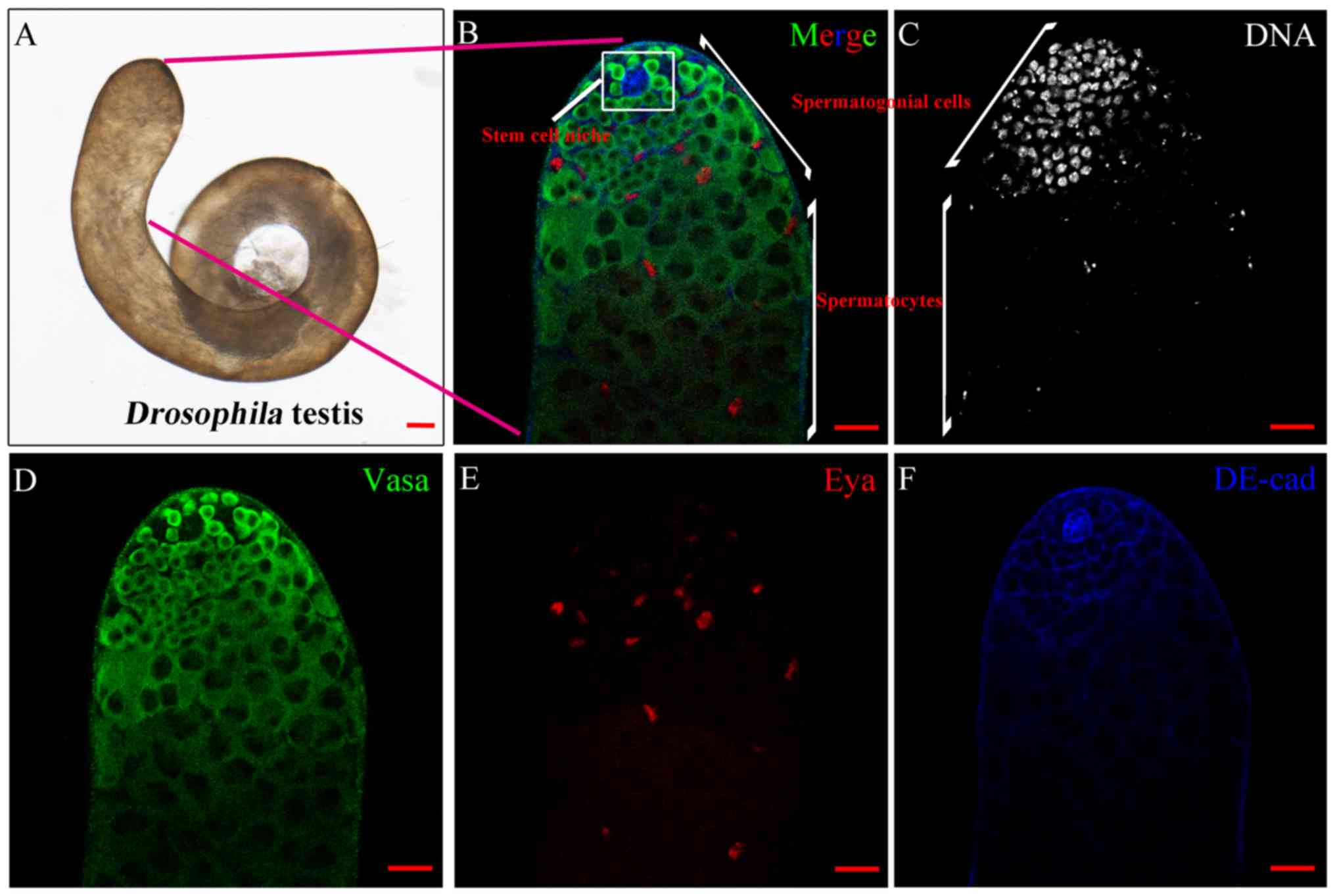
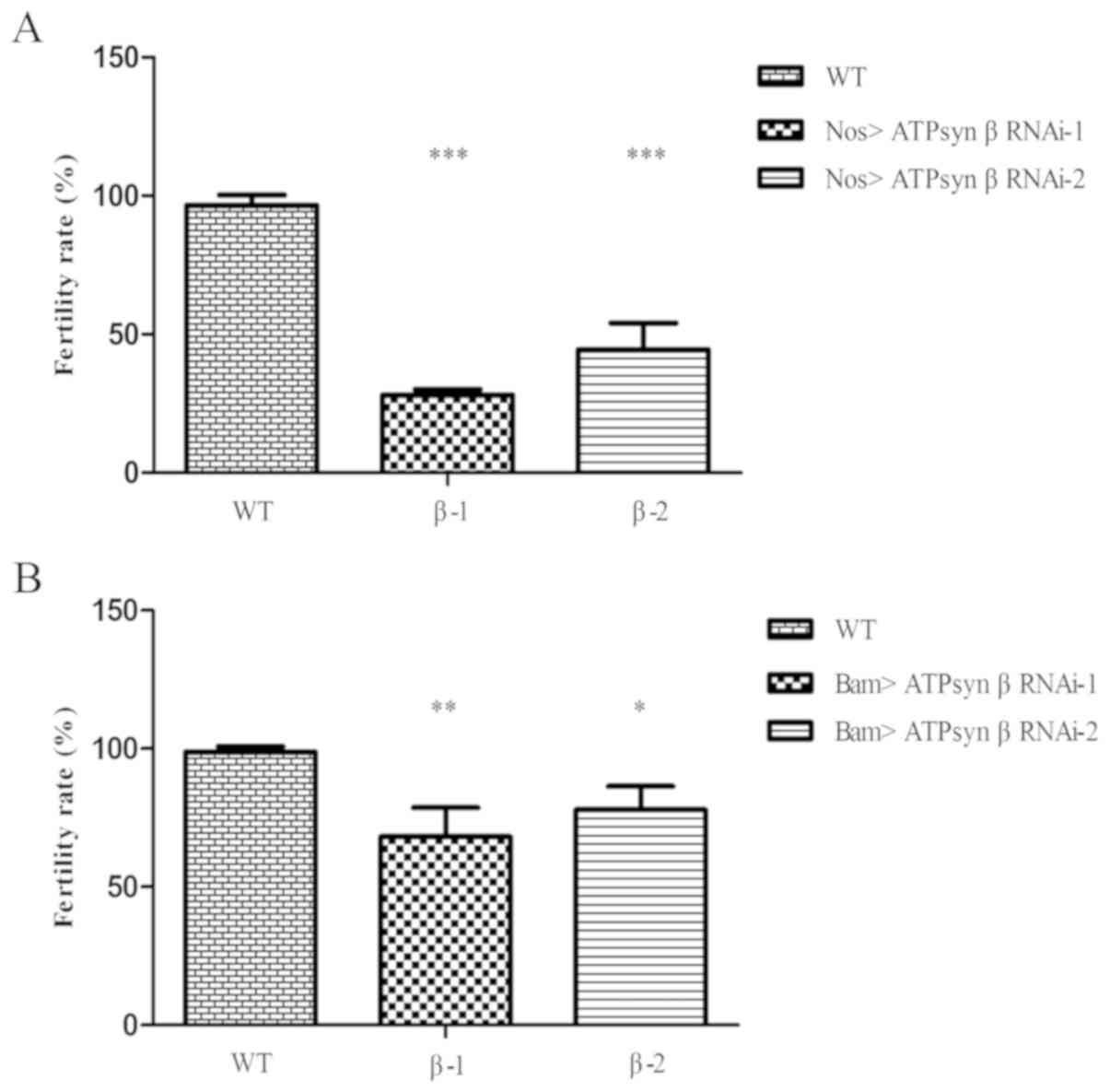
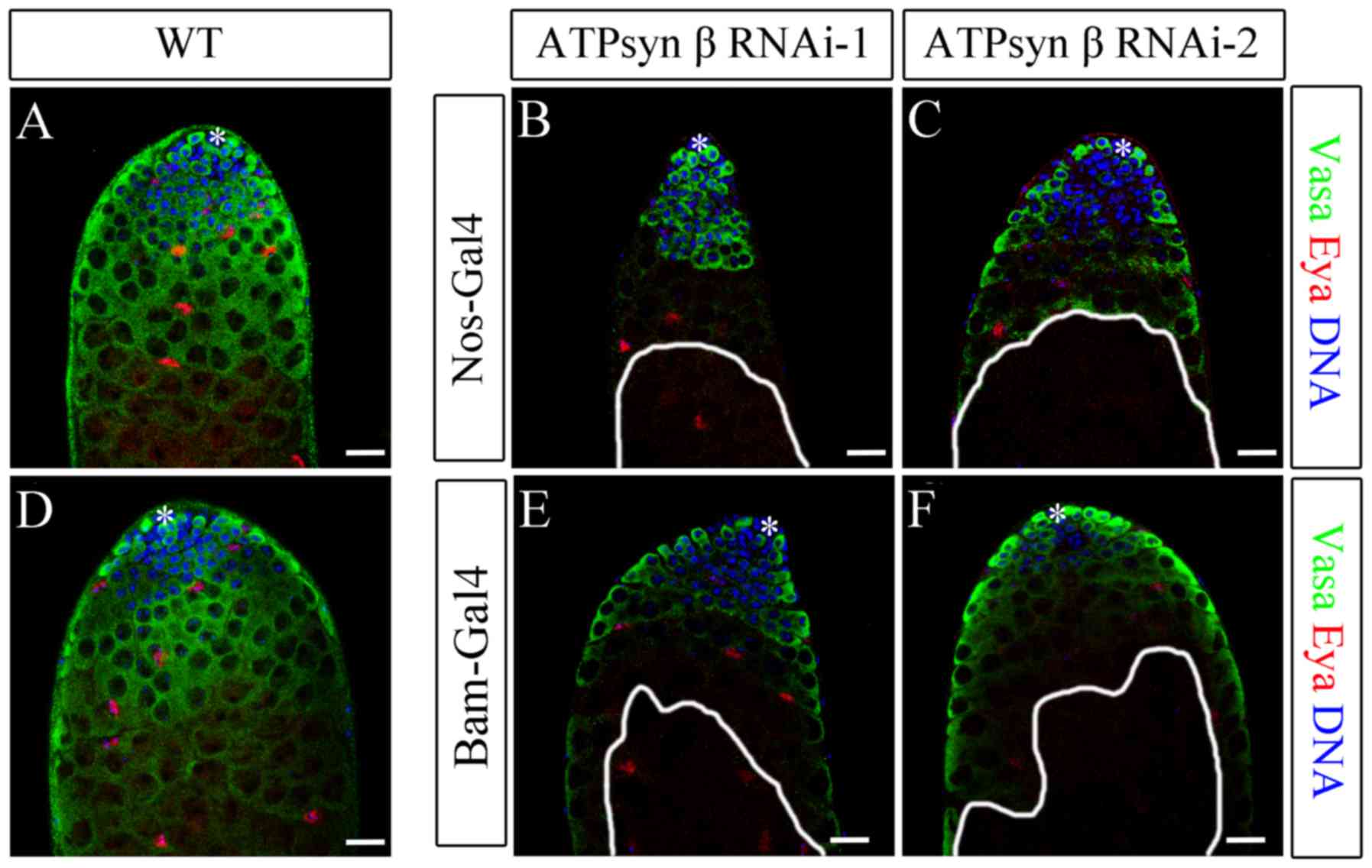
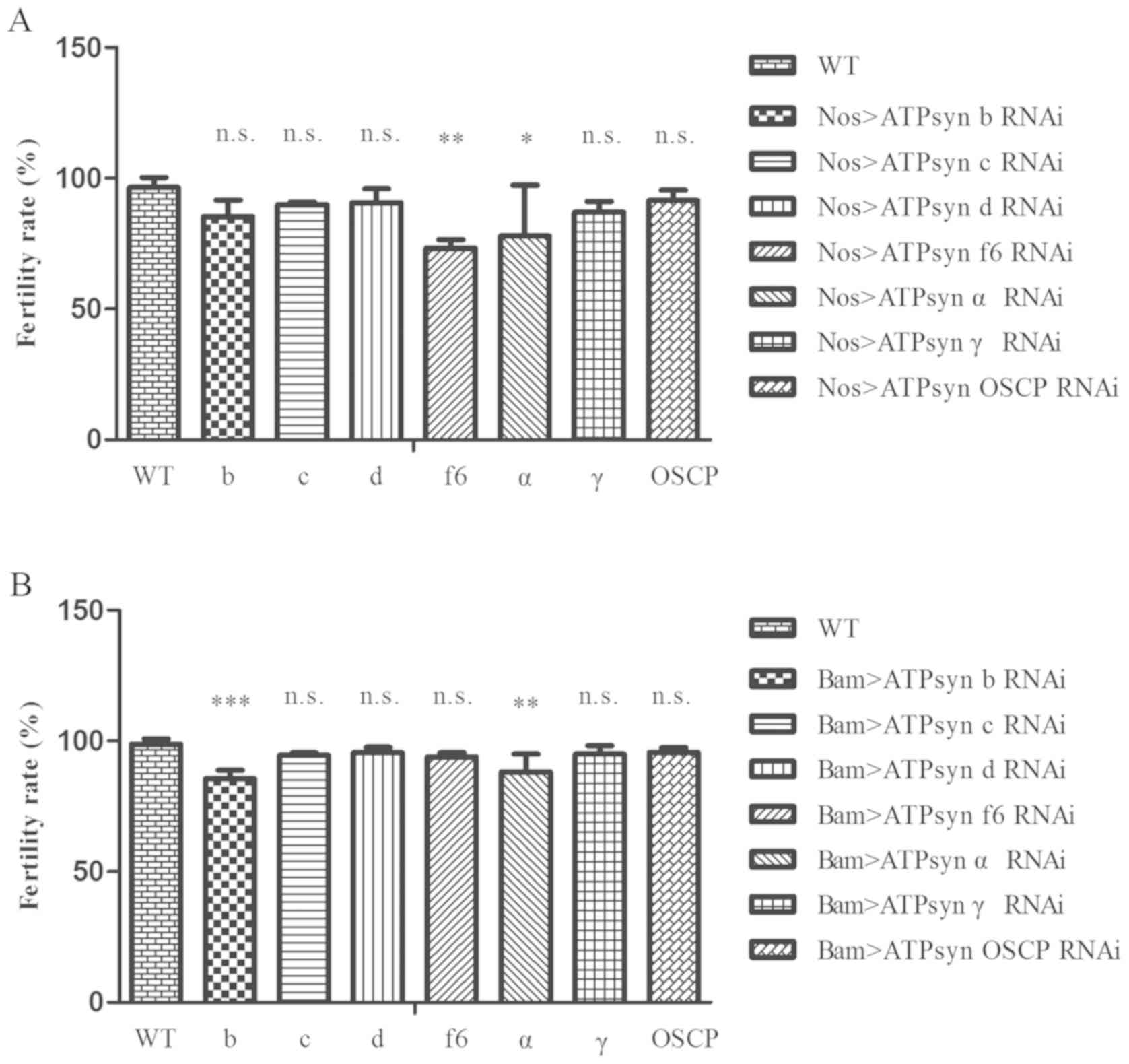
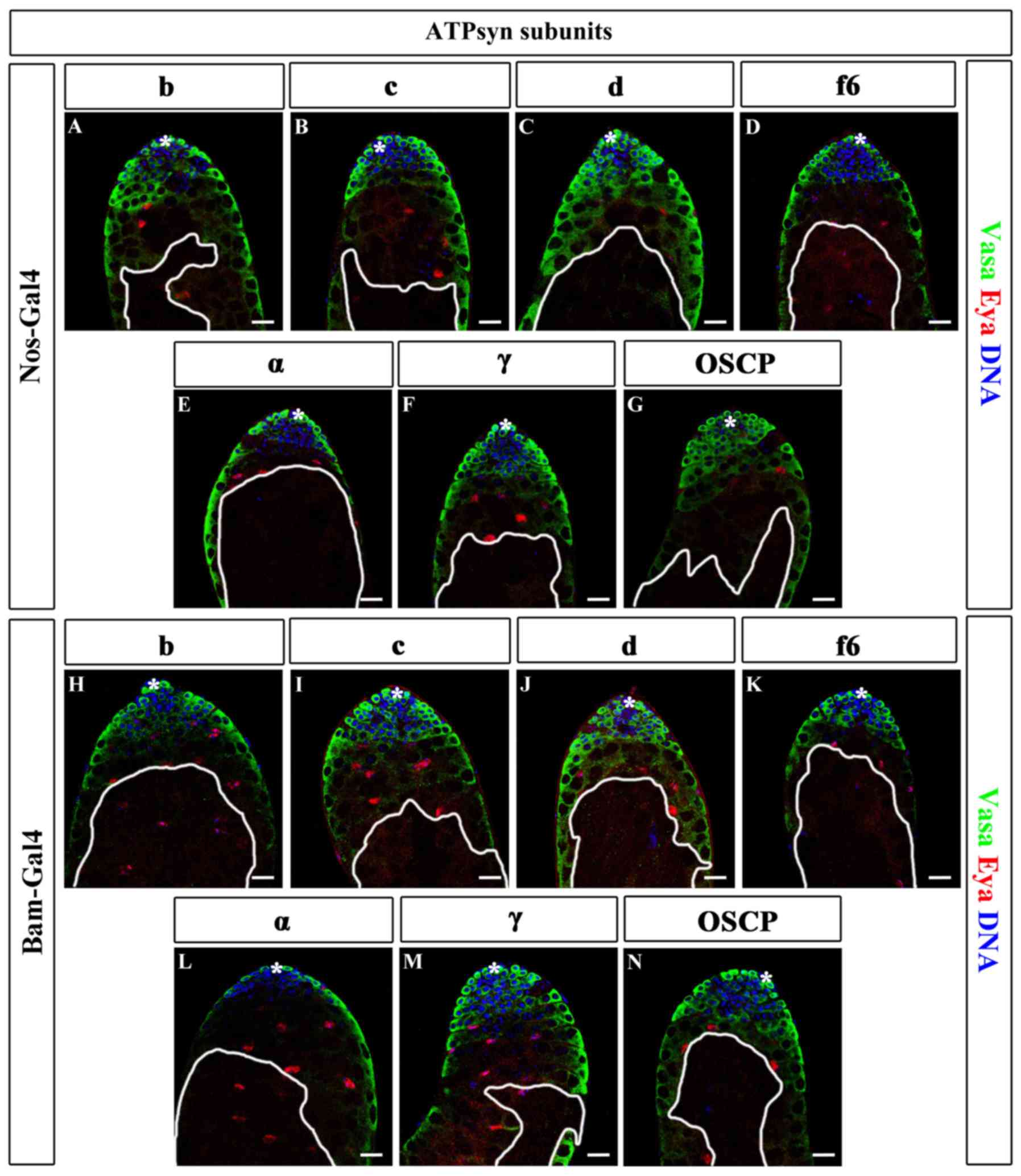
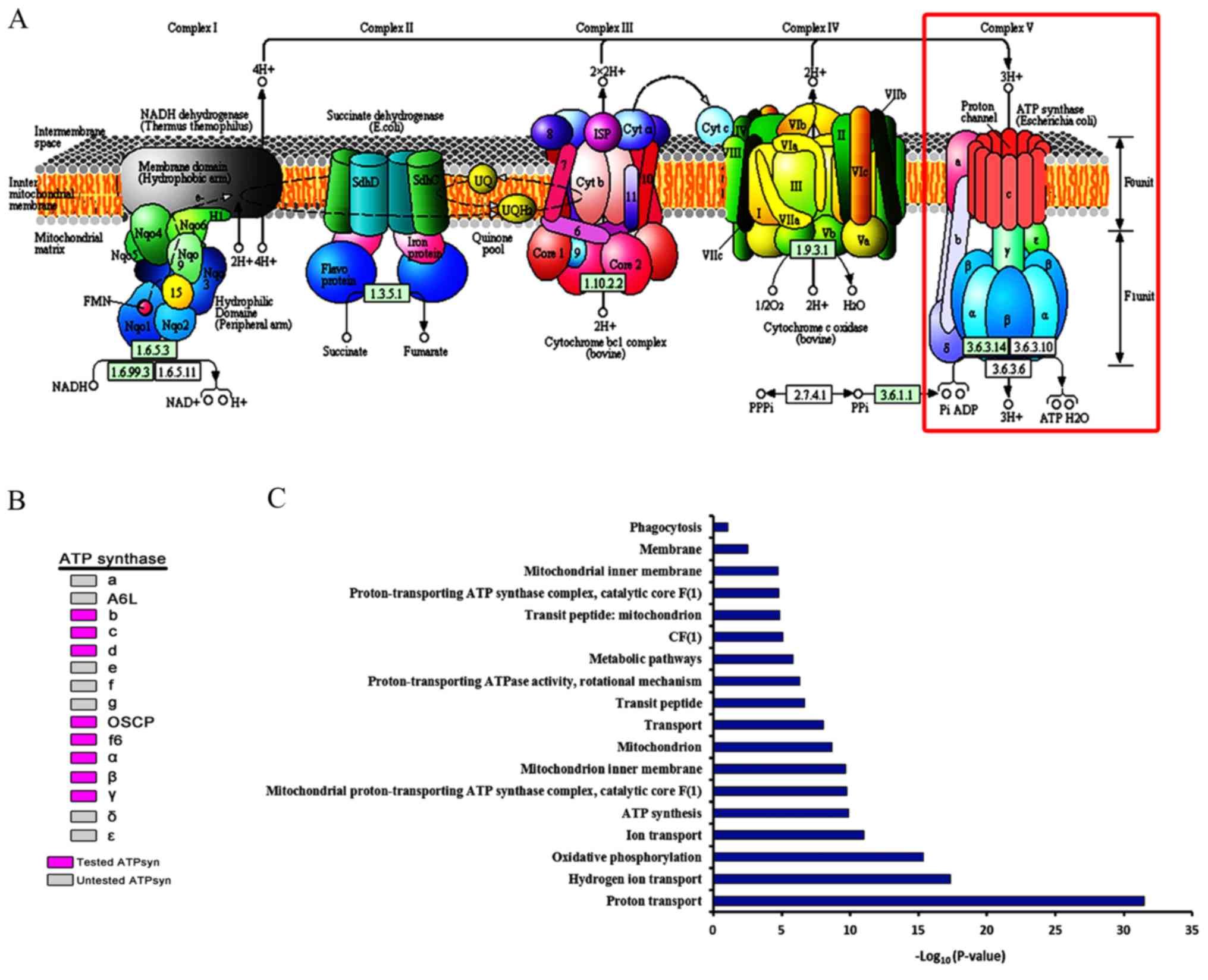
|
1
|
Hu Z, Li Z, Yu J, Tong C, Lin Y, Guo X, Lu
F, Dong J, Xia Y, Wen Y, et al: Association analysis identifies new
risk loci for non-obstructive azoospermia in Chinese men. Nat
Commun. 5:38572014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yu J, Liu Y, Lan X, Wu H, Wen Y, Zhou Z,
Hu Z, Sha J, Guo X and Tong C: CHES-1-like, the ortholog of a
non-obstructive azoospermia-associated gene, blocks germline stem
cell differentiation by upregulating Dpp expression in
Drosophila testis. Oncotarget. 7:42303–42313.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yu J, Wu H, Wen Y, Liu Y, Zhou T, Ni B,
Lin Y, Dong J, Zhou Z, Hu Z, et al: Identification of seven genes
essential for male fertility through a genome-wide association
study of non-obstructive azoospermia and RNA interference-mediated
large-scale functional screening in Drosophila. Hum Mol
Genet. 24:1493–1503. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu H, Sun L, Wen Y, Liu Y, Yu J, Mao F,
Wang Y, Tong C, Guo X, Hu Z, et al: Major spliceosome defects cause
male infertility and are associated with nonobstructive azoospermia
in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:4134–4139. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hackstein JH, Hochstenbach R and Pearson
PL: Towards an understanding of the genetics of human male
infertility: Lessons from flies. Trends Genet. 16:565–572. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
de Cuevas M and Matunis EL: The stem cell
niche: Lessons from the Drosophila testis. Development.
138:2861–2869. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Spradling A, Fuller MT, Braun RE and
Yoshida S: Germline stem cells. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
3:a0026422011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fuller MT and Spradling AC: Male and
female Drosophila germline stem cells: Two versions of
immortality. Science. 316:402–404. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu EY, Lee DF, Klebes A, Turek PJ,
Kornberg TB and Reijo Pera RA: Human BOULE gene rescues meiotic
defects in infertile flies. Hum Mol Genet. 12:169–175. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
White-Cooper H: Studying how flies make
sperm-investigating gene function in Drosophila testes. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 306:66–74. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu J, Lan X, Chen X, Yu C, Xu Y, Liu Y, Xu
L, Fan HY and Tong C: Protein synthesis and degradation are
essential to regulate germline stem cell homeostasis in
Drosophila testes. Development. 143:2930–2945. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He J, Ford HC, Carroll J, Ding S, Fearnley
IM and Walker J: Persistence of the mitochondrial permeability
transition in the absence of subunit c of human ATP synthase. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:3409–3414. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Junge W and Nelson N: ATP synthase. Annu
Rev Biochem. 84:631–657. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Walker JE: The ATP synthase: The
understood, the uncertain and the unknown. Biochem Soc Trans.
41:1–16. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mitchell P: Chemiosmotic coupling in
oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. 1966. Biochim Biophys
Acta 1807. 1507–1538. 2011.
|
|
16
|
Kucharczyk R, Zick M, Bietenhader M, Rak
M, Couplan E, Blondel M, Caubet SD and di Rago JP: Mitochondrial
ATP synthase disorders: Molecular mechanisms and the quest for
curative therapeutic approaches. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793.
186–199. 2009.
|
|
17
|
Velours J, Paumard P, Soubannier V,
Spannagel C, Vaillier J, Arselin G and Graves PV: Organisation of
the yeast ATP synthase F(0): A study based on cysteine mutants,
thiol modification and cross-linking reagents. Biochim Biophys Acta
1458. 443–456. 2000.
|
|
18
|
Hendriks WK, Colleoni S, Galli C, Paris
DB, Colenbrander B, Roelen BA and Stout TA: Maternal age and in
vitro culture affect mitochondrial number and function in equine
oocytes and embryos. Reprod Fertil Dev. 27:957–968. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sawyer EM, Brunner EC, Hwang Y, Ivey LE,
Brown O, Bannon M, Akrobetu D, Sheaffer KE, Morgan O, Field CO, et
al: Testis-specific ATP synthase peripheral stalk subunits required
for tissue-specific mitochondrial morphogenesis in
Drosophila. BMC Cell Biol. 18:162017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ramió-Lluch L, Yeste M, Fernández-Novell
JM, Estrada E, Rocha L, Cebrián-Pérez JA, Muiño-Blanco T, Concha
II, Ramírez A and Rodríguez-Gil JE: Oligomycin A-induced inhibition
of mitochondrial ATP-synthase activity suppresses boar sperm
motility and in vitro capacitation achievement without modifying
overall sperm energy levels. Reprod Fertil Dev. 26:883–897. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Maccarinelli F, Regoni M, Carmona F, Poli
M, Meyron-Holtz EG and Arosio P: Mitochondrial ferritin deficiency
reduces male fertility in mice. Reprod Fertil Dev. 29:2005–2010.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Teixeira FK, Sanchez CG, Hurd TR, Seifert
JR, Czech B, Preall JB, Hannon GJ and Lehmann R: ATP synthase
promotes germ cell differentiation independent of oxidative
phosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol. 17:689–696. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ni JQ, Zhou R, Czech B, Liu LP, Holderbaum
L, Yang-Zhou D, Shim HS, Tao R, Handler D, Karpowicz P, et al: A
genome-scale shRNA resource for transgenic RNAi in
Drosophila. Nat Methods. 8:405–407. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu M, Lim TM and Cai Y: The
Drosophila female germline stem cell lineage acts to
spatially restrict DPP function within the niche. Sci Signal.
3:ra572010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
White-Cooper H: Tissue, cell type and
stage-specific ectopic gene expression and RNAi induction in the
Drosophila testis. Spermatogenesis. 2:11–22. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Singh SR, Zhen W, Zheng Z, Wang H, Oh SW,
Liu W, Zbar B, Schmidt LS and Hou SX: The Drosophila homolog
of the human tumor suppressor gene BHD interacts with the JAK-STAT
and Dpp signaling pathways in regulating male germline stem cell
maintenance. Oncogene. 25:5933–5941. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Furuya M, Qadota H, Chisholm AD and
Sugimoto A: The C. elegans eyes absent ortholog EYA-1 is required
for tissue differentiation and plays partially redundant roles with
PAX-6. Dev Biol. 286:452–463. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Karandikar UC, Jin M, Jusiak B, Kwak S,
Chen R and Mardon G: Drosophila eyes absent is required for
normal cone and pigment cell development. PLoS One. 9:e1021432014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fabrizio JJ, Boyle M and DiNardo S: A
somatic role for eyes absent (eya) and sine oculis (so) in
Drosophila spermatocyte development. Dev Biol. 258:117–128.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bunt SM and Hime GR: Ectopic activation of
Dpp signalling in the male Drosophila germline inhibits germ
cell differentiation. Genesis. 39:84–93. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shivdasani AA and Ingham PW: Regulation of
stem cell maintenance and transit amplifying cell proliferation by
tgf-beta signaling in Drosophila spermatogenesis. Curr Biol.
13:2065–2072. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yan D, Neumüller RA, Buckner M, Ayers K,
Li H, Hu Y, Yang-Zhou D, Pan L, Wang X, Kelley C, et al: A
regulatory network of Drosophila germline stem cell
self-renewal. Dev Cell. 28:459–473. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen JV and Megraw TL: Spermitin: A novel
mitochondrial protein in Drosophila spermatids. PLoS One.
9:e1088022014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wu CH, Zong Q, Du AL, Zhang W, Yao HC, Yu
XQ and Wang YF: Knockdown of Dynamitin in testes significantly
decreased male fertility in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev
Biol. 420:79–89. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Collins CM, Malacrida B, Burke C, Kiely PA
and Dunleavy EM: ATP synthase F1 subunits recruited to centromeres
by CENP-A are required for male meiosis. Nat Commun. 9:27022018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Midzak AS, Chen H, Aon MA, Papadopoulos V
and Zirkin BR: ATP synthesis, mitochondrial function, and steroid
biosynthesis in rodent primary and tumor Leydig cells. Biol Reprod.
84:976–985. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wen J, Duan H, Bejarano F, Okamura K,
Fabian L, Brill JA, Bortolamiol-Becet D, Martin R, Ruby JG and Lai
EC: Adaptive regulation of testis gene expression and control of
male fertility by the Drosophila hairpin RNA pathway. Mol
Cell. 57:165–178. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kawasaki I, Hanazawa M, Gengyo-Ando K,
Mitani S, Maruyama I and Iino Y: ASB-1, a germline-specific isoform
of mitochondrial ATP synthase b subunit, is required to maintain
the rate of germline development in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Mech Dev. 124:237–251. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen YN, Wu CH, Zheng Y, Li JJ, Wang JL
and Wang YF: Knockdown of ATPsyn-b caused larval growth defect and
male infertility in Drosophila. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol.
88:144–54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Davies KM, Anselmi C, Wittig I,
Faraldo-Gómez JD and Kühlbrandt W: Structure of the yeast F1FO-ATP
synthase dimer and its role in shaping the mitochondrial cristae.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:13602–13607. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|