Jiang SH, Li KZ,
Li AZ, Li MC, Shi CX, Du J and Zhou HD: The protective effect of
lidocaine on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats
through NF-κB and p38 MAPK signaling pathway and excessive
inflammatory responses. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:2099–2108.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yavas G, Calik M, Calik G, Yavas C, Ata O
and Esme H: The effect of Halofuginone in the amelioration of
radiation induced-lung fibrosis. Med Hypotheses. 80:357–359. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Nagler A, Firman N, Feferman R, Cotev S,
Pines M and Shoshan S: Reduction in pulmonary fibrosis in vivo by
halofuginone. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 154:1082–1086. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wigenstam E, Elfsmark L, Ågren L, Akfur C,
Bucht A and Jonasson S: Anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic
treatment in a rodent model of acute lung injury induced by sulfur
dioxide. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 56:1185–1194. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xu X, Zhu Q, Niu F, Zhang R, Wang Y, Wang
W, Sun D, Wang X and Wang A: A2BAR activation attenuates acute lung
injury by inhibiting alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis both in
vivo and in vitro. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 315:C558–C570. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ehrentraut H, Weisheit C, Scheck M, Frede
S and Hilbert T: Experimental murine acute lung injury induces
increase of pulmonary TIE2-expressing macrophages. J Inflamm
(Lond). 15:122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Dong SA, Zhang Y, Yu JB, Li XY, Gong LR,
Shi J and Kang YY: Carbon monoxide attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury by mitofusin proteins via
p38 MAPK pathway. J Surg Res. 228:201–210. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Takaoka Y, Goto S, Nakano T, Tseng HP,
Yang SM, Kawamoto S, Ono K and Chen CL: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
dehydrogenase (GAPDH) prevents lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced,
sepsis-related severe acute lung injury in mice. Sci Rep.
4:52042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yang Q, Liu X, Yao Z, Mao S, Wei Q and
Chang Y: Penehyclidine hydrochloride inhibits the release of
high-mobility group box 1 in lipopolysaccharide-activated RAW264.7
cells and cecal ligation and puncture-induced septic mice. J Surg
Res. 186:310–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|