|
1
|
Estes C, Razavi H, Loomba R, Younossi Z
and Sanyal AJ: Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease.
Hepatology. 67:123–133. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yki-Järvinen H: Non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease as a cause and a consequence of metabolic syndrome. Lancet
Diabetes Endocrinol. 2:901–910. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
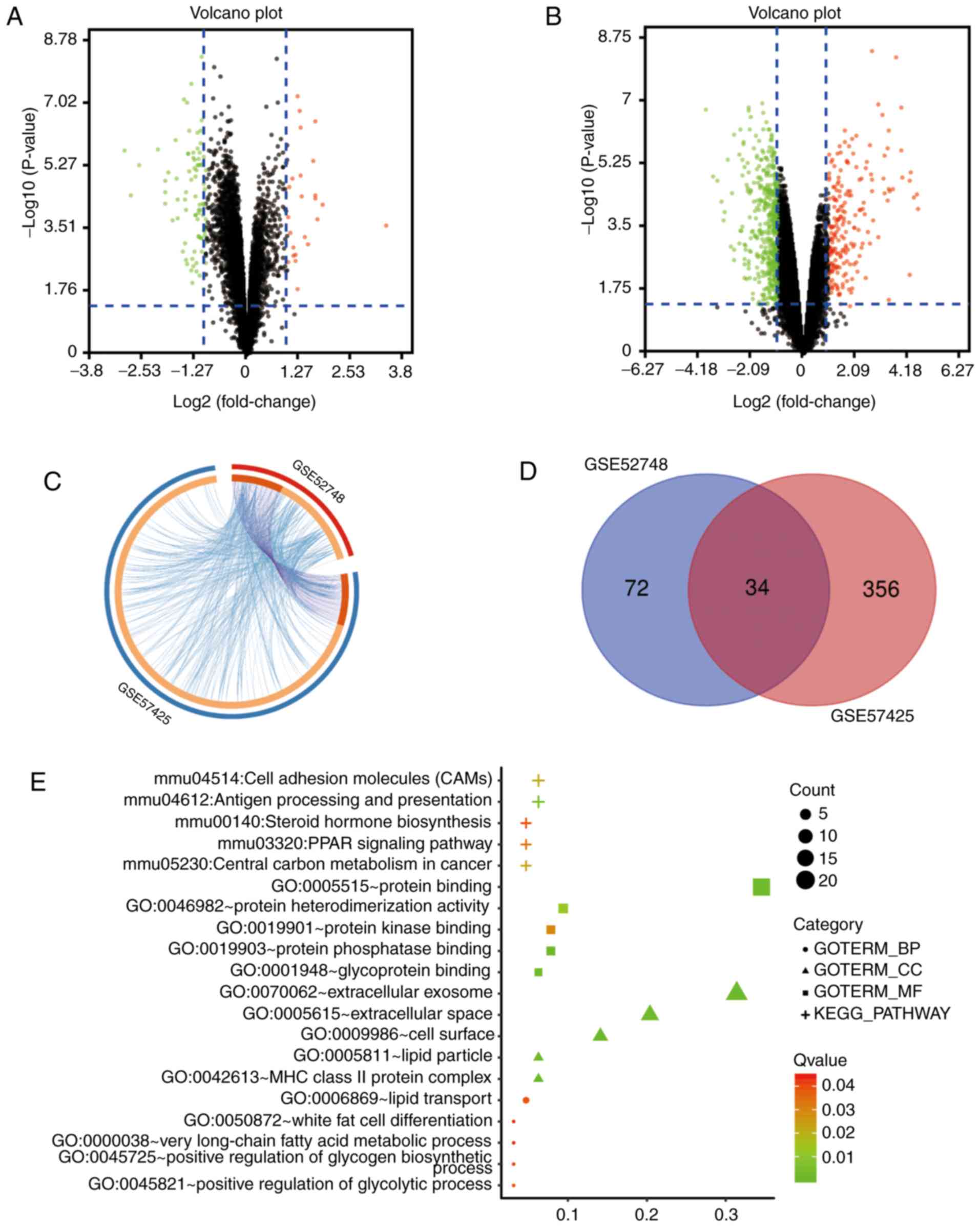
Gluchowski NL, Becuwe M, Walther TC and
Farese RV Jr: Lipid droplets and liver disease: From basic biology
to clinical implications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
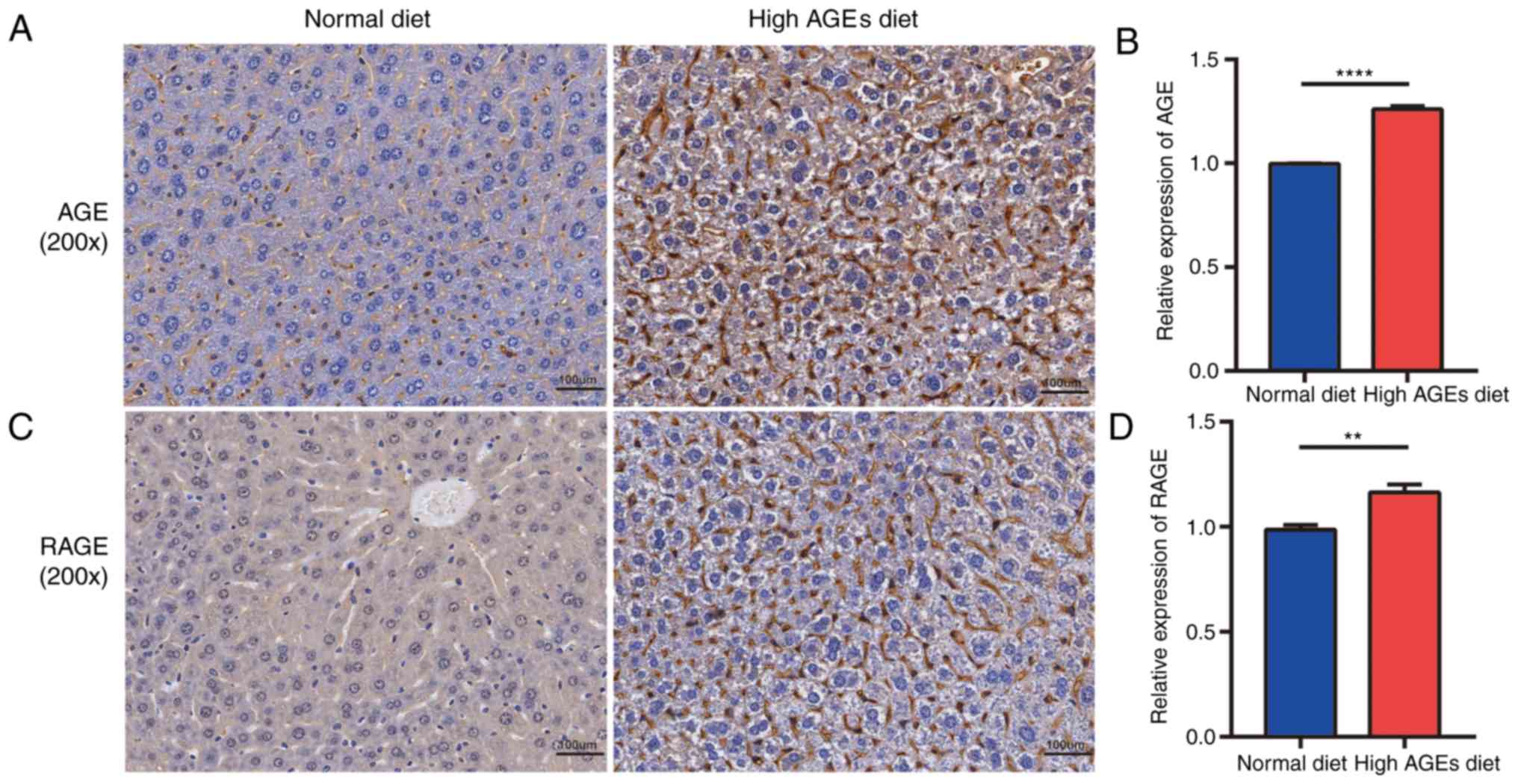
14:343–355. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
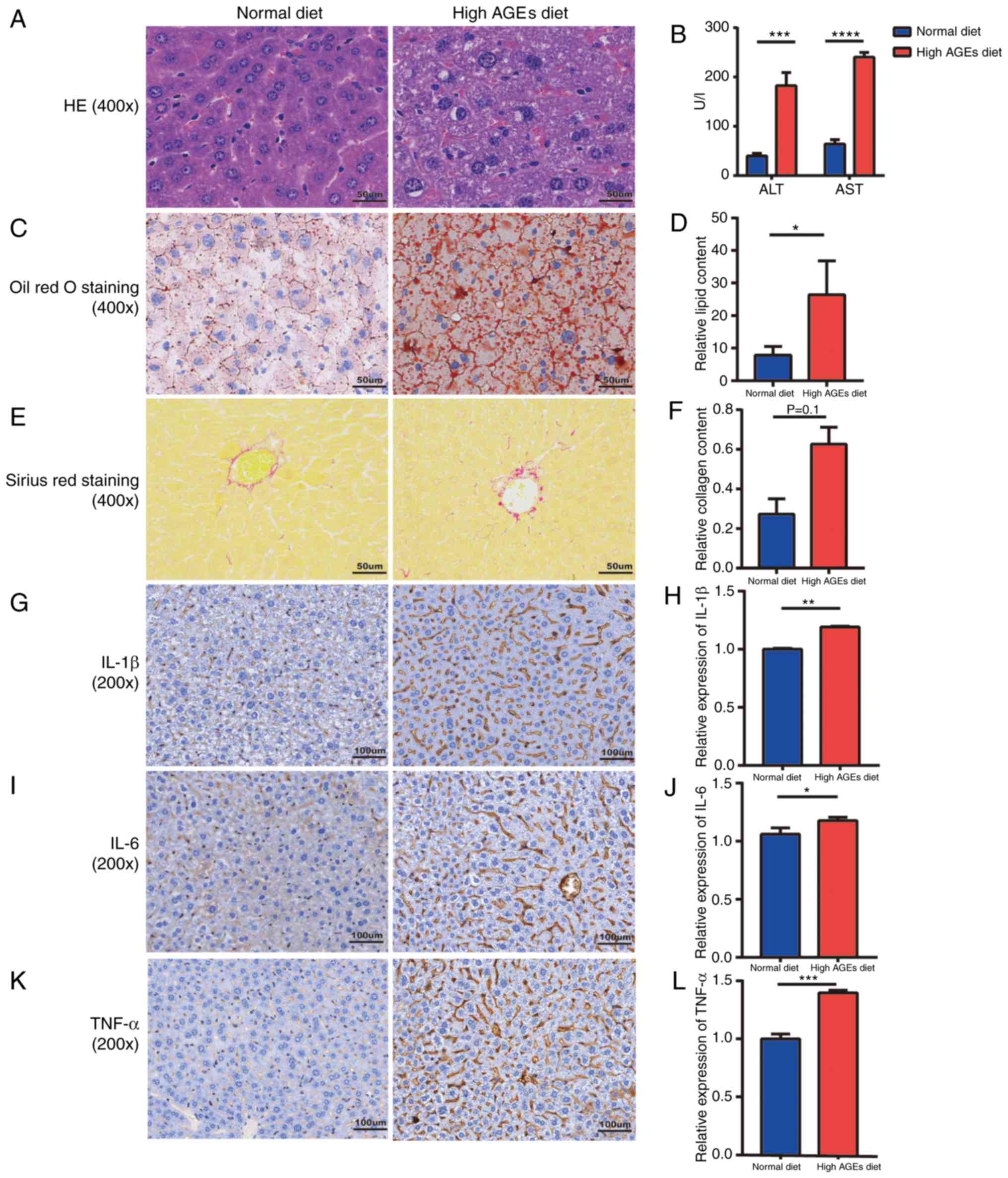
|
|
4
|
Trovato FM, Castrogiovanni P, Malatino L
and Musumeci G: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
prevention: Role of Mediterranean diet and physical activity.
Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 8:167–169. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Trovato FM, Martines GF, Brischetto D,
Catalano D, Musumeci G and Trovato GM: Fatty liver disease and
lifestyle in youngsters: Diet, food intake frequency, exercise,
sleep shortage and fashion. Liver Int. 36:427–433. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
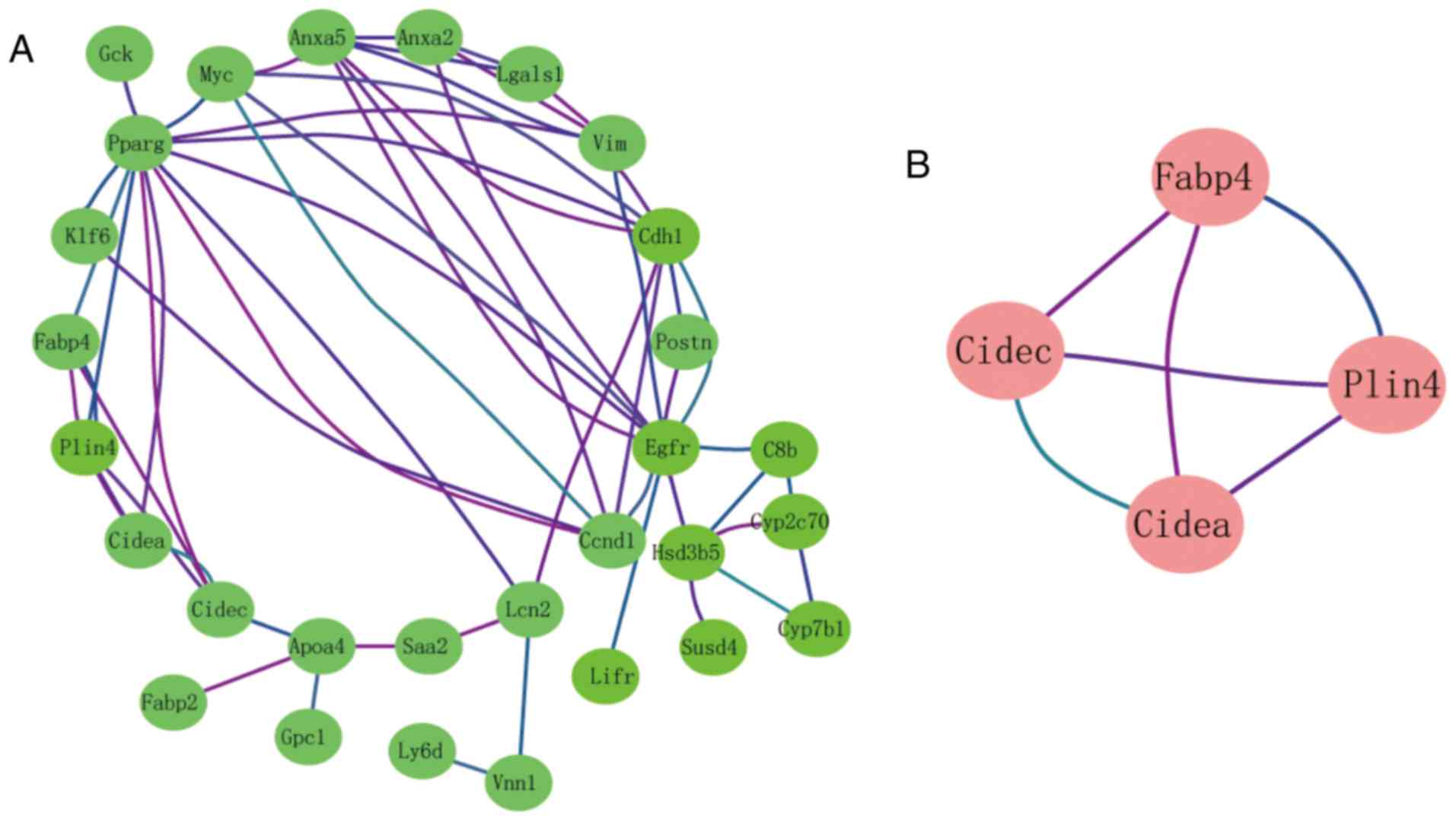
|
|
6
|
Trovato FM, Catalano D, Musumeci G and
Trovato GM: 4Ps medicine of the fatty liver: The research model of
predictive, preventive, personalized and participatory
medicine-recommendations for facing obesity, fatty liver and
fibrosis epidemics. EPMA J. 5:212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Singh R, Barden A, Mori T and Beilin L:
Advanced glycation end-products: A review. Diabetologia.
44:129–146. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Uribarri J, Woodruff S, Goodman S, Cai W,
Chen X, Pyzik R, Yong A, Striker GE and Vlassara H: Advanced
glycation end products in foods and a practical guide to their
reduction in the diet. J Am Diet Assoc. 110:911–916.e12. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Leung C, Herath CB, Jia Z, Goodwin M, Mak
KY, Watt MJ, Forbes JM and Angus PW: Dietary glycotoxins exacerbate
progression of experimental fatty liver disease. J Hepatol.
60:832–838. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ravichandran G, Lakshmanan DK, Raju K,
Elangovan A, Nambirajan G, Devanesan AA and Thilagar S: Food
advanced glycation end products as potential endocrine disruptors:
An emerging threat to contemporary and future generation. Environ
Int. 123:486–500. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chaudhuri J, Bains Y, Guha S, Kahn A, Hall
D, Bose N, Gugliucci A and Kapahi P: The role of advanced glycation
end products in aging and metabolic diseases: Bridging association
and causality. Cell Metab. 28:337–352. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang X, Wang Y and Liu P: Omic studies
reveal the pathogenic lipid droplet proteins in non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease. Protein Cell. 8:4–13. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kahle M, Horsch M, Fridrich B, Seelig A,
Schultheiß J, Leonhardt J, Irmler M, Beckers J, Rathkolb B, Wolf E,
et al: Phenotypic comparison of common mouse strains developing
high-fat diet-induced hepatosteatosis. Mol Metab. 2:435–446. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou D, Hlady RA, Schafer MJ, White TA,
Liu C, Choi JH, Miller JD, Roberts LR, LeBrasseur NK and Robertson
KD: High fat diet and exercise lead to a disrupted and pathogenic
DNA methylome in mouse liver. Epigenetics. 12:55–69. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pruis MG, Lendvai A, Bloks VW, Zwier MV,
Baller JF, de Bruin A, Groen AK and Plösch T: Maternal western diet
primes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adult mouse offspring.
Acta Physiol (Oxf). 210:215–227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dorn C, Engelmann JC, Saugspier M, Koch A,
Hartmann A, Müller M, Spang R, Bosserhoff A and Hellerbrand C:
Increased expression of c-Jun in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Lab Invest. 94:394–408. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lu Y, Liu X, Jiao Y, Xiong X, Wang E, Wang
X, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Pan L, Guan Y, et al: Periostin promotes liver
steatosis and hypertriglyceridemia through downregulation of PPARα.
J Clin Invest. 124:3501–3513. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Davis S and Meltzer PS: GEOquery: A bridge
between the gene expression omnibus (GEO) and BioConductor.
Bioinformatics. 23:1846–1847. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu Y, Ouyang Y and Yao W: shinyCircos: An
R/Shiny application for interactive creation of Circos plot.
Bioinformatics. 34:1229–1231. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL
and Ideker T: Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and
network visualization. Bioinformatics. 27:431–432. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sourris KC, Harcourt BE, Penfold SA, Yap
FY, Morley AL, Morgan PE, Davies MJ, Baker ST, Jerums G and Forbes
JM: Modulation of the cellular expression of circulating advanced
glycation end-product receptors in type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Exp
Diabetes Res. 2010:9746812010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling
C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, Ferrell LD, Liu YC, Torbenson MS,
Unalp-Arida A, et al: Design and validation of a histological
scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology.
41:1313–1321. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mehlem A, Hagberg CE, Muhl L, Eriksson U
and Falkevall A: Imaging of neutral lipids by oil red O for
analyzing the metabolic status in health and disease. Nat Protoc.
8:1149–1154. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Goodwin M, Herath C, Jia Z, Leung C,
Coughlan MT, Forbes J and Angus P: Advanced glycation end products
augment experimental hepatic fibrosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
28:369–376. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Trovato FM, Castrogiovanni P, Szychlinska
MA, Purrello F and Musumeci G: Early effects of high-fat diet,
extra-virgin olive oil and vitamin D in a sedentary rat model of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Histol Histopathol.
33:1201–1213. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Farrell GC and Larter CZ: Nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: From steatosis to cirrhosis. Hepatology. 43 (2
Suppl 1):S99–S112. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wong RJ, Aguilar M, Cheung R, Perumpail
RB, Harrison SA, Younossi ZM and Ahmed A: Nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease
among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States.
Gastroenterology. 148:547–555. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Samuel VT and Shulman GI: Nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease as a nexus of metabolic and hepatic diseases.
Cell Metab. 27:22–41. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pawlak M, Lefebvre P and Staels B:
Molecular mechanism of PPARα action and its impact on lipid
metabolism, inflammation and fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. J Hepatol. 62:720–733. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gross B, Pawlak M, Lefebvre P and Staels
B: PPARs in obesity-induced T2DM, dyslipidaemia and NAFLD. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 13:36–49. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liss KH and Finck BN: PPARs and
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Biochimie. 136:65–74. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pawlak M, Baugé E, Bourguet W, De Bosscher
K, Lalloyer F, Tailleux A, Lebherz C, Lefebvre P and Staels B: The
transrepressive activity of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor alpha is necessary and sufficient to prevent liver
fibrosis in mice. Hepatology. 60:1593–1606. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Koliaki C, Szendroedi J, Kaul K, Jelenik
T, Nowotny P, Jankowiak F, Herder C, Carstensen M, Krausch M,
Knoefel WT, et al: Adaptation of hepatic mitochondrial function in
humans with non-alcoholic fatty liver is lost in steatohepatitis.
Cell Metab. 21:739–746. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu HT, Chen CT, Cheng KC, Li YX, Yeh CH
and Cheng JT: Pharmacological activation of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor δ improves insulin resistance and
hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced diabetic mice. Horm
Metab Res. 43:631–635. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bojic LA, Telford DE, Fullerton MD, Ford
RJ, Sutherland BG, Edwards JY, Sawyez CG, Gros R, Kemp BE,
Steinberg GR and Huff MW: PPARδ activation attenuates hepatic
steatosis in Ldlr-/- mice by enhanced fat oxidation, reduced
lipogenesis, and improved insulin sensitivity. J Lipid Res.
55:1254–1266. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bensinger SJ and Tontonoz P: Integration
of metabolism and inflammation by lipid-activated nuclear
receptors. Nature. 454:470–477. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu L, Zhou L and Li P: CIDE proteins and
lipid metabolism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 32:1094–1098.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhou L, Xu L, Ye J, Li D, Wang W, Li X, Wu
L, Wang H, Guan F and Li P: Cidea promotes hepatic steatosis by
sensing dietary fatty acids. Hepatology. 56:95–107. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Reynolds TH IV, Banerjee S, Sharma VM,
Donohue J, Couldwell S, Sosinsky A, Frulla A, Robinson A and Puri
V: Effects of a high fat diet and voluntary wheel running exercise
on cidea and cidec expression in liver and adipose tissue of mice.
PLoS One. 10:e01302592015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hotamisligil GS and Bernlohr DA: Metabolic
functions of FABPs-mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 11:592–605. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Carr RM and Ahima RS: Pathophysiology of
lipid droplet proteins in liver diseases. Exp Cell Res.
340:187–192. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Carino A, Marchianò S, Biagioli M,
Fiorucci C, Zampella A, Monti MC, Morretta E, Bordoni M, Di Giorgio
C, Roselli R, et al: Transcriptome analysis of Dual FXR and GPBAR1
agonism in rodent model of NASH reveals modulation of lipid
droplets formation. Nutrients. 11(pii): E11322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Slayton M, Gupta A, Balakrishnan B and
Puri V: CIDE proteins in human health and disease. Cells. 8(pii):
E2382019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Thompson KJ, Austin RG, Nazari SS, Gersin
KS, Iannitti DA and McKillop IH: Altered fatty acid-binding protein
4 (FABP4) expression and function in human and animal models of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 38:1074–1083. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Leung C, Herath CB, Jia Z, Andrikopoulos
S, Brown BE, Davies MJ, Rivera LR, Furness JB, Forbes JM and Angus
PW: Dietary advanced glycation end-products aggravate non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 22:8026–8040. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Delgado-Andrade C, Pastoriza de la Cueva
S, Peinado MJ, Rufián-Henares JÁ, Navarro MP and Rubio LA:
Modifications in bacterial groups and short chain fatty acid
production in the gut of healthy adult rats after long-term
consumption of dietary Maillard reaction products. Food Res Int.
100:134–142. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Qu W, Yuan X, Zhao J, Zhang Y, Hu J, Wang
J and Li J: Dietary advanced glycation end products modify gut
microbial composition and partially increase colon permeability in
rats. Mol Nutr Food Res. 61:2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Snelson M and Coughlan MT: Dietary
advanced glycation end products: Digestion, metabolism and
modulation of gut microbial ecology. Nutrients. 11(pii): E2152019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|