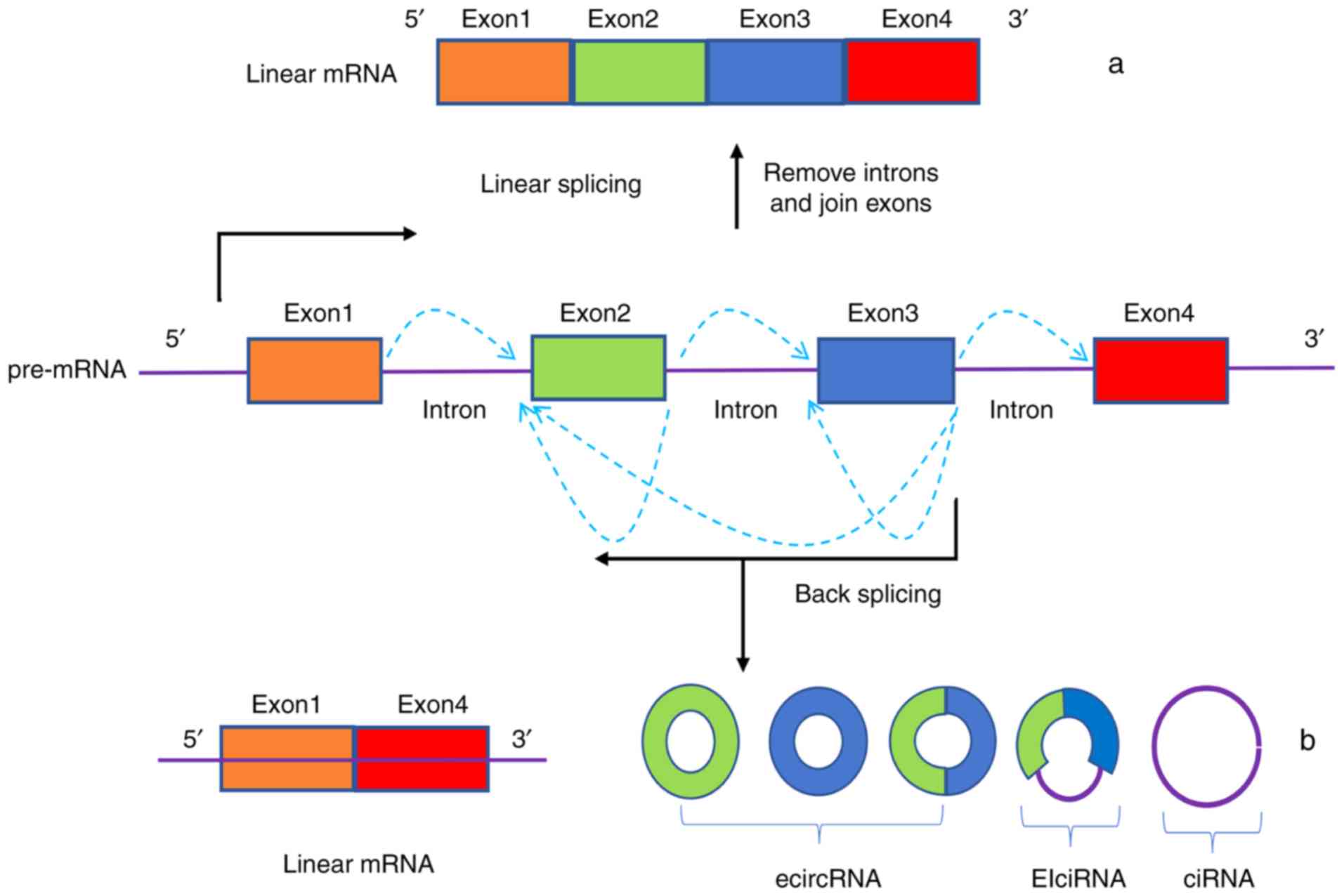
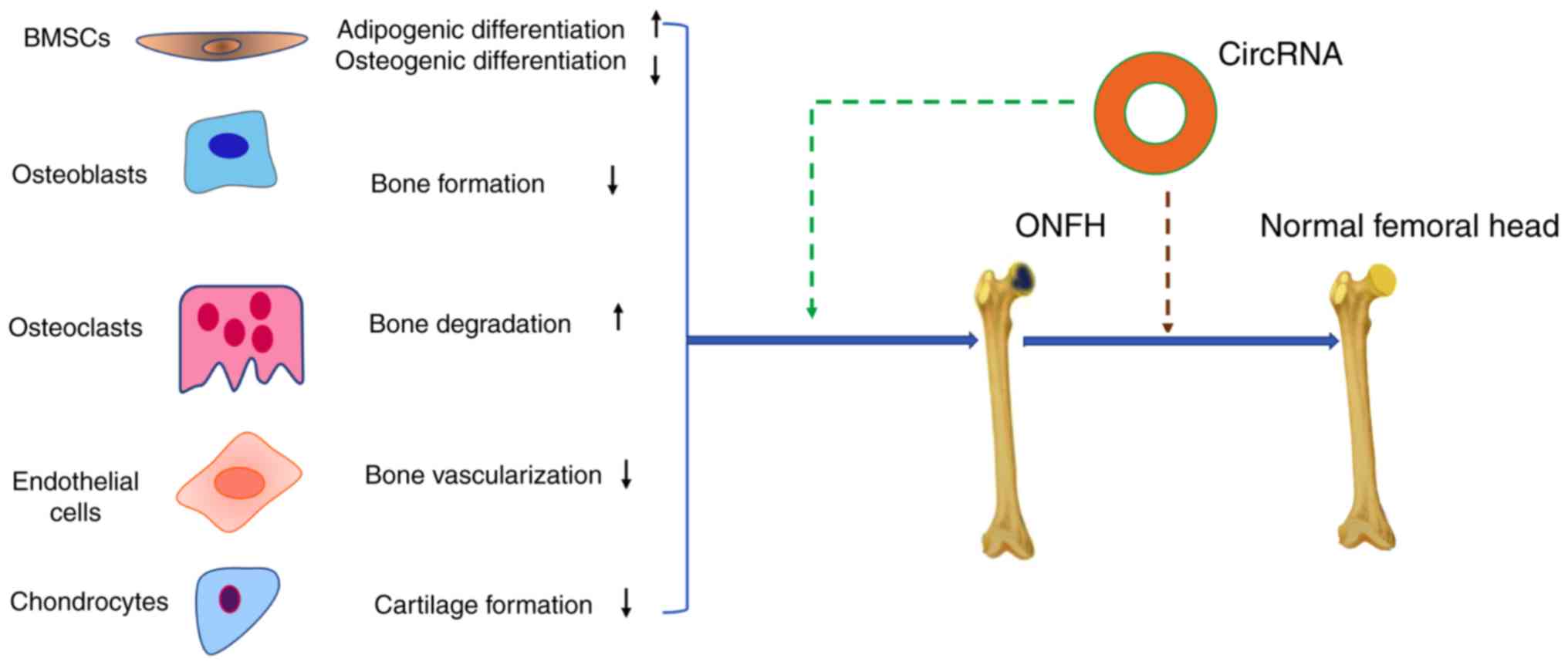
|
1
|
Sanger HL, Klotz G, Riesner D, Gross HJ
and Kleinschmidt AK: Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed
circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like
structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 73:3852–3856. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cocquerelle C, Mascrez B, Hétuin D and
Bailleul B: Mis-splicing yields circular RNA molecules. FASEB J.
7:155–160. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Salzman J, Gawad C, Wang PL, Lacayo N and
Brown PO: Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from
hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS One.
7:e307332012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen X, Han P, Zhou T, Guo X, Song X and
Li Y: circRNADb: A comprehensive database for human circular RNAs
with protein-coding annotations. Sci Rep. 6:349852016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
You X, Vlatkovic I, Babic A, Will T,
Epstein I, Tushev G, Akbalik G, Wang M, Glock C, Quedenau C, et al:
Neural circular RNAs are derived from synaptic genes and regulated
by development and plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 18:603–610. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Greene J, Baird AM, Brady L, Lim M, Gray
SG, McDermott R and Finn SP: Circular RNAs: Biogenesis, function
and role in human diseases. Front Mol Biosci. 4:382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Aufiero S, Reckman YJ, Pinto YM and
Creemers EE: Circular RNAs open a new chapter in cardiovascular
biology. Nat Rev Cardiol. 16:503–514. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Enuka Y, Lauriola M, Feldman ME, Sas-Chen
A, Ulitsky I and Yarden Y: Circular RNAs are long-lived and display
only minimal early alterations in response to a growth factor.
Nucleic Acids Res. 44:1370–1383. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Müller S and Appel B: In vitro
circularization of RNA. RNA Biol. 14:1018–1027. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F,
Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer
M, et al: Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with
regulatory potency. Nature. 495:333–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen
JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK and Kjems J: Natural RNA circles function
as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 495:384–388. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cui L, Zhuang Q, Lin J, Jin J, Zhang K,
Cao L, Lin J, Yan S, Guo W, He W, et al: Multicentric epidemiologic
study on six thousand three hundred and ninety five cases of
femoral head osteonecrosis in China. Int Orthop. 40:267–276. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lespasio MJ, Sodhi N and Mont MA:
Osteonecrosis of the Hip: A primer. Perm J. 23:18–100. 2019.
|
|
14
|
Kuroda Y, Matsuda S and Akiyama H:
Joint-preserving regenerative therapy for patients with early-stage
osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Inflamm Regen. 36:42016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mufarrih SH, Qureshi NQ, Sadruddin A,
Hashmi P, Mahmood SF, Zafar A and Noordin S: Relationship between
staphylococcus aureus carriage and surgical site infections
following total hip and knee arthroplasty in the South Asian
Population: Protocol for a prospective cohort study. JMIR Res
Protoc. 7:e102192018. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Robertson-Waters E, Berstock JR,
Whitehouse MR and Blom AW: Surgery for greater trochanteric pain
syndrome after total hip replacement confers a poor outcome. Int
Orthop. 42:77–85. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bandholm T, Wainwright TW and Kehlet H:
Rehabilitation strategies for optimisation of functional recovery
after major joint replacement. J Exp Orthop. 5:442018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hauer G, Vielgut I, Amerstorfer F,
Maurer-Ertl W, Leithner A and Sadoghi P: Survival rate of
Short-stem hip prostheses: A comparative analysis of clinical
studies and national arthroplasty registers. J Arthroplasty.
33:1800–1805. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Arbab D and König DP: Atraumatic femoral
head necrosis in adults. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 113:31–38.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Q, L VJ and Jin L: Role of
coagulopathy in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral
head. J Int Med Res. 46:2141–2148. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Petek D, Hannouche D and Suva D:
Osteonecrosis of the femoral head: Pathophysiology and current
concepts of treatment. EFORT Open Rev. 4:85–97. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kerachian MA, Séguin C and Harvey EJ:
Glucocorticoids in osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A new
understanding of the mechanisms of action. J Steroid Biochem Mol
Biol. 114:121–128. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zalavras C, Shah S, Birnbaum MJ and
Frenkel B: Role of apoptosis in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis
and osteonecrosis. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 13:221–235. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhun W, Donghai L, Zhouyuan Y, Haiyan Z
and Pengde K: Efficiency of cell therapy to GC-induced ONFH: BMSCs
with Dkk-1 interference is not superior to unmodified BMSCs. Stem
Cells Int. 2018:13402522018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xiang Shuai: The study of changed
biological behavior and aberrantly expressed transcriptome in BMSCs
in seroid-induced osteonecrosis (D). Peking Union Medical College.
2018.
|
|
26
|
Wang W, Wang Y, Piao H, Li B, Huang M, Zhu
Z, Li D, Wang T, Xu R and Liu K: Circular RNAs as potential
biomarkers and therapeutics for cardiovascular disease. PeerJ.
7:e68312019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang XO, Dong R, Zhang Y, Zhang JL, Luo
Z, Zhang J, Chen LL and Yang L: Diverse alternative back-splicing
and alternative splicing landscape of circular RNAs. Genome Res.
26:1277–1287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, Chen L, Lin M, Wang
X, Zhong G, Yu B, Hu W, Dai L, et al: Exon-intron circular RNAs
regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
22:256–264. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Conn SJ, Pillman KA, Toubia J, Conn VM,
Salmanidis M, Phillips CA, Roslan S, Schreiber AW, Gregory PA and
Goodall GJ: The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of
circRNAs. Cell. 160:1125–1134. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ashwal-Fluss R, Meyer M, Pamudurti NR,
Ivanov A, Bartok O, Hanan M, Evantal N, Memczak S, Rajewsky N and
Kadener S: circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol
Cell. 56:55–66. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kulcheski FR, Christoff AP and Margis R:
Circular RNAs are miRNA sponges and can be used as a new class of
biomarker. J Biotechnol. 238:42–51. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang L, Yang F, Zhao H, Wang M and Zhang
Y: Circular RNA circCHFR facilitates the proliferation and
migration of vascular smooth muscle via miR-370/FOXO1/Cyclin D1
pathway. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 16:434–441. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zheng Q, Bao C, Guo W, Li S, Chen J, Chen
B, Luo Y, Lyu D, Li Y, Shi G, et al: Circular RNA profiling reveals
an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging
multiple miRNAs. Nat Commun. 7:112152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pamudurti NR, Bartok O, Jens M,
Ashwal-Fluss R, Stottmeister C, Ruhe L, Hanan M, Wyler E,
Perez-Hernandez D, Ramberger E, et al: Translation of CircRNAs. Mol
Cell. 66:9–21.e27. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Abe N, Matsumoto K, Nishihara M, Nakano Y,
Shibata A, Maruyama H, Shuto S, Matsuda A, Yoshida M, Ito Y and Abe
H: Rolling circle translation of circular RNA in living human
cells. Sci Rep. 5:164352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu J, Qi X, Liu L, Hu X, Liu J, Yang J,
Yang J, Lu L, Zhang Z, Ma S, et al: Emerging epigenetic regulation
of circular RNAs in human cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
16:589–596. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Legnini I, Di Timoteo G, Rossi F, Morlando
M, Briganti F, Sthandier O, Fatica A, Santini T, Andronache A, Wade
M, et al: Circ-ZNF609 is a circular RNA that can be translated and
functions in myogenesis. Mol Cell. 66:22–37.e9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang Y, Gao X, Zhang M, Yan S, Sun C, Xiao
F, Huang N, Yang X, Zhao K, Zhou H, et al: Novel role of FBXW7
circular RNA in repressing Glioma tumorigenesis. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 1102018.doi: 10.1093/jnci/djx166.
|
|
40
|
Yang Y, Fan X, Mao M, Song X, Wu P, Zhang
Y, Jin Y, Yang Y, Chen LL, Wang Y, et al: Extensive translation of
circular RNAs driven by N6-methyladenosine. Cell Res.
27:626–641. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Du WW, Zhang C, Yang W, Yong T, Awan FM
and Yang BB: Identifying and Characterizing circRNA-protein
interaction. Theranostics. 7:4183–4191. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Du WW, Yang W, Liu E, Yang Z, Dhaliwal P
and Yang BB: Foxo3 circular RNA retards cell cycle progression via
forming ternary complexes with p21 and CDK2. Nucleic Acids Res.
44:2846–2858. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Du WW, Fang L, Yang W, Wu N, Awan FM, Yang
Z and Yang BB: Induction of tumor apoptosis through a circular RNA
enhancing Foxo3 activity. Cell Death Differ. 24:357–370. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li Y, Zheng Q, Bao C, Li S, Guo W, Zhao J,
Chen D, Gu J, He X and Huang S: Circular RNA is enriched and stable
in exosomes: A promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res.
25:981–984. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dong R, Zhang XO, Zhang Y, Ma XK, Chen LL
and Yang L: CircRNA-derived pseudogenes. Cell Res. 26:747–750.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yu CX and Sun S: An emerging role for
circular RNAs in osteoarthritis. Yonsei Med J. 59:349–355. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Houdek MT, Wyles CC, Packard BD, Terzic A,
Behfar A and Sierra RJ: Decreased osteogenic activity of
mesenchymal stem cells in patients with corticosteroid-induced
osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Arthroplasty. 31:893–898.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ong SG, Lee WH, Kodo K and Wu JC:
MicroRNA-mediated regulation of differentiation and
trans-differentiation in stem cells. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 88:3–15.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang B, Yu P, Li T, Bian Y and Weng X:
MicroRNA expression in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from mice
with steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Mol Med
Rep. 12:7447–7454. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li R, Lin QX, Liang XZ, Liu GB, Tang H,
Wang Y, Lu SB and Peng J: Stem cell therapy for treating
osteonecrosis of the femoral head: From clinical applications to
related basic research. Stem Cell Res Ther. 9:2912018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gu C, Xu Y, Zhang S, Guan H, Song S, Wang
X, Wang Y, Li Y and Zhao G: miR-27a attenuates adipogenesis and
promotes osteogenesis in steroid-induced rat BMSCs by targeting
PPARgamma and GREM1. Sci Rep. 6:384912016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang M, Jia L and Zheng Y: circRNA
expression profiles in human bone marrow stem cells undergoing
osteoblast differentiation. Stem Cell Rev. 15:126–138. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Zhao R, Li Y, Lin Z, Wan J, Xu C, Zeng Y
and Zhu Y: miR-199b-5p modulates BMSC osteogenesis via suppressing
GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
477:749–754. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Huang L, Wang Y, Jiang Y, Wu Y, Hu C and
Ouyang H: High levels of GSK-3β signalling reduce osteogenic
differentiation of stem cells in osteonecrosis of femoral head. J
Biochem. 163:243–251. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Cherubini A, Barilani M, Rossi RL, Jalal
MMK, Rusconi F, Buono G, Ragni E, Cantarella G, Simpson H, Péault B
and Lazzari L: FOXP1 circular RNA sustains mesenchymal stem cell
identity via microRNA inhibition. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:5325–5340.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kuang MJ, Xing F, Wang D, Sun L, Ma JX and
Ma XL: CircUSP45 inhibited osteogenesis in glucocorticoid-induced
osteonecrosis of femoral head by sponging miR-127-5p through
PTEN/AKT signal pathway: Experimental studies. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 509:255–261. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Mandelin J, Hukkanen M, Li TF, Korhonen M,
Liljeström M, Sillat T, Hanaemaijer R, Salo J, Santavirta S and
Konttinen YT: Human osteoblasts produce cathepsin K. Bone.
38:769–777. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chen X, Wang Z, Duan N, Zhu G, Schwarz EM
and Xie C: Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connect Tissue Res.
59:99–107. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wang C, Wang X, Xu XL, Yuan XL, Gou WL,
Wang AY, Guo QY, Peng J and Lu SB: Bone microstructure and regional
distribution of osteoblast and osteoclast activity in the
osteonecrotic femoral head. PLoS One. 9:e963612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang C, Meng H, Wang Y, Zhao B, Zhao C,
Sun W, Zhu Y, Han B, Yuan X, Liu R, et al: Analysis of early stage
osteonecrosis of the human femoral head and the mechanism of
femoral head collapse. Int J Biol Sci. 14:156–164. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Qian DY, Yan GB, Bai B, Chen Y, Zhang SJ,
Yao YC and Xia H: Differential circRNA expression profiles during
the BMP2-induced osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells.
Biomed Pharmacother. 90:492–499. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Dou C, Cao Z, Yang B, Ding N, Hou T, Luo
F, Kang F, Li J, Yang X, Jiang H, et al: Changing expression
profiles of lncRNAs, mRNAs, circRNAs and miRNAs during
osteoclastogenesis. Sci Rep. 6:214992016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Jin D, Wu X, Yu H, Jiang L, Zhou P, Yao X,
Meng J, Wang L, Zhang M and Zhang Y: Systematic analysis of
lncRNAs, mRNAs, circRNAs and miRNAs in patients with postmenopausal
osteoporosis. Am J Transl Res. 10:1498–1510. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhao K, Zhao Q, Guo Z, Chen Z, Hu Y, Su J,
Chen L, He Z, Cai X, Chen M, et al: Hsa_Circ_0001275: A potential
novel diagnostic biomarker for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 46:2508–2516. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Carulli C, Innocenti M and Brandi ML: Bone
vascularization in normal and disease conditions. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 4:1062013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Sivaraj KK and Adams RH: Blood vessel
formation and function in bone. Development. 143:2706–2715. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Yue J, Wan F, Zhang Q, Wen P, Cheng L, Li
P and Guo W: Effect of glucocorticoids on miRNA expression spectrum
of rat femoral head microcirculation endothelial cells. Gene.
651:126–133. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lane NE: Glucocorticoid-induced
osteoporosis: New insights into the pathophysiology and treatments.
Curr Osteoporos Rep. 17:1–7. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Weinstein RS, Hogan EA, Borrelli MJ,
Liachenko S, O'Brien CA and Manolagas SC: The pathophysiological
sequence of glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral
head in male mice. Endocrinology. 158:3817–3831. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Liu X, Li Q, Niu X, Hu B, Chen S, Song W,
Ding J, Zhang C and Wang Y: Exosomes secreted from human-induced
pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent
osteonecrosis of the femoral head by promoting angiogenesis. Int J
Biol Sci. 13:232–244. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhang Y, Yin J, Ding H, Zhang C and Gao
YS: Vitamin K2 ameliorates damage of blood vessels by
glucocorticoid: A potential mechanism for its protective effects in
glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in a rat
model. Int J Biol Sci. 12:776–785. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Boeckel JN, Jaé N, Heumüller AW, Chen W,
Boon RA, Stellos K, Zeiher AM, John D, Uchida S and Dimmeler S:
Identification and characterization of hypoxia-regulated
endothelial circular RNA. Circ Res. 117:884–890. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Li CY, Ma L and Yu B: Circular RNA
hsa_circ_0003575 regulates oxLDL induced vascular endothelial cells
proliferation and angiogenesis. Biomed Pharmacother. 95:1514–1519.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Dang RY, Liu FL and Li Y: Circular RNA
hsa_circ_0010729 regulates vascular endothelial cell proliferation
and apoptosis by targeting the miR-186/HIF-1α axis. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 490:104–110. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Shan K, Liu C, Liu BH, Chen X, Dong R, Liu
X, Zhang YY, Liu B, Zhang SJ, Wang JJ, et al: Circular noncoding
RNA HIPK3 mediates retinal vascular dysfunction in diabetes
mellitus. Circulation. 136:1629–1642. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Magnussen RA, Guilak F and Vail TP:
Cartilage degeneration in post-collapse cases of osteonecrosis of
the human femoral head: Altered mechanical properties in tension,
compression, and shear. J Orthop Res. 23:576–583. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Chen G, Zhong L, Wang Q, Li Z, Shang J,
Yang Q, Du Z, Wang J, Song Y and Zhang G: The expression of
chondrogenesis-related and arthritis-related genes in human ONFH
cartilage with different Ficat stages. PeerJ. 7:e63062019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Xu R, Wei B, Li J, Huang C, Lin R, Tang C,
Xu Y, Yao Q and Wang L: Investigations of cartilage matrix
degeneration in patients with Early-stage femoral head necrosis.
Med Sci Monit. 23:5783–5792. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chen B, Liu Y and Cheng L: IL-21 enhances
the degradation of cartilage through the JAK-STAT signaling pathway
during osteonecrosis of femoral head cartilage. Inflammation.
41:595–605. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zhou Z, Du D, Chen A and Zhu L: Circular
RNA expression profile of articular chondrocytes in an
IL-1β-induced mouse model of osteoarthritis. Gene. 644:20–26. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Shen S, Wu Y, Chen J, Xie Z, Huang K, Wang
G, Yang Y, Ni W, Chen Z, Shi P, et al: CircSERPINE2 protects
against osteoarthritis by targeting miR-1271 and ETS-related gene.
Ann Rheum Dis. 78:826–836. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Feng C, Liu M, Fan X, Yang M, Liu H and
Zhou Y: Intermittent cyclic mechanical tension altered the microRNA
expression profile of human cartilage endplate chondrocytes. Mol
Med Rep. 17:5238–5246. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Liu Q, Zhang X, Hu X, Yuan L, Cheng J,
Jiang Y and Ao Y: Emerging roles of circRNA related to the
mechanical stress in human cartilage degradation of osteoarthritis.
Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 7:223–230. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Rong D, Su H, Li Z, Liu S, Dong C, Fu K,
Tang W and Cao H: An emerging function of circRNA-miRNAs-mRNA axis
in human diseases. Oncotarget. 8:73271–73281. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|