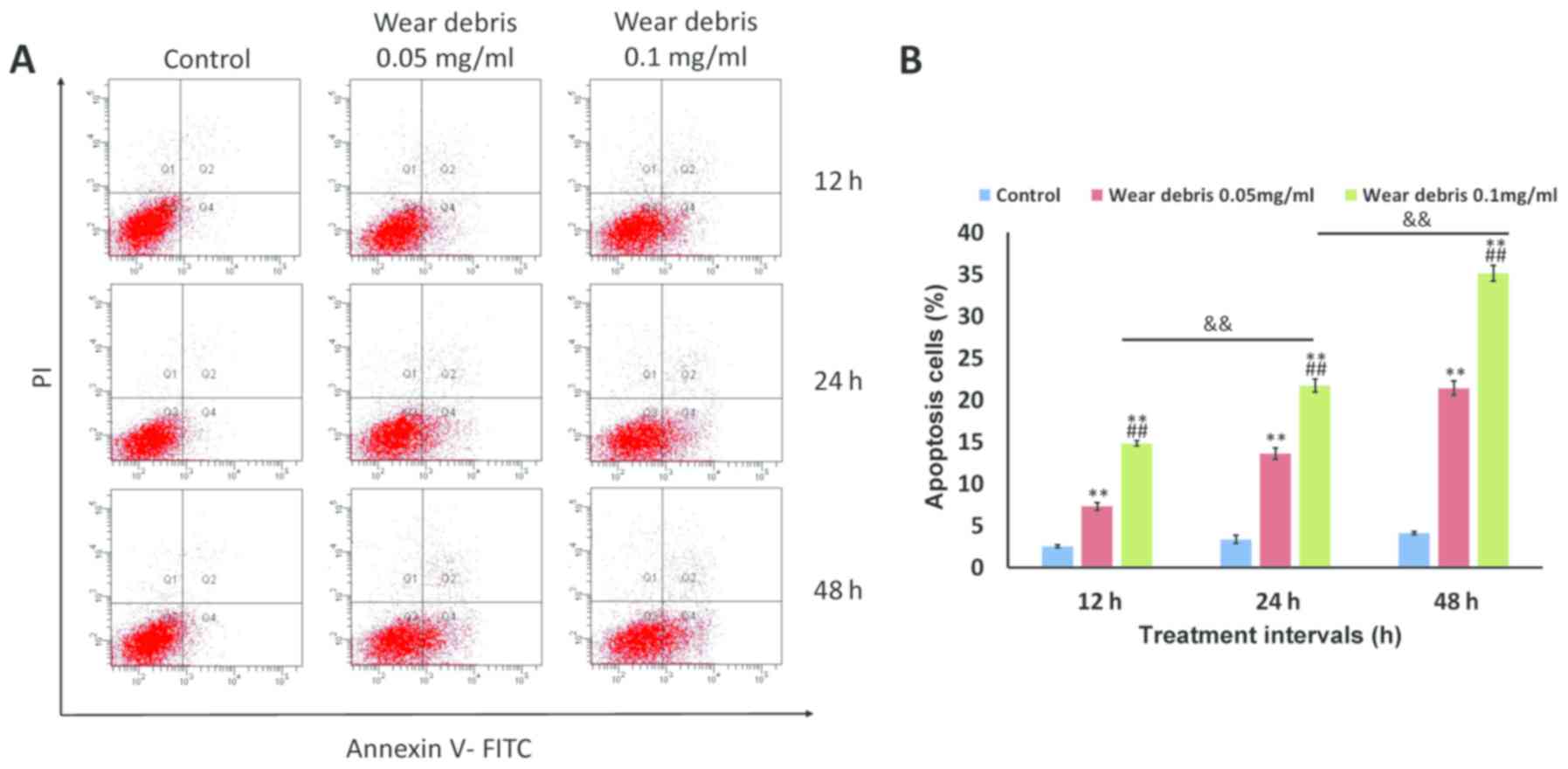
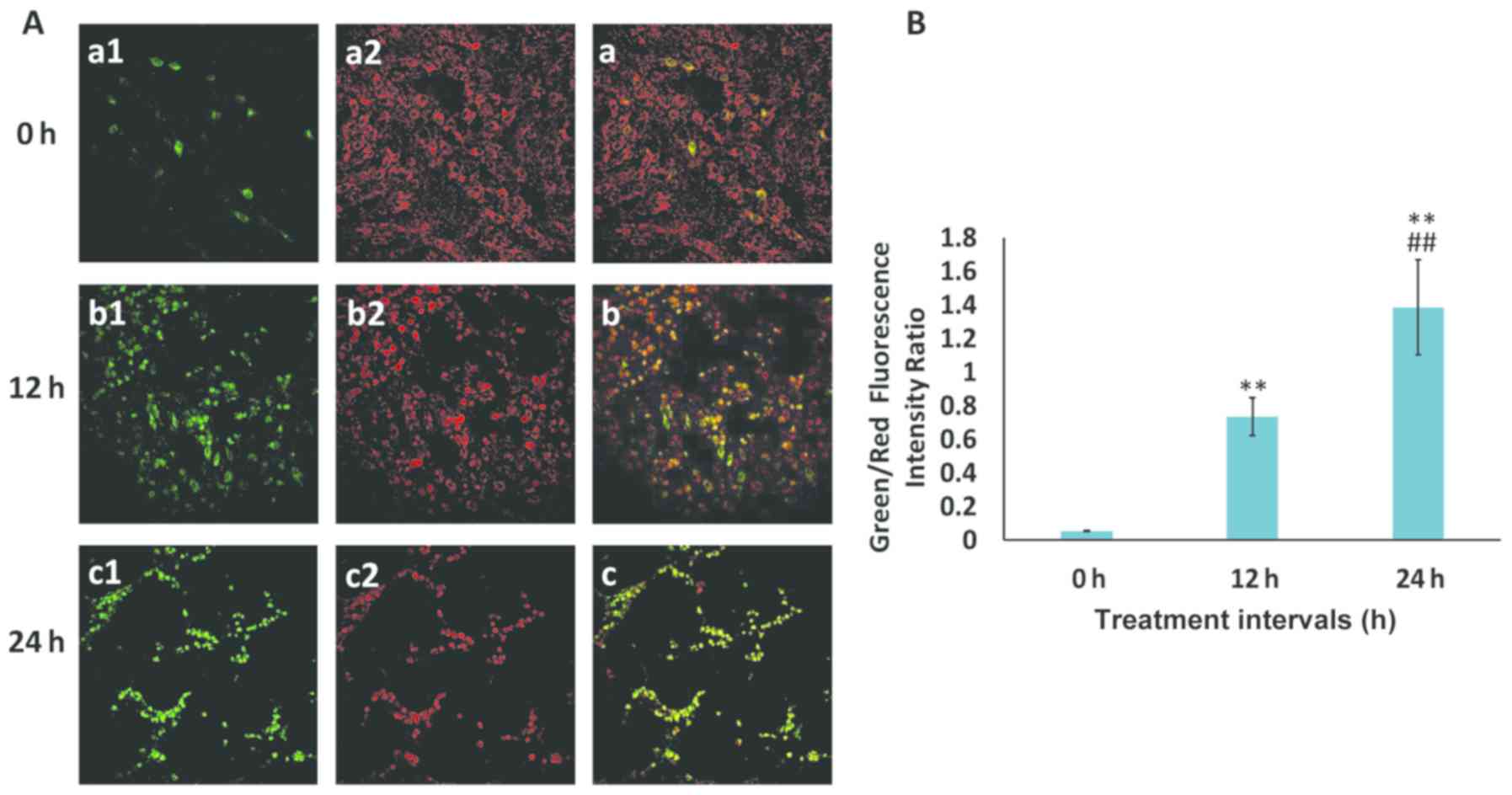
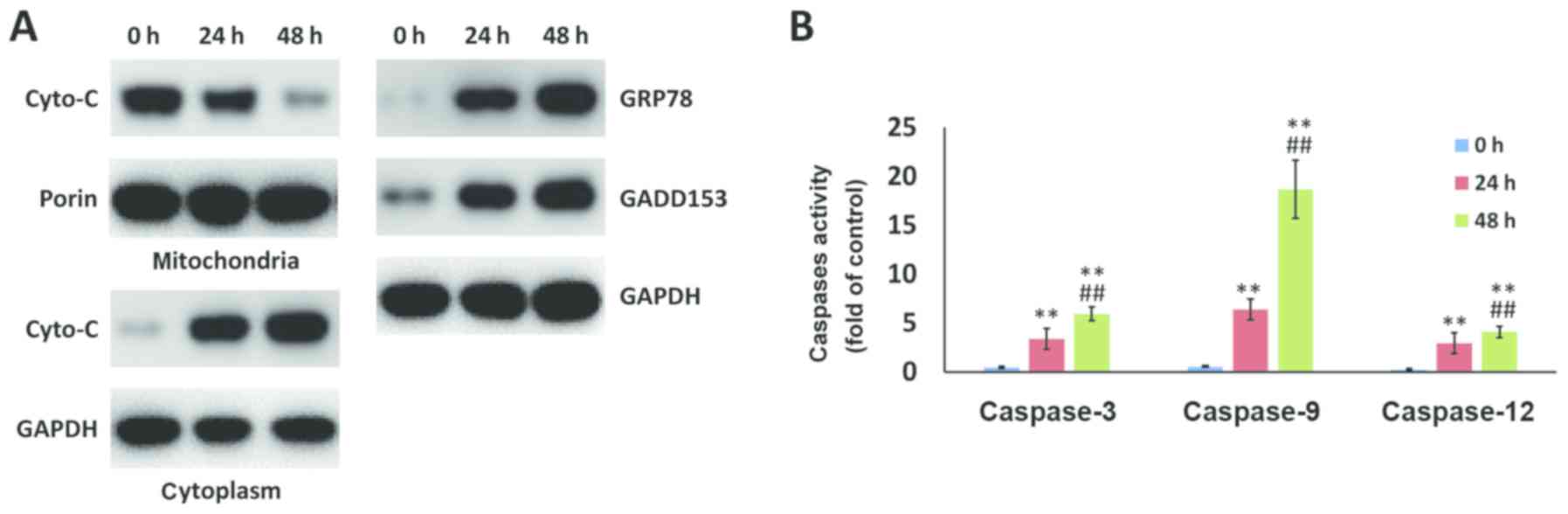
|
1
|
Meermans G, Konan S, Das R, Volpin A and
Haddad FS: The direct anterior approach in total hip arthroplasty:
A systematic review of the literature. Bone Joint J. 99-B:732–740.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Petis S, Howard JL, Lanting BL and
Vasarhelyi EM: Surgical approach in primary total hip arthroplasty:
Anatomy, technique and clinical outcomes. Can J Surg. 58:128–139.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sundfeldt M, Carlsson LV, Johansson CB,
Thomsen P and Gretzer C: Aseptic loosening, not only a question of
wear: A review of different theories. Acta Orthop. 77:177–197.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang F, Wu W, Cao L, Huang Y, Zhu Z, Tang
T and Dai K: Pathways of macrophage apoptosis within the interface
membrane in aseptic loosening of prostheses. Biomaterials.
32:9159–9167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wooley PH and Schwarz EM: Aseptic
loosening. Gene Ther. 11:402–407. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cherian JJ, Jauregui JJ, Banerjee S,
Pierce T and Mont MA: What host factors affect aseptic loosening
after THA and TKA? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 473:2700–2709. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shimizu S, Okuda N, Kato N, Rittling SR,
Okawa A, Shinomiya K, Muneta T, Denhardt DT, Noda M, Tsuji K and
Asou Y: Osteopontin deficiency impairs wear debris-induced
osteolysis via regulation of cytokine secretion from murine
macrophages. Arthritis Rheum. 62:1329–1337. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y, Yan M, Yu A, Mao H and Zhang J:
Inhibitory effects of β-tricalciumphosphate wear particles on
osteocytes via apoptotic response and Akt inactivation. Toxicology.
297:57–67. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hallab NJ and Jacobs JJ: Biologic effects
of implant debris. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 67:182–188.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Goodman SB and Ma T: Cellular chemotaxis
induced by wear particles from joint replacements. Biomaterials.
31:5045–5050. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vidovszky TJ, Cabanela ME, Rock MG, Berry
DJ, Morrey BF and Bolander ME: Histologic and biochemical
differences between osteolytic and nonosteolytic membranes around
femoral components of an uncemented total hip arthroplasty. J
Arthroplasty. 13:320–330. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yao J, Cs-Szabó G, Jacobs JJ, Kuettner KE
and Glant TT: Suppression of osteoblast function by titanium
particles. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 79:107–112. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vermes C, Chandrasekaran R, Jacobs JJ,
Galante JO, Roebuck KA and Glant TT: The effects of particulate
wear debris, cytokines, and growth factors on the functions of
MG-63 osteoblasts. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 83-A:201–211. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lochner K, Fritsche A, Jonitz A, Hansmann
D, Mueller P, Mueller-Hilke B and Bader R: The potential role of
human osteoblasts for periprosthetic osteolysis following exposure
to wear particles. Int J Mol Med. 28:1055–1063. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Posada OM, Gilmour D, Tate RJ and Grant
MH: CoCr wear particles generated from CoCr alloy metal-on-metal
hip replacements, and cobalt ions stimulate apoptosis and
expression of general toxicology-related genes in monocyte-like
U937 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 281:125–135. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thomas V, Halloran BA, Ambalavanan N,
Catledge SA and Vohra YK: In vitro studies on the effect of
particle size on macrophage responses to nanodiamond wear debris.
Acta Biomater. 8:1939–1947. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang ML, Tuli R, Manner PA, Sharkey PF,
Hall DJ and Tuan RS: Direct and indirect induction of apoptosis in
human mesenchymal stem cells in response to titanium particles. J
Orthop Res. 21:697–707. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Landgraeber S, von Knoch M, Löer F,
Brankamp J, Tsokos M, Grabellus F, Schmid KW and Totsch M:
Association between apoptotis and CD4(+)/CD8(+) T-lymphocyte ratio
in aseptic loosening after total hip replacement. Int J Biol Sci.
5:182–191. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
O'Neill SC, Queally JM, Devitt BM, Doran
PP and O'Byrne JM: The role of osteoblasts in peri-prosthetic
osteolysis. Bone Joint J. 95-B:1022–1026. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Orrenius S, Gogvadze V and Zhivotovsky B:
Mitochondrial oxidative stress: Implications for cell death. Annu
Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 47:143–183. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L and Brenner C:
Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev.
87:99–163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sano R and Reed JC: ER stress-induced cell
death mechanisms. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833. 3460–3470. 2013.
|
|
23
|
Gorman AM, Healy SJ, Jäger R and Samali A:
Stress management at the ER: Regulators of ER stress-induced
apoptosis. Pharmacol Ther. 134:306–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Minovic A, Milowsev I, Pisot V, Cör A and
Antolic V: Isolation of polyacetal wear particles from
periprosthetic tissue of isoelastic femoral stems. J Bone Joint
Surg Br. 83:1182–1190. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Maloney WJ, Smith RL, Schmalzried TP,
Chiba J, Huene D and Rubash H: Isolation and characterization of
wear particles generated in patients who have had failure of a hip
arthroplasty without cement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 77:1301–1310.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu F, Zhu Z, Mao Y, Liu M, Tang T and Qiu
S: Inhibition of titanium particle-induced osteoclastogenesis
through inactivation of NFATc1 by VIVIT peptide. Biomaterials.
30:1756–1762. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wornham DP, Hajjawi MO, Orriss IR and
Arnett TR: Strontium potently inhibits mineralisation in
bone-forming primary rat osteoblast cultures and reduces numbers of
osteoclasts in mouse marrow cultures. Osteoporos Int. 25:2477–2484.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hou JM, Chen EY, Wei SC, Lin F, Lin QM,
Lan XH, Xue Y and Wu M: Lactoferrin inhibits apoptosis through
insulin-like growth factor I in primary rat osteoblasts. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 35:523–530. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu WB, Tian FJ and Liu LQ: Chikusetsu
(CHI) triggers mitochondria-regulated apoptosis in human prostate
cancer via reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Biomed
Pharmacother. 90:446–454. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Erl W, Weber C and Hansson GK: Pyrrolidine
dithiocarbamate-induced apoptosis depends on cell type, density,
and the presence of Cu(2+) and Zn(2+). Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
278:C1116–C1125. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sinha K, Das J, Pal PB and Sil PC:
Oxidative stress: The mitochondria-dependent and
mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch Toxicol.
87:1157–1180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Haleem-Smith H, Argintar E, Bush C,
Hampton D, Postma WF, Chen FH, Rimington T, Lamb J and Tuan RS:
Biological responses of human mesenchymal stem cells to titanium
wear debris particles. J Orthop Res. 30:853–863. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pioletti DP, Takei H, Kwon SY, Wood D and
Sung KL: The cytotoxic effect of titanium particles phagocytosed by
osteoblasts. J Biomed Mater Res. 46:399–407. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang X and Hutchinson CR: Corrosion-wear
of β-Ti alloy TMZF (Ti-12Mo-6Zr-2Fe) in simulated body fluid. Acta
Biomater. 42:429–439. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cheng T, Zhao Y, Li B, Cheng M, Wang J and
Zhang X: Curcumin attenuation of wear particle-induced osteolysis
via RANKL signaling pathway suppression in mouse calvarial model.
Mediators Inflamm 2017. 57843742017.
|
|
36
|
González O, Smith RL and Goodman SB:
Effect of size, concentration, surface area, and volume of
polymethylmethacrylate particles on human macrophages in vitro. J
Biomed Mater Res. 30:463–473. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sabokbar A, Pandey R and Athanasou NA: The
effect of particle size and electrical charge on
macrophage-osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption. J Mater
Sci Mater Med. 14:731–738. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gelb H, Schumacher HR, Cuckler J, Ducheyne
P and Baker DG: In vivo inflammatory response to
polymethylmethacrylate particulate debris: Effect of size,
morphology, and surface area. J Orthop Res. 12:83–92. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Abu-Amer Y, Darwech I and Clohisy JC:
Aseptic loosening of total joint replacements: Mechanisms
underlying osteolysis and potential therapies. Arthritis Res Ther.
9 Suppl 1:S62007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Landgraeber S, von Knoch M, Löer F, Wegner
A, Tsokos M, Hussmann B and Totsch M: Extrinsic and intrinsic
pathways of apoptosis in aseptic loosening after total hip
replacement. Biomaterials. 29:3444–3450. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Devasagayam TP, Tilak JC, Boloor KK, Sane
KS, Ghaskadbi SS and Lele RD: Free radicals and antioxidants in
human health: Current status and future prospects. J Assoc
Physicians India. 52:794–804. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Santos CX, Tanaka LY, Wosniak J and
Laurindo FR: Mechanisms and implications of reactive oxygen species
generation during the unfolded protein response: Roles of
endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductases, mitochondrial electron
transport, and NADPH oxidase. Antioxid Redox Signal. 11:2409–2427.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Brand MD: The sites and topology of
mitochondrial superoxide production. Exp Gerontol. 45:466–472.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Malhotra JD and Kaufman RJ: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and oxidative stress: A vicious cycle or a
double-edged sword? Antioxid Redox Signal. 9:2277–2293. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang J, Yang X and Zhang J: Bridges
between mitochondrial oxidative stress, ER stress and mTOR
signaling in pancreatic β cells. Cell Signal. 28:1099–1104. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Buytaert E, Matroule JY, Durinck S, Close
P, Kocanova S, Vandenheede JR, de Witte PA, Piette J and Agostinis
P: Molecular effectors and modulators of hypericin-mediated cell
death in bladder cancer cells. Oncogene. 27:1916–1929. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|